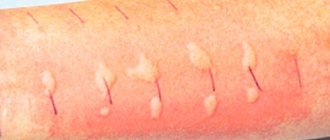
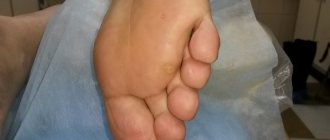
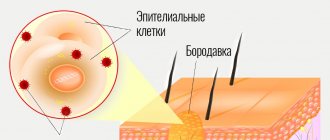
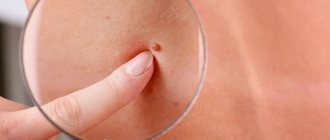
Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. They are caused by a certain type of human papillomavirus (HPV). It occurs more often in women than in men.
Cost of services in our clinic
| Appointment with a gynecologist with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Consultative appointment with a doctor based on test results and ultrasound results | 500 rub. |
| Extended colposcopy | 1500 rub. |
| Amino test for bacterial vaginosis | 300 rub. |
| Medical abortion (all inclusive) | 4500 |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
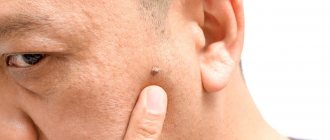
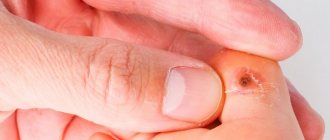
The formations affect the mucous membranes of the genitals. These are small growths, often similar to cauliflower.
Some strains of genital HPV provoke the development of cancer cells. Vaccinations are used to prevent such health problems.
Symptoms
The content of the article
In women, genital warts can grow on the external genitalia, vaginal walls, the area between the external genitalia and the anus, the anal canal, and the cervix. In men, the glans penis, scrotum or anus is affected. These growths sometimes form in the mouth or throat after oral sex with an infected person. Symptoms of genital warts:
- The appearance of small, flesh-colored or gray swelling in the genital area.
- A cluster of several warts located close to each other.
- The occurrence of itching or discomfort in the genital area.
- Bleeding during sexual intercourse.
Genital warts can be so small and flat that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. Sometimes they form large clumps. You should see a doctor if a woman or her partner develops lumps or warts in the genital area.
Do I need to tell all my sexual partners about my warts?
HPV is transmitted through sexual contact, so if you have venereal warts, you should tell your sexual partner about them . He or she needs to know that they too can be infected. Both partners can benefit from a consultation with a specialist and a medical examination.
At the same time, it is not considered necessary to inform future sexual partners about warts that are in the distant past. The fact is that it is currently unknown how long the virus can persist in the body after warts are treated.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk of infection include:
- unprotected sex with multiple partners;
- suppressed immunity (for example, people living with HIV are at increased risk of acquiring HPV);
- sexual activity at an early age.
Genital complications after illness:
- Cancer. The disease is closely related to infection of the genital organs. Certain types of HPV are also associated with cancers of the anus, penis, mouth and throat. Human papillomavirus does not always lead to cancer, but women should have regular Pap smears, especially if they are at high risk of contracting HPV.
- Problems during pregnancy. The formations may enlarge, making it difficult to urinate. Growths on the vaginal wall reduce the ability of vaginal tissue to stretch during childbirth. Large warts on the genitals or vagina bleed during labor. The mother often transmits the virus to the child, and the baby develops warts, which are especially dangerous in the throat. In this case, a thorough examination and removal of growths is required so that the child can breathe freely.
Methods for treating warts on the labia
The goal of treatment for warts on the labia is to eliminate aesthetic defects, physical discomfort, reduce the risk of complications and transmission of the virus to sexual partners. It is worth noting that classical treatment methods are aimed exclusively at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and cannot completely get rid of the virus in the body. At best, the risk of future relapses will be reduced.
Instrumental removal of warts on the labia
A variety of destructive methods of treating warts on the labia minora and adjacent areas give good results. After destruction of the structure of the neoplasm or complete removal of the growth, usually no traces remain and relapses occur quite rarely.
