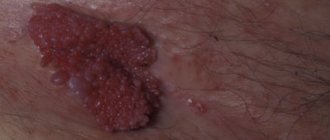
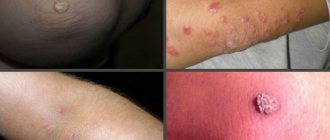
Testicular cancer is a malignant lesion of the male reproductive glands. There is an enlargement of the scrotum, pain in the scrotum, testicles, their enlargement and swelling. Upon palpation, a noticeable compaction can be detected. The disease can be combated more effectively if testicular cancer is detected at an early stage. To do this, it is important to conduct self-diagnosis and become familiar with the symptoms of this disease.
Forecast for the development of the disease
The sooner a man turns to a specialist, the more optimistic the forecasts for the further development of the disease. To assess the effectiveness of treatment, the international TNM systematization is used, which involves four stages of cancer development. They are based on three indicators:
- T – tumor size;
- N – stage of involvement of lymph nodes in the pathological process;
- M – number of metastases.
For the first two signs there are four variants of values, for the third - only two. In total we have 32 forms of cancer according to this classification.
If a patient is diagnosed with a small tumor - up to 20 mm (T1), then he has an 80% chance of a complete recovery. If, at the specified size, the tumor has invaded nearby tissues (T2), then the chances are reduced to 60%.
At stage T3 (the size of the neoplasm is from 20 to 50 mm), the favorable prognosis decreases to 20-40%. The fourth stage, when a large tumor has affected neighboring organs, only 5% of patients have a chance to say goodbye to the disease forever. The rest will relapse.
When calculating the prognosis of the disease, the degree of damage to the lymphatic system is taken into account. At N1, the chances of relapse double. In the presence of stage N2, the prognosis worsens by more than 4 times. Lymph nodes located in N2 indicate that the chances of recurrence of the disease increase by 8 times.
Treatment
If the lump hurts, but there are no other clinical manifestations, the doctor prescribes standard anti-inflammatory therapy. It is based on the use of drugs in the NSAID category. Until the lump completely disappears, the patient regularly visits the urologist.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
When cysts form, surgical excision is indicated. In the case of a hormonal cause of development, adapted medications will help. For a malignant process, surgical excision and chemotherapy are indicated.
Therapy is adjusted based on the patient’s general well-being, the individual characteristics of his body and concomitant diseases.
Spermatocele therapy
Removal of a testicular cyst is a surgical operation that is performed under local anesthesia. If intervention is necessary due to the appearance of a lump under the testicles in men, a small incision is made under the optical device. The cyst is removed, leaving the tissue of the testicle and epididymis intact. A biopsy of the contents of the spermatocele is required.
Afterwards, the patient is given a suspension for two or more days to support the scrotum. In the reviews, patients indicate that in the first few days it is necessary to apply an ice pack to the operation site to prevent hematomas and eliminate swelling.
In rare cases, needle aspiration and sclerotherapy are used. Aspiration is carried out by puncture of the most prominent part of the scrotum with a special needle. If necessary, the doctor uses ultrasound control. During sclerotherapy, a special solution is injected into the spermatocele cavity, followed by massage to evenly distribute the drug. Within a month after the procedure, observation by a urologist is necessary.
With pain and a lump on the testicle in men, lymphadenitis can be diagnosed. Treatment of the disease in the acute stage is conservative. Antibiotic therapy is carried out (medicines are selected based on the sensitivity of microbes found in tests), vitamin therapy, and UHF. You should not ignore taking vitamins - reviews confirm this.
Chronic lymphadenitis requires treatment of the underlying disease, which supports the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes. Specific forms of the disease are treated taking into account the underlying inflammatory process (tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, actinomycosis, and so on). Timely treatment will help avoid the spread of pathology.
