Why do lips dry out?
Dry lips occur due to several factors, such as:
- dry or windy weather;
- frequent stress;
- habit of licking lips;
- taking medications that affect the functioning of the salivary glands and muscles around the mouth;
- increased body temperature during illness;
- intoxication processes;
- allergic reaction to cosmetics;
- diabetes;
- kidney diseases;
- bad habits.
Lips often become dry in people who are on diets or follow a vegetarian diet. In such cases, the condition of the lips worsens due to a deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins, which are found in foods of animal origin.
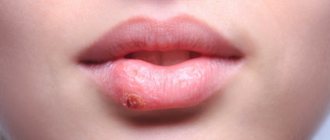
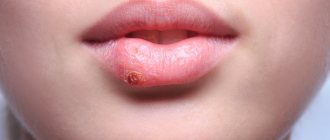
Cheilitis
Clinical manifestations of cheilitis
Exfoliative cheilitis
This type of cheilitis is classified as a group of psychosomatic diseases. It is often diagnosed in children or young adults. Patients usually exhibit two types of psycho-emotional disorders: in the dry form - depressive reactions, in the exudative form - anxious reactions. The disease is always clearly localized - the lesion appears on the red border of the lips and never moves to the oral mucosa and skin around the lips.
Dry form
Patients with the dry form of the disease usually experience congestive hyperemia of the lip border, the formation of dry gray scales, and constant peeling of the lips. The scales are easily removed, but appear again within a week. Patients often complain of severe burning and excessive dryness of the lips. The dry form of the pathology can eventually turn into exudative, which is characterized by greater severity of symptoms.
Exudative form
The exudative form of the disease is usually accompanied by swelling of the lips, pain, and the formation of a large number of scales, which sometimes reach quite large sizes and even hang from the lips. After the scales fall off, a hyperemic surface appears in their place. Patients also complain of sore lips, which makes eating difficult. When diagnosing the disease, the dry form should be distinguished from atopic, allergic and meteorological forms, and the exudative form from exametous cheilitis and lupus erythematosus.
Glandular cheilitis
Glandular cheilitis is an inflammation of the accessory salivary glands, which mainly affects the lower lip. The pathology is often diagnosed in patients over 40 years of age. The primary form of the disease can be triggered by an abnormality of the salivary glands, the secondary form can occur against the background of leukoplakia or lupus erythematosus. Simple glandular cheilitis is characterized by enlargement of the salivary glands, the appearance of red dots on the mucous membrane of the lips, and the active production of serous secretion, which accumulates in the form of dew on the inside of the lips.
In rare cases, patients are found to have a purulent form, which is accompanied by pronounced symptoms and a severe course. The clinical picture of the superficial form of purulent disease is almost the same as with simple glandular cheilitis, only the enlarged salivary glands produce purulent secretion. The deep purulent form of the disease is very difficult. The patient experiences swelling of the lips, the formation of purulent crusts and erosions on the red border. On palpation, severe pain appears.
Contact allergic cheilitis
This type of cheilitis is considered a delayed allergic reaction to chemicals that enter the body through cracks in the lips, then enter the bloodstream and ultimately lead to sensitization of the body. At the same time, the period of sensitization is very individual, since it can range from a couple of days to several years. The duration of sensitization depends on sensitivity to allergens, as well as the state of the endocrine, nervous and digestive systems.
Usually the inflammation is located on the red border of the lips, and also spreads slightly to the skin around them. Erythema appears at the site of contact between the allergen and the skin. Due to inflammation, the patient also develops small blisters, cracks and erosions, which is why he complains of itching, swelling and burning of the lips. The disease sometimes occurs without symptoms; the patient is only bothered by peeling of the lips.
If allergic cheilitis continues for a long time, then usually the red border of the patient’s lips becomes excessively dry, cracks and small furrows form on it. The symptoms of this disease are similar to those of atopic and exfoliative cheilitis, which the doctor must take into account during diagnosis.
Meteorological or actinic cheilitis
Meteorological cheilitis is an inflammation of the surface of the lips, which occurs due to various climatic irritants, including high and low air humidity, wind, and temperature changes. Often this pathology is diagnosed in men because they do not use protective lipsticks. Patients are concerned about the feeling of tightness and dryness of the lips. Damage to the lower lip is also observed - its inflammation and swelling, slight infiltration. Peeling and small scales appear on the red border. It is noteworthy that the lesion does not extend to the oral mucosa and skin around the lips.
