Pruritus, the most common dermatological complaint, is characterized by an unpleasant sensation with a continuous need for a response of mechanical irritation of the skin, as a result of which it can cause effects such as skin damage, secondary infection, and scar formation. Itching can also significantly affect the general condition and quality of life of patients, causing emotional disturbances, insomnia, anxiety, and in severe cases, depression and suicidal thoughts [1].
Itching is one of the most common subjective symptoms in dermatology, second in prevalence only to complaints about cosmetic defects. With atopic dermatitis and urticaria, 100% of patients complain of itching, with psoriasis - up to 87% of patients [2]. According to clinical and epidemiological data from H. Alexander et al. [3], 35% of skin clinic outpatients suffer from itching caused by dermatological diseases such as prurigo nodosum, lichen planus, atopic dermatitis, eczema, xerosis, etc.
There is both histamine-induced and histamine-independent itching. Histamine-induced is caused by mechanical, thermal, electrical or chemical stimulation of unmyelinated histamine-sensitive peripheral C-type nerve fibers. Nonhistamine nerve fibers are also involved in the transmission of the itch signal, and therefore many forms of itch are insensitive to antihistamines. Itching is one of the forms of the skin analyzer, close to other types of skin sensation (touch, pain). Severe itching is relieved by severe self-harm, leading to the replacement of the sensation of itching with a feeling of pain [4, 5].
In this regard, it is worth mentioning the vicious cycle of itching—scratching—itching. Damage to the skin barrier and subsequent inflammation lead to the development of itching. In the skin, inflammatory cells activate sensory nerves, mast cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. All of the above cells release itch mediators, which further increase inflammation. The itch signal is transmitted to the brain, causing the scratch reflex. Scratching further damages the skin barrier and increases inflammation. T lymphocytes and eosinophils migrate into the skin, releasing pruritogen mediators. Ultimately, sensitization of sensitive nerve fibers occurs and the activation threshold decreases. Growth factors released by eosinophils cause proliferation of nerve fibers. These changes increase the sensitivity of the skin, which becomes even more vulnerable to endo- and exogenous factors. This cycle is difficult to break. The itch-scratch-itch cycle leads to disturbances in sleep, concentration and perception, thereby limiting the social activity of patients [6].
Pathophysiology
Signals for pain and itching caused by skin causes are transmitted along the same pathways, but the afferent C-fibers differ functionally: one part of the nerve fibers is stimulated by histamine, the other by other substances that cause itching (for example, serotonin). There is evidence of similarities between neuropathic pain, itch and cough. Their common property is peripheral and central sensitization of the afferent nervous system. This explains the effectiveness of antiepileptic drugs and antidepressants for such a variety of conditions, as well as the ineffectiveness or low effectiveness of H1 blockers for some types of itch.
Mechanisms and mediators involved in the formation of the sensation of itching:
- amines (histamine, serotonin, acetylcholine);
- proteases and kinins (tryptase, chymase, kallikrein, bradykini, etc.);
- neuropeptides (substance P, neurotensin, etc.);
- cytokines (prostaglandin E reduces the threshold for susceptibility to itching);
- opioid receptors (metenkephalin, leuenkephalin, β-endorphin), naloxone reduces itching, opiates relieve pain but increase itching.
Contraindications to the use of antipruritic ointments
All contraindications are based on the functions of the active substance. Many antipruritic ointments are prohibited for use during lactation and pregnancy, as they can penetrate the systemic bloodstream and have a harmful effect on the fetus.
Some products are prohibited for newborns and elderly patients. Almost all medications cannot be used in case of hypersensitivity to the active ingredients.
When treating itching, it is necessary to refrain from sunbathing and stop contact with allergens.
It is contraindicated to use any antipruritic ointments at home if the cause of the disease is unclear. In this case, you should urgently consult a doctor, as improper treatment can have serious consequences. In particular, hormonal corticosteroids weaken local immunity, which can lead to the spread of infections. Antibacterial ointments are ineffective and even harmful for viral and fungal diseases.
