Rosacea
Rosacea
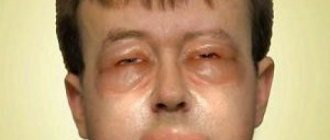
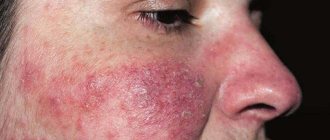
is a persistent lesion of the blood vessels of the facial skin. It manifests itself as redness of the skin of the cheeks, nose, forehead and chin, bright pink rashes, spider veins, and pustules. In later stages, irreversible thickening and infiltration of the skin of the nose, forehead, earlobes, eyelids, and chin may develop. Leads to a deterioration in the appearance of the skin, sometimes pronounced cosmetic defects, changes in appearance, and psycho-emotional problems. When the eyes are affected, keratitis and ulceration of the cornea develop.
Previously, the development of rosacea was attributed to the presence of demodicosis, but these two diseases are different in their etiology, although each of them complicates the course of the other. The pathogenesis of the development of rosacea lies in the increased sensitivity of skin vessels. If there is a genetic predisposition or the vessels are fragile and brittle, then in response to irritants such as sudden changes in temperature, dry and hot air, the vessels dilate, which is not observed in the majority of people.
The incidence of rosacea in people with a history of gastritis is much higher than in those in whom Helicobacter pylori, the bacterium that causes gastritis, has not been detected. Rosacea of a medicinal nature is observed with long-term use of corticosteroid ointments; the skin arteries become thinner, become more fragile and sensitive to minor temperature changes.
Risk factors for the development of rosacea
The incidence of rosacea is approximately the same in both sexes, but women during menopause are more susceptible to rosacea, as hormonal levels and vascular properties change. Blondes and redheads with thin, sensitive skin prone to redness are at risk for rosacea. Allergic and contact dermatitis can provoke rosacea, since the blood vessels are often dilated and subsequently their return to their previous state is no longer possible.
Genetically, residents of northern peoples are more predisposed to rosacea; living in extreme continental climates and in northern countries also increases the risk of rosacea.
Diseases and disorders of the endocrine system, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and disorders of the immune system, especially when combined with each other, lead to rosacea. The pathogenesis of rosacea is not fully understood, but most dermatologists agree that exposure to hot or cold areas, wind, and consumption of excessively burning foods, alcohol and spices provoke rosacea.
Treatment of dermatitis on the hands
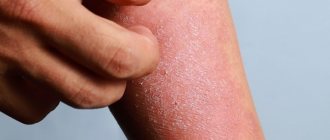
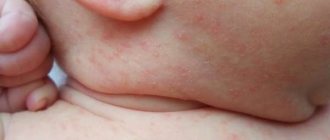
Dermatitis on the hands is a common phenomenon in our rhythm of life. It is usually the result of a combination of sensitive skin and irritation or contact allergy to some material. Along with it, a rash may appear on other parts of the body. Every person has a special protective film on their skin, its purpose is to protect against external irritants. But if for any reason you get chemicals or other substances on your hands, they can damage the film. In humans, the skin remains open and over time begins to crack; substances that can cause dermatitis on the hands will get into the cracks. Some people are genetically predisposed to it. But you need to understand that this disease is not contagious and cannot be transmitted. Skin protection when treating hand dermatitis is an important part of therapy.
Typically there is redness, often in the folds between the fingers, dry skin, itching and irritation. Sometimes there may be pimples, or blisters with serous contents, or even pustules. When working with household chemicals, for example when washing dishes, irritation and itching intensify. Contact our clinic for a consultation, we will help you.
Prevention of rosacea
Since rosacea is a chronic disease, after removing the excess capillary network, it will reappear after some time. Therefore, the prevention of rosacea consists of periodic visits to the cosmetologist’s office to eliminate newly appeared hypertrophied blood vessels. But, if between procedures you avoid overheating and hypothermia of the skin, spend as little time in the open sun as possible, adjust your diet and use cosmetics that contain horse chestnut extract and other substances that strengthen the vascular wall, then you will need to repeat the procedures no more than once every 2 -3 years.
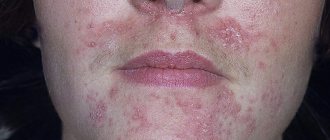
Perioral dermatitis
Perioral dermatitis
- chronic inflammatory lesion of the skin around the mouth in the form of individual or grouped red papules located against the background of normal or reddened skin.
Perioral dermatitis is most often observed in women aged 20 to 40 years. Recently, there has been an increase in the incidence of this type of dermatitis among children.
How to get rid of dermatitis?
25.01.2021
Dermatitis is a fairly common skin disease. In medicine, the term “dermatitis” is a general name for many subtypes of various skin diseases: atopic, herpetiformis, seborrheic, etc.
Essence
Most often, the disease is expressed in a short-term effect of inflammation of the epidermis. It is quite easy, especially in the initial stages, to be completely cured. The disease is mainly divided into: taxidermy and contact dermatitis . Their difference lies in the degree of impact on the body. The contact form of dermatitis occurs upon contact with any substance and has purely external signs of the disease, while taxidermy has a more extensive internal effect on the body.
Kinds
Since the concept of dermatitis is quite general, in medicine today there are many subtypes of this disease. Here are some of the most common ones:
- taxidermy;
- allergic;
- contact simple;
- atopic cutaneous;
- perioral and seborrheic.