Let's look at the main modern methods for removing warts on the labia:
- Surgical excision . A scalpel is used in this case. Currently, this technique is used only in the case of single growths, as well as when the process of malignization is suspected. The procedure is fraught with severe bleeding and the spread of infection through the bloodstream, and therefore is not used to remove multiple growths. The price of surgical removal of warts on the labia is 780-1400 rubles in Russia and 320-560 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Electrocoagulation . The process of tumor destruction is carried out under the influence of electrothermal waves aimed at destroying epithelial proteins. However, the procedure may carry certain risks: damage to deep soft tissues, a long recovery period, and the formation of post-burn scars. In addition, it is impossible to take biomaterial for histological analysis after such manipulation. Therefore, electrocoagulation is used to remove single small growths. The cost of the procedure is 800-1500 rubles in Russia and 330-550 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Cryoremoval . A common method for removing build-up is using liquid nitrogen. Pathological cells are destroyed under the influence of low temperature. The substance is applied to warts on the labia by aerosol or using an applicator. Among the disadvantages of this procedure are: the need for repeated manipulations, lack of control over the depth of penetration of the active substance, and the impossibility of taking biomaterial for diagnostics. Also, liquid nitrogen cannot be used to treat all affected areas of the genitals at one time. Scars usually do not form after this procedure, but areas of hyperpigmentation may form. The price of cryodestruction of warts on the labia minora and majora is 700-1600 rubles in Russia and 320-560 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Radio wave removal . As a rule, the Surgitron device is used. This is one of the most minimally traumatic methods for removing benign formations. At the same time, healthy neighboring areas of the epithelium are not damaged. Not only does painless excision of the growth occur, but also simultaneous coagulation of blood vessels. With this operation there is no risk of bleeding or scarring in the future. It is possible to histologically examine the removed growth. The rehabilitation period is short and proceeds without complications. The price of radio wave removal of warts on the labia is 2000-3150 rubles in Russia and 680-1500 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Laser removal . A neodymium carbon dioxide laser beam is used. The technique is also highly accurate and minimally invasive. The laser can act at a depth set by a specialist and does not damage healthy tissue. This method of destruction is suitable for removing flat, single and multiple warts. The healing process is quick and painless. The cost of the laser treatment procedure for warts on the labia is 1250-2100 rubles in Russia and 380-750 hryvnia in Ukraine. Read about the consequences of laser wart removal.
Medicines for warts on the labia
In the photo are preparations for warts on the labia
There are different groups of drugs used to treat warts on the labia. Often, various chemical agents are used to remove these tumors. These are cauterizing drugs. They provoke necrosis of cells of the pathological growth. As a rule, they contain various aggressive acids and alkalis.
Popular products include Solcoderm (about 700 rubles) and Solkovagin (from 1,100 rubles). Solcoderm contains lactic, nitric, acetic acid and some excipients. Solkovagin contains oxalic, nitric, and acetic acids. The latter remedy differs from Solcoderm in its lower concentration of active substances, and therefore is more suitable for affecting the delicate mucous membrane of the genital organs.
If you are thinking about how to remove warts on the labia, your doctor may recommend drugs from the cytotoxic group. This category includes the following products for topical use: Vartek (about 5,000 rubles), Condilin (about 750 rubles) and their analogue Condiline Nycomed (500-700 rubles). The active ingredient in these remedies is podophyllotoxin, a substance extracted from the roots of Podophyllum thyroid, a perennial medicinal plant. All of the above drugs have a cauterizing, mummifying, necrotizing effect.
In addition, it is important to suppress HPV activity in the body during the treatment of warts on the labia. For this purpose, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is used. For this purpose, the following drugs are used that suppress the pathogen: Panavir (about 300 rubles), Viferon (from 200 rubles), Reaferon (from 550 rubles), as well as analogues Acyclovir (from 100 rubles), Ganciclovir (from 1500 rubles) and others. The greatest effectiveness is observed from the introduction of these drugs directly into the foci of the disease.
Immunomodulators, for example, Imiquimod (about 5,000 rubles) and Isoprinosine (from 600 rubles), have a broad and effective effect. These drugs are prescribed, as a rule, 7-10 days before removal of warts on the labia, and the course of treatment is continued for some time after the destruction procedure.
The most positive treatment result is achieved only in the case of a combined approach, that is, a combination of drugs from different groups. With properly selected drug therapy, it is possible to avoid relapses and suppress the virus for a long time.
Folk remedies against warts on the labia
Many women continue to prefer traditional methods of treatment, despite the huge choice of methods for removing tumors on the genitals.
Self-medication of warts is permissible only in the following cases:
- Small size of neoplasms;
- Single growths on certain areas of the genitals;
- Confirmed benignity of the neoplasm.
