Molluscum contagiosum
What it looks like: single painless dense nodules of a round shape, sometimes the skin acquires a pink tint or a pearlescent sheen. The size of the rashes ranges from a millet grain to a pea. Causes of appearance : caused by a parasite - a saprophyte, which is activated when immunity decreases. What is dangerous: growth, increase in size of rashes. How to fight : mechanical squeezing of nodules followed by treatment of the affected surface with antiviral ointments and immunomodulators.
General features of growths and types
Nevi and warts are benign formations. The growths have few other common features; it is difficult to confuse them. There are controversial cases. A type of mole is a warty nevus. The shape of the seals is similar, the difference is the following features:
- big size;
- localization in the neck, head, behind the ears. The pathology is characteristic of the female sex;
- seal color is brown.
Types of warts:
- vulgar - localized mainly on the palms and fingers, the surface of the formation is rough;
- flat – occur more often in adolescence, located on the neck, face, wrist, armpits. The difference is that the surface is smooth and does not rise above the skin;
- plantar (corns) – appear as a result of wearing uncomfortable shoes, localized on the feet. The growth is papillary in shape, differs from a callus in its rough shell;
- seborrheic – occur more often in old age, localized on the back, hands and head;
- genital warts (condylomas) are localized on the genitals. The growth is pinkish in color and resembles the comb of a rooster.
Types of age spots:
- vascular – growths of red color with a blue tint, occur due to vascular pathology;
- hemangiomas - appear in infants of the first year of life, have a bright red color and are localized on the face and neck;
- age spots occur as a result of increased production of the hormone melanin. Main varieties: Mongolian spots, coffee spots, lentigo;
- white nevi occur due to a deficiency of melanocytes;
- hanging - the main difference is the presence of a base leg, which attaches the nevus to the body.
Melanoma (skin cancer)
Reasons: genetics, tanning abuse. What it looks like : a neoplasm rising above the surface of the skin, on a stalk or on a broad base, with uneven edges, with the appearance of ulceration and bleeding on the surface, unevenly colored. Why it’s dangerous: the most transient type of oncology with a high mortality rate. How to fight: surgical removal, chemotherapy.
Continued: Dangerous moles →
The difference between warts, moles and papillomas
Initially, warts, moles and papillomas are benign neoplasms. However, there is a risk that these formations will become malignant.
The formation of moles (nevi) is caused by several factors:
- hereditary
- exposure to infections and viruses
- skin damage
- ultraviolet exposure
Moles are not formed as a result of the presence of the human papillomavirus in the body, while the formation of papillomas and warts is caused precisely by the influence of this virus. Skin cells grow, which leads to the formation of warts and papillomas.
HPV infection occurs through sexual and domestic contact in the presence of microdamages on the skin.
Depending on the type of virus, characteristic neoplasms appear on the skin:
- warts
- papillomas
- condylomas
The main differences between nevi and papillomas:
- by structure: papilloma has a soft and loose structure, nevus has a dense and hard structure.
- composition: the mole contains only skin cells, the papilloma contains blood vessels.
- by color: a mole is usually dark in color, while a papilloma is close to the color of the skin.
- by location: nevi appear on any part of the body, while papillomas are usually concentrated on mucous membranes and friction areas.
- visually, the papilloma is always convex and protrudes above the skin, has torn edges, the mole is usually symmetrical and has smooth edges.
- A nevus should not cause discomfort; a papilloma, in turn, can cause pain, itching and other unpleasant sensations.
There are the following differences between papillomas and warts:
- warts are usually located on the arms and legs, papillomas in friction areas (armpits, area under the breasts, groin area) and on mucous membranes.
- As a rule, papilloma has a stalk or base.
- the edges of warts are clearer than those of papillomas.
The main risk for moles is their degeneration into melanoma.
You should immediately contact a specialist if:
- the mole has increased in size and color has changed;
- pain appeared;
- itching appeared;
- the mole has thickened;
- skin pattern has changed;
- bleeding has formed in the area of the mole;
- inflammation appeared.
