Dry mouth is an unpleasant sensation that can be a symptom of serious illnesses. If dry mouth occurs constantly or frequently, it is necessary to understand the cause that is causing it and, if necessary, begin treatment. Elimination of dry mouth, as a rule, is achieved only as a result of treating the underlying disease, which should be the true goal. In any case, the feeling of dry mouth is another reason to pay attention to your health.
Dry mouth is caused by insufficient hydration of the oral mucosa, mostly due to insufficient saliva production. In medicine, dry mouth caused by a cessation or decrease in saliva production is called xerostomia.
.
Quite often, dry mouth occurs in the morning or at night (that is, after sleep).
Symptoms associated with dry mouth
Dry mouth in most cases manifests itself as a complex of symptoms described as:
- "viscosity" or "stickiness" in the mouth;
- thirst;
- irritation of the oral mucosa (burning and itching), the appearance of a bright border of the lips, cracks on the lips and in the corners of the mouth;
- dry tongue. The tongue turns red and becomes rough. It becomes more difficult to speak, chew and swallow. Decreased taste perception;
- dry throat. The voice becomes hoarse and more hoarse;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
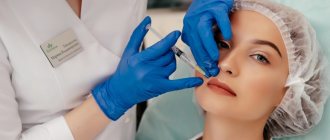
Lip treatments in Moscow
Therefore, in situations where you need help in restoring or correcting your lips, it is better to contact Dr. Korchagina’s clinic.
We offer you only the best and most effective procedures:
- lip augmentation and correction with hyaluronic acid – a minimally invasive injection technology based on the introduction of fillers with hyaluronate; manipulation helps to correct the shape of the lips, as well as eliminate dryness, peeling and pallor of the lip border;
- Botox injections - botulinum toxin injections block muscle contractions, which allows you to keep the skin of the lips smooth without creases and wrinkles;
- lip contouring – subcutaneous injection of filler gels ensures enlargement, smoothing of the lip contour, elimination of purse-string wrinkles and folds in the corners of the mouth;
- permanent lip makeup – tattooing evens out color, makes lips voluminous and bright, eliminating congenital defects and minor imperfections.
The selection of the optimal method for lip restoration is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics and skin condition of the patient.
To make an appointment for a consultation and procedures at the Korchagina clinic, write to us on the website or call us by phone.
Causes of dry mouth that are not pathological
In some cases, dry mouth is not associated with a medical condition. For example:
- Dry mouth can occur in the morning and at night due to intoxication. This is a typical situation after drinking too much the night before.
- When nasal breathing is impaired, a person breathes through his mouth during sleep. The mouth is slightly open, and the oral mucosa dries out faster. Nasal breathing can be impaired due to a runny nose, nasal polyps, or a deviated nasal septum. A similar situation occurs with snoring. The cause of snoring in most cases is a decrease in the tone of the soft palate. Muscle weakening develops with age. This is why older people snore more often, and their oral mucosa becomes dry. This reason explains dry mouth in the morning in the elderly in most cases.
- If you don't drink enough fluids in hot weather, you shouldn't be surprised by dry mouth. A similar effect can be caused by eating highly salted foods.
- Many medications can cause dry mouth.
- Smoking is another common cause of dry mouth.
- Dry mouth can be one of the symptoms of menopause.
Diseases that may cause dry mouth
Dry mouth can be caused by high fever and intoxication due to various infectious diseases (flu, sore throat, etc.). Diseases associated with large loss of fluid as a result of vomiting or diarrhea (cholera, dysentery) can also cause dry mouth. In such cases, dry mouth is one of many symptoms and does not attract special attention.
If dry mouth is combined with diarrhea, flatulence, belching, nausea and pain in the left side of the abdomen, then this may indicate pancreatitis.
Dry mouth in combination with a bitter taste, heartburn, white or yellow coating on the tongue can indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract such as gastritis, duodenitis, cholecystitis.