Whatever choice a woman makes regarding the treatment of warts on the labia, it is recommended to begin therapy only after consulting a doctor.
Various juices, infusions of plants, fruits and vegetables that contain acids and phytoncides have a certain therapeutic effect. The former have a destructive effect on pathological tissue, the latter inhibit the reproduction of the pathogen. More or less pronounced results can be obtained by applying lotions with the juice of sour apples, garlic, Kalanchoe, pineapple, and celandine.
Also, some traditional healers recommend regularly lubricating warts on the labia with iodine or vinegar. These methods are similar in their effect to chemical methods of removing growths.
However, it should be remembered that all folk recipes are less effective than outpatient methods for removing warts on the labia. In addition, they carry much greater risks compared to “medical” treatment. Home therapy can cause the formation of scars, burns, the growth of tumors and their malignant degeneration.
- See also recipes for folk remedies for papillomas in intimate places
Prevention
To avoid the development of diseases associated with HPV, it is recommended:
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse.
This significantly reduces the risk of contracting genital warts. - Get vaccinated.
The drug Gardasil protects against four strains of HPV that cause cancer and is used to prevent genital warts. Another vaccine, Cervarix, protects against cervical cancer but not genital warts.
Routine HPV vaccination is recommended for girls and boys aged 11 and 12 years. If vaccinations were not given in childhood, it is recommended that girls and women under 26 years of age, and boys and men under 21 years of age, receive the vaccine.
The drugs are effective if given before they become sexually active. Research has shown that people under the age of 21 and from 21 to 30 years of age who have received the HPV vaccine are 50% protected from infection.
Side effects from vaccines are minor and include soreness at the injection site (shoulder), headaches, low fever, or flu-like symptoms. Sometimes dizziness or fainting occurs after the injection, especially in teenagers.
Genital papillomas
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infectious disease caused by the human papillomavirus. Of the 120 known types of the virus, approximately 34 types are associated with infection of the genitals. Multiple lesions of the genital organs by papillomas are called genital papillomatosis or genital condylomatosis. Genital HPV infection is highly contagious (ability to spread), which occurs in approximately 60% of cases with a single sexual contact with a carrier of the infection. Barrier methods of contraception do not protect reliably enough for two reasons:
firstly, the size of the papilloma virus is 55 nm, which is 1000 times smaller than the pore of a latex condom. secondly, the papilloma virus can be in an inactive state, without visible formations on the skin (warts), which will not be covered by a condom, and be a source of infection for the sexual partner.
(Read more about HPV prevention)
The highest rate of detection, and therefore infection, of HPV infection occurs at the age of 18-25 years and decreases after 30 years.
Once in the body, through microtraumas of the skin and mucous membranes, the papilloma virus can remain in an inactive state for 3-8 months.
Out of 100 people infected, 10 people have a chance of clinical manifestation of human papillomavirus infection and 1 person has a risk of developing cancer. A serious threat to the health of patients are concomitant infections: genital herpes, trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonococci, which can provoke the degeneration of tissue into a tumor. With concomitant chlamydia and genital herpes, diagnosis is difficult, acute symptoms are erased and the immune system suffers more. Such diseases are difficult to treat and often recur with new condylomas after a short period of 1 to 3 months.
Chronic infectious processes, human papillomavirus infection in particular, lead to impaired reproductive functions - infertility, miscarriage, delayed fetal development, complications of the postpartum period. (Read about pregnancy and HPV)
Clinical manifestations of genital warts are varied
There are three forms of human papillomavirus infection:
1. carriage - the presence of infection is confirmed by laboratory tests, there are no visible manifestations; 2. subclinical forms, when changes are detected through careful analysis and by staining suspicious tissues with a solution of vinegar or iodine; 3. clinical forms - diagnosis is not difficult, since papillomas are visible; an additional examination is carried out to identify the boundaries of the affected surface and determine the oncogenicity of the type of papilloma virus.
In addition to external manifestations - genital warts, papillomavirus infection is characterized by itching, inflammation, pain, redness of tissue, and swelling. With a combined infection, white discharge, including bloody discharge, is possible if a vessel is affected. If genital warts are large, they can lead to dysfunction of organs, such as dysuria or urinary incontinence, which can be felt during sexual intercourse. The location of genital papillomas is varied: they can be on the skin of the labia majora and minora, perineum and around the anus, mucous membrane of the vulva, vagina, cervix and cause inflammation of the cervical canal. Men are also characterized by the location of condylomas on the skin of the external genitalia, around the anus, on the glans penis and urethra.
