If the skin does not look very fresh and healthy, if there are problems on it, then such skin is usually called problematic. Problematic skin can affect anyone at any age. If your skin is perfect when you are young, it may deteriorate later. Hormonal changes greatly affect her condition. In addition, if you experience stress, if there are many other unfavorable factors in your life, your skin condition will worsen. Skin can be dry, oily, or combination. Skin types are also distinguished by age. This is young skin, mature, or aging. If a person turns to a dermatologist, then most often he turns to him with problem skin.
Table of contents
- Expression and fine wrinkles
- Uneven skin color
- Wrinkles around the eyes
- Loose skin
- Rosacea
- Post-acne scars
- Changing the contours of the oval face
- Enlarged pores
- Accurate diagnosis of signs of aging and results of aesthetic procedures
- Principles of treatment
The first signs of aging and other aesthetic defects are changes in the structure, color and/or function of a skin area that cause concern to the patient.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for correcting signs of aging and other aesthetic defects:
- Thermage (Solta Medical)
- Maximus (Pollogen by Lumenis)
- GeneO+ (Pollogen by Lumenis)
- UltraPulse (Lumenis)
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
- Antera 3D (Miravex)
Solar (senile) lentigo
Widespread hypermelanosis, which occurs due to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation and manifests itself as focal darkening of the skin. In the United States, lentiginous spots affect 90% of fair-skinned people over the age of 60. The changes develop gradually - they accumulate over many years of ultraviolet irradiation of exposed areas of the face and body. A sign of skin aging, lentigo can also occur after regular and/or long-term sessions of visiting a solarium.
Age spots are flat or slightly concave discolorations that are light brown or dark brown. They can often be found on open areas - the face, the backs of the arms and hands, and in the décolleté area ( Fig. 1 ). Single lesions gradually increase in size and merge into larger zones of hypermelanosis. Lentigo after solarium is distinguished by its presence in atypical places that are not subject to active insolation - for example, in the groin.
Senile lentigo can degenerate into lentigo maligna - this happens infrequently, but the possibility of such an event cannot be excluded. Find out more about lentigo and its treatment here.
Rice. 1. Senile lentigo on the arms (Skin Evolutions Clinic)
Fine wrinkles and fine lines are the first sign of aging
Expression wrinkles are bends in the facial skin texture that are visible to the eye; they appear when the superficial muscular aponeurotic system (SMAS) contracts. There are superficial (fine lines) and deep (folds). Fine wrinkles are a reflection of early changes in skin texture - these are small folds that occur due to chrono- and photoaging.
The timing of the appearance of expression lines and fine wrinkles depends on a person’s race and skin phototype, genetics, nutrition, facial activity, geography and other factors. Caucasians are more prone to fine lines and wrinkles, while Asians and African Americans can have smooth skin for a long time. Associated factors are: bad habits, frequency and time spent in the sun or in a solarium, stress, BMI less than 18.5, diseases of internal organs and other factors.
Typically, between 40 and 50 years old, facial wrinkles visible to the eye form, and after 50 years, static wrinkles begin to form - first in the form of fine lines, gradually deepening to large furrows ( Fig. 2 ). Learn more about fine lines and wrinkles and their treatment options here, and about fine lines and treatment options here.
Rice. 2. Medium to large skin wrinkles (Mayo Clinic)
Seborrheic dermatitis of the facial skin: treatment and diagnosis
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease that develops as a result of the activity of a fungus of the Malassezia genus. Sebum becomes a favorable environment for fungal activity. In this regard, the pathology is especially common in people with oily skin.
The disease develops gradually. The first symptoms are yellowish-red scaly spots and blistering rashes. Dense crusts, skin defects and cracks may form on the scalp.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is carried out in the following areas:
- Dieting.
Eating fatty, sweet, or too spicy foods provokes excess secretion of sebum. This creates a favorable environment for fungal activity. - Drug therapy .
The patient may be prescribed antimicrobial drugs in the form of tablets. To strengthen the immune system, vitamin and mineral complexes and immunostimulants are used. Sometimes hormone therapy is used. - External means.
A dermatologist must prescribe external agents in the form of ointments, creams, and aerosols. Their action is aimed at destroying the Malassezia fungus.
Drug treatment
Timely therapy allows you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms and restore skin health.
Uneven skin color
Among the causes of this condition, the most important is not skin aging, but a person’s prolonged exposure to the sun or regular visits to solariums. Uneven skin color also occurs when microparticles are deposited in the skin due to environmental pollution, after taking certain medications, with hormonal fluctuations, against the background of chronic inflammation, diseases of internal organs, vascular pathologies, disturbances in the microbial composition of the skin, etc.