As stated earlier, the degree of danger of warts and papillomas depends on the type of HPV:
- high risk - 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 52, 58, 59, 68;
- low risk - 6, 11, 26, 41, 42, 50, 61, 73, 82 and subsequent;
- no risk - 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
Accordingly, papillomas and warts that have a high risk of transformation from benign to malignant must be monitored and removed.
Source: https://estet-portal.com/statyi/kak-otlichiti-rodinku-ot-papillomy-article-4464-html
Pigmented moles
There are many types of pigmented moles.
- Dysplastic nevi . Moles are irregularly shaped without clear boundaries with a slight elevation in the middle. The size of neoplasms is up to 12 mm. Such moles appear on the body, in places covered by clothing or under hair.
- Borderline nevi (lentigo) . A cluster of several identical birthmarks, similar in appearance to freckles. Lentigo varies in color from brown to black. They appear in adults; children, as a rule, are not susceptible to borderline nevi.
- Intradermal nevi . Convex birthmarks that rise above the skin. The color of the mole ranges from flesh-colored to black. The size of an intradermal nevus can be up to 1 cm. The shape of the neoplasm is nodular, with a wide base, tapering towards the apex.
- Epidermodermal nevi . Flat moles of different colors, slightly raised above the skin. Localization - on the soles, palms and genital area. They have a size of up to 1 cm.
- Blue nevi . Smooth and dense new growths are dark blue in color with a clear border. The shape of the mole is round or oval. Nevi reaching up to 2 cm in size can cause discomfort.
- Sutton's nevi . Brown birthmarks surrounded by a halo of lightened skin, similar to vitiligo. They may go away on their own and usually do not require treatment.
- Complex nevi . Complex pigmented nevi are usually dark brown in color. Moles look like warts, about 1 cm in size.
- Giant nevi . These are large pigmented spots. Similar moles appear on both the body and face. They can grow and occupy a large area of skin.
Many types of moles do not need to be removed. You can decide for yourself which moles to remove and which not. This is one of the most common cosmetic surgeries.
However, it happens that nevi degenerate into malignant neoplasms, and this can lead to cancer.
The Medicenter network of clinics provides painless procedures to remove various types of moles.
What is a wart?
Photo of warts on the body
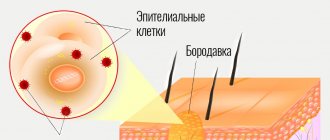
Warts, unlike moles, have a different nature of origin. They are caused by human papillomavirus of various strains. Under its influence, epidermal cells begin to divide pathologically quickly. This is how the skin grows in the form of nodules and papillae.
These are also benign growths, but like moles, warts can develop into malignant tumors.
Factors contributing to the activation of HPV are:
- Increased sweating due to heat, as well as hyperhidrosis;
- Various mental traumas, stress, chronic fatigue;
- Poor state of the immune system;
- Improper lifestyle - unbalanced diet, poor sleep, low physical mobility, bad habits;
- Hormonal fluctuations.
This virus is easily transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, as it is highly contagious. You can pick it up in any public place, especially where there is high air humidity. Most often, warts occur in children due to the way their immune system works.
The appearance of warts depends on which strain of the pathogen has “settled” in the human body. There are more than 100 types of HPV. Some types cause papillomas and condylomas, while others are responsible for the appearance of the following types of warts:
- Vulgar (ordinary) . These are growths with a dense structure, they are covered with the stratum corneum of the skin and resemble a rounded nodule. They have a lumpy, rough surface, the color ranges from yellowish to grayish. Usually appear on the hands, elbows, knees. They are painless and do not cause noticeable discomfort.
- Plantar . Affects the feet and toes. They are similar to corns, but have a number of distinctive features: they are painful, may have black dots on the surface (traces of clogged capillaries), and if damaged, can bleed heavily. Their color is usually yellow or brownish.
- Flat (youthful) . The difference between moles and warts of this type is that viral growths can go away on their own over time. The factor that causes their appearance is hormonal fluctuations during adolescence. Once hormones stabilize, juvenile warts go away on their own. Most often, these tumors are found on the hands, elbows, neck and face. They do not cause significant discomfort. The color is practically no different from healthy skin.
There are also senile warts, but the cause of their appearance is not viral. They arise due to the natural aging processes of the body and resemble loose plaques with a horny coating.