Classification
By prevalence
Localized:
- non-specific:
dry skin, parasitic diseases, skin diseases (eczema, bullous pemphigoid, etc.), fungal skin lesions, allergic skin manifestations, insect bites, contact dermatitis;
- specific for oncological diseases:
melanomatosis (for cancer of the anus and vulva), glioblastoma, metastatic skin lesions, paraneoplastic syndrome.
Generalized:
- non-specific:
primary skin diseases, endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus), carcinoid syndrome, diseases accompanied by cholestasis, blood diseases (for example, Vaquez disease), neurological diseases, senile pruritus, psychogenic pruritus, pruritus caused by infectious diseases, iatrogenic pruritus ( side effects of drugs);
- specific for oncological diseases:
chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, lymphomas, mycosis fungoides (a type of T-cell lymphoma), multiple myeloma, paraneoplastic syndrome.
By genesis
Central:
• neuropathic: brain abscess, brain injury, brain tumor, multiple sclerosis;
• neurogenic: cholestasis, opioids, paraneoplastic process;
• psychogenic: psychosomatic disorder manifested by itching.
Peripheral:
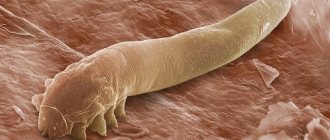
• cutaneous, “pruritoceptive”: cutaneous mastocytosis, medications (± rash), infestations (scabies, lice, fleas, mites), primary skin diseases, plant burns, urticaria;
• neuropathic: postherpetic neuralgia.
Mixed: central and peripheral – uremia.
Cream for irritation on the skin of the face and body La-Cri
To combat skin irritation represented by dryness, flaking, redness and itching, you can use La Cree Cream for Dry Skin. The cream contains natural ingredients: shea butter, jojoba and wheat germ, beeswax, string and licorice extracts. These active components improve the water-lipid balance of the skin, fight irritation, nourish and moisturize the skin, make it elastic and firm. This product is not only great for adult skin care, but can also act as a children's anti-irritation cream.
Diagnostics
Anamnesis
- Localization : focal or generalized.
- Onset : acute onset is the least characteristic of systemic diseases.
- Duration.
- Nature/character : severe, constant itching, worsening in the evening - scabies;
- “burning” itching – perpetiform dermatitis;
- “tingling” – polycythemia.
Physical examination
- Careful examination of the skin: primary lesions;
- excoriation of the skin in various areas (pediculosis, scabies);
- inflammatory papules on the legs with a small vesicle in the center (flea bites);
- “butterfly” sign in the upper central part of the back (hepatobiliary pathology);
- uremic chills.
Laboratory research
Complete blood count with leukoformula, urea, creatinine, liver tests (markers of cholestasis - alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), determination of bilirubin), thyroxine (T-4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), blood glucose.
Localization of itching
When choosing a particular drug, it is important to take into account the localization of unpleasant sensations.
In the anus
Causes of itching in the anal area can be parasites, infections or proctological diseases. You can relieve unpleasant symptoms with the following medications:
- Mesoderm . Relieves swelling and itching, not used in case of syphilis.
- Heparin ointment . Treats hemorrhoids and thrombophlebitis. Contraindications are skin damage and bleeding tendency.
- Proctosedyl . It is used for proctological diseases, including hemorrhoids, anal fissure or eczema. Do not use the product for skin tuberculosis and fungal infections.
- Gepatrombin-G . Relieves inflammation and eliminates blood clots. Not used for bacterial infections and tumors.
In intimate places
Itching in intimate places can be accompanied by gynecological diseases: genital herpes, vaginosis, gardnerellosis. All these pathologies are characterized by rash and severe discomfort. In this case, medications such as:
- Acyclovir, Biopin, Miratex . Used in the presence of genital herpes.
- Clotrimazole, Doxycycline, Fluconazole . Used to treat fungal diseases, candidiasis (thrush).
- Oxycort . Relieves allergies, treats dermatitis and diaper rash.
- Hydrocortisone . Used in the treatment of psoriasis and dermatitis.
- Prednisolone . Eliminates skin diseases and eczema.