Uneven skin color manifests itself as areas of hyper-, hypo- or depigmentation, focal or extensive changes in shade ( Fig. 3 ). Find out more about uneven skin tone and how to correct it here.
Rice. 3. Uneven skin tone due to rosacea (Skin and Lasers Surgery Specialists)
Oily facial skin: causes and treatment
Oily facial skin is associated with excessive activity of the sebaceous glands. This type of skin requires systematic care, otherwise acne, ulcers, and comedones appear. First, skin defects appear on the forehead, chin, cheeks, and then throughout the facial area. After healing, scars, scars, and rough bumps form at the site of the inflammatory foci. The skin takes on a dull blue or gray tint.
Often, disruption of the sebaceous glands is associated with a genetic factor. However, there are other reasons for excess oiliness of the skin:
- hormonal imbalance;
- abuse of fatty foods;
- low-quality cosmetics;
- violation of autonomic function;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- neuropsychological tension;
- endocrine pathologies.
In fact, oily skin type does not require treatment, but proper care (if the problem is not caused by a primary disease).
Dry skin on the face: causes and treatment
Dry tissue occurs when there is insufficient sebum secretion. In medicine, this phenomenon is called xerosis. The causes of dryness can be different:
- genetic predisposition (dry skin from birth);
- dermatological diseases - atopic and allergic dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, neurodermatitis;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- unhealthy diet, bad habits;
- stress, neuro-emotional tension;
- dehydration;
- use of low-quality or inappropriate cosmetics;
- living in a dry climate;
- aggressive exposure to sunlight;
- diseases of internal organs - renal and liver failure, hypovitaminosis, blood diseases, oncological processes, hypothyroidism.
Treatment is carried out comprehensively, after identifying the main cause of tissue dryness. If necessary, the doctor prescribes medications, moisturizing creams and ointments, and gives recommendations for lifestyle correction.
Wrinkles around the eyes
This is a clear sign of aging of the facial skin around the eyes of varying degrees of severity - from fine lines to large creases. Their main causes are chrono- and photoaging. A significant aggravating factor is smoking, which enhances the destructive effect of matrix metalloproteinases on extracellular matrix proteins (collagen, elastin) and contributes to the earlier appearance of wrinkles around the eyes.
One of the classifications of periorbital wrinkles is the following ( Fig. 4 ):
- Type I - wrinkles extend from the outer edge of the eye to the eyebrow and zygomatic process.
- Type II - wrinkles extend from the outer edge of the eye to the zygomatic process.
- Type III - single wrinkles are limited to the outer edge of the eye.
Find out more about wrinkles around the eyes and how to treat them here.
Rice. 4. Types of periorbital wrinkles (Tamura BM, Odo MY Classification of periorbital wrinkles and treatment with botulinum toxin type A. Surg Cosmet Dermatol 2011; 3(2): 129)
https://www.surgicalcosmetic.org.br - page 131, figure 2
Sources
- Anci E., Braun C., Marinosci A., Rodieux F., Midun E., Torres MJ., Caubet JC. Viral Infections and Cutaneous Drug-Related Eruptions. // Front Pharmacol - 2022 - Vol11 - NNULL - p.586407; PMID:33776753
- Lassi ZS., Padhani ZA., Das JK., Salam RA., Bhutta ZA. Antibiotic therapy versus no antibiotic therapy for children aged 2 to 59 months with WHO-defined non-severe pneumonia and wheeze. // Cochrane Database Syst Rev - 2022 - Vol1 - NNULL - p.CD009576; PMID:33469915
- Marusinec R., Kurowski KM., Amato HK., Saraiva-Garcia C., Loayza F., Salinas L., Trueba G., Graham JP. Caretaker knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) and carriage of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing E. coli (ESBL-EC) in children in Quito, Ecuador. // Antimicrob Resist Infect Control - 2022 - Vol10 - N1 - p.2; PMID:33407927
- Yousif MK. Mothers' false beliefs and myths associated with teething. // Qatar Med J - 2022 - Vol2020 - N2 - p.32; PMID:33329998
- Willems J., Hermans E., Schelstraete P., Depuydt P., De Cock P. Optimizing the Use of Antibiotic Agents in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Narrative Review. // Paediatr Drugs - 2022 - Vol23 - N1 - p.39-53; PMID:33174101
- Shahrin L., Chisti MJ., Shahid ASMSB., Rahman ASMMH., Islam MZ., Afroze F., Huq S., Ahmed T. Injectable Amoxicillin Versus Injectable Ampicillin Plus Gentamicin in the Treatment of Severe Pneumonia in Children Aged 2 to 59 Months: Protocol for an Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. // JMIR Res Protoc - 2022 - Vol9 - N11 - p.e17735; PMID:33136058
