Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 10.03.2019 Date of update: 12.11.2020
- Drug therapy
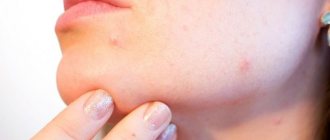
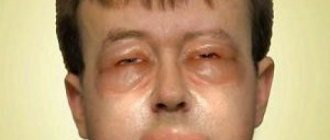
Eczema on the face is quite common. And since the disease begins acutely, it is severe stress for the patient. After all, if rashes on the body can be hidden with clothes, then on the face they will always be visible. When a rash appears on the skin of the face, the only correct solution is to seek medical help. The Moscow Paramita clinic knows how to help such a patient.
Causes of eczema on the face
Eczema is a chronic dermatological disease of an allergic nature. The reasons for it are varied. Moreover, there may be several of them. But most researchers believe that the disease is based on a hereditary predisposition on the part of the nervous and immune systems. Against this background, trigger factors (decreased immunity, stress, various diseases or effects on the skin) cause the first symptoms of eczema. Subsequently, the disease quickly acquires a subacute and chronic course with frequent relapses.
Eczema of any localization can spread throughout the body, so do not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
Predisposing factors are:
- prolonged stress, high loads;
- foci of infection in the body;
- decreased immunity after acute illnesses, surgeries, etc.;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- any chronic diseases, especially often caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine diseases, hormonal imbalances;
- allergic diseases;
- exposure to allergens contained in hygiene products that affect the skin and cause allergies;
- skin irritation due to frequent hygiene and cosmetic procedures.
Clinical manifestations
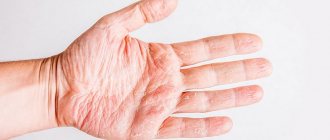
It is not difficult to determine the presence of mucous membrane. To do this, it is worth examining the wound surface, from which a clear liquid with a pinkish tint is slowly oozing. As it accumulates on the surface of the wound, the plasma begins to flow down the body, sticking to the skin and causing bruising.
The surface of the wound itself is shiny dark pink. A small crust forms along the edges, slightly rising above the surface of the wound itself. After removal of the plasma, dryness and tightness immediately appear in the wound, which causes pain, which intensifies with movement.
Types and first symptoms of eczema on the face
Symptoms of the disease depend on the type of eczema. There are several of them.
True
True eczema (idiopathic) on the face, when acute, has a weeping form. Weeping eczema on the face develops due to the large number of blood vessels in this area. The disease begins acutely and has several characteristic stages:
- erythematous (initial)
- redness of the skin - symmetrical itchy red spots appear; - papular
- elevations form on the reddened surface - papules; - vesicular
- bubbles (vesicles) with transparent contents appear on the papules; severe itching bothers you; - erosive
- the bubbles burst, forming erosion; serous wells appear on their surface - serous fluid comes out of them and accumulates on the surface in the form of dew drops; - cortical
– erosions dry out and crusts form; after they fall off, first dry peeling remains, and then pigment spots on the skin.
The transition from acute to subacute and chronic occurs gradually. The surface of the affected areas becomes bluish, vesicles appear on it during an exacerbation and there are significantly fewer of them than during an acute course. Gradually, the surface becomes dry and pronounced peeling appears on it. This is dry eczema on the face. But sometimes even a chronic course can be weeping.
Microbial
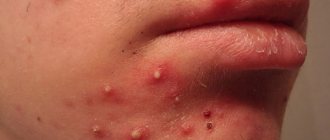
Microbial eczema on the face develops against the background of some existing skin infection. On the face it can be bacterial (streptococcal, staphylococcal) or fungal (candidomycosis). Microbial appearance on the face can take the following forms:
- Sycozoform
- develops against the background of skin infections in the mustache and beard area in men; Sometimes sycosis develops from cuts during shaving. - Paratraumatic
- inflammation develops against the background of infected wounds and burns. - Coin-shaped (numular, plaque)
- with rounded rashes, on the surface of which all the characteristic stages of eczema develop; sometimes this form has an abortive course and then itchy, dry red flaky spots appear on the skin - eczematids, similar to manifestations of psoriasis.
