Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
A mole, or nevus, is a benign skin formation that consists of cells filled with melanin pigment. This gives them their characteristic dark shade. Almost every person over 8–10 years old has moles. They appear in large numbers during puberty, which is explained by hormonal surges.
Pregnant women also often develop new moles, which is associated with endocrine changes. However, it is not at all necessary to resort to their removal during pregnancy if they do not bother you. It is necessary to show skin growths to a doctor; usually only observation is required.
Surgical removal of a mole is resorted to not only for cosmetic reasons. There are certain medical indications for removal.
When deletion is indicated
Epidermal nevi are benign formations and are harmless to health. However, any nevus carries a potential threat; there is a possibility of degeneration into a malignant tumor - melanoma. This is one of the most dangerous types of cancer. Therefore, it is important to monitor existing moles and consult a doctor if there is the slightest change.
You should visit a dermatologist as soon as possible in the following cases:
- the mole has increased in size, changed color, shape, outline;
- pain, itching, bleeding, burning, peeling, ulceration appeared, the surface became lumpy and uneven;
- the nevus was injured.
There is a high risk of degeneration for nevi located in open areas of the body. This is due to intense exposure to ultraviolet rays during the hot season. Also subject to removal are nevi that are constantly injured by elements of clothing - the handle of a bag, a collar, elastic bands of underwear, etc. Those formations that are located on the hairy areas of the body are also at risk - there is a possibility of tissue damage during shaving, waxing or sugaring.
General characteristics of formations
A mole is a pigment formation of one of the shades of the brown palette. The base contains melanin and the melanocyte cells that produce it. Melanins are high molecular weight pigments. They are characterized by a heterogeneous structure and complex chemical composition. Pigments are found not only in moles, but also in all skin, hair, iris, inner ear and even some parts of the brain.
Content:
- General characteristics of formations
- Indications/contraindications for the procedure
- What you need to know about melanoma?
- How to properly prepare for mole removal
- Technique of the operation
- Possible complications and side effects
- Features of rehabilitation
It is important not to confuse nevi and birthmarks. Moles do not form in the prenatal period, but as a person grows older and are closely related to his lifestyle. The cause of the formation of pigment spots can be a hereditary factor, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, or hormonal changes.
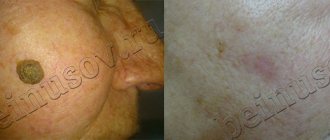
Each mole is a separate formation with a unique life cycle. At first it is a flat spot, which can increase and rise slightly above the skin as it grows and develops. The size and location of the formation depends on the level of melanocytes. If they are in the epidermis (top layer of skin), the mole will be flat. The deeper the melanocyte is immersed in the dermis, the higher the formation is located on the surface of the human body.
Convex nevi, which rise slightly above the skin, should not frighten their owners. This condition has no negative consequences and is considered a variant of the norm. The main thing is that the mole is miniature, round and uniform (in terms of color and structure) throughout its life cycle.
Can a mole disappear on its own and how safe is it? Yes, the formation can disappear without the influence of mechanical factors. This happens gradually and can alert a person. First, a white outline is formed around the formation, which resembles an orbit. This contour begins to increase and gradually covers the surface of the entire formation. The nevus disappears, and a small white spot remains in its place. Most often this occurs after severe sunburn. The disappearance of moles can also be a harbinger of the rare disease vitiligo.
If you notice changes in a mole (increase/decrease, uneven edges, change in shade or structure), be sure to consult a specialist.
Selecting a removal method
So, an oncologist or dermato-oncologist recommended removing the mole, or you decided to get rid of the formation. Consult with a specialist which removal method is best for your situation.
In many cases, histological examination of a removed mole is a mandatory procedure. It is important to evaluate the structure of the nevus tissue and make sure that the formation is truly benign and that nothing threatens your health. In this case, traditional mole removal with a scalpel is one of the most suitable methods. Some modern instruments do not leave a trace of tissue, so it will not be possible to study them in the laboratory.
If a large mole is located on the face or open areas of the body, discuss with a specialist the prospects of using a laser or radio wave removal method. These methods have fewer cosmetic consequences - they do not leave noticeable scars, so it is often advisable to resort to them. Remember that health is more important - if the doctor insists on conventional surgical removal, you should listen, because the prevention and early diagnosis of cancer depends on this.
