Fibroadenoma is a benign breast tumor that most often occurs in teenagers and women under 30 years of age. It is often confused with breast cancer, but it is better limited and mobile to the touch.
Fibroadenoma consists of two types of tissue: connective and glandular.
A fibroadenoma can be described as a hard, smooth, and rubbery collection of tissue with a specific shape. This is a painless knot that looks like a small, smooth ball.
This tumor increases during the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy as a result of hormonal stimulation.
Some women may develop multiple fibroadenomas in their breast tissue.
After menopause, the tumor usually decreases in size.
Fibroadenoma can vary from 1 to 10 cm, usually has an oval or round shape.
The breast consists of lobules - glands that produce milk, and milk ducts through which milk flows to the nipple. These structures are the main components of the breast at a young age.
Fibroadenomas develop from the lobules of the mammary glands as a result of increased sensitivity of the glandular tissue to the female sex hormone estrogen.
If the patient chooses surgery, this tumor is very easy to remove because it is well isolated at the edges.
There are two types of fibroadenoma:
- Pericanalicular fibroadenoma is a predominant glandular component in combination with wide tubules or cystically dilated tubules.
- Intracanalicular fibroadenoma is the predominant connective component, manifesting as a nodule that occurs primarily in the upper outer quadrant of the breast. It can be felt as a tangible moving node. Additionally, this type of tumor is sensitive to hormonal stimulation, meaning that it grows when it enters the menstrual cycle.
Both types of breast fibroadenoma do not show a tendency to malignant changes, so the prognosis is good.
In addition to these two main types of fibroadenoma, there are two more subtypes:
- Tubular adenoma of the mammary gland is clinically equivalent to a regular adenoma of the mammary gland, with a predominance of the glandular component. This occurs during lactation (the production and secretion of milk from the glandular tissue of the breast).
- Juvenile giant fibroadenoma of the mammary gland - can grow up to 20 cm in a short time. It develops during puberty, so at this age it can show signs of very rapid growth and become very large.
Simple fibroadenomas do not increase your risk of breast cancer, but complex fibroadenomas may increase your risk slightly.
When to see a doctor?
If there is a lump in your breast, you should definitely consult a doctor. Although fibroadenoma is not dangerous, its condition should be monitored regularly.
If a new lump appears that looks different or is accompanied by other signs, such as nipple discharge, you should see your doctor. These symptoms may indicate breast cancer.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, it is recommended to remove the fibroadenoma. The tumor can grow during this period under the influence of hormones.
Fibroadenoma also increases during breastfeeding. If the tumor is large, it can block the milk ducts, which leads to additional complications.
What are Montgomery tubercles?
, the Montgomery tubercles are called the Montgomery glands or the areola. These are small anatomical formations localized along the periphery of the nipple. Their average number is 10-12, but it can be either 4 or up to 28 pieces. These formations were first described by the Irish obstetrician William Montgomery; today they have been studied enough to talk about their maximum development at the time of pregnancy and lactation. In other periods of a woman’s life, they stand out to a lesser extent, although there are exceptions.
Montgomery's tubercles are considered to be vestigial glands, but there are several points of view - either sebaceous or mammary. Proponents of the first point of view (that these are sebaceous) argue that these glands are capable of secreting a lipoid factor, which slightly protects the areola from drying out and has weak bactericidal properties. Their opponents are based on the fact that the Montgomery tubercles reach their greatest development with the onset of pregnancy - they can increase both in the first week of pregnancy and even after childbirth - and after some time they return to their previous state. This development is associated with hormonal changes in the body and the transformation of the breast at the time of childbirth.
All scientists agree on one thing - the Montgomery glands are today a vestigial element. At the same time, some researchers find the meaning of these formations for modern man. A study was conducted at the National Research Center of Dijon (France) that proved that a larger number of Montgomery tubercles in a nursing woman provides active nutrition, and therefore an accelerated rate of development for children. In addition, there is a point of view that these rudimentary glands still contain some substance that is captured by the child’s receptors, encouraging him to suck mother’s milk. The researchers' goal is to identify this secret and use it in the future to accustom premature babies to their mother's breast.
Fibroadenoma - tests and diagnosis
During a clinical physical examination, your doctor will examine both breasts. A fibroadenoma usually feels like a moving lump.
The examination is followed by an ultrasound examination, which accurately determines the size of the fibroadenoma, its shape, the appearance of the edge, its relationship to the surrounding tissue and a rough estimate of the structure of the fibroadenoma.
When a more precise analysis of the structure is required, cytological and pathohistological examination of fibroadenoma is performed.
During a cytological puncture (biopsy), a sample is taken for histological analysis. A biopsy is used to exclude or confirm malignancy of the tumor.
Fibroadenomas can be very durable in structure. Therefore, it is difficult to obtain cells with a thin needle that can be used to make a real diagnosis. A wide needle biopsy is performed under local anesthesia.
A thick needle is inserted into the fibroadenoma tissue approximately 5-6 times. The procedure is painless, there is no risk of complications. The applied bandage can be removed the very next day.
Symptoms
After pregnancy, most women first notice the appearance of Montgomery formations in the nipple halo. The tubercles become lighter or darker than the surrounding tissues, protrude or take the form of micro-papillae. Natural changes may be accompanied by slight discomfort or temporary itching.
Quite rarely, the development of inflammatory processes at the exit sites of secretory channels is noted. The liquid secreted by the Montgomery tubercles has little antibacterial activity, is quite fluid and is excreted in minimal, almost imperceptible quantities, so pathologies of these glands are extremely rare.