Note! It is important to know what types of moles and warts there are in order to accurately determine what kind of tumor you are dealing with. But it is optimal if the diagnosis is made by a specialist during a visual examination, as well as based on the results of laboratory tests.
How do moles differ from papillomas and warts?
One of the main differences between moles (nevi) and warts and papillomas is the reason for their appearance: if some moles are “laid” in the womb, and others appear under the influence of external factors, then the appearance of papillomas and warts is preceded by the penetration of the human papillomavirus into the body.
HPV can be infected through household or sexual contact, and depending on the type of virus that has entered the body, typical neoplasms may appear in different parts of the body: papillomas, warts, condylomas.
And if moles cannot be infected, then HPV can penetrate the skin if there are microdamages on it or due to sexual transmission.
Methods for removing warts and moles
If indicated, destruction of formations is carried out. Removal of moles and warts is carried out if the growths are at risk of injury, look unsightly, or degenerate into a malignant formation. When removing suspicious growths, cells are collected for histological examination.
Basic methods for removing warts and moles
- Medicinal - the use of cauterizing drugs (Stefalin, Ferezol). Medicines are used as prescribed by a doctor; not all growths can be removed by cauterization.
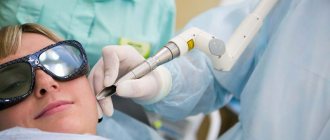
- Laser removal is a targeted laser treatment on the damaged area. The method is bloodless and painless. Suitable for removing small formations.
- Radio wave method - destruction with a radio knife, using the Surgitron apparatus.
- Diathermoelectrocoagulation is exposure to high frequency electric current.
- Cryodestruction – removal with liquid nitrogen.
- Methods of operative surgery - destruction occurs under local anesthesia in a hospital setting. The method is traumatic and requires a long time to heal.
- Traditional methods (bandaging with thread and hair, using celandine juice). The effectiveness of treatment at home using these methods has not been proven; in order to avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to use them under the supervision of a doctor.
The removal method is determined by the doctor. Not all hardware methods allow taking cells for histology. In case of degeneration, a surgical method is used.
Definition
real wart looks like a benign formation located on the skin. Due to the fact that all warts have a viral etiology, this formation can be triggered by intensive reproduction of the virus inside the cell. From the outside it looks like a skin growth.
A mole is a benign formation on the skin, colored with pigment. It does not cause any harm to health until it begins to increase in size or change color.
Conclusions TheDifference.ru
- A mole is a formation located above the skin, a wart is a skin growth.
- A mole has a dark red tint, a wart has a grayish-yellowish tint.
- A mole never disappears on its own; a wart can disappear under certain circumstances.
- A mole is soft and pleasant to the touch; a wart may be rough and uneven.
- Moles can be found on different parts of the body; warts appear exclusively on the legs and arms.
- Moles can only be round, warts can be of any shape.
Why is it dangerous?
The danger of this condition, in which there is a growth of papilloma inside a mole, lies primarily in the malignancy of the pathological process, that is, certain types of moles, under the influence of certain factors, can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
During the process of degeneration, dark-colored inclusions appear in the structure of the nevus, which, as they progress, begin to grow and outwardly resemble a wart.
In addition, when the papilloma enlarges, it is quite easy to injure it, which can cause bleeding. Against this background, an infection can penetrate into the resulting wound and spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. This condition, in turn, can lead to the development of sepsis or an abscess.
Diagnostics
If a papilloma formation is detected on a mole, you must seek help from a specialist. First of all, the doctor will collect the necessary information regarding the patient’s medical history, the time when the growth of an additional tumor was noticed, and what symptoms accompany the process.
After this, a visual inspection of the affected area is carried out, which allows you to determine the size and color of the growth.
If this data is insufficient, an additional diagnostic examination is carried out, including several methods:
- biopsy - necessary to take a fragment of the affected tissue;
- histology – a histological examination of a previously taken sample of material is carried out to determine the nature of the neoplasm and the mole itself on which it appeared, which makes it possible to determine the degree of malignancy of the pathological process;
- PCR diagnostics to detect urogenital infection.
Also, if necessary, a laboratory blood test can be performed, which will also show some deviations from the norm in the presence of the disease.