What you need to know about melanoma?
Every mole on the human body can degenerate into a malignant melanoma. What it is? Melanoma is one of the types of malignant tumors. It also contains melanocyte cells (producing melanin), but in melanoma the cells are more aggressive.
They constantly divide, displace healthy cells, enter the vascular bed and spread throughout the body. As soon as the first aggressive cell approaches the brain or, for example, the lungs, it settles inside the organ and begins to rapidly divide. This process is called metastasis.
Melanomas are extremely dangerous because they quickly metastasize and divide at an incredible rate. The main thing is to detect the pathology in time. Surgical removal of melanoma will prevent the process from spreading throughout the body and guarantee a complete cure. Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner or complete refusal of treatment can result in death.
Preparing for the intervention
No preparation is required for surgery: you can eat and drink water without restrictions, and you do not need to take medications. However, it is important for women to plan the day of surgery taking into account the menstrual cycle; it is better to do this after menstruation. The recommendation applies to any surgical intervention. Also, in cases where the nevus is located on open areas of the body, it is better to remove it from October to April. This will eliminate the need to hide the wound and protect it from ultraviolet rays.
If you are taking medications that affect blood clotting, tell your surgeon. You should not stop taking medications on your own—check with your doctor.
How to remove moles safely, painlessly, without a trace
You can remove moles like this:
Laser destruction.
Involves exposure of tissue to a directed laser beam. The essence of the technique is that the laser, penetrating the nevus cells, heats the intracellular fluid to a boil. The cells of the mole are destroyed and evaporate. As a result, only a small mark remains, covered with a crust, and it completely disappears within 5–7 days after the operation.
Laser exposure today is considered one of the most effective and safest ways to remove skin lesions, since during the operation the specialist can control the depth and radius of exposure without touching healthy surrounding tissues.
In addition, laser removal of moles is carried out under local anesthesia, absolutely without pain. Another undeniable advantage of the laser destruction method is the simultaneous sealing (coagulation) of blood vessels, which eliminates the risk of bleeding during the procedure.
The only drawback of this technique is the inability to take cells from a removed mole for histological analysis to exclude skin cancer. That is why this method of removal is used most often in cases where a mole is removed for aesthetic reasons and does not cause suspicion among the doctor.
Electrocoagulation.
This technique is based on the effect of low frequency electric current on tissue. Under the influence of current, the cells are destroyed and the nevus disappears. The method, as in the case of laser treatment, is used with preliminary local anesthesia.
Electrocoagulation has a significant advantage over most modern hardware techniques - the ability to take tissue for histological examination.
Radio wave knife.
A safe modern technique for removing skin tumors, which is most often used for moles located in the superficial layers of the skin and having a small size.
In this case, the pigmented area is irradiated with a device emitting high-frequency waves - up to 4 MHz. After the procedure, only a small wound remains on the patient’s skin, which usually heals within a few days without leaving any trace. It is this factor that determines the priority of a radioknife when removing moles in the most visible places - the face and neck.
Cryodestruction.
The technique is based on the effect of ultra-low temperatures of an applicator with liquid nitrogen on the tissue of the removed nevus.
This method is used extremely rarely today due to the high likelihood that scars will remain on the skin, as well as due to the impossibility of taking tissue for further analysis.
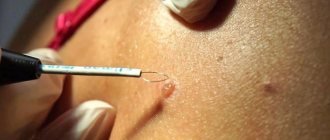
Surgical method.
Despite the fact that doctors tend to avoid surgical interventions, in some cases this technique is the most rational way to remove moles. The surgical method is used to excise flat nevi that grow deeply into the surrounding tissue, as well as when melanoma is suspected or diagnosed.
Surgeons remove a small area of surrounding skin along with the mole and stitch the edges of the resulting wound. Stitches are usually removed after 7–10 days. During the operation, both local and general anesthesia can be used.
Features of surgical removal
Surgical removal of nevi has several advantages:
- the mole is removed forever - there is no risk of reappearance;
- the operation requires only one visit to the surgeon;
- minimum contraindications;
- possibility of histological study of tissues.
However, there are also disadvantages - the need for reliable local anesthesia, the likelihood of a mark/scar forming at the site of the removed mole, and a relatively longer recovery period.