- Miconazole, Pimafucin . Antifungal drugs used during pregnancy and lactation.
In the groin of men
The causes of discomfort in the groin can be:
- weakened immunity;
- violation of hygiene rules;
- genital herpes;
- sexually transmitted diseases.
List of the most effective drugs:
- Baneocin . Antibacterial agent, prescribed for eczema, secondary infection, ulcers after genital surgery.
- Triderm . A complex drug that is effective against dermatoses and lichen simplex.
- Celestoderm . A hormonal drug containing an antibiotic. Used to treat dermatoses.
In the ears
Causes may be an allergic reaction, skin diseases or fungal infection. To eliminate unpleasant manifestations, use one of the following ointments:
- Sinaflan . It has a pronounced anti-allergenic and anti-inflammatory effect. Use with caution during puberty and in children.
- Lorinden . Indications: dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis.
- Bactroban . Antibacterial ointment with the active ingredient mupirocin. Used to eliminate bacterial infections, furunculosis. Use with caution in children under one year of age, patients with severe kidney pathologies and the elderly.
On foot
The following can eliminate fungal infections, allergic reactions or redness on the legs:
- Advantan . Relieves allergic reactions and inflammation.
- Elokom . Glucocorticosteroid drug for the treatment of lichen planus.
- Sinaflan. An anti-allergy drug that is also used to relieve inflammation.
On hands
If your hands are affected, medications that relieve redness, discomfort and dryness will help:
- Pimecrolimus . Used from 3 months, treats dermatitis. Can be used long-term or short-term, ineffective against infections (viral, fungal and bacterial). Contraindicated in patients with reduced immunity.
- Fucidin . Antibiotic, has bacteriostatic properties.
- Levomekol . Broad-spectrum antibiotic with a regenerating effect. Eliminates inflammation, kills germs.
On the face
Often itching in the face is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Edema . The allergic reaction causes swelling of the tissue around the eye sockets and in the area of the nasolabial triangle.
- Rash . It can appear in different forms: small spots, bubbles with clear liquid. This symptom cannot be left untreated, since after opening the pimples, the wound can become infected.
- Erythrema . Redness of the skin in the form of round spots of various sizes, sometimes in large areas.
- Peeling . More typical for dermatitis, easy to treat.
There are quite a lot of ointments that can help in this case. Some of them are more effective in certain situations:
- Allergy to the sun: Actovegin, Solcoseryl, Radevit.
- Allergy to cold: Levomekol, Elokom, Levosin.
- Diathesis: zinc ointment, Akriderm, Diaderm.
- Allergy to cosmetics: Kremgen, Elidel or Fucidin.
Patient management
General events
- If your skin is dry, use soap substitutes with a moisturizing effect instead of soap, and apply moisturizing cream to your skin 2-3 times a day.
- Review the list of medications you are taking: if a possible cause of itching is a medication, it needs to be changed.
- For atopic/contact dermatitis: topical corticosteroids once a day for 2-3 days if there is inflammation but no infection.
- For scabies: topical permethrin or malathion.
- For cholestatic itching due to obstruction of the common bile duct: duct stenting – if possible.
Nonspecific treatment
It is carried out taking into account the condition of the skin - different approaches to local treatment on intact and macerated skin.
Antipruritic agents for topical use : 0.5−2% cream with levomenthol (menthol) is effective on intact skin if the itching is localized or more intense in a certain area.
Sedating antihistamines can be prescribed 1 hour before bedtime; if the effect does not persist for a day, two-time use is possible:
- Hydroxyzine/Atarax, Vistaril 25 mg orally at night;
- promethazine/Pipolfen 25 mg orally at night;
- diphenhydramine/Diphenhydramine 50 mg orally 1–2 times a day;
- Dimetindene/Fenistil 1 mg orally daily plus Fenistil gel (0.1% dimethindene) topically 3 times a day will help in most difficult cases.
Some non-sedating antihistamines may have an antipruritic effect (eg, loratadine/Claritin, cetirizine/Zodac, Zyrtec).
