- Current (contact) - occurs directly when a person comes into contact with a live part, when an electric current passes through the body.
- Arc - caused by the thermal effect of an electric arc on the human body: such burns are usually serious and deep.
Voltage is of great importance: for example, at low voltage (up to 240V), alternating electric current is dangerous - it causes muscle contraction, and the person who has come under the electric shock seems to “stick” to the current source and cannot in any way withdraw the limb.
High voltage, on the contrary, usually “throws away” the victim. However, at voltages above 370V, serious damage occurs - burns of 3rd and 4th degree of severity with charring of body parts.
Electrical burn: causes
When electric current enters the human body, it forms an electrical "loop". When contacting a bare wire, a person closes the current circuit, resulting in tumors and injuries at the radial exit and entry points. There is also a risk of injury to the brain and internal tissues of the body.
The most dangerous is a closed loop. This is a condition where current passes through the legs or arms. The second most powerful effect is the lower loop, when an electric current passes through the feet.
There are several main causes of electrical burns. You need to know and avoid them:
- Contact with exposed wires at home or business.
- Touching electrical appliances with exposed wires.
- Old wiring without the necessary insulation.
- Touching a high voltage line.
- Lightning strike.
- Poor socket connection.
Contact with exposed wires is one of the main causes of electrical burns.
When an electrical shock occurs and a red burn occurs, a person feels severe pain throughout the body. After this, breathing and pulse may stop or become very slow.
Types and features
There are 2 types of electrical damage.
- Contact (electric) burns are caused by direct interaction with a current conductor. Such injuries often occur when working with low-voltage electrical equipment, so electrical burns are characterized by a mild degree of injury.
- An arc burn results from the thermal effects (temperatures that can exceed 350°C) of an electric arc without current passing through the body. An electric arc burn often leads to very serious damage that extends into the deep structures of the skin.
In case of electric shock, in addition to burns, phenomena occur that are uncharacteristic of other types of damage (thermal, chemical).
- Many patients have characteristic marks in the area of contact with the current - oval, round, or in the form of stripes (in case of lightning) yellowish or brown areas. These marks have clear boundaries and are about 5-10 mm in size. Over time, they disappear, but the speed of restoration of skin sensitivity and its properties depends both on the degree of damage and on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- When an electric shock occurs, the current travels through the body in a path called a loop. As a result, burn damage occurs not only in the area of contact with the current source, but also at the point of its exit from the body (usually this is the area of the body in contact with the surface of the earth or metal). A full loop, characterized by the passage of current through both arms and legs, is the most dangerous. A more favorable prognosis for the victim is when the current passes only through the lower limbs (lower loop).
Electric shock causes various types of damage:
- thermal - often a current discharge is accompanied by a high-temperature effect, as a result of which the victim’s clothing catches fire, and a thermal burn is added to the electric shock;
- electrolytic – the composition of the blood changes, internal tissues are destroyed;
- mechanical - due to convulsive involuntary contraction of muscles caused by the influence of current, tissues are torn, deep (sometimes right up to the bone) wounds are formed on the skin, dislocations and even bone fractures often occur;
- biological - the functioning of the nervous system and the function of thermoregulation, cardiac activity are disrupted (myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest may occur), blood pressure increases, arrosive bleeding, pulmonary edema, glomerulonephritis, functional liver failure may develop;
- electroophthalmia - inflammation of the eyes caused by radiation burns of the cornea, retina (with a short circuit and the formation of an electric arc, in addition to a visible bright flash, intense ultraviolet radiation occurs, affecting the structures of the eyeball);
- metallization of the skin - tiny particles of molten metal are absorbed into the skin, the skin becomes hard and rough, and the victim has a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the area of damage.
Electrical burn: features
An electrical burn on the skin is formed due to the entry of an electrical charge into the body, which is converted into thermal energy. For this reason, the redness closely resembles a regular burn after contact with fire.
The severity of the damage depends on the time of exposure, as well as the voltage. The main symptom after electric shock is the appearance of red dots at points of contact with electricity.
Important: Solcoseryl is the best remedy for burns
A discharge with a voltage of 230 volts is dangerous due to alternating current: as a result, muscles contract, spasms occur, and a person is unable to move away from the source of the lesion.
Stronger tension will push the victim away. A current with a voltage of 220 volts can cause damage of 3 and 4 degrees. As a result, the skin will darken.
Electrical burn: types of burns
To provide proper assistance to the victim, you need to know all types of electrical burns. According to the method of receiving the discharge, they are divided into three main types.
Household
In most cases, people get household burns at home due to negligence and failure to comply with safety precautions. When repairing an outlet or replacing a light bulb, there is a risk of getting an electrical burn if the power in the house has not been turned off first. This variety is the most harmless, but sometimes leads to death. To avoid electric shock, before starting repair work, be sure to turn off the toggle switch on the meter.
Production
People receive industrial electrical burns at work while performing their job duties. Electric shock threatens electricians who are constantly in contact with electrical devices.
Natural
This type of burn occurs due to natural disasters. In most cases, the cause is lightning damage. People rarely survive such an incident because the body is subjected to severe stress.
