Information about a number of other diseases: Basal cell carcinoma, Graves' disease, Balanitis, Delirium tremens, Beriberi, Infertility in women, Infertility in men, Insomnia, Rabies, Blepharitis, Myopia, Bundle block, Addison's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Bowen's disease, Von Willebrand's disease, Gunter's disease, Cushing's disease, Crohn's disease, Parkinson's disease.
What is Gunther's disease?
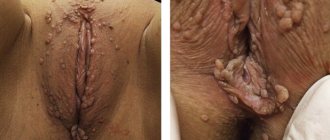
Gunther's disease is a fairly rare hereditary disease, during which disruptions in pigment metabolism and accumulation of porphyrin in the soft tissues begin. This substance has a nitrogen-containing pigment, included in hemoglobin, which gives blood cells the red tint familiar to people. The process begins development in the red bone marrow, interconnected with the action of red blood cell synthesis.
Why does sun allergy occur?
Allergic reactions vary from person to person, so science still cannot answer this question. But doctors identify groups of people whose risk of photodermatitis is increased. Among them:
- children of the first years of life and the elderly - some have an immature immune system, while others are weakened due to age;
- people with metabolic disorders and chronic diseases of the digestive system and thyroid gland;
- people with fair skin, blond or red hair;
- future mothers;
- allergy sufferers.
The reaction can also occur in an absolutely healthy person who has never suffered from allergies before. This happens due to external and internal factors.
External factors. Allergens get on the skin and increase its sensitivity to the sun. Plant pollen is highly allergenic. The juice of some meadow grasses provokes sunburn. Contact with the skin of hogweed juice is especially dangerous, as it causes instant itching, the formation of blisters, and after they heal, the appearance of pigment spots. Some substances in cosmetics and perfumes can act similarly. Most often, photodermatosis is caused by:
- eosin - found in lipsticks and lip balms;
- para-aminobenzoic acid - included in sunscreen products;
- retinoids - components of anti-aging cosmetics;
- essential oils;
- unsaturated fatty acids;
- fruit acids.
A tattoo increases the risk of sun allergy. The paints contain cadmium salts, which reduce local immune defense and can change the skin's reaction.
pixabay.com/
Internal factors. Taking certain medications can make your skin sensitive to ultraviolet light. Among them:
- antibiotics of the tetracycline group;
- hormonal agents;
- antiallergic drugs;
- expectorants (licorice);
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs of the NSAID group (ibuprofen, diclofenac, etc.).
Solar urticaria can occur due to an individual immune reaction to genetic, hereditary diseases. It is typical for people with disorders of the immune system and metabolic processes. If parents have photodermatitis, it is highly likely that it will appear in children.
How to detect?
The first symptoms indicating the presence of Gunther's disease begin to appear already in the first year of the baby's life. In special situations, they may occur several years later. The main symptoms of the presented process include:
- Scarlet color of urine, caused by a large amount of pigment in the body;
- Colored tooth enamel, which is evidence of the deposition of porphyrins on the teeth;
- Chronic photosensitivity is a process during which a burn may appear in the patient’s body due to the penetration of ultraviolet radiation through glass. Causes rashes;
- High level of hair on the epidermis;
- Significant growth of the liver and spleen;
- Destruction of red blood cells in the circulatory system.
Types of photodermatosis
Allergy to the sun can occur in different ways. There are three types of photodermatosis.
1. Solar eczema. External damage to skin that has been exposed to sunlight. It occurs only in open areas, but with prolonged exposure to the sun it can spread under clothing. Allergy to the sun looks like bubbles, blisters, red spots. After a few hours, purulent pimples may appear in place of the blisters. Solar eczema is the most common type of photodermatitis. It does not cause deterioration in well-being, but cannot be considered only a cosmetic problem and requires treatment.
2. Systemic lupus erythematosus. It appears on the face and body as solar eczema. But in addition to the rashes, you feel unwell. Nausea, dizziness, confusion, headache, chills may occur. Lupus erythematosus is a dangerous reaction of the body that requires the help of a doctor.
3. Solar urticaria. Unlike the first two types of photodermatosis, the severity of which directly depends on the duration of sun exposure, solar urticaria occurs almost instantly. It spreads rapidly and can affect large areas of the skin within a few minutes. This form of allergic reaction is rare and is usually the body's response to ultraviolet light coming into contact with a strong allergen on the surface of the skin.
pixabay.com/
How to cure?
Currently, scientists have come to the conclusion that it is impossible to fully recover from this condition. However, it is possible to reduce the number of relapses. In addition, doctors in some cases use bone marrow transplantation. Doctors advise people suffering from Gunther's disease to spend a minimum amount of time in the sun. The following are used as braking:
- Nicotinic and ascorbic acid;
- Riboflavin;
- Cyanocobalamin.
What consequences can the disease lead to?
According to clinical data, such a disease can cause numerous metabolic problems in the patient’s body. All patients live for a short period of time.
Treatment of sun allergies
The doctor should choose treatment tactics depending on the degree of skin damage. Therefore, at the first opportunity, you need to show the victim to a doctor. Proper first aid measures will reduce the severity of the reaction.