Antihistamines for external use (for example, Fenistil cream) on intact skin are used for no longer than a few days in cases where itching is caused by the release of histamine (for example, acute drug rash).
TCAs with antihistamine properties : doxepin/Doxepin in a dose of 10-75 mg orally at night. Antidepressants will help in cases where anxiety or depression occurs.
Specific treatment
Table 1 and Appendix 1 present the principles and regimens of drug therapy for itching of various etiologies.
Circumstances accompanying the disease
It is important to choose the right antipruritic drug: it may be ineffective for a number of diseases. Before starting use, you must obtain the approval of your doctor.
Pregnancy
Any medications used at this time should be carefully selected by the attending physician. Particular attention should be paid to anti-allergy ointments.
A woman’s body can react unpredictably to any medications during pregnancy, so it is important to select medications that cause the least harm. These include:
- Fenistil-gel . Can be used on small areas of skin starting in the second trimester.
- Psilo-balm . Allowed at any time if the benefit to the mother outweighs the harm to the child.
- Desitin . It has a minimal number of contraindications, so it is most often used to relieve irritation.
- Advantan, Afloderm and other hormonal ointments. Allowed only under strict medical supervision.
- Bepanten, Panthenol, Radevit, Emolium . They have no contraindications for use during pregnancy, relieve dryness, and enhance tissue regeneration processes.
Hives
Urticaria manifests itself as a reaction to insect bites, food, or contact with an irritant. The following medications will help relieve such symptoms:
- Psilo-balm. Effectively eliminates irritation.
- Zyrtec . Used to treat the chronic form of the disease, it is not prescribed in old age and in cases of renal failure.
- Gistan-N . Used after 2 years to treat urticaria and relieve itching.
- Nezulin . The drug with plant extracts is effective against inflammation.
Chicken pox
Varicella (chickenpox) is a disease caused by the herpes virus type 3. Accompanied by a vesicular rash with severe itching. First of all, for this pathology, it is necessary to use an ointment based on acyclovir or valacyclovir: these are antiviral drugs that are effective against the herpes virus.
To relieve itching you can use in parallel:
- Beloderm . It has an anti-exudative effect, relieves pain and inflammation.
- Infagel. Fights the virus, stimulates the immune response, and forms a film on the surface of the rash.
- Viferon . An immunomodulator, approved for use at any age, it effectively eliminates the rash.
Eczema
Regardless of whether the skin lesions are wet or dry, the following ointments are allowed for use:
- Sinaf . A strong corticosteroid hormone, used with caution and after a doctor's permission for short periods of time.
- Iricar . Homeopathic medicine, approved for long-term use. It has no side effects and no proven effectiveness. Normalizes the physiological condition of the skin.
Haemorrhoids
The disease is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the anus, the formation of nodes and pain. You can relieve symptoms with ointments:
- Proctosan . Dries, relieves pain.
- Celestoderm. Relieves allergic reactions, eliminates inflammatory processes.
- Heparin ointment . Dissolves blood clots and relieves swelling characteristic of this disease.
Hyperemia
In this case, itching occurs due to irritation of the nerve endings on the surface of the skin. Reasons include:
- skin diseases;
- parasites;
- disturbance of emotional state;
- diseases of internal organs;
- burns;
- allergic reactions.
For treatment, almost any ointment is used to eliminate itching: containing menthol, anti-parasitic, antifungal, antihistamine, hormonal, calcineurin inhibitors.
Vitamin deficiency and thyroid disease
Vitamin deficiency causes itchy skin due to malnutrition and immune processes. The reason why itching occurs in diseases of the thyroid gland is the same violation of absorption and metabolism of vitamins. Therefore, these conditions are treated with the same medications.
It is most effective to take herbal preparations, as well as products that contain the missing vitamins: Nezulin, Radevit, oil solution of vitamins A and E.
Increased skin sensitivity
For hypersensitivity, homeopathic medicines or anesthetics are used. Traumeel ointment has proven itself positively. It helps relieve irritation, has an anti-inflammatory, wound-healing effect. The course of treatment varies and depends on the severity of the disease.