Diagnostic measures for genital papillomas
It is possible to diagnose human papillomavirus infection in every medical institution: antenatal clinic and dermatovenerologist’s office. The specialist determines the order of the examination, starting with the examination.
During the initial examination, you can detect not only external manifestations - condylomas, but also, armed with a colposcope with a magnification of 7-30 times, examine in detail the membranes of the vulva, vagina, and cervix. Additionally, differential staining is performed to identify pathological areas, from which a sample is taken for cytological analysis (the condition of the cells is assessed).
In-depth methods for diagnosing tissue damage by the papilloma virus include the cytological technique, which was developed in the 30s by the Greek pathologist Georg Papanikolaou. Currently, the Papanicolaou cytological method (PAP-test) is recommended by WHO to be carried out once every 3 years based on the period of degeneration of PVI into cancer, and averages about 10 years. Thus, the PAP test is a screening method for diagnosing early stage precancer. In our country, the most common staining of smears is Romanovsky-Giemsa.
Cytological screening on a federal scale is recommended by WHO among women aged 25-64 years, which can reduce mortality from cervical cancer by 84%. Cytological examination has a sensitivity of approximately 60-80% and a specificity of 60-85%.
Laboratory methods should complement cytological diagnostics, which is aimed at identifying the type of papilloma virus based on the degree of oncogenicity. Molecular biological methods include the PCR hybridization reaction and the Hybrid Capture method, which is called the “Digene test”. Using the PCR method, viruses are identified long before the first cytological, and even more so, clinical signs of the disease appear.
Currently, new molecular biological tests have been introduced into practice aimed at determining the activity of HPV and assessing the immediate prospects for the course of the infection. They are called molecular biomarkers, in one case they indicate oncoproteins of viruses, which indicates an increased risk of neoplastic progression, in another case, they are an indicator of changes in the state of the host cell.
Treatment of genital papillomas (warts)
Treatment of genital papillomas is carried out only by a specialist; independent prescription of therapy is not acceptable, as it is associated with a high risk of complications, including the degeneration of warts into malignant tumors.
The treatment regimen represents a step-by-step process, taking into account the nature of the combined infection, the clinical form and location of the papilloma, the state of immunity, endocrine disorders, the depth of damage and the ability of the tissue to regenerate.
At the first stage, the opportunistic flora is usually rehabilitated. On the second, the immune system is stabilized and the field is prepared for radical methods of therapy. A doctor who knows how to remove papillomas will always take into account the characteristics of the patient’s clinical picture of the disease and suggest the optimal method for him. Today, the effectiveness of mono-destruction, or destruction of a wart without the use of targeted drug therapy, is estimated at 25-50% effectiveness, which indicates a high risk of recurrence of the disease. When choosing a method for removing condylomas, a specialist can be guided by the need to obtain materials for research and the depth of impact on the affected area. The principle of radical therapy is the same for papillomas of various locations; removal of the altered tissue is necessary in most cases.
The use of complex therapy significantly increases the chance of suppressing the activity of the virus and, based on repeated tests, providing a quantitative assessment of the detection of viral DNA, which indicates the effectiveness of therapy. Complex therapy using antiviral agents directly affecting the papilloma virus is most effective, and average rates reach 93-96% of cases. Increasing the level of interferon or using interferon preparations can increase antiviral protection for a certain period. However, the viruses themselves have adapted to the body’s resistance and produce proteins E7 and E6, which suppress the production of interferon.
Unique in its therapeutic effect is the drug Panavir, which suppresses the viral activity of a wide range of viruses and is indicated for anogenital papillomas. The effectiveness of Panavir® against human papillomavirus infection has been confirmed by more than 80 medical publications by specialists over a ten-year period of studying its use. The etiotropic effect or influence on the cause of the disease - the virus, in genital papillomatosis, is supplemented by the induction of the body's own interferon. The effect of Panavir® on interferon production has been well studied and is reflected in the application regimen. Other therapeutic effects of Panavir® have been studied and substantiated: anti-inflammatory effect, wound healing, prevention of secondary infection when using local forms - gel.
Currently, doctors can combine different forms of the drug, for example, Panavir® has been developed for systemic (general) use - a solution for intravenous injection. If for some reason such a regimen is not possible, the doctor prescribes Panavir® in the form of rectal suppositories at night.