Dry mouth can also occur with:
- diseases of the salivary glands;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis);
- neoplasms of the oral cavity (benign and malignant);
- damage to nerve endings that contribute to the functioning of the salivary glands;
- anemia;
- vitamin A deficiency;
- systemic diseases (scleroderma, Sjogren's disease, cystic fibrosis).
Heilit (Zaeda)
Exfoliative cheilitis
It is a disease of the red border of the lips.
It is diagnosed mainly in women and is clinically manifested by peeling of the lips. The pathogenesis of exfoliative cheilitis includes neurological disorders - excitement, anxiety, depression. There is also a connection between the incidence of exfoliative cheilitis and hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. It has been proven that once it occurs, exfoliative cheilitis is inherited as a change in the immune system. Peeling is present only on the red border of the lips and does not spread to the mucous membrane and skin. The disease rarely spreads to the entire red border, so part of the red border in the area of the corners of the mouth and in areas bordering the skin remains free from peeling. If exfoliative cheilitis occurs against the background of dry skin, then in addition to peeling, patients note dry lips, burning, and sometimes the appearance of scales that are bitten or peeled off by hands. Exfoliative cheilitis has a long, sluggish course, with periods of remissions and exacerbations; not prone to self-healing.
During the examination, dry lips are revealed, the presence of scales tightly fused with the red border, due to which the edges of the red border look raised. Removal of the scales is usually painless; after their removal, a bright red surface without erosion is exposed. 5-7 days after removal, the scales appear again, fresh scales look like mica, and later they also adhere to the red border of the lips. With the exudative form of cheilitis, patients complain of soreness and swelling of the lips; Over time, large crusts appear, making speech and eating difficult.
Glandular cheilitis
The pathogenesis of glandular cheilitis involves congenital or acquired proliferation of the minor salivary glands, which contributes to their infection. In people with congenital anomalies of the minor salivary glands, symptoms of glandular cheilitis are observed in almost all cases. Patients with chronic periodontal diseases, tartar, and dental caries are at risk, since these diseases contribute to infection of the dilated ducts of the salivary glands.
Glandular cheilitis occurs both due to infection of the ducts of the salivary glands, and due to intoxication with toxins and waste products of microorganisms. Persons of both sexes suffer mainly after 30 years of age, while lesions of the lower lip are twice as common.
In the initial period of the disease, patients note slight dryness of the lips, which is compensated by lip care products and cracks that appear against the background of dryness. Subsequently, deep bleeding cracks and painful erosions form. Patients with grandular cheilitis tend to lick their lips, which further aggravates the symptoms of dryness, sometimes this leads to the appearance of weeping cracks against the background of dry and flaky skin of the lips. Later, the cracks are permanent due to impaired elasticity of the skin of the lips.
Contact allergic cheilitis
Occurs in response to exposure to a stimulus. The main causes of allergic cheilitis are substances that are part of lipsticks and lip care products. Allergic cheilitis can develop as a result of the bad habit of keeping foreign objects in the mouth: pens, pencils. Occupational allergic cheilitis develops in musicians in response to prolonged exposure to mouthpieces of wind instruments in the mouth.
Patients complain of severe itching, burning, swelling and redness of the lips. Moreover, after contact with an allergen, the symptoms of cheilitis are more pronounced. Sometimes the bubbles can be larger in size and after they are opened, cracks and erosions are exposed. When allergic contact cheilitis is chronic, the main clinical manifestations are peeling and slight itching without an inflammatory reaction.
Meteorological (actinic) cheilitis
It is part of a group of diseases whose pathogenesis involves hypersensitivity to cold, wind, solar radiation and radiation. Actinic cheilitis is more often diagnosed in men aged 20 to 60 years and often occurs in response to ultraviolet radiation. The survey determines general weather sensitivity, in particular sensitivity to solar radiation.
With the exudative form of cheilitis, patients complain of itching and burning of the lips, as well as the appearance of erosions and crusts. Sometimes, with meteorological cheilitis, small bubbles appear, after opening which painful erosions are exposed, which then dry out into crusts.