The child has
According to statistics, electrical injury is diagnosed in every 10th child admitted to the burn department, and in 25% of cases the injury leads to death. At risk are children from one to 5 years of age (injured when they come into contact with a faulty electrical device connected to the network, when playing with sockets) and teenagers (they receive an electric shock when entering electrical substations, train cars, power line supports). And very rarely the cause of injury is a lightning strike.
Providing first aid to a child and treating an electrical injury is carried out in the same way as for adults. But a child’s body needs much more time to fully recover. And even after a long period of time, children can develop serious complications:
- damage to the nervous system - asthenia (a disorder accompanied by a decrease in physical and mental performance), encephalopathy (brain damage), neuritis (inflammation of peripheral nerves), paresis (partial paralysis);
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system - cardiac muscle conduction disturbances, microcardiodystrophy;
- autonomic disorders - hair loss, hyperhidrosis (increased sweating throughout the body or in certain areas);
- hearing impairment, hearing loss;
- cataract (clouding of the lens of the eye, leading to blurred vision or complete blindness).
Electrical burns are the most dangerous injuries, often leading to disability or death. It is extremely important to observe safety precautions when working with industrial electrical installations and household appliances. To prevent injury to a child, it is necessary to block access to sockets, monitor the serviceability of electrical equipment and the integrity of the insulation of electrical wires, and conduct explanatory conversations about the inadmissibility of playing with electrical appliances and near energy facilities.
Electrical burn: degrees
There are four degrees of electric shock. Each of them differs in the degree of damage to the tissues of the human body.
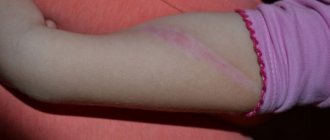
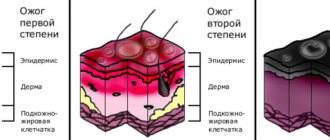
- A first-degree burn affects the upper part of the skin, causing mild swelling and hyperthermic attacks. This degree is the safest and has a favorable outcome. Treatment can be done even at home.
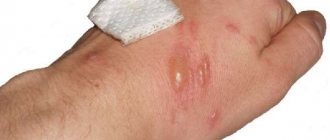
- In the second degree, the skin is affected deeper - up to the germ layer. At the site of the electric shock, you may notice blisters with liquid inside (it is not advisable to puncture them). When receiving the second degree, a person feels severe pain after an electric shock. If the area of redness is small, then you can do the treatment yourself.
- With third-degree damage, the inner layers of the skin die, blisters with bloody discharge appear - over time, they begin to burst. At the site of the electric shock (medium), the skin will turn red, and if the injury is very severe, the dermis will become dark. This indicates necrosis of the affected layer. In this case, the cells will not be able to regenerate on their own.
- The fourth degree is the most dangerous. Not only the skin is damaged, but also muscle fibers and bones. First aid should only be provided by a competent doctor. In this case, the epidermis will have to be transplanted.
Important: First aid for a burn on the palm
What do 1st and 2nd degree electrical burns look like?
Determining the degree and type of skin burned is an extremely important task, therefore, if a person was shocked in front of eyewitnesses, you should ask the crowd who can determine this without error. In case of inaccuracy, the victim may die from incorrectly provided first aid.
What do 3rd and 4th degree electrical burns look like?
First aid for chemical burns
A feature of chemical burns is that they quickly cause necrosis of the skin and mucous membranes. Chemicals quickly penetrate tissues and affect the entire body, causing poisoning, disruption of the circulatory system and internal organs. Most chemical burns of the skin occur in industrial conditions, burns of mucous membranes occur more often in domestic conditions.
The first aid algorithm will depend on what substance caused the burn:
- In case of chemical burns, call an ambulance immediately.
- Remove the victim's clothing and remove the substance from the skin as quickly as possible with a dry cloth.
- If the burn was caused by acid: pour a soda solution on the skin for 15-20 minutes at the rate of 1 teaspoon per glass of water or cold soapy water. In case of a burn with hydrofluoric acid, rinse the wound with running water for 2-3 hours.
- If the burn was caused by alkali: rinse the skin with running water, and then treat with a solution of citric or boric acid (1/2 teaspoon per glass of water) or table vinegar diluted half with water.
- If the burn is caused by quicklime: remove the substance from the skin using a clean, dry cloth. Do not use a damp cloth or water as it will generate heat and worsen the damage. Afterwards, treat with any vegetable oil and apply a dry, sterile bandage.
- If phosphorus caused the burn: first remove the substance with tweezers, and then rinse the damaged area under strong water. Keep in mind that phosphorus will ignite in air. Treat the wound with a 5% solution of copper sulfate and cover with a clean, dry cloth. Do not lubricate the burn with fat, oil, or ointment, as in this case phosphorus is absorbed into the skin.
If possible, place a small amount of the chemical in a jar and give it to doctors. This will help them more accurately determine the cause of the burn and select the most effective treatment regimen.
Clinical manifestations
Signs depend on the severity of the lesion. But there are also the main symptoms that are present when receiving this type of injury:
- Onset of weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Severe pain.