As a rule, this chronic disease worsens after exposure to any aggressive climatic factor. It is extremely rare for doctors to diagnose malignancy of the affected area, but precancerous processes are still detected. When diagnosing the disease, it is worth considering that its symptoms are similar to the symptoms of diseases such as atopic and allergic cheilitis.
Atopic cheilitis
Atopic cheilitis refers to inflammation of the red border of the lips, which is considered one of the manifestations of neurodermatitis. The disease occurs due to a genetic predisposition. Allergens can be medications, foods, dust, decorative cosmetics, and pollen.
Often the course of atopic cheilitis is long, the disease either subsides or worsens again. The disease usually goes into an acute stage in the cold season, but in the summer it goes into remission. During periods of exacerbation, patients complain of peeling, redness and itching of the skin of the red border of the lips. Swelling and infiltration of this area also gradually appears.
Excessive dryness and infiltration often lead to cracks, due to which the patient experiences pain when opening the mouth. During remission of the disease, patients experience peeling and thickening of the skin near the red line of the lips. It is noteworthy that inflammation almost never spreads to the oral mucosa. The atopic form of cheilitis must be distinguished from pathologies such as streptococcal cheilitis, contact and allergic cheilitis.
Macrocheilitis
Macrocheilitis refers to swelling of the lips and paralysis of the facial nerve. The attack begins suddenly with swelling of one or both lips at once. At first, patients are bothered by itching of the lip, then they notice that it has begun to grow rapidly. With this type of cheilitis, a shapeless swelling of the lip may occur, it may acquire a bluish tint, and the edges may turn out. Over time, the swelling becomes so large that the lip increases in size three times.
There is uneven swelling of the lips, as one of them appears more swollen than the other. In patients, swelling is constantly observed, but it either increases or gradually subsides. During the day, the intensity of swelling usually changes. Another pronounced sign of the disease is paralysis of the facial nerve. The patient feels an unpleasant sensation in the mouth, the palpebral fissure widens and the corners of the mouth droop due to the loss of tone in the affected part of the face. Usually, incomplete paralysis is observed, since the patient retains autonomic, sensory and motor functions.
More than 60% of patients are diagnosed with a folded tongue, which is considered a developmental abnormality. In this case, there is pronounced swelling of the tongue, which leads to its enlargement. It is worth noting that not all patients are diagnosed with all the main symptoms of this type of cheilitis. Sometimes the disease can manifest itself with just one pronounced clinical sign.
The course of macrocheilitis is always chronic. At the very beginning of the disease, relapses occur, which alternate with long periods of remission. However, over time, the disease becomes chronic, and its exacerbations are extremely rare - usually after stressful situations and viral infections. During diagnosis, this pathology should be distinguished from angioedema, lymphangioma, erysipelas, and hemangioma. Typically, difficulties in making a diagnosis arise when the disease manifests itself with only one leading symptom.
Hypovitaminous cheilitis
Hypovitaminous cheilitis occurs due to a lack of B vitamins. Because of this, signs of the disease appear such as burning and dry tongue. In addition, there is redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, the appearance of cracks and peeling on the red border of the lips. Often the cracks are quite painful and often bleed. With this type of cheilitis, patients' tongue becomes enlarged and teeth marks appear on it.
What should beautiful and healthy lips look like?
Beautiful and healthy lips are characterized by the following signs:
- evenness and smoothness of the skin;
- symmetry of the corners of the mouth;
- the presence of a pink or red tint to the lips;
- absence of peeling, cracks and purse-string wrinkles;
- convex volume of the labial border;
- absence of jams, pigmentation and pathological manifestations.
It is also important to pay attention to the presence of a hollow above the upper lip and a cupid's arch, which should be clearly defined.
Diagnosis of diseases of the oral mucosa
Modern medicine has a wide range of diagnostic tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Only a doctor can give the correct classification of the disease. For this purpose, he can use the following methods:
- Mucosal smear for microscopic examination;
- Conducting allergy tests;
- Analysis for viral infections (herpes, tonsillitis);
- General examination to identify the primary disease.
Top 10 tips on how to care for your lips
To keep your lips smooth and hydrated, follow these tips:
- Regularly exfoliate the skin of your lips with special scrubs or a damp, thick towel.
- Moisturize and nourish your lips with herbal balms; in the summer, you should additionally use products with SPF filters.
- Maintain a drinking regime of drinking 2 liters of clean water per day.
- Include in your diet foods high in omega-3 fatty acids (nuts, vegetable oils, vegetables and herbs, fatty fish).
- Stop smoking, as tobacco smoke dries out the thinnest skin of the lips and leads to the formation of purse-string wrinkles.