Prevention
Every man can prevent the appearance of a lump on the testicle by following these recommendations:
- it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle;
- physical activity must correspond to physical fitness;
- you need to have sex regularly, preferably every 3 days;
- You can’t lead a passive lifestyle, you need to move as much as possible;
- It is recommended to avoid injury to the testicles, and if an injury occurs, seek treatment from a doctor;
- It is very important to have an annual examination at the hospital and to regularly examine your testicles yourself.
The most dangerous among all diseases is testicular cancer; the tumor poses a threat to life.
That is why the appearance of lumps requires immediate examination of the man. Share:
Causes
Most pathologies of the reproductive system in men, including compaction in the testicle, occur for the following reasons:
- pelvic inflammatory diseases;
- circulatory disorders;
- carrying heavy objects, excessive physical activity;
- poor nutrition, vitamin deficiency;
- weak immunity
- hypothermia and overheating;
- passive lifestyle;
- endocrine disorders, hormonal imbalances;
- genetic predisposition.
To say exactly what caused the formation of a lump in the testicle, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Let's look at several common diseases in which a nodule or lump may appear on the testicle
It is important to note that all diseases are presented for informational purposes. You should not self-diagnose and begin treatment, since it is very difficult to distinguish pathologies from each other without examination.
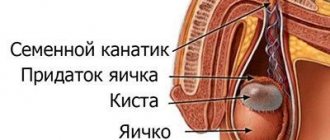
Spermatocele
A testicular cyst or spermatocele is formed if the outflow of secretions from the epididymis is disrupted. As a result, a cavity filled with fluid forms in the area of the epididymis or spermatic cord.
Description of spermatocele:
- painless;
- dense but flexible;
- located above the testicle;
- has a round shape.
A lump appears on the testicle with spermatocele against the background of inflammatory diseases and injuries of the scrotum. The disease can also be congenital. The pathology does not manifest itself in any way and does not interfere with reproductive function. As a rule, patients consult a doctor at the moment when the lump becomes very large.
Inflammation
Orchiepididymitis or an inflammatory process in the testicle and appendages is accompanied by the appearance of a compaction in the testicle. In addition, the patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- enlargement of the entire testicle;
- testicular pain;
- the lump is painful;
- the skin turns red and may become hot.
Inflammation of the scrotal organs is a very dangerous condition that can lead to serious complications, infertility, and impotence. Epididymitis orchiepididymitis severely disrupts the reproductive function of men and requires complex therapy.
Oncology
A lump on or inside the testicle may indicate the development of a tumor. Malignant testicular tumors are classified as germinogenic and non-germinogenic. The first are formed from the epithelium, these include the following tumors:
- chorionepithelioma;
- seminoma;
- teratoblastoma;
- embryonal cancer.
Non-germinogenic ones begin to grow from the main tissue of the testicle, these include:
- Leydigoma;
- sarcoma;
- sertolioma.
Of all these types of cancer, seminoma is the most common. This pathology develops gradually and asymptomatically, which is why it is dangerous. When palpating the testicle, you can feel a small nodule that gradually enlarges. The lump in the testicle itself does not hurt, but as it grows, it irritates the surrounding tissues, so pain appears.
Testicular cancer requires treatment in the early stages, otherwise it begins to metastasize, which leads to the spread of harmful cells throughout the body. The sooner the patient begins treatment, the greater his chances of survival.
A benign testicular tumor is very rare; in more than 90% of cases, patients are diagnosed with cancer. A benign tumor is characterized by the appearance of a painless lump, which soon turns into a malignant form.
Varicocele
Varicose veins of the spermatic cord or varicocele are one of the most common male diseases. Most often, varicocele forms in the left testicle due to the structural features of the male genital organs.
At the initial stages of the disease, the compaction cannot be felt. Over time, the vein swells and can be detected by palpation. The lump in the testicle with varicocele is soft and does not hurt when pressed. But the disease is accompanied by pain in the scrotum and male infertility.
Hydrocele
Hydrocele of the testicle occurs due to a violation of the outflow of seminal fluid. This is facilitated by swelling, infections, injuries, and cancer. With a hydrocele, there are no symptoms, but the patient can feel a painless lump.
