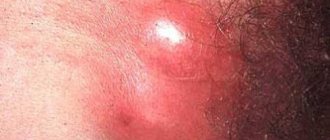
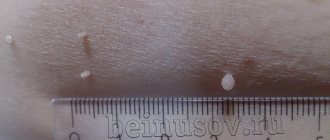
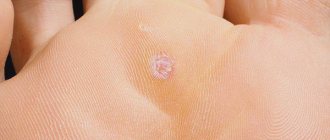
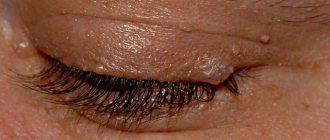
Papillomas in the groin (genital warts, genital warts) are observed quite often in adults. They are one of the varieties of viral warts and look like papillary soft formations on a small stalk, prone to merging with each other. As a result of the merger, colonies are formed, the surface of which resembles a cauliflower inflorescence (see photo).
The groin area is one of the favorite localizations of papillomas caused by certain strains of HPV
Neoplasms in the groin area cause discomfort in patients and create problems in intimate life, so if they appear, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Why do condylomas appear?
The cause of growths in the groin area is infection of a person with the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Susceptibility to infection is high. The course of the infection is chronic, with periodic relapses, which more often occur against the background of a weakening of general or local immunity.
Genital warts in women can be localized on the labia, mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, and in men on the skin of the foreskin, glans penis, and around the anus.
HPV infection usually occurs through unprotected sexual contact (oral, vaginal, anal) with an infected partner.
Pregnant women with papillomas in the groin can transmit the infection to the fetus during its intrauterine development or infect it at the time of birth.
The human papillomavirus is quite widespread. Over 50% of sexually active adults are infected with it. About 100 strains of this virus have been described in the literature. Some of them have high oncogenic properties, that is, they can provoke the development of precancerous and malignant neoplasms in the body of an infected person.
In many infected people, the infection does not manifest itself clinically, and genital warts appear only when the immune system is significantly reduced.
Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of contracting human papillovirus infection include:
- sexually transmitted diseases (genital herpes, candidiasis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia);
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- having many sexual partners;
- decreased immunity associated with various factors (severe stress, infectious diseases, poor nutrition, alcohol abuse);
- pregnancy.
Options for the development of papillomas in the groin
Depending on the characteristics of the immune reactions of the human body, various ways of developing human papillomavirus infection can be observed:
- regression of genital warts until their complete disappearance (more often observed in women in the postpartum period);
- absence of disease dynamics over a sufficiently long period of time;
- growth and appearance of new tumors;
- malignant transformation of growths.
Depending on the risk of malignant tumors, HPV strains are divided into several groups:
- high oncogenicity;
- average oncogenicity;
- low oncogenicity;
- non-oncogenic.
Women who have been diagnosed with HPV infection with high oncogenicity should be monitored by a gynecologist and regularly undergo oncocytological examination for the purpose of early diagnosis of cervical dysplasia, which is a precancerous disease.
Pathogenesis and symptoms of the disease
HPV infection is transmitted from person to person. Simultaneous infection with several strains of the virus is often detected. Papillomavirus enters the body through damage to the skin or mucous membranes. It can remain in epithelial cells for a long time and not manifest itself clinically. Under the influence of various provoking factors leading to a decrease in the body's defenses, the virus begins to actively multiply. After a sufficiently large number of viral copies accumulate in the epithelial cells, the development of skin manifestations of the disease begins.
During latent infection, HPV is in episomal form, that is, located outside the chromosomal apparatus of cells. Having multiplied in large numbers, the virus enters the intrasomal form, characterized by the integration of viral DNA into the chromosomes of the affected cells. This leads to their uncontrolled and rapid division and growth. As a result, genital warts appear. Genital warts usually appear simultaneously; less often, their formation takes several days.
Papillomas in the groin in men are usually located in the area of the coronary sulcus, frenulum and the inner layer of the foreskin. Less commonly, they are located in the scrotum, body of the penis, urethral opening, or the area around the anus.
In men, papillomas are often located in the penis area
The formation of a genital wart in the area of the external opening of the urethra is accompanied by the appearance of dysuric symptoms and the spraying of a stream of urine.
The favorite localization of papillomas in the groin in women is the labia minora. Somewhat less frequently, growths appear on the labia majora, in the perianal area, in the vagina, on the cervix or in the area of the urethral opening. Genital warts of the vagina and cervix are usually detected only during a gynecological examination of the patient.
In most cases, the size of papillomas in the groin area does not exceed 2-3 cm. However, in patients with immunodeficiency or in pregnant women, neoplasms can reach a much larger size and become gigantic.