- De Wolf D., Genouw A., Standaert C., Victor A., Vanoverbeke N., De Groote K., Martens L. Endocarditis prophylaxis in daily practice of pediatricians and dentists in Flanders. // Eur J Pediatr - 2021 - Vol180 - N2 - p.397-405; PMID:32780192
- de Sá Almeida JS., de Oliveira Marre AT., Teixeira FL., Boente RF., Domingues RMCP., de Paula GR., Lobo LA. Lactoferrin and lactoferricin B reduce adhesion and biofilm formation in the intestinal symbionts Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. // Anaerobe - 2022 - Vol64 - NNULL - p.102232; PMID:32634470
- Basha GW., Woya AA., Tekile AK. Prevalence and risk factors of active trachoma among primary school children of Amhara Region, Northwest Ethiopia. // Indian J Ophthalmol - 2022 - Vol68 - N5 - p.750-754; PMID:32317440
Loose skin
Flabbiness of the skin occurs due to loss of elasticity and changes in the architectonics of connective tissue. These changes appear on any part of the body, but most clearly on the face.
The most important cause of sagging is age-related degradation of collagen and elastin. With aging, collagen fibers lose their ability to create an ordered network, begin to stick together with glucose molecules and form non-stretchable threads. The same thing happens with elastin fibers. Skin sagging is caused by photoaging, inflammasomes, chemotherapy in cancer patients, age-related syndrome due to hormonal changes in the body, micronutrient deficiency, smoking, etc.
Externally, loose skin is characterized by decreased tone, wrinkles, dryness, a tendency to sag, and a pale or yellowish tint ( Fig. 5 ). Find out more about sagging skin and how to correct it here.
Rice. 5. Skin laxity and other signs of aging compared to a youthful face (Health & Heldi)
Cosmetological problems of the face and skin
I can say for sure that there are at least three reasons!
First, there is no system. What does system mean? This is when we take a comprehensive approach to the problem of rashes. When a patient comes to me, I don’t look at a specific pimple and don’t think about what I should put on it to make it go away. I'm thinking about what to do to prevent a person from having these rashes anymore. This is a nutritional correction, this is a home care correction, these are the same procedures. All treatment can only be done in combination!
How many times do I come across the fact that when female patients come to me, I ask them:
Dialogue - Do you often go to cleanses? - Well, yes, about once every two months or once a month - Okay, how do you take care of your face? - Well, I bought something myself... — They did so many cleanings for you and weren’t you prescribed care? - No, no one prescribed care for me...
Initially, this is a flawed approach to working with a problem face, because in addition to procedures, there must be a system of facial skin care. I'm not even talking about the examination and the rest.
The second reason is the frequent change of doctors. In fact, people with problem skin (I learned this from my practice) are very emotional and labile, they take everything very seriously, they want to solve their problem as quickly as possible. It is really very difficult, emotionally, to see terrible rashes on your face every day.
And of course, when a patient comes to a cosmetologist, he expects some quick results. The doctor cannot immediately give quick results; moreover, sometimes the first steps in treatment can aggravate the process and the person gets upset, gives up everything halfway, waits two or three months and then goes to another doctor. The next doctor starts all over again and everything from scratch.
Understand that when you change doctors constantly, you are harming yourself first of all. Acne treatment cannot be quick; the effect cannot appear in a month, especially with severe acne. An examination and treatment adjustment is required. It also happens that we sometimes change medications during the treatment process.
First of all, you need to find a cosmetologist who will give you a certain level of trust and answer your questions in detail. Find a cosmetologist who will not evade answers. And only if you trust, start your treatment with this doctor. This is probably the best option! And if you change doctors like gloves, you will be treating your acne for 15 years, until it goes away on its own.
The third point is ignoring the cosmetologist’s prescriptions. I can prescribe everything for examinations, home care, procedures... But, for some reason, a person decides not to do something. Or the appointment sheet has been collecting dust on the shelf for 5 months. The examinations that need to be taken have not been completed: blood and urine tests. Purchased care just sits at home and is not used for some reason. Procedures are skipped.
Well, what can we say in this case?