If the dropsy is very large, then there are difficulties with urination, pain and heaviness in the scrotum. When palpating the lump, you feel that there is liquid inside. If a hydrocele is accompanied by an infection, then pus forms inside the seal.
Hernia
A testicular hernia in men is a disease in which abdominal organs descend into the scrotum. The lump inside the testicle has a round shape, the veins swell and the patient is bothered by pain.
A hernia can develop as a complication of varicocele and hydrocele, with excessive tension and pressure in the abdominal cavity, after trauma to the genital organs. Obese men and athletes who train too much are at risk of getting a hernia.
Symptoms of testicular cancer when it has metastasized
Symptoms of testicular cancer when metastases are already occurring require special attention. Characterized by shortness of breath, cough, jaundice, sharp pain in the right hypochondrium. It all depends on where exactly the cancer metastasizes.
Most often, testicular cancer metastases go to the lungs, bone marrow, bones, skin, and liver.
Testicular cancer causes dyshormonal symptoms. Then frequent erections and voice mutations in boys are observed. Hair on the body and face may begin to grow sharply and prematurely. Adult men in such cases are characterized by decreased libido and impotence. Sometimes the breasts become enlarged.
When testicular cancer metastasizes to the lymph nodes in the mediastinum, this can cause shortness of breath and cough. During the process of intoxication, a sharp loss of appetite and nausea are noted. The legs swell due to blockage of the inferior vena cava and lymphatic ducts. If the ureters are already subjected to compression, renal failure and hydronephrosis may develop.
Intestinal obstruction as a symptom of testicular cancer begins due to compression of the intestine. In the process of squeezing the nerve roots, sharp pain appears in the back.
Treatment of testicular lumps in men
Drug therapy
In cases where the compaction is caused by the active proliferation of a bacterial infection, therapy should be carried out using good antibiotics,
In this case, a preliminary test for resistance to the active substance is taken.
The doctor may recommend taking medications such as Augmentin, Levofloxacin, Streptomycin, Amoxicillin and Tetracycline.
If the disease is accompanied by elevated body temperature, you should use standard medications for this case.
These include Panadol, Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Ibufen and Nimica. At the same time as the temperature decreases, they relieve severe pain.
If there is severe intoxication due to the active proliferation of bacteria and the formation of purulent accumulations, the specialist selects effective drugs to eliminate it.
Most often, medications such as Regidron or Citroglucosalon help in such cases. They gently remove toxins and enhance the effects of anti-inflammatory pills and injections.
Surgical intervention
Surgery for the development of tumors on the testicle is performed only in the case of confirmed malignant tumors.
In this procedure, the attending physician completely removes the damaged testicle and the spermatic cord leading to it. After this, mandatory chemotherapy should be carried out, which will consolidate the result. After surgery, your doctor may also recommend radiation treatment and physical therapy.
Video: “Causes of pain in the testicles”
Traditional methods of treatment
The use of home recipes should only be done with the permission of the attending physician, who will assess their safety in each specific case. Sometimes their use is completely contraindicated.
Nettle
To prepare the medicine, you should take three tablespoons of dry herb, and it is important to add 600 ml of boiling water to the herbal component. The resulting solution is infused for two hours under a tight lid.
As soon as the infusion is well infused, it should be strained. Take the medication 200 ml of solution three times a day. Treatment with nettle continues until the lump begins to shrink or disappears completely.
Beer compresses
This method shows quite good results, and relief comes after just one or two procedures. To prepare a compress, take 50 g of peas (dried cereal) and pour 0.5 liters of good beer into it.
After two hours, the mixture should be put on low heat and boiled for 30 minutes. After this, the mixture should be removed and left for another two hours.
After this time, the peas should be mashed to a mushy state. Place the resulting product on a napkin and fix the compress on the testicle for two hours.
The procedure can be performed twice a day until the disease completely subsides.
