Causes of birthmarks in newborns
Medicine does not know a clear answer about the reasons for the appearance of postpartum red spots in children. The defect appears as a pigmented area of skin that has:
- rich pink, red, brown color;
- smooth or rough surface;
- flat or protruding areas above the skin level;
- small or giant area;
- smooth or asymmetrical edges;
- different localization.
A detailed description of spots in children depends on their type, causes of occurrence, and the course of pregnancy. The main reasons for the appearance of birth pigmentation in newborns are:
- Hypoxia of blood vessels from compression during childbirth or late pregnancy:
- infectious diseases of the expectant mother;
- prematurity of the child.
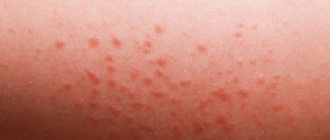
If we are talking about vascular pink or red pigmented moles, they are most often localized on the child’s head: in the back of the head, on the chin, forehead, nose, bridge of the nose, cheeks, eyelids, and the baby’s upper lip. Brown pigmentation, called moles or nevi, can be located on any part of the body, just like hemangiomas. The formations are benign, but require careful observation by a specialist and subsequent removal, since they carry the risk of cells degenerating into melanoma and spoiling the appearance. Defects never go away on their own, unlike vascular birthmarks, which disappear on their own.
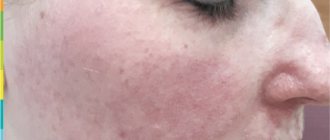
Hormonal rash in infants and causes
In the first weeks after birth, 30-35% of babies develop symptoms of a characteristic rash. Neonatal cephalic pustulosis is also affectionately called “newborn bloom.” Young parents may hear other options: acne or baby acne, milia, three-week rash. These are all names of the same diagnosis. Hormonal rash predominantly occurs at the end of the first week of life, but the typical time frame can be extended to 3 months. Main causes:
- increased levels of estrogen in the blood;
- activation of the sebaceous glands;
- blockage of follicles;
- proliferation of yeast-like fungi.
Mechanism of development in the body
Hormonal rash in a child directly depends on the mother’s hormones. Excessive amounts of estrogens accumulated in the body after birth must be eliminated from the body, and hormonal levels should be normalized. Under the influence of the same factor, including adrenal androgens, the sebaceous glands are activated. They actively produce excess subcutaneous fat. The skin and pores do not have time to cope with the incoming amount. This leads to clogged pores and follicles. And the proliferation of yeast-like fungi contributes to the development of the inflammatory process. In 52% of cases, the Malassezia species was detected in smears. All processes are closely interconnected.
Types and features of localization
Classification of birthmarks will allow you to better understand the nature of pigmentation: red and pigmented birthmarks. If the former are characterized by hypoxia or vascular hyperplasia, the latter appear due to the accumulation of melanocytes (cells that synthesize melanin) in a limited area.
Birth red moles are associated with deformation of blood vessels during childbirth due to mechanical compression of the baby's head. The localization of formations speaks in favor of this theory. Depending on the presentation of the fetus, the mother’s pelvic bones put pressure on the baby’s occipital region or face, which is why the vessels in the places of compression experience hypoxia and turn red. If the neck and back of the head are compressed, the formations are called a stork bite, if on the face - an angel's kiss, in some cases the formations are found in the lumbar region, where they reach 4 cm in size. The marks have clear edges, irregular shape, pronounced color from pink to bright red , do not rise above the surface of the skin, do not itch, and do not make themselves known in any way, except for their non-standard coloring. Over time, vascular moles disappear, becoming pale, but maintaining their outline until they disappear completely. There is no heredity factor.
Another type of vascular spots spreads throughout the newborn’s body, but is much less common than spots on the head. The formations are caused by the same reasons as the bite of a stork, however, their structure is caused not by hypoxia, but by hyperplasia - the proliferation of vascular tissue in certain areas. The phenomena are called salmon spots, have a less bright color, and a hereditary factor can be traced in their formation. Vascular hyperplasia tends to spread in the first month of a baby’s life and requires supervision by specialists. The color of the formation may change to purple and bluish; they rise above healthy skin. The disappearance of salmon nevi is characterized by a reduction in area rather than fading, which distinguishes them from stork bites.
