Papillomas are a widespread phenomenon in modern society. According to medical statistics, they are observed in one form or another in 80% of people and are benign small tumor-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes of different parts of the body. They are only one of the manifestations of infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), of which there are more than 190 types. Among them, viruses with high, medium and low oncogenic risk are distinguished. Therefore, in addition to an aesthetic drawback, papillomas can pose a serious danger to human life and health, since some of them can transform into malignant tumors.
General information
Oncology of the auricle is a less common type of pathology, however, we should not forget the threat it can pose. In 85-90% of cases, tumors are localized on the auricle and in approximately 10-15% the tumor is localized in the middle ear.
Among the most common benign tumors of the outer ear are fibromas and papillomas , and more rare ones are chondromas , lipomas and angiomas . Malignant formations are represented by sarcomas (oncology is more often diagnosed in children) and directly cancerous tumors ( carcinomas , melanoblastomas ), which are more susceptible to adults and elderly people.
Diagnosing a neoplasm
If a formation is identified, it is necessary to consult with a therapist who will refer you to the right specialist.
It is right to start diagnosing a new growth that has appeared on the skin by visiting a therapist or pediatrician. These doctors will refer you to a specialist - a dermatologist, otolaryngologist, or oncologist.
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm, which without proper attention and in an advanced form can sometimes transform into malignant.
The causative agent of papilloma is the human papillomavirus (HPV). According to various sources, it is noted that the world's population is infected with the virus from 60% to 95%.
The virus may not manifest itself, but under favorable circumstances:
- poor nutrition;
- negative habits;
- stress;
- infectious diseases;
- wounds, scratches;
- decreased immunity.
He may discover an unpleasant neoplasm. There are about 32 types of HPV and a large number of subtypes.
A doctor specializing in the treatment of HPV can easily identify papilloma when examining a patient.
To diagnose the degree of development of each tumor formed, various types of studies are used:
- probing;
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- biopsy;
- CT scan;
- microscopy.
Pathogenesis
Excessive growth and proliferation of cells during the formation of neoplasia usually involves structural elements of the skin, subcutaneous fat, cartilage, bone, vascular networks and nerve sheaths. The mechanism of development is based on malignant metaplasia.
Benign angiomas are considered the most complex, because in this case the tumor in the ear is represented by telangiectasias or repeating networks of veins and capillaries, which can have expansions in the form of cavities. They are prone to bleeding.
When the sebaceous glands are blocked on the earlobe, atheroma - an epidermal cyst of the sebaceous glands. It is usually encapsulated, smooth and round in shape, the contents of the thick mass contain fat, cholesterol , detritus and epithelium. It can grow over time, fester and break through.
Anatomy of the auricle
Epitheliomas (carcinomas) of the ear are localized at the top of the helix and begin with a warty nodule, which gradually enlarges and spreads over the entire auricle, gradually “corroding” it and causing overgrowth of the ear canal. A detailed study of neoplasia reveals atypical keratocytes (with deposits of keratin ), in which the process of normal cell maturation is distorted, starting from the spinous layer and ending with the upper layer of the epidermis. Tumor cells exhibit a high percentage of pleomorphism and numerous mitotic figures. In other cases, the oncological process immediately begins with the condition of an ulcer, which has limited edges and a tendency to spread in depth and breadth. Penetration of more than 4 mm and extension of 2 cm significantly increases the risk of malignancy. In both cases, regional lymph nodes are involved in the pathological process.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the ear
In children, sarcomas with round-cell, spindle-cell osteo-, angio- and melanosarcoma are more often found. The size and consistency may vary, the color from bluish to red.
The disease is usually characterized by a long-term benign course, which is replaced by rapid tumor growth, ulceration of the skin and exposure of bleeding masses, which then disintegrate. In some cases, a malignant ear tumor grows from the mesenchymal tissue remaining in the newborn in the supratympanic space.
Methods for diagnosing papillomas in human ears
Diagnostic measures should begin with a visit to the therapist’s office. This doctor will then refer the patient to a specialized specialist - an otolaryngologist, dermatologist or oncologist.
In most cases, a visual examination is sufficient to determine the nature of the papilloma on the ear. However, sometimes special studies are required to clarify the diagnosis. In such cases, a specialist may recommend undergoing the following examinations:
- Otoscopy . A special device with a mirror and a funnel is used. An otolaryngologist performs the examination.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging . Required when small papilloma is localized on the ear outside or on the surface of the eardrum.
- Microscopy . The growth is studied using a special magnifying microscope.
- Probing . A special probe is used, which is inserted into the ear canal and examines the surface when tumors are localized deep in the ear.
- Biopsy . This is a diagnostic procedure that involves taking biological material for examination to determine the presence of malignant cells. Usually performed on a tumor that has already been removed.
Also, if HPV is suspected, a general and special blood test is required. A blood test will help identify the virus, find out its strain, as well as the viral load on the body. This will allow you to prescribe the correct drug therapy if necessary.
Classification
Depending on the degree of malignancy and the structure of formations on the auricle, they are distinguished:
- benign (fibromas, papillomas, chondromas, lipomas, angiomas);
- malignant (sarcoma, carcinoma, cancer itself and melanoma );
- tumor-like (cysts, atheromas, keloids, exostoses ).
According to its structure, ear cancer can be polymorphic cell, basal cell, squamous cell keratinizing and non-keratinizing, spinobasal cell and papillary.
Middle ear tumors
Benign tumors are represented by fibromas, angiomas, endotheliomas, and osteomas. Treatment of tumors is surgical, angiomas are treated with electrocoagulation, osteomas are treated with x-ray therapy.
True cholesteatomas are rarely found in the area of the temporal bone scales, in the mastoid process, sometimes spreading to the tympanic cavity and cranial fossae. In recent years, glomus tumor has often been observed. This tumor ranks first among middle ear tumors in frequency. It develops from glomus (glomeruli), often found formations along the tympanic nerve, the auricular branch of the vagus nerve, and less commonly the superior petrosal nerve. Glomus have a capsule, consist of numerous capillaries and special glomus cells, and are innervated by parasympathetic nerves (glossopharyngeal and vagus). The tumor is characterized by slow growth, but is infiltrative in nature and often produces bleeding. Treatment is radiation therapy or surgery followed by radiation.
Malignant tumors of the middle ear (sarcoma) are extremely rare, most often in children. Treatment is surgical.
Much more common is middle ear cancer, which, as a rule, develops due to chronic suppurative otitis media, and is therefore diagnosed late. Most often, the tumor originates from the attic-antral region or the area of the tympanic ring. This type of tumor is characterized by rapid infiltrative growth, especially in young people, with spread to the parotid gland, lower jaw joint, inner ear, cranial cavity, and is characterized by early metastasis to regional lymph nodes.
Causes
Factors predisposing to the development of ear tumors are physical influences (insolation, radiation, trauma), carcinogenic (heavy metals, aromatic amines, pesticides, sources of PAHs, smoke particles, etc.) and the following chronic diseases:
- chronic eczema ;
- perichondritis;
- warts;
- birthmarks;
- chronic otorrhea.
Preceding diseases include psoriasis , systemic lupus erythematosus and diseases that occur with damage to the ear, as well as causing scar formation, such as after acute otitis externa .
Traumatization of the auricle, for example, when piercing or extinguishing granulations with a solution of silver nitrate , can lead to the formation of a keloid. Without causing discomfort, they can reach significant sizes - the size of a chicken egg, so they often become a cosmetic problem.
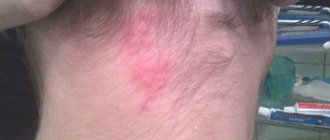
Types of papillomas
Papillomas can vary in color, size and location of appearance
Neoplasms can appear anywhere, both on human skin and internal organs.
There are special places for papillomas to be located - on the folds of the body, on the neck, eyelids, ears, armpits, chin, nasolabial folds and genital area. Due to growths on exposed parts of the body, a feeling of discomfort appears, and sometimes unpleasant changes in a person’s appearance.
The forms of neoplasms can be varied - these are pedunculated papillae, flat, round, rough, warty.
They can be light or dark brown in color.
Warts-papillomas on the ear do not grow to large sizes, but can narrow the ear canal and significantly reduce hearing.
Ear papilloma reveals itself when cleaning the ears, interfering with the hygiene procedure. Unpleasant discomfort, pain, burning, itching occurs.
Symptoms of ear cancer
The first signs of ear cancer: the formation of a dense granulating bleeding polyp or nodule that may block the ear canal. Malignant lesions may appear as flat ulcers with limited margins. The main symptoms are:
- hearing loss, up to conductive hearing loss;
- painful unilateral headache ;
- ear pain;
- bleeding, granulation or, in some cases, a weeping surface;
- rapid growth;
- purulent and other discharges, often with a sharply unpleasant odor.
Fibromas and papillomas usually have a fairly dense structure, and their localization is mainly concentrated in the area of the entrance to the external auditory canal.
Benign neoplasm on the earlobe
4 stages of ear cancer development
- At stage I, the tumor does not extend beyond the auricle and does not affect the cartilage tissue.
- At stage II, lesions of the perichondrium and the cartilage itself occur.
- Stage III is characterized by involvement of the entire auricle and regional lymph nodes in the pathological process.
- At stage IV, the tumor process spreads to neighboring nearby organs.
Oncology of the auricle can lead to serious pathological changes with damage to the meninges, pairs of cranial nerves, base of the skull, temporomandibular joint, salivary glands, which causes significant discomfort, severe shooting pain as signs of a burn , difficulty chewing, etc.
Treatment of earlobe atheroma
This pathology must be treated in a clinic. Self-medication in such a situation will not only not help, but will also provoke complications. There is no conservative treatment for such a tumor. In practice, the following treatment methods are used:
- surgery (Removal during surgery is the most reliable way to cure the ear. To carry out the removal, the parts of the ear where the cyst has arisen are subjected to local anesthesia. To perform the operation, you do not need to go to the hospital. It is performed on an outpatient basis.);
- laser removal (this method is used for small lesions);
- radio wave method (during this method, the tissues of the lobe are heated, and the cyst cells seem to evaporate. The procedure is also carried out under local anesthesia).
There are situations when atheroma becomes inflamed and suppuration occurs. In this case, it is necessary to urgently contact an ENT doctor to open the tumor and prevent inflammation of nearby tissues. An otolaryngologist will open the atheroma, empty its contents and prescribe a course of antibacterial therapy. About a month after the autopsy, after the inflammatory process has subsided, it will be necessary to perform an operation to directly remove the formation. If repeated surgery is not performed, a relapse may develop and the cyst will appear again.
Diet for ear cancer
Diet for cancer
- Efficacy: no data
- Duration: until recovery or lifelong
- Groceries cost: 2500 - 4800 per week
The diet of cancer patients should be as healthy as possible. It may seem quite specific to some people. The menu should mostly include:
- plant products - vegetables, fruits, legumes, herbs, cereals and whole grain baked goods;
- poultry and eggs;
- seeds, nuts and natural vegetable oil;
- seafood;
- milk and fermented milk drinks, cheeses and feta cheeses;
- drink green and herbal teas, freshly squeezed juices and compotes.
It is recommended to avoid red meat, sausages, smoked meats, fatty and spicy foods, alcohol, mayonnaise and other packaged sauces, confectionery, sweets, fast food and other products of questionable composition and quality.
People's experience in the fight against papillomas
A child can become infected with papillomavirus while still in the womb
Doctors constantly warn that you should not self-medicate. However, many successful ways to get rid of warts and papillomas have appeared among the people, which will not harm the human body.
Here are some proven methods:
- lubricate the papilloma with a mixture of 100 g of celandine, 3 g of aspirin, 25 g of iodine, 2 g of boric acid;
- Squeeze juice from cabbage leaves and make compresses on papilloma;
- apply a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution to the growth for 5 days;
- lubricate the ear with celandine juice;
- make compresses for a month from a mixture of baby cream with 2 cloves of garlic;
- dry the papilloma with cotton wool and the white of a raw egg.