- Wash off makeup not with soap, but with two-phase makeup removers. In addition, while washing your face, it is good to do simple exercises to strengthen the orbicularis oris muscle. It is necessary to tightly compress and unclench your lips, and also pronounce the letters A, O, U, Y.
- Take complexes containing vitamins A, C, E and group B.
- Apply only high-quality cosmetics to your lips that do not contain camphor, phenol, aniline dyes and heavy metal salts.
- It is recommended to add lip masks to winter care, or replace them by applying a restorative cream at night.
- It is important to remember that cosmetic procedures play a huge role in maintaining external beauty. Therefore, do not forget about professional salon care for thin and delicate lip skin.
Treatment of cheilitis
Treatment of the disease depends on the causes of its occurrence. For example, to treat allergic cheilitis, drugs are used that reduce the body’s sensitivity to allergens - antihistamines, as well as vitamins. Zinc ointment, anti-inflammatory creams containing glucocorticoids, salicylic acid, and sulfur are used externally. Avoid substances that irritate the mucous membrane of the mouth and lips. After eating, rinsing with chamomile infusion or soda is useful. To determine the allergen, it is necessary to conduct allergy tests.
For fungal cheilitis, antifungal drugs are prescribed in combination with vitamin B2 and ascorbic acid. An examination by a dentist and, if necessary, complete sanitation of the oral cavity and thorough treatment of problem areas with oil solutions of vitamins are recommended. To prevent relapses, a diet with limited carbohydrates is prescribed. In the treatment of exfoliative cheilitis, corticosteroid and photoprotective ointments, 2% boric salicylic acid ointment are widely used. In the presence of an exudative form of exfoliative cheilitis, Bucca radiation is effective.
Diagnosis of this disease is carried out by several doctors: a therapist, a dentist, an allergist. A combination of systemic (general) and topical (local) drug therapy produces a good effect.
Back to articles
Lip treatments in Moscow
Therefore, in situations where you need help in restoring or correcting your lips, it is better to contact Dr. Korchagina’s clinic.
We offer you only the best and most effective procedures:
- lip augmentation and correction with hyaluronic acid – a minimally invasive injection technology based on the introduction of fillers with hyaluronate; manipulation helps to correct the shape of the lips, as well as eliminate dryness, peeling and pallor of the lip border;
- Botox injections - botulinum toxin injections block muscle contractions, which allows you to keep the skin of the lips smooth without creases and wrinkles;
- lip contouring – subcutaneous injection of filler gels ensures enlargement, smoothing of the lip contour, elimination of purse-string wrinkles and folds in the corners of the mouth;
- permanent lip makeup – tattooing evens out color, makes lips voluminous and bright, eliminating congenital defects and minor imperfections.
The selection of the optimal method for lip restoration is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics and skin condition of the patient.
To make an appointment for a consultation and procedures at the Korchagina clinic, write to us on the website or call us by phone.
general characteristics
Diseases of the oral mucosa can be infectious, inflammatory, viral or fungal. When an infection enters the oral cavity, the mucous membrane is the first to suffer. It can become inflamed, bleed, and become thinner. Conventionally, such diseases are classified as stomatitis. But besides stomatitis, there are many more problems that lead to deterioration in human health.
In almost all of the diseases described below, the symptoms will be similar: pain, rashes of various types, discoloration of the tissues of the oral cavity.
Oral diseases can be treated by a dentist, ENT specialist or therapist. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult any of these doctors for examination.
Constantly dry lips in a child may be a symptom of a disease
If your baby’s lips are constantly dry: in any weather, under any diet, cosmetics do not help them, perhaps this is how the body indicates the presence of a more serious disease.
- Problems with the thyroid gland.
- Diabetes mellitus is also accompanied by increased thirst.
- With dryness, cracking and the appearance of various crusts - fungus, psoriasis.
- Autoimmune diseases are a complex of diseases usually associated with damage to the skin and bone tissue. They are based on the body's immune reaction against itself.
In these cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor for a serious diagnosis.
Sources:
- I.I. Ryumina, V.V. Zubkov, Newborn skin care, Healthy Child magazine, 2017
- V.V. Chebotarev, N.V. Chebotareva, M.S. Askhakov, E.V. Bronnikova, Sensitive skin: causes, methods of therapy, journal Medical Bulletin of the North Caucasus, 2015
- Drobinskaya, A. O. Fundamentals of pediatrics and hygiene of children of early and preschool age / A. O. Drobinskaya. - Moscow: Higher School, 2016. - 400 p.
Photos of diathesis
Photo album on the disease