Treatment? This is not a treatment! You just went, spent time and money and in the end nothing! If you are prescribed something, then please do it! If you have any questions about treatment - ask! It often happens that I am prescribed a drug and then the patient calls me and asks: “But I read on the Internet that this drug causes so many complications! Well, it's just creepy! And you can’t get pregnant after 3 years and my hair will all fall out and I’ll be covered all over with pigmentation!!!” The Internet is the doctor of all Rus'! What can I say?
Yes, there are a lot of negative reviews on drugs, I understand! Yes, you can read, it is logical that if you are looking for something, if you doubt some points about the prescriptions, ask your doctor this question after you have read this! The doctor will explain everything to you in detail - he will tell you everything. If you still have questions, this is a separate topic! And if you interrupt treatment simply because you read something negative and did not give feedback to your cosmetologist! Well, excuse me, no treatment!
The next doctor will prescribe the same thing for you, you will read it again on the Internet and, strictly speaking, the acne treatment will end there. Therefore, give feedback to the cosmetologist and do everything that a competent doctor prescribes for you. He will always guide you in the right direction and will definitely help cure acne.
Very often, prescriptions for drugs such as antibiotics are scary. Systemic antibiotics - taken orally. The prescriptions for combined oral contraceptives and retinoids are scary, and in that order they are scary! The worst ones are retinoids. You must understand that for each acne disease (moderate and severe) there is its own treatment.
When you have pneumonia and you are in the hospital with a temperature over 40, you don’t set conditions for the doctor, like, I want this antibiotic or I want Grandma Agafya’s poultice. You will be prescribed an antibiotic, you want to survive and you allow yourself to be given this antibiotic. It's the same with acne. Yes, this is not a life-threatening condition, I agree. But you must understand that for each degree of severity of the condition, there is a specific treatment.
I can try to cure severe acne by cleansing, but I think you understand perfectly well that this will lead to no result. I can try to cure severe acne with some kind of ointment. Yes, you will feel better, it will definitely make you feel better. Will there be a result? No, there will be no result!
Therefore, here you can be afraid! But, you need to ask questions to the doctor! He will answer and you will already be thinking whether or not to decide in favor of the drugs that the doctor prescribes for you.
You must understand that in this case of your choice, you take responsibility for the fact that the result will come very slowly, or it will not come at all. Reason: You did not follow the recommendations of the attending cosmetologist (dermatologist).
Rosacea
This sign of aging is characterized by facial flushing, telangiectasias, rough skin, and inflammatory papulopustular changes.
The exact pathogenesis of the disease has not been studied: the role of heredity, skin microbiome, dysregulation of the immune system, and abnormal signal transmission to nerves and blood vessels has been suggested. An important aspect of rosacea are triggers - provoking factors, which are individual for each person and are determined experimentally.
During attacks of rosacea, a person experiences erythema on the face, sometimes with telangiectasia. Over time, inflammatory papules and pustules appear in the area of the nose, forehead and cheeks ( Fig. 6 ); rhinophyma, conjunctival vascular injection, chalazion and episcleritis may appear. Learn more about rosacea and its treatment options here.
Rice. 6. Rosacea with inflammatory elements on the cheeks (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
Demodex: facial skin treatment
Demodicosis develops as a result of tissue infection by a subcutaneous mite that lives in the sebaceous glands. The parasite causes disruption of the morphological structure of the skin and the immune status of a person. Infection with Demodex is one of the factors provoking rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne.
Demodicosis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- elements of rashes - ulcers, acne, papules;
- continuous hyperemia;
- pale gray color;
- enlarged pores, excessive sebum secretion;
- greasy shine in the light;
- itching, peeling;
- inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- general swelling.
Acne on the face
Treatment of micro-mites under the skin of the face requires an integrated approach with local and general medications. The basis of treatment is antibacterial drugs and agents that reduce sebum production. For local therapy, antiparasitic ointments, gels, and shampoos are used, which disrupt the functioning of the Demodex nervous system.
During the treatment of demodicosis, doctors recommend:
- clean the facial area only with medications prescribed by the doctor or thermal water;
- use dry wipes instead of towels;
- Avoid mechanical removal of pimples and ulcers;
- give up decorative cosmetics, get rid of the products you used before your illness;
- exclude alcoholic drinks and smoking;
- use pillows and blankets with synthetic filling;
- Avoid solariums and sunbathing on the beach.