Microbial eczema begins on the surface of the skin affected by the infection, first on one side, but then it acquires a recurrent course and a symmetrical character - the same lesion appears on the healthy side.
Seborrheic eczema
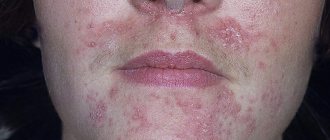
Seborrheic eczema on the face is a consequence of increased sebum secretion against the background of neuroendocrine disorders. Sebum changes its chemical composition, becomes thicker, and clogs the sebaceous ducts. An infection develops in the closed ducts, and then an allergy develops.
Signs of seborrheic lesions: reddish nodular rashes on the face (eyebrows, cheeks) and at the border with the hair. After some time, their heads turn yellow - a sign of suppuration. The entire affected surface is covered with grayish-yellow greasy scales. Itching is moderate.
At the border with the scalp, with seborrheic eczema, a red border is formed, covered with fatty scales, it is often called the crown. The resulting large plaques have uneven scalloped edges. When the acute stage of the disease ends, the lesions fade from the center to the periphery, forming ring-shaped figures.
Occupational eczema
The reason is exposure to irritating substances during professional activities. It is rare in the facial area, but sometimes such cases occur. Over time, contact dermatitis (inflammation of the skin) develops on the skin, acquiring the character of a symmetrical inflammatory process.
Methods for treating eczema on the face
The causes of eczema on the face and its treatment are interrelated. Therefore, before starting treatment, the doctor carefully questions and examines the patient, if necessary, prescribes additional examination and consultation with specialists. Only after this the doctor draws up a comprehensive therapy plan:
- drug treatment;
- modern European and traditional oriental healing techniques.
Red spots on the skin after stress
Diagnosis of skin diseases
Drug therapy
Today, experts are inclined to believe that drug therapy (ointments, creams, tablets) for this disease has a purely symptomatic effect, that is, it eliminates the symptoms (rashes) without affecting the cause. Therefore, drug treatment is prescribed mainly for quick relief from unpleasant symptoms.
The drug treatment for eczema on the face includes the following:
- antihistamines
- relieve swelling, inflammation, itching (Claritin, Suprastin - taken orally); - calcium preparations
- reduce vascular permeability, relieve swelling (calcium gluconate, calcium chloride - taken orally, administered intravenously); - glucocorticoid hormones
– very quickly relieve inflammation, swelling and itching; prescribed for acute disease in the form of tablets (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) and products for external use - ointments, creams, solutions (Advantan, etc.); drugs of this series can only be used as prescribed by a doctor, since they have many side effects and the patient’s body quickly gets used to them, after which the therapeutic effect of the drug decreases and eczema is difficult to treat in the future; - antibacterial and antifungal drugs
; prescribed for microbial appearance; if inflammation is severe, combination drugs are prescribed, which include antibacterial and hormonal agents (Triderm, etc.); Skin-Cap creams, aerosols and shampoos with activated zinc have a good anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antifungal effect; - lotions
- with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions; are used in weeping forms of the disease.
Modern European and traditional Eastern methods of treatment
In specialized clinics, they try to combine drug therapy with non-drug methods and, whenever possible, avoid prescribing glucocorticoids. For this purpose, the following modern Western and traditional Eastern techniques are used:
- plasma therapy - the introduction of platelet-enriched patient’s own plasma into eczematous areas of the skin; the method is based on the fact that platelets have a pronounced restorative effect on all cells of the body;
- autohemotherapy – stimulation of reparation processes in the skin by intramuscular injection of blood taken from the patient’s own vein;
- herbal medicine – the ability to treat a disease with herbal preparations can reduce the burden of chemical drugs on the body;
- reflexology (RT, Zhen-Jiu therapy) – influencing acupuncture points (AP) on the human body in various ways. AT was discovered by doctors of Ancient China and Tibet, the effectiveness of this method has been proven by thousands of years of practice and modern research; RT can be treated in different ways, here they are:
- acupuncture (zhen therapy) is an ancient method that allows you to treat acute inflammatory phenomena and prevent the development of relapse of the disease;
- cauterization (moxotherapy, juju therapy) - more correctly - warming up the AT with wormwood cigars; a milder method of exposure, used more often to prevent relapses;
- acupressure (acupressure) - impact on the AT with fingers or some other instrument;
Treatment options
Although a wound is a natural defense mechanism, it must be treated to prevent infection. To do this, drying ointments, wound healing creams, and antibacterial therapy are used if bacteria have already penetrated the wound.
