- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
It is well known that a baby’s skin is soft and smooth, pleasant to the touch. Sometimes they say about it “velvet”, “silky”, it serves as a standard for the tenderness of the skin. Therefore, the appearance of any formations on the skin always causes concern among caring parents. The most common neoplasms in children are considered to be molluscum contagiosum and viral papilloma (HPV).
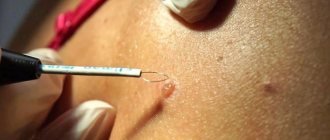
Removal of papillomas and skin tumors with laser and liquid nitrogen
We provide the following types of services:
- Removal of papillomas for children with nitrogen or laser
- Removal of skin tumors in children
At the Healthy Generation clinic, papillomas are removed using the most painless techniques and modern medical equipment. Caring for the health of you and your child is our main goal. The Center’s doctors are ready to see you and provide all the necessary assistance in the treatment and removal of skin lesions. Phone numbers for inquiries.
Diagnosis of HPV
The pediatrician will definitely pay special attention to diagnosing HPV and genital warts in a child. If you see that your child has a wart, immediately visit a doctor and start treatment. There is no need to hope that “it will go away on its own” and “no big deal.” Just the opposite: scary, threatening cancer or big problems in the future. You especially need to monitor the presence of papillomas and warts if you have a daughter.
Any child with genital warts needs a full medical examination, which includes the following:
- Examination of the child's anus and genital area.
- Questioning parents about whether they have HPV infection, genital or common warts.
- Questioning the mother for an abnormal Pap smear result that may indicate HPV infection.
- Interview parents for any signs of possible child sexual activity and possible child abuse.
In mature girls, a colposcopy and Pap smear may be done to look for signs of problems that could lead to cervical cancer. Early detection of the problem allows for treatment.
Immunological testing for HPV types is possible to identify high-risk strains that can cause cancer.
Removal methods: laser, liquid nitrogen
Human papillomavirus infection
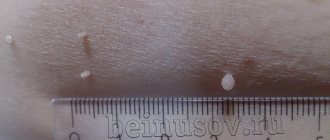
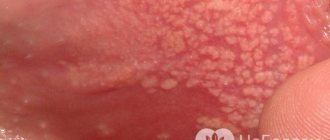
- a group of infectious diseases caused by HPV (human papillomavirus), characterized by the development of specific formations on the skin and mucous membranes. Most often, the virus is transmitted through household contact, intimate contacts, and transmission from mother to child during labor is also possible. Clinically, these neoplasms are small soft nodules of flesh-colored or pink color, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, grow and merge into formations that resemble cauliflower in shape and reach a diameter of up to 2 centimeters or more. In addition to cosmetic disadvantage and physiological discomfort, this virus can cause the development of a number of cancers.
In recent years, the number of requests from children for help in the treatment of this disease has been increasing, which is most often caused by decreased immunity, vitamin deficiency, as well as weakening hygienic control on the part of children's and sports institutions.
Existing methods for treating external manifestations of the disease include removal of papillomas with a laser, freezing with liquid nitrogen, and electrocoagulation. But the most effective method is removal with CO2 laser beams.
Removal of papillomas in young children is preferable with liquid nitrogen - the cryodestruction method . Removal with liquid nitrogen allows you to quickly and effectively get rid of papilloma and gain healthy skin. This method does not require anesthesia, does not leave scars on the face or body, and has no side effects.
It is not recommended to remove papillomas either independently or using folk remedies, since this process must be carried out under the supervision of specialists. Methods for the prevention and removal of papillomovirus in our clinic always depend on the number of papillomas, including the general health of large and small patients.
How is the virus transmitted to children?
HPV is spread through skin-to-skin or blood contact:
- A pregnant mother can pass the infection to her baby through the bloodstream before birth or through the vaginal canal during childbirth. This is called perinatal transmission.