The drug is not prescribed to people with fungal infections, AIDS, multiple sclerosis and skin tuberculosis.
Overheating and hypothermia
Overheating or hypothermia causes frequent exacerbations of diseases such as:
- pityriasis rosea;
- herpes;
- dermatitis and other immune reactions.
Thus, the selection of ointment depends on the specific manifestations and exacerbation of a particular disease.
Senile itch
Older people may experience a condition where the whole body itches. There are no specific remedies that relieve itching caused by age. At the time of its exacerbation, it is worth using hypoallergenic cosmetics.
Nezulin is sometimes recommended - the indication is dermatitis. The drug is absolutely safe for older people, due to the fact that the active substances are essential oils.
Ointments containing dexpanthenol and plant extracts are also very effective.
Insect bites
Medicines that can relieve itching after bites of mosquitoes and other insects include:
- Fenistil . Relieves discomfort and restores skin after damage.
- Mi&Co . Healing cream, eliminates inflammation, relieves allergic reactions.
- Bora plus . Antiseptic, prescribed for infectious lesions and mosquito bites.
Irritation after shaving
Shaving is a stressful procedure for both men and women. As a rule, irritation goes away almost immediately, but in some cases it persists for a long time. To remove it, you can apply Baziron ointment to the skin.
The drug is antibacterial, eliminates itching, fights rashes and hyperemia. It can be used to reduce the severity of allergic reactions.
Baziron is used after each shaving procedure. Side effects: redness, burning and itching. Do not use to treat children under 12 years of age.
Mechanical pressure
Mechanical damage or pressure often causes itchy skin. It may be caused by:
- accessories;
- tight clothes;
- blow;
- cuts;
- scratching after an insect bite.
If the integrity of the skin is compromised, the wound should be treated with an antiseptic solution, and then treatment should be chosen depending on the symptoms. It is effective to use non-hormonal drugs, but they are contraindicated in the presence of infection.
Neurodermatitis
A neurotic disorder that is accompanied by severe itching. Often associated with atopic dermatitis, but is actually a group of skin diseases. The following ointments are used:
- Anti-inflammatory non-hormonal: Desitin, Radevit, Gistan.
- Hormonal: Dermovate, Akriderm, Celestoderm.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: Pimecrolimus, Tacrolimus.
Itching in children
Not all anti-itch drugs are approved in pediatrics. List of the most effective and accessible:
- Fenistil . Indications: sunburn, insect bites, allergies. Apply after 3 months.
- Gistan . Herbal preparation. Indications: dermatitis and itching during allergic reactions.
- Skin cap . There are practically no contraindications for use in children.
- Desitin . They treat diaper rash, rashes, weeping ulcers, and burns.
- Protopik . Effective even for severe dermatitis. There are no contraindications, but the drug can only be used at the age of 2 years.
Useful tips
Systemic treatment is often not necessary if the skin condition improves.
If your skin becomes dry, stop using soap; bathing in warm rather than hot water, lubricating the skin after bathing and at night, applying a damp cloth for 15–20 minutes, then applying cream or ointment.
For damp skin - protective cream (zinc paste), drying dressings with Burov's liquid (aluminum acetate 8%, diluted 1:10–1:20).
Local anti-itch remedies
Zinc oxide has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and antipruritic effects, and is used in concentrations of 10–50% in creams, liniments, lotions, ointments and pastes that are effective in the treatment of localized forms of itching.
Menthol, when applied to the skin and mucous membranes, dilates blood vessels, causing a feeling of coldness and then numbness, significantly reducing itching. It is used in powders, ointments, and lotions in concentrations of 1–10%.
Camphor , when applied to the skin, produces a warm sensation followed by mild anesthesia, which reduces itching. It is used in the form of liniments, lotions and ointments in concentrations of 2–20%.
Important
It should be remembered that products with menthol and camphor cannot be used simultaneously on one area of the skin.
Calamine , a lotion containing zinc carbonate (calamine), zinc oxide and a small amount of phenol, is widely used in the treatment of itching and atopic dermatitis.