Drying ointments
The main task in the treatment of bedsores is to ensure the outflow of fluid and drying of the wound surface. The following ointments are suitable for this:
- Baneocin has a disinfectant, bacteriostatic and drying effect. It has a dense structure, but at the same time promotes the unhindered outflow of plasma from the wound.
- Chlorhexidine - has the ability to destroy pathogenic microflora on the surface of the wound, gently drying it. Does not cause burns or other complications.
- Dioxidin is an antibacterial agent with a drying effect. It fits well on the surface of the wound and does not spread.
Baneocin is a drug for the treatment of wet wounds
The first step of moisturizing uses drying ointments to limit the release of plasma from the wound. The duration of use is 2-3 days, after which the expected amount should be reduced several times.
Wound healing drugs
Their action is aimed at accelerating metabolic processes in the wound, which stimulates the active production of new epithelial cells that promote rapid wound closure. They are applied under a bandage if the wound has a large area, or openly when the skin damage does not exceed 1 cm in diameter.
The most effective drugs with a wound healing effect are:
- Solcoseryl - activates natural regeneration processes in the wound, acting on it locally and without penetrating into the blood. It is well tolerated by patients and does not cause side effects.
- Bepanthen - contains dexpanthenol and provitamin, which together provide maximum wound healing effect.
- Levomekol - helps eliminate hardening and accelerate the healing process. It has a fairly liquid consistency, so it is used as a bandage.
- Methyluracil has a complex effect on the wound, dries, disinfects and restores damaged cells.
- Actovegin - saturates cells with nutrients, which accelerates regeneration processes.
Methyluracil - a drug for the treatment of wet wounds
The choice of one or another product with a wound healing effect is best done under the guidance of the attending physician, since there are certain contraindications and side effects.
Weeping wound: antibacterial agents
First aid when treating wounds and before using wound healing agents can be treated with antiseptics, such as:
- Miramistin; Furacillin;
- Iodicillin;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- saline.
- Further treatment with antibacterial ointments is indicated when a purulent-inflammatory process occurs, in which the wound becomes hyperemic, swollen and painful. Purulent plugs may be released from its cavity. The most popular antibiotic ointments:
ointment with streptocide;
- streptonitol.
- Antibiotics in the form of oral tablets may also be prescribed.
Treatment of eczema on the face at the Paramita Clinic
The Moscow Paramita clinic uses all the latest medicinal and non-medicinal treatment methods. The doctors of the clinic know how to treat eczema on the face, as they were trained in the best European and Eastern medical institutions and know all the intricacies of the approach to treatment.
To avoid relapses, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease.
Read more about our unique method of treating eczema
The clinic practices:
- drawing up an individual treatment plan for each patient;
- inclusion in the individual plan of the entire range of treatment procedures necessary for a given patient;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and, if necessary, adjusting it;
- conducting courses of preventive anti-relapse treatment.
Everyone who comes to the Paramita clinic for help is completely satisfied with the results of the treatment; one or two courses of treatment per year are enough for them to forget about skin problems.
Sign up for a free initial appointment
What to do if eczema on the face worsens?
In case of exacerbation and the appearance of characteristic rashes on the face, accompanied by itching, a dermatologist may prescribe hormonal medications (solutions, creams, ointments) that will quickly relieve inflammation and itching.
At the Paramita clinic they do things differently. Mostly non-drug treatment methods are prescribed. Reflexology courses are excellent for relieving acute symptoms. After the first session, inflammation and itching are significantly reduced, and after the second or third, all symptoms disappear if the patient came at the initial stage of the disease. Advanced stages can be stopped in the fifth or sixth session. To consolidate the treatment, it will take 10 to 15 sessions.