In the dry form of meteorological cheilitis, the main complaints are dryness and burning of the lips, and sometimes pain. In the case of a long course of actinic cheilitis, malignancy is possible; in the presence of factors such as smoking and dusty conditions in the room, the likelihood of malignancy increases. Often actinic cheilitis over time degenerates into precancerous diseases - limited hyperkeratosis, abrasive precancrosis cheilitis Manganotti, etc.
Atopic cheilitis
It is one of the manifestations of atopic dermatitis or neurodermatitis. An important pathogenetic link in atopic cheilitis is an allergic predisposition. In this case, allergens can be drugs, cosmetics, products, microorganisms and their toxins.
Patients with atopic cheilitis complain of redness of the lips, which is accompanied by itching and flaking of the red border of the lips, characteristically affecting the corners of the mouth. After the acute process subsides and during remissions, peeling and lichenification are noted. Constant dryness and infiltration of the corners of the mouth contributes to the appearance of cracks. Patients with atopic cheilitis have clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, dryness and flaking of the facial skin.
Macrocheilitis
Macrocheilitis is part of the Melkerson-Rossolimo-Rosenthal syndrome; the other components of the triad are facial neuritis and the folded tongue symptom. In the pathogenesis of this symptom complex, the infectious-allergic factor and hereditary predisposition are of great importance.
Patients complain of enlargement and itching of the lips, sometimes the swelling spreads to other parts of the face. Swelling with this type of cheilitis lasts indefinitely, sometimes a spontaneous improvement in well-being is possible, but after this a relapse occurs. The color of the lips and skin is not changed, although in places of swelling the skin is shiny and has a bluish-pink tint.
Usually one or both lips, cheeks, eyelids and other parts of the face in the area of innervation of the facial nerve are affected. In this case, neuritis of the facial nerve manifests itself in the form of a skewing of the face in the healthy direction, and the nasolabial fold is smoothed out. Because all three symptoms of the triad are not always present, diagnosing Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome can be difficult.
Hypovitaminous cheilitis
It develops with a lack of B vitamins, with a particularly pronounced lack of vitamin B2. Patients complain of burning and dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue and lips. During the examination, it is clear that the mucous membrane is slightly swollen, reddened, and on the red border of the lips there is fine scaly peeling and small vertical cracks against the background of dry and reddened skin of the lips. Cracks with hypovitaminous cheilitis are prone to bleeding and pain. Often, simultaneously with the development of cheilitis, changes are also observed in the tongue - it increases in size, and teeth marks become noticeable on it.
Eliminate dry mouth
If dry mouth is caused by drinking alcohol and smoking, then it can only be eliminated by getting rid of the bad habit. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of salty and sweet foods. Pay attention to how you breathe - through your nose or mouth. If nasal breathing is difficult, the cause must be diagnosed and nasal breathing restored. To do this, you will have to see a doctor. It is also important to monitor the humidity in the room.
Dry mouth can be the first symptom of many diseases. Therefore, if you often experience a feeling of dry mouth, it is necessary to understand its nature, determine the cause and, if necessary, consult a doctor and begin treatment for the disease that caused this symptom.
Treatment of cheilitis
This disease requires special treatment, depending on the cause, type and degree of the inflammatory process. The main methods of treating cheilitis:
- local treatment of the surface of the skin of the lips with disinfectant solutions, ointments, vitamin oil solutions;
- physiotherapeutic methods: Bucca radiation, ultrasound, laser therapy;
- a course of vitamin therapy;
- rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs.
If necessary, to eliminate the causes of the disease, specialized specialists may be involved: a dermatologist, an allergist, an infectious disease specialist.
Which doctor should I contact for dry mouth?
If you complain of dry mouth, you can contact your dentist or general practitioner (GP or family doctor). After identifying the cause that caused the feeling of dryness, you may be redirected to an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist or rheumatologist.
Most likely, you will need to undergo various tests (general blood count, general urinalysis, blood test for thyroid hormones, biochemical blood test, serological test), and, if necessary, undergo some instrumental studies (ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography).