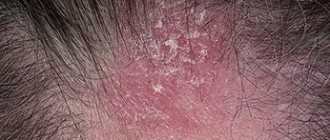
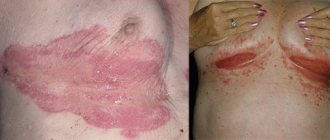
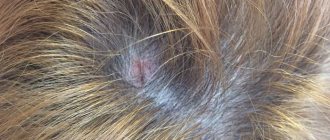
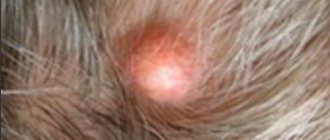
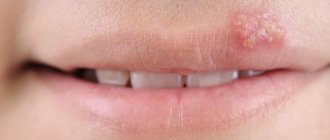
Rosacea is a common non-infectious chronic skin disease with a number of typical symptoms:
- Redness of the skin and the appearance of spider veins in the cheeks, cheekbones, nose and forehead;
- Itching and burning in the affected areas;
- Large rosacea - papules and pustules in the affected areas.
Around the world, about 10% of men and women of all ages suffer from the disease. Most often, rosacea manifests itself at the age of 30–40 years and begins with the expansion of small blood vessels in the skin of the face (less commonly, the chest and abdomen).
Not just acne
Rosacea or rosacea is a fairly common skin disease. The disease is characterized by persistent redness of the facial skin, spider veins, nodules and pustular pimples. Most often, rosacea occurs in people aged 30 years and older, and men get sick less often than women, but the course of the disease is more severe in the stronger sex. Rosacea begins with simple redness of the skin, which people do not pay attention to at first. Redness occurs as a reaction to frost, heat, hot and alcoholic drinks, spicy food or stress.
Rosacea: causes
The disease can occur quite easily, especially in those who are susceptible to it. For example, if redness of the skin occurs quite often, then you need to think about measures to prevent the disease in the future. To do this, you can consult a specialist and take certain preventive measures.
The main causes of rosacea (rosacea):
- increased sensitivity of blood vessels (thin, fragile and brittle vessels);
- genetic predisposition;
- the presence of a disease such as gastritis;
- long-term use of a number of medications (corticosteroid ointments).
Risk factors and possible causes of rosacea:
- drinking hot or alcoholic drinks, hot or spicy foods;
- influence of weather conditions (too hot or too cold climate);
- allergic reactions to cosmetics;
- changes in hormonal levels (for example, during menopause);
- a certain type of appearance (women with blond or red hair, as well as thin, sensitive skin);
- gastrointestinal disorders (reaction to certain types of foods);
- instability or disorders of the immune system;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Only a doctor can accurately determine the reasons after examining the patient and/or performing diagnostic procedures.
Rosacea in children
Sometimes this disease has to be diagnosed not only in adults, but also in children. Most often, the causes of the childhood form of the disease can be factors such as:
- individual anatomical and physiological characteristics of the child;
- hormonal changes, when periods of active growth and rest alternate sharply and frequently, which can lead to a malfunction of one or another body system;
- complex disruptions of the endocrine system caused by serious diseases;
- congenital predisposition, when there are a number of hereditary diseases (often heredity leads to a chronic form of the disease, in which case rosacea in a child affects the nose and cheeks);
- failure to maintain personal hygiene can also lead to the appearance and development of the disease, especially during the period of hormonal changes, when child skin care must be carefully selected and balanced.
Diagnosis, as well as treatment, of this disease in children should be carried out only by a specialist, so as not only to prescribe a competent course, but also not to harm the child, especially when it comes to changes in hormonal levels. As in cases with adults, if a disease is detected in a child, you should never self-medicate; this can lead to serious complications and harm his health.
Our medical center uses comprehensive diagnostics and treatment of skin diseases. For this purpose, specialized expert clinical and clinical biochemical microscopy, cultural diagnostics and dermatoscopy will be used. For each client, an individual treatment and recovery program is selected, as well as a whole program of preventive measures.