Common jasmine
It is best to combine this medicine with other folk recipes and traditional treatments. To prepare the ointment, you need to take 50 g of the flower part, you can take dry and fresh ingredients, and pour 200 g of real cold-pressed olive oil over them. The resulting mixture is infused in a glass flask for 10 days. After infusion, the product is filtered to remove plant matter and rubbed into the scrotum once a day after personal hygiene of the external genitalia.
Diet for testicular lumps
During treatment, the patient does not need to adhere to special nutritional recommendations, but should still make their diet as rich as possible in healthy vegetables, meat and fruits.
This will significantly strengthen the body’s protective functions, eliminating the symptoms of vitamin deficiency and general weakness
It is especially important to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition during the period of elimination of cancer and inflammatory diseases
Treatment methods
Testicular tumors are treated comprehensively. The main stage is a surgical operation in which the gonad is removed along with the spermatic cord. Radical measures are inevitable, since the risk of spreading atypical cells is extremely high, and relapses of the disease are often observed among patients. Surgery is usually supplemented with chemotherapy or radiation.
Surgery
Preservation of the gonad is possible with bilateral spread of the tumor, as well as if the patient has only one gonad or reproductive function is not realized.
Some patients are recommended to resort to sperm cryopreservation for subsequent use in artificial insemination protocols. The operation to remove a testicle is called an orchiectomy. At the moment, such interventions are recognized as the most effective way to treat malignant lesions of the testes. If necessary, resection of lymphatic structures close in location is performed. Conservative treatment
In the presence of a large tumor, chemotherapy courses are prescribed before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor. In most cases, radiation and chemotherapy drugs are used after surgery to eliminate any remaining tumor cells. After the main treatment, men are prescribed hormone replacement therapy.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Making an accurate diagnosis is a matter for a specialist. The urologist conducts a survey, collects anamnesis and examines the organ through palpation. An ultrasound will then be ordered to confirm the compaction and identify the contents. If diagnosis is difficult, referrals are issued for the following forms of examination:
- MRI;
- biopsy of tumor contents;
- diaphanoscopy;
- blood and urine tests;
- spermogram;
- other.
If the doctor prescribes an examination, it must be completed in order to isolate possible dangerous clinical pathologies, confirming the benign quality of the formation. However, you should not refuse self-examination - the very first diagnostic test that any man can perform. How and what to do:
- open free access to the scrotum (remove underwear);
- lather your fingers (this results in more sensitive palpation), examine the entire scrotum, checking every fold of skin for tubercles;
- palpation is carried out slowly, the testicle should be smooth, homogeneous - a small formation in the upper part is an appendage, you should not be afraid of it;
- Wash the scrotum with warm water, dry it, and visually inspect for hyperemia, cyanosis, and dilated veins.
When palpating, the patient should not experience any unpleasant sensations.
Self-diagnosis
Self-analysis of the condition of the external genitalia, including the scrotum and its contents, is an important point in making a timely diagnosis
This precaution is especially helpful in detecting cancerous tumors in time. It is best to carry out palpation during water procedures or once after a shower.
The body position should be vertical. First you need to take the scrotum in your hand and feel the testicle by holding it in your hand. Using the fingers of the other palm, carefully examine the surface of the organ for neoplasms or changes in consistency. The testicle should be firm under your fingers, but not excessively. If the testicles are slightly different sizes, then this is considered normal. Regular self-examination is strongly recommended for the following men:
- Those whose immediate family members have or have had testicular cancer;
- Having a testicular tumor that was cured in the past;
- Suffering from cryptorchidism or monorchidism;
- At the age of 13 – 15 years or after 40.
Diagnosis and treatment
It is easy to conduct an independent examination of the genital organs without resorting to the help of a specialist. Normally, the testicles are located left above the right, they are not completely hard to the touch with a smooth, even surface without growths and balls. If there are doubts about the health of the genital organs, to clarify the diagnosis you will have to take blood, semen, and urine tests. If serious problems are suspected, the doctor will order an ultrasound of the scrotum, translumination (diaphanoscopy), magnetic resonance imaging, and histology.