Clinical picture
Subjectively, patients characterize itching as a “crawling” sensation, tingling, slight burning of the skin, etc. The intensity of itching can vary: from mild to severe. Itching leading to sleep disturbance is considered severe. Biopsy itch is a severe itch in which scratching leads to significant self-damage to the skin. With this form of itching, the pain that appears when excoriating the skin brings satisfaction. Clinically, the patient's condition with prolonged itching will be characterized by excoriations (linear skin lesions with hemorrhagic crusts), post-inflammatory pigmentation, scars, lichenification, and secondary pyoderma. Prolonged itching negatively affects the general well-being of the patient: the development of insomnia and associated nervous system disorders are possible [7].
The fastest possible relief and cessation of itching is a priority in the treatment of itchy dermatoses. Symptomatic therapy for itching should be prescribed as early as possible to interrupt its cyclic course. Therapy for itching should be effective and safe, well tolerated by patients and have a positive effect on quality of life [8].
Care Tips
- Prevention of scratching: short-filed nails, lightly rubbing itchy areas.
- After washing, dry your skin carefully using wet movements, use a soft towel or a hair dryer on a cold setting.
- Avoid long hot baths. Try a bath with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) or medicated oils.
- Use loose clothing and loose bedding/blankets.
- Avoid overheating and sweating, especially during night sleep.
- Increase the humidity in the bedroom so that your skin loses less moisture.
- Wear cotton gloves at night to prevent scratching.
- Avoid damaging the skin with alcohol-containing rubbing, woolen clothing, and excessive hygiene procedures.
- Cleanse your skin gently using moisturizers.
- Use cooling, soft compresses.
- You can use an anesthetic mixture: aftershave cream with menthol 50 ml, Diphenhydramine 1% 3–5 ml, Lidocaine 2% 1–2 ml, Novocaine 0.5% 5–10 ml. Mix and serve chilled.
- Use relaxation and positive visualization techniques.
Cream for facial irritation
Unlike other areas of the body, which are usually covered by clothing, the face always remains open. In this regard, it suffers more from the effects of adverse weather conditions - exposure to sunlight, frost and wind. Men may experience irritation after shaving, so it is advisable for them to use special shaving creams and foams.
Irritation on the skin of the face is often caused by a reaction to substances contained in masks, peelings, foundations and decorative cosmetics - parabens, derivatives of formaldehyde and acetic acid, hydroxy acids, alcohols, etc.
To eliminate redness, peeling and itching of the face, creams for sensitive skin prone to irritation are usually used. They may include allantoin, retinol, hyaluronic acid, tocopherol, antioxidants, beta-glucan, herbal components (aloe vera, chamomile, verbena, green tea, algae polysaccharides).
Causes of allergies and types of rashes
There are many causes of allergies, the main ones being:
- food products (chicken protein, fish, seafood, cow's milk, citrus fruits, chocolate, nuts and many others);
- chemical detergents and cleaners;
- medications;
- household dust;
- pets (their fur, fluff, saliva);
- insect bites;
- helminth infestations (parasitic worms provoke allergic reactions in humans);
- environmental factors - cold, frost, sun;
- physical procedures associated with current (the cause of a rare form of allergy to physical activity and current).
Allergies often manifest themselves in the form of red, scaly spots that can be located on any part of the body surface.
Main types of rashes:
- Urticaria: rashes in the form of blisters, often multiple, can be located on any part of the body. Accompanied by redness, itching, local swelling. They usually go away within a day. Quincke's edema (swelling of the deep layers of the dermis and subcutaneous fatty tissue) of the upper respiratory tract often develops along with urticaria.
- Atopic dermatitis: The rash in adults is usually localized on the flexor surfaces of the arms and legs, on the back of the neck and behind the ears. The lesions are accompanied by redness, itching, and crust formation.
- Contact dermatitis: the cause is direct contact of the allergen with the skin, therefore it mainly occurs on the hands. The affected area exhibits hyperemia, weeping, swelling, and itching.
- Eczema can be localized on any part of the body, but most often it is the face and hands. It presents as hyperemic areas of the skin with severe swelling and multiple blisters.