Pore cleansing
To give up smoking
A diet that limits the amount of carbohydrates and fats alleviates unpleasant symptoms. Lack of fat reduces sebum production, that is, it limits favorable conditions for the parasite. You should avoid spicy foods, fried, salty, smoked foods, and sausages. It is better to boil or steam the permitted foods.
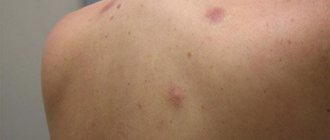
Post-acne scars
These are skin changes in areas where acne inflammatory elements are healing, associated with the formation of connective tissue. The vast majority of post-acne scars appear on the site of papules and pustules; much less often they occur in the area of comedones.
If the skin is damaged at the level of the papillary dermis, recovery can occur without gross defects - only depigmented areas with focal atrophy remain. With complete destruction of the basement membrane, a scar is formed ( Fig. 7 ) with the growth of coarse fibrous collagen, deformation of blood and lymphatic vessels. If collagen synthesis exceeds its destruction, the scar becomes hypertrophic - it bulges above the skin. If fibroblast activity becomes excessive, a large keloid develops due to tumor-like proliferation of immature connective tissue.
There are no post-acne scars:
- Hypertrophic.
- Keloids.
- Atrophic:
- chipped (icepick scars);
- rounded (rolling scars);
- rectangular (boxcar scars).
About half of acne scars disrupt the structure and/or function of the skin. They disfigure the patient’s face, negatively affect his emotional state and self-esteem, and can provoke psychological disorders and complexes about his appearance.
Find out more about acne scars and their treatment methods here.
Rice . 7 . Chip atrophic post-acne scars (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
Publications in the media
The morphological elements of the rash are the external expression of pathological processes that occur in the skin. Depending on the time of existence, the dynamics of the inflammatory process and under the influence of other reasons (scratching, secondary infection, etc.), the rash may change its original appearance during its evolution. Therefore, it is necessary to distinguish which rashes represent a typical picture of the disease, and which are the result of their further development. There are primary and secondary morphological elements • Primary morphological elements are rashes that appear on unchanged skin. Primary elements are divided into cavity and cavityless. Cavity-free elements include a spot, a blister, a nodule, a node, and a tubercle. Cavity elements have a cavity filled with serous, bloody or purulent contents. These include vesicle, bladder and abscess • Secondary morphological elements are rashes that appear on the skin as a result of the evolution of primary elements. These include hyperpigmentation, depigmentation, scaling, erosion, abrasion, ulceration, fissure, crust, scar, atrophy, lichenification and vegetation.
Primary morphological elements of the rash
A spot (macula) is characterized by a change in the color of the skin or mucous membrane in a limited area. The density of the spot does not differ from healthy areas and does not rise above the surrounding tissues. There are inflammatory and non-inflammatory spots. Inflammatory spots are caused by dilation of the blood vessels of the skin, disappear when pressing on them with a glass slide or finger and reappear when the pressure stops. They range in color from pale pink to bluish-red. Inflammatory spots measuring 2-25 mm - roseola; 2-3 cm or more - erythema. Roseola can be circumscribed or confluent; they are the most common symptom of infectious diseases. Non-inflammatory spots are characterized by the absence of inflammatory phenomena and do not disappear with pressure. With emotional excitement, neurotic reactions, large confluent and quickly disappearing non-inflammatory spots appear - erythema of shame, anger, etc. Among the spots caused by improper development of blood vessels in the skin, the most common are hemangiomas, which are a malformation of small veins and capillaries. Spots caused by persistent non-inflammatory dilatation of skin capillaries are called telangiectasias. When the permeability of the walls of blood vessels increases or they are damaged, hemorrhagic spots appear. According to size and shape, they are usually divided into: petechiae (petechiae) - pinpoint hemorrhages; purpura - hemorrhages with a diameter of 1–2 cm; ecchymoses - hemorrhages more than 2 cm in diameter; linear hemorrhages (vibices), bruises (sugillationes). The color of hemorrhagic spots changes sequentially over 2–3 weeks from red, then blue, green, yellow, light brown, dirty gray. When pressing on hemorrhagic spots, their color does not change. Hyperpigmented spots appear as a result of the deposition of melanins in the skin. There are congenital (most often nevi) and acquired (photodermatoses, freckles, etc.) hyperpigmented spots. When the content of melanin in the skin decreases or disappears, depigmented spots appear. There are congenital depigmented spots (albinism) and acquired ones. Non-inflammatory stains include stains from artificial injection of paints (tattoos, professional stigmas).