- Children with warts on their hands can transmit the virus through skin-to-skin contact. The spread of the virus to the genital area occurs when touching it with your hands. This route of infection is called autoinoculation.
- A caregiver with warts can transmit the virus through skin contact with the child's hands or genitals. This is called heteroinoculation.
- HPV can be transmitted from a person's skin to the child's genital area through sexual contact - in the event of violence.
- Rarely, HPV can be transmitted through contact with inanimate objects or surfaces. If an adult who has warts uses a towel and then a child uses the same towel, the virus can be passed on to the child. This is called fomite transmission.
HPV is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, even if there are no warts or papillomas on the skin. After infection, the virus remains in the body. A person may be a carrier
Telangiectasia in children (spider veins)
Spider hemangioma, vascular “star” or “mesh” is a superficial dilatation of the arteries of the skin found in both children and adults. According to statistics, spider veins occur in 90% of the population. They are usually localized on the skin of the face, less often the body. It does not pose an oncological risk and is a cosmetic defect. Sometimes it goes away on its own. If there is no positive dynamics for 2-3 years, or an increase in the size of the formation, it is recommended to remove it using a laser, electrocoagulation or liquid nitrogen (used mainly in children).
TELEANGIECTASIA is a congenital or acquired persistent uneven dilation of small vessels of the skin or mucous membranes in the form of bluish-red spots, most often on the face and legs. It may be a symptom of a disease of the skin or internal organs.
Why is papilloma on the back dangerous?
Although most formations are benign and do not manifest themselves in any way, they pose a threat to health. Doctors identify two dangers of papillomas on the back:
- The papilloma virus is an additional factor that encourages the formation of a malignant tumor. Although it is worth noting that growths on the skin are not as dangerous as those on mucous surfaces.
- Warts on the back are more often injured than on the head or arms. Often thread-like growths are torn off while changing clothes. This leads to the appearance of a conglomerate of papillomas in place of the previous one. As a result, you have to spend more time and money to remove the problem.
- If the papilloma on the back has been damaged, a bacterial infection can penetrate through it.
In this regard, it is recommended to get rid of the consequences of HPV from the back, especially if they have a thin leg. Since children are unable to take care of themselves and take care, if a papilloma is found on the child’s back, it must be removed immediately.
Soft fibroma
A benign skin tumor that usually appears in people over 35 years of age. It is a soft neoplasm of the skin, most often on a stalk of flesh-colored or light brown color, gradually taking the shape of a hanging pouch from 2 to 5 mm in diameter. Favorite localizations are the inguinal and cervical folds, armpits and occasionally the face. In the initial growth phase, it is indistinguishable from the so-called viral filamentous warts. The reason for contacting a doctor is a cosmetic defect or the patient’s oncological suspicion. Fibroids are not dangerous to health, however, injury caused by friction of fibroids on clothing or adjacent areas of the skin can cause inflammation, bleeding and lead to the development of an infectious process. You can avoid the danger by removing the fibroid. The most effective treatment methods are laser removal, electrocoagulation, and cryosurgery. When removing a small formation (up to 05 mm), anesthesia is not required.
Preventing HPV infection
Like many other viruses, HPV becomes active and causes disease in people with weakened immune systems. That is why children are susceptible to the development of papillomatosis. In some people, HPV can clear up without treatment if the body mounts an immune response to the virus.
It is especially important to vaccinate girls, because... For them, HPV infection is fraught with the development of cancer. The best and most modern means of protecting against papillomavirus is vaccination. Girls should receive the vaccine (Gardasil, Cervarix) before they become sexually active
The most common vaccine is called Gardasil, which is currently used to immunize school-aged girls - nine years of age and older. The vaccine provides immunity against two strains of HPV that cause cervical cancer and two strains associated with genital warts. Vaccination is carried out with three injections of the vaccine over six months. It is recommended to get vaccinated before becoming sexually active. The vaccine is effective in protecting against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18. Vaccination is also possible after the onset of sexual activity before the age of 26 years. For boys, vaccination protects against colorectal cancer caused by HPV.