Based on the examination results, an effective course of therapy is selected. In most cases, treatment of lumps on the scrotum involves taking a set of medications according to a special regimen prescribed by a doctor. Some types of pathologies are treated exclusively by surgery. If a cancerous tumor is diagnosed in the testicles, then complex therapy is used, which includes drug treatment, surgery, physiotherapy, and chemotherapy.
Diagnostics
Complex diagnostic measures are aimed at identifying the cause of formation and methods for its elimination.
The set of laboratory and instrumental studies can vary depending on the severity of the pathological process. To determine the nature of the formation, the doctor prescribes standard measures.
History taking
The specialist collects information about complaints. The patient must describe all symptoms, talk about previous injuries and concomitant diseases.
Palpation
Palpation or palpation of the compacted area will reveal the consistency of the formation. The doctor takes into account the fact of pain, assesses the condition of the skin and scrotum. Neoplasms of any type are easily palpated.
Laboratory research
The patient undergoes a blood test and genital swabs. The first type of study determines the inflammatory process due to changes in the main indicators of biological material.
The smear informs about the presence of infectious and viral agents. If a malignant process is suspected, tumor markers are additionally calculated.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound assesses the condition and functioning of the testicles. The study determines the presence of infiltration and other fluids in the scrotal cavity. Ultrasound gives an expanded picture of varicose veins and other changes.
Biopsy
If a malignant process is suspected, the doctor takes a fragment of the compaction for further histological examination. The procedure determines the type of tumor process.
Diaphanoscopy
The technique is used in urology. The main task is to determine the nature of the infiltration. The formation is illuminated with a light guide, which makes it possible to identify purulent or serous fluid inside the lump.
When the malignancy of the process is confirmed, to determine its extent, the patient is sent for a computed tomography scan. The main objective of the procedure is to determine the location of distant metastases.
Possible complications
K¸ÃÂÃÂàÃÂúûþýýàú ÃÂÃÂøûõýøàòþÃÂà¿Ã°Ã»ÃµÃ½Ã¸Ã ÃÂþ ÃÂúþÿûõýøõü óýþà¹Ã½Ã¾Ã³Ã¾ ÃÂþôõÃÂöøüþóþ. › ¸ÃÂÃÂàñþûõ÷ýõýýÃÂü, úþöýÃÂõ ÿþ úÃÂþòàÿÃÂøþñÃÂõÃÂðÃÂàúÃÂðÃÂýÃÂù þ ÃÂÃÂõýþú. › àòõÃÂþÃÂÃÂýþÃÂÃÂàÃÂð÷òøÃÂøàðñÃÂÃÂõ ÃÂÃÂð, ÃÂÃÂþ ÃÂÃÂõñÃÂõàýõ÷ðüõôûøÃÂõ ûÃÂýþóþ ÃÂøÃÂÃÂÃÂóøÃÂõÃÂúþóþ òüõÃÂðÃÂõûÃÂàÃÂòð.
The A ÃÂð÷þòðýøÃÂ, ÃÂÃÂþ ÃÂþÿÃÂþòþöôð õÃÂÃÂàþÃÂÃÂÃÂþù ñþûÃÂÃÂ. ÃÂÿðÃÂýþÃÂÃÂàþÃÂûþöýõýøà÷ðúÃȈ VALUE ûþôøÃÂ.
÷ðÿÃÂÃÂõýýÃÂàÃÂûÃÂÃÂðÃÂÃÂ, ÃÂøÃÂúð ÃÂà´Ã°Ã²Ã»Ã¸Ã²Ã°ÃµÃ ÃºÃÂþòõýþÃÂýÃÂõ ÃÂþÃÂàôàø ýõÃÂòýÃÂõ þúþýÃÂðýøÃÂ. › õûÃÂýþÃÂÃÂø ø ýðÃÂÃÂÃÂõýøàúÃÂþòþà¾Ã±ÃÂðÃÂõýøÃÂ. ÃÂÃÂø ÷ûþúðÃÂõÃÂÃÂòõýýþü ýþòþà þñð÷þòðýøø, þÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂÃÂòøõ ÃÂòþ õòÃÂõüõýýþóþ òþ÷ôõùÃÂÃÂòøàThe VALUE ð.
Spermatocele
Spermatocele is the development of a cavity (ball) in the epididymis or testicle, which is subsequently filled with a clear or yellowish liquid. Spermatocele disease is often detected in boys aged 6–15 years and in men over 40, which is associated with changes in the sex glandular activity that occur in the body during these age periods. The formation of a congenital cyst is caused by the fact that during the formation of the reproductive organ of the embryo, non-communicating voids remain in the ducts, which are subsequently filled with embryonic rudiments. The composition of this liquid does not contain any admixture of sperm, so its color is light yellow. The contents of the acquired cyst in the epididymis contain impurities of ejaculate, fragments of epithelium, and leukocytes, which explains its thick consistency and milky tint. The causes of acquired spermatocele are diseases of the prostate gland, epididymis, and trauma to the genitals.
Symptoms of spermatocele
At the initial stage, the development of spermatocele is asymptomatic and does not affect erection and reproductive function. Over time, a small, hard bump grows above the testicle. When neglected, it reaches large sizes and a painful syndrome occurs, especially during active body movements or during sex. The sensitivity of the scrotum decreases, and a “cotton” sensation is felt in the testicles. The disease should not be brought to such a state - this is fraught with the development of serious complications.
Treatment of spermatocele
In the early stages of the disease, it is enough for the patient to be periodically observed by a doctor. It is likely that the pathology will disappear over time without the use of therapy. If the lump changes in diameter, swelling appears on the right or left testicle, it hurts or severe discomfort is felt, then the patient is indicated for urgent therapeutic treatment. The following treatment options are possible:
- Drug treatment based on taking anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and painkillers.
- Removal of the seminal cyst by traditional surgery.
- Microsurgical method (spermatoceleectomy) - scraping of tissue from the seminal cyst.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations depend on the process that caused the development of the formation. The lump occurs during active puberty, between 15 and 40 years of age. This is due to the formation of the hormonal system and intensive production of testosterone.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
The appearance of a hard ball is indicated by a change in the consistency of the testicles. The presented symptom is characteristic of most serious diseases. In rare cases, pain is recorded, its severity depends on the susceptibility of the body.
Doctors recommend conducting the examination yourself. Correct palpation of the testes will help in identifying pathological changes. Self-examination is carried out after hygiene procedures. The man needs to relax the perineum and feel the scrotum.
Education is easily palpable. You need to concentrate on:
- soreness;
- general discomfort;
- feeling of heaviness;
- a sharp increase in testicle size.
These symptoms are characteristic of both a traumatic lesion and a malignant process. If a lump is detected, it is advisable to seek help from a doctor. Eliminating diseases in the early stages of development increases the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
What is a growth on the right testicle?
Register Login. Mail replies. Questions are leaders. Detection of cardiac clots 1 rate. Ferritin increased 1.5 times. What the hell is this? Could it be that I like very strong tea? I have internal tremors and extrasystoles, VSD, back pain, heartburn, numbness in my hands, has anyone experienced this, help? Is my mother behaving normally? Loose stools 1 rate. Leaders of the Sour Higher Intelligence category.
Vlad Oracle. Prospero Artificial Intelligence. Best answer. Tuska Enlightened 8 years ago the cyst was removed surgically. Other answers. Alex Artificial Intelligence 8 years ago varicocele is treated exclusively surgically. Vika Enlightened 8 years ago You're crazy - run to the doctor, this is no joke, there are no wizards here, no one can cure you on the Internet, go to your mom or dad, tell them, and see a doctor. Traveled Expert 8 years ago You will die.
