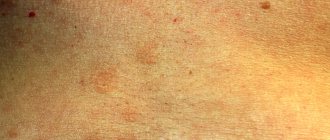
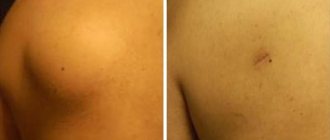
The appearance of dubious spots on the skin, which sometimes itch and flake, is a serious reason to consult a doctor and check for dermatological diseases.
Pityriasis rosea (Giber's disease, roseola exfoliates, pityriasis, pithiasis) is an acute skin disease with specific rashes, a peculiar course and a tendency to seasonal relapses. It manifests itself in the formation of pink spots on the skin of the chest, back, limbs and other parts of the body, located along the lines of maximum extensibility (Langer's lines). Over time, the rashes become like large medallions. From the moment the first maternal plaque (large spot) is detected until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear, 30-45 days pass.
At CELT you can consult a dermatologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
Causes of pityriasis
Despite the fact that Gibert's disease is very common, the mechanism of the disease is not fully understood. The following factors are believed to play an initial role:
- Exposure to viruses (type 7 herpesvirus, etc.), bacteria and other infectious agents. This is confirmed by tests that prove the presence of pathogens in the body. Very often, skin disease appears against the background of influenza, acute respiratory infections and other infections.
- Attachment of allergic reactions.
- Bites from bedbugs, lice and other blood-sucking insects.
- Reduced immune defense.
- Frequent hypothermia and stress.
- Violation of gastrointestinal functions and metabolism.
- Introduction of vaccines.
Most frequently asked questions from patients
What causes pityriasis rosea?
There is no clear answer to this question. Research continues. Presumably, the cause may be herpes virus type 6 or 7. When immunity decreases, it becomes more active, which triggers the process of various types of rashes (plaques, vesicles, blisters). The disease can be triggered by stress, poor ecology, hormonal fluctuations, and chronic diseases.
Is pityriasis rosea contagious?
Pityriasis rosea in humans is considered non-contagious, but rare cases of the disease affecting entire families are known. Much depends on the state of the immune system and the body’s defenses, which can resist viruses, bacteria and infections.
Is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis rosea?
One type of therapy for this dermatological disease is light therapy. Moderate exposure to ultraviolet radiation has a positive effect on the condition of the skin, stimulating its regeneration. Combustion must not be allowed. This will lead to increased itching in the area of the spots.
Symptoms of pityriasis
Clinical manifestations of pityriasis rosea are caused by exposure to infectious pathogens and the development of allergic reactions. The skin disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- General weakness, enlarged lymph nodes, elevated body temperature.
- The formation on the body of small pinkish and mauve spots that have a symmetrical shape and appear along Langer’s lines. Rashes appear on the back, limbs, chest, neck, groin and other parts of the body.
- The appearance on the skin of 2-3 bright red maternal plaques (their diameter is 4 cm), dotted with scales. After a week, small pink rashes form from these large spots.
- Dropout spots spread throughout the body and increase in size (their diameter is 1-2 cm), can peel off, and resemble medallions in shape.
- Severe skin itching.
- Increased irritability.
With proper therapy, the symptoms of pityriasis disappear after 5-8 weeks, and the patient fully recovers. Longer therapy is required if the rash has dense nodules, blisters or papules. In exceptional cases, pityriasis rosea turns into eczema, purulent inflammation of the skin, folliculitis, streptococcal infections, etc. develop. The development of complications is facilitated by the patient’s excessive sweating, a tendency to allergies, constant friction of the skin and improper treatment.
Atypical forms of the disease
Sometimes Zhiber's disease proceeds according to a non-standard pattern:
- the presence of severe itching (usually it is minor);
- increase in body temperature against the background of general malaise;
- maculopapular rashes that last much longer than 6-8 weeks;
- complications leading to eczema.
Whether complications arise or not depends on the behavior and condition of the patient. Problems arise from rubbing the skin or frequent washing, ill-conceived local therapy, increased sweating and a predisposition to allergic manifestations.
Mechanical or chemical action on inflamed areas does not alleviate the condition, but increases itching and prolongs the duration of the disease. Only a qualified doctor can help with treatment (if necessary).
Diagnosis of pityriasis
If you find suspicious spots on the skin, you should promptly contact a dermatologist. During a visual examination, the doctor assesses the nature of the rashes, their shape, size, location on the body and is able to make the correct diagnosis. After dermatoscopy, the following studies are additionally carried out: biochemical tests of blood and urine, RMP (microprecipitation reactions with antigens), skin scrapings from injured areas.
A more complex diagnosis is carried out if the skin disease lasts more than six weeks. In these cases, discharge from the affected lesions is sent for bacterial culture. A biopsy and subsequent histological studies will help make the correct diagnosis. In order to distinguish Zhiber's disease from other types of lichen, toxicerma, psoriasis, complicated syphilis and other pathologies, fluorescent diagnostics are carried out, scrapings are checked for the presence of pathogenic fungi, RPR tests are done for syphilis, etc.