Initial appointment
Most often, diagnosing rosacea requires only an examination by a doctor at an initial appointment, but to determine the causes and select precise methods of combating the disease, a series of tests is most often required.
Diagnostics
The following may be prescribed as additional diagnostic tests (to exclude various diseases):
- bacteriological culture to study the microflora of the skin to exclude folliculitis;
- if there is severe peeling of foci of inflammation in rosacea disease at any stage, then a test is performed to exclude a fungal infection;
- a biopsy may be prescribed (rarely necessary and only to exclude lupus erythematosus dioxide).
Treatment plan
The course of treatment is always aimed at significantly improving the patient’s quality of life, that is, eliminating symptoms and eliminating all external and internal causes of these symptoms.
If others arise against the background or in parallel with the disease, then the doctor selects a more complex set of measures, which will require more time for both treatment and restoration of health.
Repeated appointment
Based on the examination results, a course of treatment is prescribed, which may include:
- if the patient has pustules and profuse rashes, then for effective treatment, gels, ointments, creams and anti-rosacea products, which include antibiotics, are prescribed;
- prescribing antibiotics in tablet form for a stronger effect if ointments do not help;
- it is also possible to prescribe local lotions and compresses with certain remedies or infusions of medicinal herbs;
- Laser treatment for rosacea has an equally good and long-lasting effect.
To get rid of the vascular network, methods such as photocoagulation or local cryotherapy can be used. Since there are no exact and specific treatment regimens, the regimen is selected individually in each case. The disease can be triggered by any food, which means that a diet for rosacea is prescribed for treatment.
The doctor also draws up an individual plan for subsequent visits to monitor the treatment. If the course of treatment requires it, re-diagnosis or additional examinations for the presence of other diseases will be required.
Control reception
It is prescribed after the patient has completed a whole course of treatment for rosacea (rosacea) on the face. A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled 21–30 days after the start of treatment. Physiotherapy complexes may be prescribed at this appointment for quick rehabilitation and recovery after taking antibiotics, as well as to consolidate the results of treatment and strengthen the immune system.
The disease can be cured, but the extent and timing of recovery are strictly individual and are discussed at a doctor’s appointment.
Prevention
Following all the doctor’s recommendations for rosacea will help you forget about the manifestations of this disease for a long time. You should:
- avoid hypothermia or overheating of the skin;
- spend less time in the open sun or apply good rosacea sunscreens with a high protection factor to your face;
- adjust your diet (exclude spicy and very spicy foods, it is not recommended to consume excessively hot or cold food, drinks and alcohol, or any other foods that cause a rush of blood to the face);
- use individually selected medications, creams and remedies for rosacea;
- exclude any individual factors that cause symptoms of the disease;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- do not squeeze out pustules and acne to avoid spreading the disease and causing infection, which can cause even more serious consequences and long-term treatment;
- exclude any individual factors that cause the appearance of symptoms of the disease.
Although the disease is fairly easy to diagnose and its causes can be determined, treatment is not always easy. As a rule, patients consult a doctor late, when the disease has already reached a serious stage and parallel diseases have arisen. Therefore, one of the recommendations that experts give is not to delay visiting a doctor, even if the symptoms do not cause you much discomfort and pass quickly.
To make an appointment or consultation with a dermatologist
in our center, you can use the online form on the website or call the phone number listed at the top right.
Symptoms
Rosacea affects the skin of the face - cheeks, forehead, nose. Prolonged redness and spider veins appear, then small bright red nodules appear - papules, in the center of which purulent pimples appear. The rashes do not leave scars behind. A patient with rosacea feels itching and hot flashes to the face. The course of the disease is accompanied by frequent exacerbations and can last indefinitely. Over time, the skin of a patient with rosacea becomes rough and thick, and knobby formations appear. In some cases, lumpy hypertrophy of the skin of the nose develops - rhinophyma; deformation of the eyelids, ears, chin and forehead is also observed. There are no comedones with rosacea.