Factors influencing healing
It is important to change dressings frequently. Ideally, change the bandage every 3-4 hours. If you carry out the procedure every other day, the risk of developing hardening increases.
Healing is affected by the method of treatment. Properly selected drugs that have a drying effect, but do not interfere with the outflow of exudate, will speed up the regeneration process. Treatment of weeping wounds without the supervision of a specialist is fraught with the development of complications.
We should not forget about the individual characteristics of the body. The younger and healthier the patient, the faster the metabolic processes in the body occur. In older people, the regeneration process slows down due to natural aging processes. In the case of pathologically reduced immunity and chronic diseases, wound healing will also occur more slowly.
Treatment with folk remedies at home
Folk remedies should be used with caution and only as prescribed by a doctor, as they can not only be beneficial, but also harmful. Therefore, patients should use them only after consulting a doctor. Traditional medicine recommends:
- rosehip flower ash cream; take the tops and flowers of the rose hips, dry them and burn them; mix a teaspoon of ash with three teaspoons of any hypoallergenic cream and lubricate the affected areas on the face with it 2 – 3 times a day;
- ointment made from nuts and fish oil; take several walnuts, bake them in the oven until brown, remove the shell, crush the kernel to a powder, dilute with fish oil to a paste and lubricate the affected areas of the skin 2 - 3 times a day.
Weeping wound - treatment with antibiotics
Please note! Antibiotic ointments and creams significantly reduce the production of exudate in the wound, so if it is not treated properly, it will remain and accumulate, increasing the risk of infection within the wound.
Antibiotics are selected only by the attending physician, and the duration of the course depends on the specific case. wound healing process.
When the wound is small and shallow, treatment can be carried out at home using traditional medicine recipes. However, traditional treatments should always be a priority.
Weeping wound: folk recipes
To limit the mucous process and restore regeneration, the following recipes are used:
Steamed onion compress - take 1 onion, peel off any dirt, rinse and bake with the skin in the oven or microwave for 10-15 minutes. When the onion becomes soft, strain it with a blender. Grated warm baked onion is placed on a sterile bandage and applied to the wound. You may experience throbbing sensations, sharp pain, and other symptoms that will subside over time. Onions are a natural antiseptic that helps wound healing.
- Compress from a decoction of herbs - for 1 glass of boiling water, take 1 teaspoon of sage, chamomile and thyme, 1 tablespoon of eucalyptus. Leave in a water bath for 10-15 minutes, strain and let cool to room temperature. Moisten the bandages with decoctions and then pour over the wound.
- Antiseptic spray - you need to take 20 ml of saline solution, into which 3 drops of tea tree essential oil, 2 drops of fir oil, 1 drop each of lavender and eucalyptus oil are added. Apply to a spray bottle and spray onto the wound before applying each healing cream.
- Steaming the onion wrap will help with the healing process.
Do not replace ointments and creams with traditional medicine recipes. These two treatment methods can be used simultaneously, but with the consent of the doctor. In some cases, the use of alternative medicine is not appropriate.
A key factor in ensuring proper regeneration of damaged tissue is proper hygiene. When treating a wound in a conditionally sterile room using gloves and sterile dressings, the risk of pathogenic microorganisms being attached is minimal.
Prevention of facial rashes
To prevent relapse of the disease, as well as in the case of a genetic predisposition (one or both parents suffer from eczema), the following rules should be followed:
- adhere to a diet: exclude spicy, fried foods, sweets, baked goods, strong broths, chicken, citrus fruits from the diet;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, play sports, walk in the fresh air, get enough sleep;
- use only hypoallergenic creams, shampoos and other hygiene cosmetics;
- if there are rashes on the skin, you need to protect your face from direct sunlight (wear a hat with a brim in the summer, use sunscreen); During the period of remission you can sunbathe.
Treatment of eczema on the face is a problem, so you need to contact a dermatologist at the initial stage of the disease, and then regularly carry out maintenance treatment.