Rarely, the virus causes recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, in which viral warts grow in the larynx, causing a benign tumor of the larynx in children. These tumors are treatable, but, unfortunately, are completely incurable. In large numbers, neoplasms caused by HPV can cause airway obstruction.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading pediatricians in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.
Seborrheic keratosis
Or keratopapilloma, “senile wart” - the most common benign human tumor, manifested by both single and multiple warty plaques of a round shape covered with dense crusts that are greasy to the touch from yellow-brown to gray-black. The appearance of the first elements can begin at 35-40 years. Favorite localization: face, chest, back. For an experienced dermatologist, diagnosing the disease is not difficult, but in some cases a histological examination is required. The reason for contacting a doctor is a cosmetic problem or the patient’s concern about the possible malignancy of the process. There are many methods for treating seborrheic keratosis, the most effective, in our opinion, is removal with CO2 laser beams.
Orlov Alexey Vladislavovich, dermatologist, CMN
> See also in the section pediatric dermatology: removal of warts
Methods of infection
Instructions for use of Feresol solution and substitute analogues
The causes of the virus are varied. There are three ways to become a carrier of human papilloma infection:
- household;
- sexual;
- contact
As a rule, if the skin is damaged, scratches or cuts appear, the virus can enter the blood. Small doses of the pathogen are killed by the immune system, but when there is too much of it, the disease becomes more active. Thus, the appearance of papilloma in men is associated with the widespread tradition of shaking hands. Children can transmit the virus to each other in schools, sections and other public events. To do this, it is not necessary to touch the carrier; the source can be personal belongings.
Between men and women, HPV is often transmitted through sexual intercourse. However, contraception is not reliable protection.
The greatest risk of infection for both men and women occurs in the following public places:
- toilets;
- saunas;
- swimming pools.
Men are at risk, as many of them do not comply with personal hygiene standards. This may be why men have more growths on their backs. There is a risk of contracting papilloma warts through cuts caused by careless shaving.
Types of papillomas
The most common types of papillomas are:
- Simple or otherwise vulgar papillomas. This is a large papule, at first it is small, as it grows its surface becomes rough, the color of such papillomas differs little from healthy tissue. Several small ones can form around one wart at once;
- Acrochords are thread-like formations. At an early stage, a yellowish-colored compaction appears on the skin, which, gradually stretching out, acquires a thin stalk. Locations: eyelids, neck, groin area, area under the breast;
- Flat - seals that rise slightly above the body. They are similar in appearance to moles, but unlike them they have a dense structure. They can be located in groups, most often covering the anal area, scrotum in men, labia in women, back, neck;
- Genital warts. These are papillary neoplasms, most often several of these papillomas appear in one place at once, which leads to their rapid growth and acquisition of a “cauliflower” or “cockscomb” shape. Localization of condylomas - vagina, labia, groin area, penis in men;
- Plantar warts. They are distinguished by the germination of the main part deep into the tissues, which leads to the inclusion of nerve endings in the pathological process and, accordingly, causes pain. The visible part of plantar papillomas is flat, yellow, and dense.
The most likely oncogenic nature of the origin of papillomas located on the mucous membranes. But in any case, when viral growths appear on the body, consultation with a dermatologist, oncologist and treatment, which involves removal of warts and antiviral therapy, is necessary.
Papillomas and traditional medicine
Doctors are categorically against self-medication of papillomas. Most traditional medicine recipes suggest treatment methods that are scientifically useless.
Lotions
Various compresses and lotions affect only the outer part of the papilloma. Typically, the subcutaneous part of the growth is larger than the external wart. It is impossible to “remove” it by acting only on the skin.
Mechanical removal
Traditional methods of treatment such as tightly tying the papilloma with a thread or cutting it off with a razor are dangerous and useless. Since the cause of warts is a virus, removing the papilloma itself is useless. With reduced immunity, they will appear again - usually in the same place as before.