Removal steps:
- Pain relief with local anesthetics.
- Excision of nevus within normal tissue.
- Stitches (if the mole is small, this may not be necessary).
- Application of a special bandage.
Sutures are removed on average on the 5th–7th day. The overall healing period ranges from 7 days to 21 days depending on the health condition. The surgeon will give recommendations on how to care for the postoperative area at home. You can go home immediately after the intervention. As a rule, only the use of antiseptic solutions is required. You can also come to the clinic for dressing changes.
The doctor sends the material obtained as a result of excision to the laboratory for histological examination. A laboratory assistant examines it under a microscope for any atypical structure. You will receive the results within a few days, and if suspicious cells are detected, the specialist will definitely refer you to a dermato-oncologist.
As a measure to prevent skin cancer, your doctor may recommend giving up tanning beds and reducing the time you spend in direct sunlight. It is necessary to use sunscreen with a suitable protection factor, do not drink alcohol in excess and do not smoke. Patients with a large number of moles may be advised to visit a dermatologist for preventive purposes once a year.
Mole removal with nitrogen
Cryodestruction is the instant freezing of a piece of tissue with liquid nitrogen. The substance, located at very low temperatures (from -100 to -180 ° C), causes freezing, destruction and rejection of tissue with a rapid recovery period.
The main advantage of cryodestruction is that dead tissue is not removed after destruction, but serves as a kind of bandage that protects the wound from infections. The wound heals painlessly. First, a crust forms, under which new, healthy tissue begins to grow.
However, the wound does not need to be treated with anything additional during the entire recovery period. This method is least suitable for the face, and the wound healing time here is much longer than with laser or radio wave removal.
Initially, after the scab falls off, the nitrogen-frozen area of skin will be lighter than the rest of the skin. But later everything will return to normal and traces of cryodestruction will become invisible.
However, the doctor is not in all cases able to control the depth of nitrogen exposure. Based on this, there is a possibility of frostbite of the tissues around the area, which can lead to the appearance of a scar. It is also possible that the mole will not be completely removed and the procedure will have to be repeated.
Who is contraindicated for
Surgical removal of a nevus is contraindicated in the presence of the following diseases:
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases;
- infectious disease - viral, fungal, bacterial;
- fever of unknown origin, increased body temperature and other symptoms of intoxication.
Also, surgery may be postponed during pregnancy or breastfeeding - in each case, the doctor makes a decision taking into account the symptoms and condition of the formation.
Palliative surgery for melanoma with metastases
At an early stage, complete removal of melanoma is possible. Even if regional lymph nodes are affected, there is still a chance of remission. If distant metastases are detected, treatment can only be palliative. It aims to relieve symptoms and prolong life, but not to cure. Is there a chance to cure a patient if he only has 1-2 metastases that can be removed surgically? If only one metastasis is found during a CT scan or MRI, most likely there are others, they are just very small and could not be detected. The chances of remission are very low. However, surgical treatment can still help. The surgeon can remove some metastases to improve the functioning of the affected organs, eliminate symptoms, and increase the patient’s life expectancy. In later stages, other, non-surgical treatment methods come to the fore. For example, immunodrugs from the group of checkpoint inhibitors help to greatly increase survival.
Laser removal equipment
There are several classes of laser devices for removing moles. The most commonly used is a diode laser. Beams of light with the required wavelength are formed inside the device, and from there they travel through a light guide to the mole. The wavelength of the laser light is selected so that it is primarily absorbed by water or blood, that is, it heats them up very quickly. Rapid heating by the laser causes instant evaporation of water from the mole and does not heat up the skin around it or the fatty tissue underneath it. The less healthy tissue heats up, the faster the wound heals and the fewer scars.
The results of using techniques that reduce pain.
After implementing the pain management principles described above in our clinic, I conducted an internal study. 131 people took part in the survey. After the mole was removed, everyone was asked the same question: “How painful was the painkiller injection for you?” There were 3 possible answers:
- It hurts (only 8% of respondents chose this option)
- Sensitive (57% answered)
- Doesn't hurt (35%)
The same results in chart form:
Thus, we can quite reasonably say that the removal of moles, as well as warts and papillomas in our clinic is carried out almost painlessly.
Sign up for deletion