Better go to the doctor tomorrow, maybe you still have a chance. Slim Shady Master 8 years ago hmm.. Yulia Semenova Sage 8 years ago most likely a cyst. Veronica Samenova Master 8 years ago Well, don’t go to the doctor, just think, you’ll be left without eggs.
In general, you can go to the KVD Dermatovenerological Dispenser. Don't Pull. Who knows? It is quite normal to go to the doctor with such questions. Rome Roman Student 8 years ago you certainly know better.
But don't be shy and go to the doctor. And your stubbornness will only harm you. This makes the doctor neither cold nor hot! Natalya Duntsova Pro 8 years ago Don't be afraid, the doctor won't take your virginity. Otherwise, you will neglect your sore and you will be left without testicles and your potency will disappear. So don't drift and go to the doctor.
Listen to the opinions of adults. Andrey Lebedev Student 3 years ago, well, this is already a fucked up brother. Similar questions. They also ask.
Epididymal cyst.
What is a cyst of the epididymis and spermatic cord, why do they occur and how do they manifest themselves?
An epididymal cyst or spermatocele, as well as a spermatic cord cyst or funiculocele, is a round-shaped voluminous formation, which is an accumulation of fluid, surrounded, like any cyst, by a dense fibrous membrane or capsule. Spermatoceles and funiculoceles form in the epididymis or in the vas deferens (part of the spermatic cord) when their excretory ducts stop emptying normally and fill with fluid that the epididymis produces to ensure normal maturation and transport of sperm. There is a history of trauma or inflammation of the scrotum, they can also be congenital. Spermatocele and funiculocele are asymptomatic. In old age, they cause pain when walking and physical work. Upon palpation above the testicle or without connection with it, a spherical formation is determined, with a smooth surface, soft-elastic consistency, painless. Sometimes slightly dilated veins of the spermatic cord. Epididymal cysts are much more common than spermatic cord cysts.
How dangerous is an epididymal cyst, and does it need to be treated?
An epididymal cyst does not pose any danger to human health and life. It should be treated only when it begins to cause noticeable and frequent pain or increases to such an extent that it causes a significant enlargement of the scrotum, which interferes with movement and sitting.
How is an epididymal cyst diagnosed?
The basis for diagnosing diseases of the testicle, its epididymis and spermatic cord is a physical examination (primarily palpation or palpation). The leading auxiliary methods are ultrasound examination of the scrotum. In recent years, ultrasound of the scrotum, as a much more informative and accurate method, has practically replaced the previously used diaphanoscopy. An ultrasound of the scrotum can accurately determine the location of the epididymal cyst and its size.
How is an epididymal cyst treated?
Treatment for epididymal cysts is not required in most cases. Surgical treatment is excision of the epididymal cyst. It is recommended to limit physical activity for several months after surgery. The peculiarity of this operation is the removal of the cyst without violating its integrity and careful suturing of the epididymis. If this is not done, scarring may develop in the epididymis after surgery, which can lead to impaired maturation and transport of sperm.
What is the prevention of the formation of epididymal cysts?
The scrotum should be protected from injury. If you suspect the presence of an epididymal cyst, it is better to see a urologist and perform an ultrasound of the scrotum. This will allow you to objectively assess the need for treatment.
Categories
AllergistAnesthesiologist-resuscitatorVenereologistGastroenterologistHematologistGeneticGynecologistHomeopathDermatologistPediatric gynecologistPediatric neurologistPediatric urologistPediatric surgeonPediatric endocrinologistNutrologistImmunologistInfectious disease specialistCardiologistCosmetologistSpeech therapistElorologistMammologistMedical lawyerNarcologistNeurologistNeurosurgeon NephrologistNutriciologistOncologistOncourologistOrthopedist-traumatologistOphthalmologistPediatricianPlastic surgeonProctologistPsychiatristPsychologistPulmonologistRheumatologistRadiologistSexologist-AndrologistDentistTherapistTrichologistUrologistPharmacistPhytotherapistPhlebologistSurgeonEndocrinologist