Recovery period after papilloma removal
Regardless of which method of surgery for genital warts is used, the procedure is followed by a course of rehabilitation, during which the patient should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Refrain from intimacy;
- Women are not recommended to use vaginal suppositories and tampons;
- Do not douche;
- Do not wet the postoperative wound during the first 2-3 days;
- Do not scratch or subject the resulting crust to mechanical impact;
- Maintain regular genital hygiene and treat the surgical wound with prescribed medications.
Compliance with these recommendations will reduce the recovery period and prevent the occurrence of adverse complications (infection, bleeding, inflammation of the postoperative wound).
You can carry out effective and prompt removal of papillomas using any of the existing destructive methods in our clinic, where experienced and professional specialists work. The availability of advanced equipment and an individual approach to the patient will be the key to successful and safe treatment of any skin tumors. The price of the papilloma removal procedure will depend on the qualifications of the doctor who performs the operation, as well as the location, size and number of condylomas.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 9644 Date of publication: 09/17/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow
Diagnostics
If formations similar to the description of condylomas are detected in the groin area, the patient should consult a doctor (gynecologist, urologist or venereologist).
Genital warts require differential diagnosis with a number of physiological conditions and diseases:
- micropapillomatosis of the labia;
- papular necklace of the penis;
- condylomas lata with syphilis;
- molluscum contagiosum.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following research methods are used:
- colposcopy;
- urethroscopy;
- smear for cytology from the cervix;
- histological examination of neoplasm tissue;
- PCR diagnostics;
- immunological analysis for the presence of antibodies to the human papillomavirus in the blood.
If papillomas are detected in the groin, the patient must be examined for sexually transmitted diseases and HIV infection.
be careful
The presence of papillomas and warts on the body is the first sign of malignant melanoma!
We hasten to warn you that most drugs that “treat” warts and papillomas are a complete deception of marketers who make hundreds of percentage points on drugs whose effectiveness is zero. They do not cure the disease, but only mask the symptoms.
The pharmacy mafia makes huge money by deceiving sick people.
But what to do? How to treat if there is deception everywhere? Doctor of Medical Sciences Anatoly Makhson conducted his own investigation and found a way out of this situation. In this article, the Doctor also told how to 100% protect yourself from melanoma, for only 149 rubles! Read the article in the official source via the link.
Treatment
The main method of treating genital warts is their removal, which can be done using various methods under local anesthesia and on an outpatient basis. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications. Let's consider the main methods of surgical treatment of papillomas in the groin:
| Method | Short description |
| Laser coagulation | It is carried out using a carbon dioxide or neodymium laser. The laser beam evaporates the condyloma tissue layer by layer. A dry black crust (scab) remains at the site of formation. After it falls off on days 7-12, an unchanged mucous membrane remains at the wound site |
| Radio wave method | The destruction of tumor tissue occurs under the influence of radio waves of a certain frequency. The procedure is practically painless, but does not allow tissue sampling for histological examination. |
| Cryodestruction | The neoplasm is deep frozen with liquid nitrogen. In nulliparous women, removing papillomas in the groin using this method is not recommended |
| Electrocoagulation | Papillomas are removed using an electrode to which a high frequency current is applied. The advantages of the method are the possibility of collecting material for histological analysis, low risk of postoperative complications |
| Chemical method | It is carried out using cytotoxic drugs (fluorouracil, feresol, imiquidom, podophyllin, podophyllinotoxin) |
Regardless of the method of removal, the risk of recurrence of genital warts is quite high – up to 30%. This is due to the fact that the virus persists in epithelial cells for many years. Therefore, after surgical treatment, patients are recommended to undergo antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy.
You should not try to get rid of papillomas in the groin on your own at home. Such attempts are associated with a high risk of complications, such as infection, increased growth, and malignancy.
Choosing the most effective method for removing papilloma
Before choosing the most appropriate method of treating genital warts, the patient undergoes a preliminary comprehensive diagnosis, which includes an examination by a dermatologist, as well as a number of instrumental and laboratory tests. A consultation with an oncologist will also be required to confirm or deny the malignancy of the tumor. If papillomas are removed using painkillers, the patient should consult with an anesthesiologist who will select the optimal painkiller, its dose and method of administration (injection, gel or spray).
The choice of papilloma removal method will depend on the following factors identified during the diagnostic process:
- Age and health status of the patient (presence of chronic diseases, mental disorders);
- Presence of allergic reactions;
- The nature of the neoplasm;
- Number, size and prevalence of condylomas.
Forecast
Modern treatment methods do not completely rid a person of HPV infection. As a result, there is always a fairly high risk of relapse of the disease.
The human papillomavirus has weakly expressed antigenic properties. This is the cause of an insufficiently active response to infection by the immune system. In this regard, there is a possibility of re-infection if the sexual partner has not received the necessary treatment.
Women with papillomas in the groin are recommended to have an annual colposcopy and a cervical smear examination for oncocytology.
Women infected with HPV strains that cause the formation of papillomas in the groin are recommended to undergo regular gynecological examinations