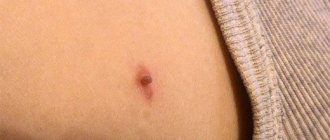
Hemangiomas on the body of a newborn are red dots of small diameter located throughout the body. The formations are a proliferation of vascular nodules, do not cause discomfort to the baby, fade over time, are flat and protruding, the surface is smooth. Hemangiomas are removed when they are on the face. The treatment method is chosen by the doctor.
There are 2 main types of hemangiomas: simple (strawberry) and cavernous (cavernous). Strawberry is a convex nodule of vessels the color of ripe strawberries. By the age of 10 they go away on their own. The quantity is of concern: if a child has more than 3 such formations, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the internal organs in order to exclude pathologies. Cavernous hemangioma looks like spongy tissue filled with blood, does not have clearly defined boundaries, deforms when pressed, and then returns to its previous appearance. In the first six months, cavernous hemangioma grows, increasing in size, and disappears by puberty. During the period of growth growth, the child receives medical advice from vaccinations in order to differentiate the possible consequences of education and vaccination.
Port-wine stains/flaming nevus are dense formations on a child’s skin with intense, uniform coloration over the entire area. Features of the defect are a rich purple-red color, elevation above healthy tissues, the formation increases in size as the child grows, and is most often localized on the face, although it is also found in other parts of the body. A flaming nevus does not become inflamed, does not secrete fluid, does not itch or flake off, and over time vascular nodules form on it. Doctors monitor the connection between the fiery spot and disturbances in the functioning of the brain, and recommend consulting with a neurologist and ophthalmologist to rule out possible defects in eye development. Since flaming spots cause psychological discomfort and cause complexes, they can be easily removed using modern hardware techniques.
Non-vascular formations in infancy - nevi, appear in places where melanocytes accumulate; a failure in their uniform distribution in the skin occurs in utero; it is impossible to influence the process. The color of moles ranges from flesh-colored and light brown for raised ones to black for flat ones.
Why do diaper rash appear on a baby's neck?
This phenomenon is provoked by a number of factors, such as:
- Lack of compliance with temperature standards;
- The child’s clothes are too hot/tight, do not allow air to pass through, and also rub the baby;
- Excessive use of skincare products that lead to acid imbalance and cause increased skin sensitivity (soaps, baby creams, oils, etc.);
- Irregular air baths;
- Untimely bathing of a newborn, especially in the summer (hot) period;
- Increased temperature due to ARVI.
All of the above points lead to increased moisture on the skin, and since during infancy there are natural folds in the neck area, irritation and redness of damp skin develop more actively there.
As for diaper rash in the neck area, the rash is most often caused by tight clothing in the collar area, which reduces the access of oxygen to these areas of the skin.
How to get rid of birthmarks
Most birthmarks disappear on their own as the child grows older; this does not apply to nevi. A postpartum spot, if it is on the face and interferes with the normal development of the child, should be removed. It is necessary to get rid of pigmentation under sterile medical conditions with an experienced doctor so that the procedure is painless and has no consequences for the small patient.
Infrared radiation is actively used in cosmetology to remove postpartum spots. The principle of action of the rays is based on the ability to heat the area of influence and enhance regeneration processes in tissues.
Laser therapy is the most popular method of removing skin defects. The action of the technique is based on the gradual evaporation of the tissues of the pigmented area, allowing you to act only on the nevus, leaving healthy tissues untouched.
Surgical removal of birthmarks is used if the affected area is large and there is a suspicion of the presence of malignant cells in the skin. The disadvantage of the operation is a possible scar. An experienced doctor will reduce the risk of its occurrence to a minimum.
What needs to be done to still avoid diaper rash on the neck of a newborn?