Sources
- Anderson KR: Treatment with dapsone in pityriasis versicolor vesicularis rosea, 1971;
- Andrews GK: Skin Diseases 1954;
- AranjoT. et al.: Human Herpesviruses 6 and 7, 2002;
- Bernhardt R.: Skin diseases: 1922;
- Bjornberg A, Hellgren L: Pityriasis rosea. Statistical, clinical and laboratory research, 1962;
- Buckley K: Rash resembling pityriasis rosea in a patient receiving omeprazole, 1996;
- Gutowski W.: Attempt to treat Gibert's pink dandruff with bismuth and penicillin, 1950;
- Kempf W. et al.: Pityriasis rosea is not associated with human herpes virus, 1999;
- Parson JM et al: Update on pityriasis rosea, 1986;
- Sharma PK, Yadav TP: Erythromycin for pityriasis rosea, 2000;
- Wass I.: Treatment of pityriasis rosea with nonspecific substances, 1948.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Pityriasis rosea in pregnant women
Pityriasis occurs more often in women than in men. It is especially dangerous when the skin disease occurs in pregnant women. If you notice any rashes, it is important to immediately visit a dermatologist and undergo treatment. It is unacceptable to risk the baby’s health and expect the plaques to disappear on their own. If the disease is not treated, then bacterial infections appear, which are much more difficult to deal with.
If a pregnant woman has not been diagnosed with pityriasis rosea, it is nevertheless important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- clothing made from cotton and linen is preferable to synthetic and woolen fabrics
- limiting heavy physical activity
- For hygienic purposes, use only warm water
- timely moisturizing of damaged skin areas
Epidemiology of the disease
Among all skin diseases, pityriasis rosea accounts for 1 - 3%. People of different ages are affected, but most cases occur between the ages of 20 and 29 years. Women get sick much more often than men. The disease is more often registered in the cold season (spring - autumn). People with weakened immune systems are more likely to get sick. They may develop pityriasis rosea again.
Rice. 3. Pink lichen of Zhiber in men.
Treatment of pityriasis
When a patient is diagnosed with Gibert's disease, the dermatologist develops an individual treatment regimen to avoid dangerous complications. There is an opinion that pityriasis rosea will go away on its own in a few weeks. As a result, complications arise, and the patient comes to the dermatologist with an advanced form of the disease.
Drug treatment includes the following medications:
- antihistamines that relieve the patient from itching, swelling and redness on the body
- corticosteroid, desensitizing and antipruritic ointments. Medicinal compositions containing betamethasone, hydrocortisone, etc. are applied to the affected skin and lightly rubbed in. The medications eliminate rashes, get rid of peeling, and effectively restore the skin.
- drying agents containing zinc to accelerate skin healing
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are indicated in cases where a bacterial infection is associated with pityriasis rosea. It is unacceptable to start taking antibacterial drugs on your own, since they are selected individually, taking into account laboratory tests.
- antifungal medications: drugs containing clotrimazole and other active substances are prescribed topically in the form of gels and ointments
- antiviral drugs containing acyclovir and other active components. Dermatological tests have confirmed that if antiviral drugs are prescribed in combination with antibiotics from the first days, the patient quickly recovers.
- neutral water-shaken preparations Dermatologists prescribe pharmacy talkers containing zinc oxide, menthol and anesthesin to patients with pityriasis rosea. These products relieve itching and pain in damaged areas and speed up recovery.
- iodine is an aggressive, but extremely effective remedy. Injured skin is treated with iodine in the morning and evening. Initially, the skin begins to peel off more actively, but then there are no extra scales left on it. Not all experts recommend that their patients cauterize damaged areas with iodine, since this drug can be harmful if used incorrectly.
Recommendations for patients
During the treatment period, the patient is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet: avoid nuts, citrus fruits, chocolates, honey, etc. Products containing artificial colors should be excluded from the menu. It is worth limiting the consumption of fried foods, carbonated drinks, fast food, strong alcohol and coffee.
- Limit water treatments within reasonable limits and give preference to the shower.
- Refuse to use aggressive hygiene and cosmetic products for the body. Gels and other detergents should not dry out the skin.
- Give preference to underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Moderate sunbathing - ultraviolet light helps the skin recover faster.
- Follow the recommendations of a dermatologist, apply to the skin only products recommended by a specialist.
- Folk remedies can be used only after consultation with your doctor.
How to avoid infection
Due to the fact that the nature of the occurrence of Gibert's disease has not been thoroughly studied, there are no methods to prevent this disease. The main recommendation is to monitor the state of the immune system, as it will help avoid infection.