A blister (urtica) is an acutely inflammatory, cavityless element slightly raised above the skin, ranging in size from 2-3 mm to 10 cm or more, usually disappearing quickly and without a trace. It occurs as a result of limited acute inflammatory edema of the papillary layer of the skin with simultaneous dilation of the capillaries. The developed urticarial element has a pale porcelain-white color in the center and pinkish-red along the periphery, accompanied by itching and burning. Blisters are observed with urticaria, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, etc.
Papule , or nodule (papula) is a cavity-free formation of dense or soft consistency protruding above the skin level. Papules are divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory, according to their depth into epidermal, dermal or epidermal-dermal. The size of the papules varies. There are miliary (1-1.5 mm), lenticular (2-3 mm), nummular (2-3 cm) and larger papules - plaques. The shape and outline of the papules are different. They can be flat, hemispherical, cone-shaped, polygonal, etc. The surface of the papules can be smooth or covered with scales.
A tubercle (tuberculum) is a limited and dense formation protruding above the surface of the skin from pink-red to bluish-purple, ranging in size from 1-2 mm to 10 mm. They are formed as a result of the accumulation in the dermis of an inflammatory infiltrate such as an infectious granuloma. The tubercles can disintegrate, forming an ulcer, or resolve by replacing the infiltrate with connective tissue with the formation of a scar or cicatricial atrophy of the skin in their place.
A node (nodus) is a limited dense formation with a diameter of 1 to 5 cm or more, round or oval, located in the deep layers of the dermis or subcutaneous fatty tissue. The nodes may rise above the surrounding skin or be determined only by palpation. Nodes are divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory. Inflammatory nodes are characteristic of infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.), erythema nodosum; the color of the skin over them varies from pale pink to bluish-red; Nodes of this kind most often ulcerate and end with a scar, but can resolve without leaving a trace. Non-inflammatory nodes occur with various skin tumors or as a result of the deposition of metabolic products in it.
Bubble (vesicula) is a superficial (within the epidermis) and slightly protruding above the surrounding skin cavity formation with serous or serous-hemorrhagic contents, ranging in size from 3 to 5 mm. Blisters are observed in eczema, dermatitis, lichen simplex, etc.
A bubble (bulla) is a cavity element measuring from 0.5 to 5 cm or more with serous, bloody or purulent contents. The blisters can be located under the stratum corneum, intraepidermal or subepidermal. Blisters are found in pemphigus, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, acute dermatitis, etc.
An abscess (pustula) is a cavity element with purulent contents. Varieties: pustule developing around the hair follicle - folliculitis; superficial pustule not associated with the hair follicle - phlyctena; non-follicular pustule developing in the dermis - ecthyma; pustules located around the sebaceous glands - acne.
Secondary morphological elements of the rash
Skin dyschromia (dischromia cutis) is a pigmentation disorder that occurs at the site of resolved morphological elements of the rash. Hyperpigmentation appears as a result of an increase in melanin content or hemosiderin deposition in the skin. A decrease in melanin deposits in the skin causes secondary hypo- or depigmentation. Secondary hypo- or hyperpigmentation disappears without a trace.
Scale (squama) is an accumulation of rejected cells of the stratum corneum that have lost contact with the underlying epidermis. The scales can be loose, easily scraped off (psoriasis, parapsoriasis), or tightly attached to the skin (lupus erythematosus), small-lamellar (measles, pityriasis versicolor), large-lamellar (scarlet fever, toxicoderma).
Erosion (erosio) is a skin defect within the epidermis. Erosion occurs due to the opening of a vesicle, blister, or disruption of the integrity of the epithelium on the surface of the papules.
Abrasion , excoriation (excoriatio) is a skin defect that appears as a result of mechanical damage.
An ulcer (ulcus) is a deep skin defect that involves the epidermis, dermis and often underlying tissues. It develops as a result of the disintegration of such primary elements as a tubercle, node, pustule. Ulcers can also occur as a result of tissue necrosis caused by trophic disorders due to vascular changes (atherosclerosis, chronic venous insufficiency). After the ulcer heals, a permanent scar always remains in its place.
Crack (rhagas, fissura) - linear defects (tears) arising due to loss of elasticity and infiltration of individual areas of the skin. There are superficial cracks (fissurae) that develop within the epidermis and heal without a trace. And deep cracks (rhagas), involving, in addition to the epidermis, also part of the dermis, and sometimes deeper-lying tissues and leaving behind scars. Most often, cracks form in places of natural folds and in areas subject to stretching (in the corners of the mouth, above the joints, etc.).