- Photodermatitis in a child. If the skin is red and the child complains of itching or scratching, you need to take him out of the sun. Rubbing the reddened areas with a cool, damp cloth and drinking plenty of fluids will help. If you have an antihistamine on hand, you should give it to your baby right away. It is important to understand what caused the reaction and avoid contact with the allergen. When photodermatitis passes, you need to go out into the sun carefully, increasing your exposure time gradually from 15 minutes to 2 hours. Protect your baby's body with light-colored cotton clothing and wear a wide-brimmed hat on his head.
- Photodermatitis in an adult. First aid tactics are the same. The only difference is that adults are usually attentive to the well-being of children and pay much less attention to their own condition. If the skin lesions are already significant, it is necessary to help it with special care products. Compositions with panthenol and hyaluronic acid are suitable. Upon returning home, take enterosorbent: these drugs remove allergens from the body and reduce the intensity of the allergic reaction.
pixabay.com/
Contact your doctor - a dermatologist or allergist - as soon as possible. The first attack of sun allergy can develop into chronic eczema, so it is important to stop it as soon as possible. For treatment, antihistamines are prescribed orally and anti-inflammatory drugs topically.
Creams with corticosteroids reduce tissue swelling. Blisters should not be opened as this may lead to infection. If the skin is damaged, use wound healing agents with panthenol and sea buckthorn oil.
Additionally, the doctor may recommend a course of enterosorbents for 7–10 days and taking vitamin supplements to improve the barrier function of the skin. Enterosorbents should not be taken simultaneously with other medications. At least 2 hours should pass between doses.
Why is it important to wear sunglasses?
Zoya Evgenievna Kotina, pediatric ophthalmologist:
— 85% of people are aware of the risk of skin cancer, but only 7% of the population are aware that ultraviolet radiation also causes eye diseases. Eye diseases such as pinguecula, pterygium, photokeratitis, cataracts, retinal dystrophy are ophthalmoheliosis (ophthalmos - eye, helios - sun), that is, diseases caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin of the eyelids and the structure of the eye.
Ultraviolet B rays from the sun destroy eye tissue 600 times more intensely than A radiation. But both of them have a negative effect on all tissues of the eye - the skin of the eyelids, the conjunctiva, that is, the mucous membrane of the eyeball, the cornea, the iris, the lens and the retina.
The conjunctiva is easily damaged by excess UV radiation. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays leads to changes in it, causing the formation of bubbles (pingueculae) and thickening (pterygium). In some cases, pterygium can creep onto the cornea, which leads to decreased visual acuity and subsequently requires surgical treatment. However, surgical removal of pterygium does not always lead to a good result. Patients who have been diagnosed with pinguecula and pterygium require constant wearing of sunglasses and drug treatment.
Form is everything
It's not enough to just wear something with dark lenses over your eyes. Sunglasses should be large and form-fitting to protect your eyes from both direct and peripheral rays.
The cornea is also vulnerable to UV radiation. With an acute reaction to sunlight - photokeratitis - severe pain in the eyes, narrowing of the palpebral fissure (blepharospasm), lacrimation and even photophobia are possible.
Between the cornea and the lens there is intraocular fluid with a high concentration of ascorbic acid - vitamin C. This acid protects the DNA of the lens from damage and is a filter for ultraviolet A- and B-rays. But under their influence, as well as due to irreversible changes in the protein, the lens turns yellow and loses transparency with age. Daily intense exposure to UV radiation leads to the development of early cataracts - clouding of the lens - and requires surgical treatment.
Despite the presence of its own UV filter inside the eye, about 2% of sunlight reaches the retina and is focused in its central part - on the macula. If you do not use sun protection, early retinal degeneration may develop, leading to blindness.
Clouds do little to attenuate UV radiation, and cloudy days are especially dangerous for eye health
The source of UV radiation is not only direct, but also reflected - from snow, building walls, the surface of water, sand - rays. The latter are potentially more dangerous in terms of their effects on eye tissue. Cloud cover does little to attenuate UV radiation, and cloudy days, when most people neglect UV protection, are especially dangerous for eye health. Only rain, fog and low clouds can significantly block UV radiation.
Our eyes need protection outdoors all day long, all year round. Wearing wide-brimmed hats or visors reduces UV exposure, and frequent use of sunglasses reduces the risk of developing cataracts by 40%. But in our country, many people wear sunglasses no more than 30% of the time they spend outdoors, and a quarter of the population never wears them at all.
The effects of UV radiation can accumulate over a person's life. However, children's eyes are especially vulnerable to UV exposure because their pupils are larger, their lenses are clearer, and they spend more time outdoors. And the younger the child is, the less protected his lens and retina are. However, unfortunately, only 3% of children regularly wear sunglasses.
If a child has learned to walk and run, then when outdoors he should wear a hat with a wide brim or a visor and specially shaped sunglasses. In children of the first year of life, their eyes may not close completely during sleep, so it is better to lower the visor in the stroller. If you wear contact lenses, it is best to choose ones that have a UV filter and pair them with sunglasses.