Complications
The disease itself in most cases goes away without leaving a trace. However, sometimes complications arise in the form of eczema, staphylococcus or streptococcus; ring-shaped lichen can develop, which quite often becomes chronic and even after a few years a relapse can occur. Then treatment is done with antibiotics. To prevent such problems, we strongly recommend that you undergo comprehensive treatment in our clinic. Don't forget about your health and the health of your family!
Complications and consequences
One of the complications of pityriasis rosea is its transition to an atypical form - Vidal's ring-shaped lichen. It is characterized by huge spots and tends to become protracted. Such lichen can recur for several years.
The result of pityriasis rosea and its treatment can also be:
- Adverse skin reactions, for example, drug hypersensitivity syndrome.
- Transition of pathology into eczema, folliculitis or streptococcal impetigo.
- Accompanying the disease with serious diseases, for example, purulent skin lesions.
With inadequate treatment, it is also possible that an allergic component may join the main course of the disease. This also applies to improper skin care.
The disease occurs secondarily extremely rarely. If infection does occur, the main location of the plaques will be in thin areas of the skin or areas of concentration of sweat glands.
Ointments used for pityriasis rosea
For severe, disturbing itching, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic creams and formulations are prescribed. Ointments are used to treat the disease:
- Hydrocortisone – has an anti-inflammatory effect, relieves itching;
- Olettrinovaya is an antibacterial drug;
- Prednisolone - a composition with healing properties that can relieve inflammation;
- Loriden A - ointment with antipruritic, anti-parotid, anti-edematous effects;
- Sinalar – eliminates inflammation due to antibacterial properties;
- Lassara paste is an antiseptic that discolors stains;
- Rioloxol - antibacterial and anti-inflammatory;
- Flucinar – effectively relieves itching, eliminates flaking and inflammation;
- Sulfur – inhibits the inflammatory process.
Tsindol suspension also helps dry the skin, eliminate inflammation and itching. Ointments are applied to the pink plaques in a thin layer in accordance with the instructions and directions of the doctor. The treatment course is 2-3 weeks, the frequency of use of each drug is determined individually. At the same time as using medications, you should be careful with the affected skin.
However, any ointments, like all other medications, should be used exclusively as prescribed by a doctor, so as not to aggravate the situation. In addition, the effectiveness of each of the listed external remedies greatly depends on the patient’s age, the state of his immunity, the degree of spread of lichen, the presence of chronic pathologies and other characteristics of the body.
During pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy, pityriasis rosea is very dangerous. It can cause spontaneous abortion and have a negative effect on the fetus.
A woman may feel:
- increased fatigue;
- pain in the head area;
- lack of sleep;
- decreased appetite.
This symptomatology is typical for the normal state of pregnancy, but if it is accompanied by the appearance of any kind of spots, you should urgently consult a specialist.
Complications can also arise if the disease manifests itself in the second and third trimesters. In the first case, this is fraught with hypotension and slowness of the baby’s movements. And in the second - premature birth.
The reason for the development of roseola exfoliating in pregnant women is the same reduced immunity coupled with hormonal changes.
Visually, lichen in pregnant women looks the same as everyone else’s, and treatment should be selected taking into account the patient’s position.
Calling a dermatologist to your home for pityriasis rosea
When the first signs of pityriasis rosea appear, you should consult a doctor. Today there is a convenient service for calling a doctor to your home, which provides many advantages:
- Saving time - no need to go to a medical facility or wait for your turn at the office door. You can simply arrange a doctor’s visit at a time convenient for you;
- Comfort – communicating with a doctor at home is much easier, because the doctor is not distracted by other patients and clinic staff, he can spend as much time as necessary on examination and consultation;
- Calmness – for children of all ages, a visit to a medical facility is often stressful, which plays a negative role in the development of many diseases, including pityriasis rosea. A doctor’s home visit will save the child from unnecessary worries;
- No risk – the development of pityriasis rosea often occurs against the background of weakened immunity. In such circumstances, contact with other patients is undesirable, but it is almost impossible to avoid it in the corridors of the clinic, as well as in public transport on the way to the medical facility. At home, such a risk is eliminated;
- If the disease is accompanied by fever, calling a doctor at home will be the best solution;
- Examination at home is the most convenient option for older people, mothers with small children, and patients with disabilities.
The quality of medical care at home is no different from that provided in a medical facility. The doctor gives the necessary recommendations, provides full consultation, diagnoses the disease and prescribes adequate treatment.
Common symptoms and manipulations in dermatology:
- Skin rashes
- Calling a dermatologist to your home
- Itching in the urethra
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash
- Prevention of casual sex
- Skin neoplasms
- Pyoderma
- Pityriasis rosea
- Streptoderma
- Scabies
- Peeling skin
- Fungal infections
- Skin infection
- Pus on the skin
- Blisters on the skin
- Papillomas on the foreskin
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Skin structure