A crust (crusta) forms on the skin as a result of the drying of the weeping surface. There are serous, purulent and bloody crusts. Their color depends on the nature of the drying discharge and the particles of dust, medicinal substances, etc. mixed with it. Crusts can be thin, flat, thick, conical, layered, dense, loose, etc. Elements of a mixed nature—crust-scales—occur in cases where exudate impregnates the scales.
A scar (cicatrix) is a coarse fibrous connective tissue growth that replaces deep skin defects. Fresh scars are pink-red in color, while older ones are hyperpigmented or depigmented. Scars can be flush with the surrounding skin, raised above it (hypertrophic scars) or sunken (atrophic scars). Cicatricial changes - cicatricial atrophy - can be observed without a previous ulcerative lesion, as a result of the replacement of infectious granulomas (with tuberculosis, syphilis) or extensive infiltrates (lupus erythematosus) with connective tissue. Unlike ordinary scars, cicatricial atrophy develops in smaller quantities and more delicate connective tissue. At the same time, the affected skin becomes sharply thinner, easily gathering into folds like tissue paper.
Lichenification (lichenificatio) - thickening, hardening of the skin, accompanied by an increase in its normal pattern, hyperpigmentation, dryness, and roughness. Lichenification is observed in neurodermatitis, chronic eczema, etc.
Vegetation (vegetatio) is formed as a result of the growth of the spinous layer of the epidermis and the papillary layer of the dermis. It is a villous-like formation that develops on the surface of papules, inflammatory infiltrates, erosions, etc. Their surface can be covered with a stratum corneum or eroded.
ICD-10 • R21 Rash and other nonspecific skin eruptions
Changing the contours of the oval face
The gradual loss of an even facial contour is one of the first signs of skin aging and is usually observed in men and women after 45–55 years. The main reason for changes in facial contours is aging.
With age, the quality of the skin gradually deteriorates, the ligamentous apparatus of the muscular aponeurotic layer weakens, the volume decreases and redistribution of subcutaneous adipose tissue occurs in the middle and lower third of the face, and bone tissue is resorbed. Outwardly, this is manifested by a violation of the clear line of the oval of the face, loss of volume in the cheek-zygomatic region, the formation of deep nasolabial folds and “marionette lines”, drooping of the corners of the lips, and deepening of the chin fold. The face begins to look loose ( Fig. 8 ).
Find out more about changing the contours of the oval of the face and methods of non-surgical correction here.
Rice. 8. Changing facial contours over time (Pinterest
How are age-related skin changes treated?
Cosmeceuticals – medicinal cosmetics – help many women fight age-related changes in their facial skin. It contains peptides that restore the barrier function of the skin, stimulate the synthesis of important components, and reduce the contraction of facial muscles. Priority is given to drugs with antioxidants, especially complex ones, as they create a cascade effect and have a prolonged therapeutic effect. Unfortunately, this method is not suitable for everyone due to the inaccessibility of high-quality cosmeceuticals and their high cost.
It is much more effective to combat age-related skin changes with the help of hardware cosmetology.
- Laser resurfacing
A laser pulse in the form of many microbeams heats the skin in a targeted manner. Micropores are formed on it, surrounded by undamaged areas. They promote immediate skin contraction - eliminating enlarged pores, hyperkeratosis and wrinkles. The result is noticeable after the first procedure.
- Laser peeling
The laser beam is divided into thousands of microbeams, penetrates deep into the skin and removes old cells in it. It also triggers the synthesis of young collagen. This procedure evens out the complexion and improves skin tone. After a course of several sessions, fine wrinkles and pronounced enlarged pores disappear, and a pleasant natural shine returns. Laser peeling is indicated for dull complexion and moderate pigmentation.
- Photorejuvenation
Melanin and oxyhemoglobin in unaesthetic skin tissues absorb light flashes, they heat up and are destroyed. The modification of collagen fibers begins - the restoration process with a rejuvenating effect begins. Intense pulsating light affects pigment spots, vascular “mesh”, gradually reduces their severity, and also promotes skin lifting. The color is evened out, the skin becomes elastic, the tissues are tightened.
- Laser biorevitalization
The device generates waves of a certain type, which open transport channels in the skin for the passage of hyaluronic acid. The substance penetrates deep, is evenly distributed there and saturates the cells with moisture and nutrients. Cellular respiration and microcirculation increase - fine wrinkles are smoothed out, skin tone improves.
Laser rejuvenation is trending today
Enlarged pores
They are expanded recesses of the skin, which are the mouths of the hair follicles and at the same time openings for removing the secretions of the sweat and sebaceous glands. Pores become visible to the eye with a diameter of 250–500 microns or more.