- Vomit.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Increased heart rate.
- Rapid breathing.
- change in skin color.
Other symptoms may also appear depending on what area of the body was exposed to the electrical current. If the electrolyte has passed through soft tissue or skin, then the treatment will need to be the same as for a regular thermal burn.
Symptoms
Electrical burns manifest themselves with all the local symptoms inherent in other types of injuries. This:
- pain;
- skin redness;
- swelling;
- the appearance of blisters on the damaged surface filled with serous or hemorrhagic fluid;
- in case of severe damage - open wounds on the skin.
A severe electrical burn is indicated by a complete lack of sensation in the area of injury.
In addition to local manifestations, electric shock may be accompanied by:
- weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness;
- difficulty breathing (becomes shallow);
- increased heart rate;
- convulsions, tics;
- paralysis;
- loss of consciousness.
An electric shock can also cause other functional disorders that cannot be predicted with certainty. It all depends on the strength and location of the damaging factor. With a strong blow, rupture of internal organs (liver, spleen, kidneys), falling into a coma (usually short-term), and cardiac arrest can occur.
First aid
If after an electric shock there is a change in skin color, as well as severe pain, you should immediately call a doctor. First aid for electrical burns is based on the duration of exposure to the current, as well as the degree of damage.
First of all, the charge must be removed from the body, that is, the person must be removed from the source. Particular care must be taken: wear protective rubber gloves on your hands, and shoes without rubber or iron inserts on your feet. If you violate the instructions, there is a risk of getting hit yourself. You can also use a long wooden plank to throw the person away from the fireplace. In this case, you should be at a safe distance. The current supply is stopped by turning off the switch.
After this, you can call an ambulance and, upon arrival, accurately describe the situation to the doctors and report the approximate time of exposure to the current.
First aid for electrical burns
If a person is unconscious after an electric shock, their breathing and heartbeat should be checked. If there is no pulse, cardiac massage and artificial respiration are performed.
The legs are raised to a level above the head. This will restore your heart rate.
Next, the legs, face, fingers and neck are examined. If incoming and outgoing burns are found, bandages are applied to these areas.
Important: Why do spots appear after a sunburn and how to deal with it?
Actions for sunburn
- At the first sign of injury, take the victim to the shade and cool the skin with cold water. It is best to take a cool shower for 15-20 minutes, then apply a cooling compress to the skin.
- Apply the medication, preferably in spray form. For example, drugs containing panthenol.
- Give the victim plenty of fluids.
- Monitor his condition. If dizziness, nausea, vomiting, chills, or fever occur, call a doctor. It is also worth calling a doctor if there is extensive skin damage.
To prevent sunburn, be sure to use SPF before going out in the sun and avoid sunbathing during dangerous times – from 11 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Regardless of the type and degree of damage, even if it is a small thermal burn, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the victim. In case of loss of consciousness, problems with breathing or pulse, call a doctor immediately.
When providing first aid, do not forget about your own safety and use latex gloves. If during the process the victim was given any medications, for example, painkillers, be sure to convey the information to the doctor, indicating the name of the drug.
Electrical burn: diagnosis
Before starting treatment for an electric burn, the doctor carries out diagnostic procedures:
- Carefully examines the victim.
- Conducts interviews with eyewitnesses - any details are important. It is advisable to obtain information about the exact time of contact with current
- Learn about the causes of injuries.
This information is enough to create a complete picture. After this, the specialist will be able to determine the area of damage and the degree of burn. After studying the data, the doctor prescribes the correct treatment.
The following is taken from the patient for analysis:
- Blood.
- I'm peeing.
The victim’s internal organs must be examined, since the electrolyte could damage them.
Electrical burn: treatment
If the victim was electrocuted at home, treatment is usually carried out on their own. At home, electric current affects small areas of the skin, and therefore all damage heals within several weeks.
It is forbidden to use iodine or brilliant green, since the skin area is highly irradiated.
For gentle care, use special creams that are sold in pharmacies and have antibacterial and antiseptic properties. Preparations containing sodium fusidine are usually used - when used, rotting of the tissue can be avoided.
During the week you need to:
- Treat the affected area of skin every day.
- Change bandages.
- Use analgesics if pain occurs.
- Use antihistamines.
The victim must not be left alone.
In case of an electrical burn, it is necessary to treat the affected area of skin and change the bandages every day.
If a person struck by an electric current is sent to a hospital for treatment, several recovery methods are used:
- Medication therapy to reduce pain and restore skin. It is used for the first and second degrees.
- Surgical procedures for severe damage (third, fourth degree).
Possible complications
If you receive an electric shock, the following complications may occur:
- Pulmonary paralysis.
- Scars and scars on the skin.
- Destruction of the spinal column and bones.
- Convulsions.
- Brain damage.
- Changes in vital organs.
To avoid electric shock, you need to follow safety rules in enterprises and work only in protective equipment. Work is carried out only after receiving confirmation that the place is de-energized and safe.
For home protection, it is enough to turn off the electricity supply before starting any repair work. It is also necessary to ensure that the electrics in the house are in good condition. Only in such cases can the risk of getting a burn be reduced to zero.