- Monitor the temperature and humidity in the room where the child lives;
- Give your child air baths more often so that the baby’s skin can breathe;
- Choose high-quality fabrics when choosing clothes, and also pay attention to the collars on clothes. Not only should the collar not press, it is also important that the cutouts are deep and do not create occlusion;
- Wipe the natural folds of the baby’s skin more often, especially at high temperatures and humidity;
- Choose high-quality products for washing your child’s clothes, diapers and bedding;
- Give preference to hypoallergenic cosmetics for newborn skin care. Pay attention to the availability of clinical trials and dermatologist approval.
When do birthmarks go away in babies?
Do not be afraid of red nevi on a child’s body; most of them are not dangerous and do not carry the risk of degenerating into a tumor. However, the mother needs to observe the baby’s skin, and at the slightest change in the appearance of the formations, draw the pediatrician’s attention to the existing dynamics.
Red and pink vascular spots should go away on their own. If a cosmetic defect is located on visible parts of the body, it should be removed in childhood to prevent the child from developing complexes and psychological problems.
Hormonal rash in babies: treatment
By medical standards, hormonal rash in newborns is not considered a disease. This means that this temporary phenomenon does not require special treatment. It is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician or dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis, but you should not self-medicate. At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), doctors will conduct an examination and, if necessary, do laboratory tests (scraping, smear). During the period of appearance and exacerbation of rashes, it is important to follow hygiene rules. Under no circumstances should you remove closed comedones to prevent infection. Otherwise, hormonal acne may progress to the stage of suppuration. This is already considered a serious case, requiring special care. A rash due to hormonal imbalance after birth appears and will go away on its own. The following procedures are not recommended:
- dry papules with alcohol solutions;
- smear with iodine or brilliant green;
- wipe with herbal infusions;
- apply baby cream and ointments;
- use adsorbents;
- give antibiotics;
- use powder with talcum powder, etc.
Useful tips for parents
A hormonal rash on a newborn’s face or body, if properly cared for, is not a cause for concern. It is recommended to follow simple rules. They consist of daily water procedures, the need to take air baths, and it is also necessary to protect the child from overheating. Sweaty skin will complicate the healing process and can cause inflammation in the affected areas. Hormonal rash is considered a physiological phenomenon in babies, but proper care will help speed up the cleansing of the skin. To avoid causing additional irritation, use hypoallergenic powders for washing. Another important point is that a child can scratch himself. Trim your nails carefully or use special anti-scratch mittens.
Not just a defect
The term "hemangioma" comes from the Greek "haima" - "blood" and "angeon" - "vessel" and means a benign vascular tumor. This neoplasm looks like a bright red or slightly bluish spot. This defect is usually congenital or appears in the first weeks of life. Hemangiomas come in different sizes and can be located both on the face and body of the child. Sometimes there are several such spots at once. The reasons for their occurrence are not completely clear, but there is an assumption that this can be caused by colds that the expectant mother suffered from in the first two months of pregnancy, when the formation of the child’s vascular system is underway.
The most common myth about hemangioma is that it can develop into cancer. In fact, such cases are extremely rare. But waiting until everything resolves itself, as, by the way, the second myth advises, is also not always worth it. Indeed, despite the fact that sometimes hemangiomas do go away on their own, this does not always happen. And usually this takes many years (from one and a half to ten or more). Neoplasms located on areas of the body covered by clothing eliminate themselves. And spots on the face, head and neck, as a rule, do not disappear. Hemangiomas grow with the child and especially rapidly - up to six months. They increase in size most quickly in premature babies. It is better to show a baby with such a tumor to a doctor as soon as possible. Indeed, in addition to a cosmetic defect, a vascular tumor threatens with very unpleasant things.
Article on the topic
Cut or leave? 5 signs that it is better to remove a mole
If the hemangioma is located where it is easily damaged, for example by constant rubbing against clothing, it can lead to the development of infected ulcers. Another potential danger is damage to nearby tissues. So, if, for example, the hemangioma is located in the eye, ear, nose or mouth, the baby may experience visual impairment, hearing impairment and even difficulty breathing. In addition, a vascular tumor can begin to grow in width, growing into internal organs. And if the hemangioma is extensive, then it is possible that thrombocytopenia will develop - a deficiency of platelets in the blood, due to which the blood begins to clot poorly.