The main cause of enlarged pores is sagging skin. As we age, the main connective tissue proteins (collagen and elastin) begin to degrade, causing the skin to gradually sag and pores to enlarge. Excessive synthesis of sebum plays a certain role, which accumulates in the pores along with horny scales and dirt particles, causing them to swell and become visible. One of the reasons for enlarged pores is the “love of peelings.” Repeated application of chemical peels is accompanied by an inflammatory reaction that does not have time to subside, leading to changes in the dermal layer of the skin and enlargement of pores.
Enlarged pores appear as visible crater-shaped depressions on the skin, round or irregular in shape ( Fig. 9 ). There is a tendency for their number to decrease with age.
Find out more about enlarged pores and how to correct them here.
Rice. 9. Enlarged pores on the cheeks and nose (Only m health)
Rosacea of the facial skin: treatment
Rosacea or rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disease of a non-infectious nature. The pathology is associated with a violation of the tone of blood vessels in the upper layer of the epidermis. As a result, persistent foci of inflammation are formed - acne, ulcers, areas of pronounced redness. Pathology develops especially often in older women and men, usually after 40 years.
Facial rosacea
Medicine knows more than 10 types of rosacea - persistent edema, granulomatosis, fibrous lesions, etc. The disease begins with the periodic appearance of erythema (redness), which disappears after a few hours. Next, the choroid plexuses become visible, a bluish color, papules, and pustules appear. At the last stage, fibrous tissue grows and the oval is deformed.
Doctors take a comprehensive approach to the treatment of rosacea, prescribing effective medications and personal recommendations for caring for the facial area. The following groups of drugs are used:
- Medicinal gels, creams, ointments containing metronidazole, anti-inflammatory, antiparasitic components;
- Antihistamines - to relieve severe inflammation and allergies;
- Vitamins that strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- Antibiotics - used in case of secondary infection.
Doctors recommend following a diet during treatment and rehabilitation. You should avoid fast food, alcohol, salty, smoked, fried foods, and coffee. It is important to minimize the influence of possible irritants - solar radiation, frosty air, dry wind. Daily care products should not contain fatty acids, alcohol, acetone, or hormonal additives. To treat facial skin in later stages, cryodestruction, laser therapy, and electrocoagulation are used. These procedures help eliminate dilated vascular networks.
Accurate diagnosis of signs of aging and results of aesthetic procedures
Accurate diagnosis and reliable confirmation of the results of aesthetic interventions are coming to the fore today. This approach to assessing the signs of skin aging allows not only to make a correct diagnosis, but also to document the results of the procedure, which is significant evidence of the success of the cosmetologist. To do this, you can use a three-dimensional modeling system - for example, Antera 3D .
Antera 3D consists of a high-definition camera with a special housing that blocks outside light from entering the shooting field. There are LEDs around the camera lens; when shooting, they turn on alternately, illuminating the skin in different spectral ranges. In a few seconds, more than a hundred photographs are taken in different lighting conditions, from which a computer algorithm models a three-dimensional photo.
Features of the Antera 3D three-dimensional modeling system :
- Skin texture - the degree of uniformity and smoothness.
- Wrinkles - linear dimensions, depth, severity index.
- Hypertrophic scars - volume, area.
- Deep wrinkles and furrows - precise localization, depth measurement.
- Skin neoplasms - volume, area, shade.
- Pores - number, severity index.
- Melanin - uniform distribution, skin tones.
- Hemoglobin - uniformity of distribution, content in the skin.
Several versions of Antera 3D allow you to choose the tool that suits a particular specialist.
What is senile skin pigmentation?
Pigmentation, caused by a restructuring of the hormonal system in the body, usually does not look aesthetically pleasing and does not decorate a woman at all. The amount of melamine in the skin changes due to age-related changes, lack of vitamins and amino acids, and endocrine diseases. Most often, older people suffer from the following formations:
- Chloasma
Spots from yellow-brown to dark brown shades are localized on the forehead, temples, cheeks, and surfaces of the eyelids. Small formations merge into large ones, forming a clearly visible cosmetic defect.
- Lentigo
Specks of different colors from yellow to black are called “liver spots.” They appear in areas most exposed to ultraviolet radiation - on the hands, face, décolleté, and upper back.
- Vitiligo
These white, flat formations are called “reverse pigmentation.” They stand out sharply against dark skin.
Chloasma - an unpleasant companion of old age