For external and local use, Panavir® gel is used both a week before destruction to prepare the surgical surface and prevent re-infection with HPV, and after removal of genital warts to speed up the healing process and reduce symptoms of inflammation after surgery. The course of treatment is also prescribed by the doctor. It should be noted, given the volume of drug consumption for a course of treatment for anogenital condylomas, the manufacturer has released a new package - a 30 gram tube.
Prevention of the spread of human papillomavirus infection and associated diseases: cervical cancer and others
As measures to prevent the incidence of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, as well as other organs of the reproductive system, both women and men, modern medicine can offer methods of protection. Currently, highly effective vaccines are being produced to prevent infection with oncogenic types of the virus, including 16 and 18. Vaccination, initially intended for girls from 12 years of age, is already expanding the indications for male adolescents. However, not everything is so rosy; along with the high efficiency, the cost of the drugs is quite high and the cost of vaccination falls on the family budget. (Read more about HPV prevention)
During studies of the prophylactic drug Panavir® Inlight, interesting and convincing results were obtained to prevent the spread of the papilloma virus among married couples. Panavir® Inlight can be used as protection against infection with the human papillomavirus during intimate relationships.
At the same time, the use of the drug does not affect the sensuality of sexual partners and remains unnoticeable, since it has neither color nor odor, and does not leave marks on the skin or underwear. Panavir® Inlight spray is recommended for use before sexual intercourse, which will protect against transmission of infection, but not against pregnancy. Panavir® Inlight is a liquid gel (does not contain oils or alcohol) and comes in a spray bottle, so it is easy to use for irrigation by both men and women.
Reviews about Panavir, questions, doctor's comments
Elena Vladimirovna asks: 2021-01-31 22:44:54
Hello, there are small warts on the scrotum and at the base of the penis, less than 5 mm, how to use Panavir gel?
Korobkova Elena Vladimirovna Obstetrician-gynecologist answers: Good afternoon. Apply to affected areas of the body 4 times a day. Thank you.
Elena asks: 2020-12-10 09:30:45
Hello! Please tell me. I have warts in an intimate place, I take cycloferon intramuscularly and apply Panavir gel. Will it help me get rid of warts?
Korobkova Elena Vladimirovna Obstetrician-gynecologist answers: Good afternoon. If the elements are single and no more than 5 mm in diameter, then there is a chance of getting rid of them; for other indicators, surgical removal by a doctor is necessary. Thank you.
PAP tests
It is important for women to undergo regular pelvic examinations and undergo a vaginal cytology smear (Pap smear). These studies contribute to the timely detection of changes in the vagina and cervix caused by genital warts or early signs of cervical cancer. A smear is taken during a gynecological examination of a special one from the outer and inner surface of the cervix. The procedure is painless and takes 5-10 seconds. The cells are examined under a microscope.
Medicines for the treatment of genital warts
Preparations that are applied to the skin:
- Imiquimod.
This cream enhances the immune system's ability to fight genital warts. Sexual contact should be avoided while the cream is on the skin. This weakens the effect of condoms and the diaphragm and causes skin irritation on your partner. Side effects include skin redness, blisters, body pain, cough, rash and fatigue. - Podophyllin and Podofilox
. Podophyllin is a plant-based resin that destroys the tissue of warts on the genitals. When using Podofilox, you need to know the precautions to avoid causing irritation. This drug is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Side effects: mild skin irritation, itching. - Trichloroacetic acid.
This remedy burns genital warts and is used to remove internal warts. Side effects include mild skin irritation, ulcers or itching. - Synecatechin (Veregen).
The cream is used to treat external genital warts and warts in or around the anal canal. Side effects include skin redness, itching or burning.
You cannot self-medicate so as not to provoke serious complications.
Visiting a doctor, diagnosis, treatment
The discovery of warts or condylomas is a reason to go to the doctor. It is difficult to predict what the doctor will do. Russian recommendations provide for a bunch of tests: for the presence of HPV and determination of its genotype, morphological examination of warts, testing for other sexually transmitted infections. Many Western sources do not recommend this, since it does not affect treatment tactics.
Anogenital warts are treated with surgical (excision, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation) and medicinal methods (medicines are applied directly to the affected area). Unfortunately, the likelihood of wart recurrence is high. Over time, they are rediscovered in at least 30% of patients. This may occur due to the circulation of an old human papillomavirus infection in the blood or due to re-infection.