Inflammation of the Montgomery tubercles: symptoms
The following symptoms indicate the presence of inflammation:
- Pain with minor mechanical impact.
- Change in skin color over the tubercles: redness, sometimes cyanosis.
- Increased body temperature (fever) or a feeling of overheating in the nipple area.
- The presence of cloudy or bloody discharge when pressed.
- Small rash around the nipple, cracks or growths.
- Change in color of the halos (usually redness).
Any of the listed symptoms is a deviation from the norm and requires consultation with a mammologist or dermatologist.
Breast ultrasound
If the woman is under 30 years old, the doctor may recommend an ultrasound instead of a mammogram because dense breast tissue in younger women is more difficult to examine with a mammograph.
If the woman is over 30 years old, the doctor will recommend a mammogram of both breasts followed by an ultrasound to evaluate the tumor.
Using an ultrasound, your doctor can determine whether a breast lump is solid or filled with fluid. When the mass is hard, there is a high probability that it is a fibroadenoma. A mass full of fluid indicates a cyst.
Pathological conditions
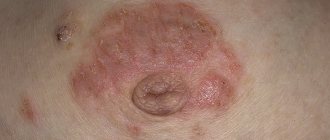
Some pimples around and inside the nipple of the breast are a consequence of the development of pathology.
- Eczema. A complicated form of allergy, the result of excessive friction or hormonal imbalance.
- Neurodermatitis. An allergic reaction develops after nervous stress and mental disorders.
- Atheroma. A subcutaneous clot of adipose tissue forms not only on the dermis, but also on the nipples. Blockage of the duct leads to the accumulation of secretions, which leads to the formation of a wen. The symptom is the presence of a rolling ball inside.
- Telit. Redness of the entire surface of the nipple is called by this medical term.
- Mastitis. The inflammation is located inside the mammary gland and spreads to the nipple and areola (blood is often released from them).
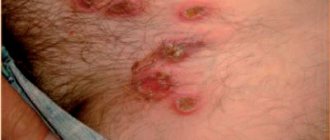
White pimples that appear around the nipples in women are a sign of furunculosis. Entering the epidermis through wounds, pathogenic microflora causes inflammation, often transforming into a purulent process.
READ ALSO: Pimples on the head in the hair: in men and women, treatment of ulcers on the skin of the back of the head and not only, reasons why pimples appear that itch in an adult, photo
If they appear, then urgent treatment is needed: some nodules lead to necrotic processes and abscesses. Doctors recommend opening pustules, but only under the supervision of a specialist.
There are three answers to the question of which doctor you should contact. When there is a suspicion that the activity of the mammary gland is impaired, then go to a mammologist, or a skin specialist - a dermatologist. If you suspect the development of a neoplasm, it is better to visit an oncologist.
Paget's disease is a malignant disease that is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers and pain. In most patients, the pathology is localized on the nipple, less often - near the areola.
Conclusion
Suddenly appearing pimples on the nipples in women are mainly related to anatomical formations, but there are also manifestations that are caused by diseases.
Doctors warn! Shocking statistics - it has been established that more than 74% of skin diseases are a sign of parasite infection (Accarida, Giardia, Toxocara). Worms cause enormous harm to the body, and the first to suffer is our immune system, which should protect the body from various diseases. The head of the Institute of Parasitology shared the secret of how to quickly get rid of them and cleanse your skin, it turns out that’s enough. Read more .
White bumps are the consequences of the effects of herpes on the body, and doctors can only eliminate them with medication. Purulent processes are also dangerous, so they should be neutralized as soon as possible.
News MirTesen
Fibroadenoma - treatment
In most cases, fibroadenomas do not require treatment. However, some women, for safety reasons, prefer to remove the seal. If the doctor determines the presence of fibroadenoma during clinical trials, then surgery will probably not be needed.
You can avoid surgery because:
- surgery can distort the shape and texture of the breast;
- fibroadenoma can sometimes shrink or disappear.
Typically, they only need to be monitored regularly for size and appearance using ultrasonic inspection.
Prevention
It is impossible to avoid the manifestation of physiological changes during pregnancy. After lactation ends, Montgomery's tubercles usually shrink and return to their pre-pregnancy state.
Proper breast care during pregnancy helps prevent clogged or infected glands:
- daily washing of the glands with warm water without soap and shower gels;
- using glycerin compounds, baby cream, or a doctor-recommended product to soften the skin of the breasts and nipples;
- contrast shower for the chest to increase blood flow and strengthen delicate skin;
- Regular use of pads in your bra if your milk is leaking or your nipples are sensitive.
Mammologists and gynecologists strongly recommend that pregnant women carefully select underwear for their growing breasts. Squeezing, tugging of the mammary glands or constant contact of the skin with synthetic fabric is unacceptable.
Fibroadenoma - surgery
Fibroadenomas of very large sizes (the relative ratio of the size of the fibroadenoma and the breast itself is important), which grow quickly and are painful, must be removed surgically. Sometimes this is done for psychological reasons.
Your doctor may recommend surgery to remove fibroadenoma if you think the test results are alarming.
Fibroadenoma removal procedures include:
- With cryoablation, the doctor inserts a thin “stick” through the skin into the fibroadenoma and freezes the tissue with gas.
- Some fibroadenomas are too large to be frozen, and cryoablation is only used if the diagnosis confirms that it is a fibroadenoma.
- The surgeon sends the removed breast tissue to the laboratory for examination.
After fibroadenoma is removed, it is possible for them to develop again - they recur.
It is necessary to check your breasts regularly, regardless of whether there was fibroadenoma or not.
If lumps form on your breasts, consult your doctor to rule out the possibility of a malignant neoplasm.