Acne forms
The non-inflammatory form of the disease is comedones, which occur as a result of blockage of the mouth of the follicle with thickened sebum and particles of the epidermis. The inflammatory form of acne (acne) manifests itself:
- common acne (so-called juvenile acne);
- conglobate acne (large spherical inflammatory elements prone to suppuration and cyst formation);
- fulminant (more common in male adolescents, occurs quickly and strongly suppurates, may be accompanied by symptoms of intoxication);
- mechanical (occur in places of friction and skin irritation).
In addition, the following forms of acne are distinguished:
- steroid (when taking hormones);
- infantile (occurs in the first months of life);
- professional (appears as a result of exposure of the skin to oils, herbicides and other chemicals).
Stages of development
Dermatologists distinguish several stages of rosacea:
- the erythematous stage is characterized by dilated capillaries, spider veins, which occupy small symmetrical areas on the face, less often moving to the neck and chest;
- the papular stage is expressed by congestive redness, the presence of stars, superficial red or bluish nodules, hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands. Superficial pustules appear, which quickly disappear;
- The hypertrophic stage is characterized by persistent redness and bright red acne. These acne appear in groups, are usually follicular in nature, and last for several weeks. Gradually, a persistent papulopustular rash occupies the entire surface of the face, the skin of which becomes swollen and porous. The skin of the face thickens, acquires a bluish-purple color, becomes lumpy, and rhinophyma develops.
The lupoid or granulomatous form of the disease occupies a separate place and is characterized by the appearance of yellowish-brown or brownish papules, which give the “apple jelly” symptom on diascopy. According to the observations of our specialists, this stage of the disease is most often a consequence of treatment with corticosteroid ointments.
Stages of the disease and symptoms
Rosacea is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission. During periods of exacerbation, 3 main stages can be distinguished:
- Erythematotelangiectatic
. In the area of the cheeks, cheekbones and nose, small vessels, spider veins and red spots - erythema - appear. Their appearance is accompanied by burning and itching. - Papulopustular
. Swelling of the face appears, and large pink-red acne (papules) appear in the area of the cheekbones, forehead, nose and chin. A person may initially mistake them for an allergic reaction or regular acne. - Pustular nodular
. Erythema and papules spread throughout the face, papules merge with each other, and the skin becomes denser. The inflammation is not relieved and the swelling intensifies. Scars and depressions appear on the skin.
At all stages of the disease, there is a risk of ophthalmic rosacea - damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes due to the development of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, chalazion, keratitis, etc.
The disease should not be taken lightly. It is better to consult a doctor at the first stage in order to begin treatment before the consequences become irreversible.
Treatment
Therapy for rosacea is a complex matter and largely depends on the stage of the disease. The course is selected individually. The doctor prescribes astringent and disinfectant lotions, pastes; electrocoagulation, dermabrasion, and cryotherapy work well. In particularly severe cases, antibiotics are prescribed. Vitamin therapy comes to the rescue in the treatment of rosacea. It is important to get rid of concomitant diseases: vegetative-vascular dystonia, gastrointestinal and hormonal disorders. Lifestyle requires complete correction. During treatment, it is important to follow a diet and eliminate provoking factors.
Prevention
Rosacea is a vascular neurosis, which means that to prevent it, all provoking factors must be eliminated. Such factors include stress, heat and frost, wind and temperature changes, hot food and drinks, and alcohol. If occupational hazards have led to the development of rosacea (working in hot shops, staying at the stove for a long time, working in any weather in the field, on construction, at sea), you should change your profession or eliminate these hazards. When going outside, you need to protect your skin with special creams. Skin care products also need special ones designed for skin with rosacea.
Rosacea is not a contagious disease and is not life-threatening. However, rosacea, of course, does not bring joy, especially to women. So you shouldn’t start the disease if there is a chance to stop it at the very beginning.
Other articles by the author
- Exudative psoriasis
- Nail psoriasis
- Psoriasis of the palms and soles
- Red spots on the body
- Guttate psoriasis
- Plaque or vulgar psoriasis
- Rosacea
- Seborrhea. Acne vulgaris
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Lichen planus
- Hives
- Psoriasis