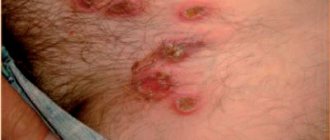
Contact dermatitis
Caused by various external irritants when exposed to the surface layers of the skin. Factors that cause dermatitis can be of different nature and varying degrees of impact. For example, contact with chemicals or drugs can cause a short-lived inflammatory process in the absence of an irritant, which goes away on its own. Also, simple contact dermatitis can be caused by such factors as: temperature (hypothermia or overheating), pressure, friction, some plants (hogweed, nettle). Treatment in the case of simple contact dermatitis directly depends on the duration of exposure and the degree of damage to the skin.
Allergic skin dermatitis
The main difference between this type of dermatitis and simple contact dermatitis is the reaction of the epidermis to the irritant. With contact dermatitis, the reaction appears immediately, but it can take up to several weeks an allergic reaction And only upon repeated contact with the allergen do skin inflammations appear. The area of the injured area can be much larger than the contact area. With a long course of the disease, self-opening blisters form on the skin when it dries, which leave scales and crusts on the surface of the skin. dermatitis also called eczema .
Seborrheic and perioral dermatitis
This type of dermatitis has a chronic course and is formed mainly in those areas of the epidermis that have sebaceous glands: forehead, scalp, nasolabial folds, cheeks. Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by the yeast Malassezia. Almost all people are carriers of these microbes, so the disease cannot be called infectious. Our own immunity the best protector against seborrheic dermatitis . Therefore, the best prevention of seborrheic and perioral dermatitis is its strengthening.
Atopic dermatitis
It is a type of allergic dermatitis . The difference lies in the number of allergens that cause inflammatory processes on the skin. With atopic dermatitis there can be a lot of them, and the disease itself is genetic and, as a rule, has a chronic form.
To properly get rid of dermatitis, it is necessary to identify the source of infection, as well as determine the extent of the disease. After which the specialist will be able to prescribe a course of treatment.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic
Causes of perioral dermatitis
The exact causes of perioral dermatitis are not yet known. In many cases, the disease occurs in patients after long-term use of topical medications containing corticosteroids.
The development of perioral dermatitis can be triggered by severe chapping of the facial skin, increased sun exposure, the use of fluoride-containing toothpaste and decorative cosmetics such as makeup base and foundation. In women, a connection between the disease and hormonal changes has been noted: the appearance of rashes during pregnancy and against the background of various gynecological diseases, increased manifestations of dermatitis before the onset of the menstrual cycle. In some cases, perioral dermatitis appears when using oral contraceptives.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the head, treatment
Seborrheic dermatitis on the head manifests itself in the form of ordinary dandruff, but you should not ignore it. If the disease starts and you do not go to the clinic in a timely manner, hair loss may begin. Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the head should begin immediately.
Seborrhea is characterized as a malfunction in your body associated with hormonal disorders, in which a change in the functionality of the sebaceous glands occurs. They begin to produce an increased amount of “sebum”. In this regard, the work of the natural protective barriers of the skin is disrupted, but a favorable environment appears for the influence of pathogenic bacteria and organisms. The disease is subject to cyclicality, which means that dermatitis on the head mainly begins in the winter, and in the summer there comes a more or less calm period. If the ends of your hair begin to split, then this may be one of the signs of seborrheic dermatitis on the head. Dermatologists, in addition to general medications, also prescribe special products for washing your hair. These are shampoos for the treatment of dermatitis on the head, which contain zinc pyrithione, tar, and iron sulfide. In severe forms of the disease, after a special shampoo, a lotion containing cliochenol with hydrocartisol is prescribed. But in any case, if you notice signs on your head, consult a doctor immediately!
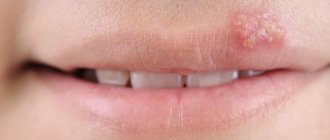
Symptoms of perioral dermatitis
Perioral dermatitis rashes are single or grouped typical spherical papules. They are colored red or red-pink and are located against a background of reddened or unchanged skin. The rash may be accompanied by discomfort, a feeling of skin tightness, burning or itching. But in approximately 25% of cases, patients do not note any subjective sensations.
Rashes with perioral dermatitis are located on the chin, under the nose, in the area of the nasolabial folds, and in the corners of the mouth. Occasionally, the periorbital form of the disease occurs with damage to the skin of the corners of the eyes, lower and upper eyelids, and bridge of the nose.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face is caused by a fungus that begins to multiply and secrete waste products. All this causes redness of the skin, peeling and itching. Increased greasiness appears, as a result of which the skin acquires an oily sheen in the affected areas. Typically, symmetrical areas of the face are affected. Do not despair - such seborrheic dermatitis can be treated with antifungal drugs, which are used topically and, if persistent, internally. Of course, in total, skin requires careful care. First, the skin is treated with an antifungal emulsion, which after some time is thoroughly washed off and treated with salicylic alcohol, then hydrocortisone ointment is applied, the use of which is not recommended for a long time. Treatment of lesions with fucorcin is prescribed. But in any case, the doctor will first conduct the necessary examinations and tests before prescribing treatment for seborrheic dermatitis on the face. A single medicinal effect and late seeking help is fraught with relapses and the appearance of large foci of rash. If you notice signs and symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis on your face, call us and make an appointment for a consultation.