from February 4, 2021
Keratosis or hyperkeratosis is a non-inflammatory form of dermatosis, which is accompanied by excessive keratinization of the skin.
For healthy skin of any person, the process of keratinization is a normal physiological state. The process of keratinization provides one of the most basic functions of the skin - protective.
MECHANISM OF KERAINIZATION IN NORMAL AND IN HYPERKERATOSIS
Normally, as a result of their vital activity, skin cells gradually move from the lower layer to the upper, while gradually accumulating keratin - a protein that makes them more durable and resistant to external influences. The top layer of skin is nothing more than completely keratinized cells or horny scales, which are peeled off and replaced with new ones during human life. Such cells lack viability, but at the same time, thanks to keratin, they provide protection to living cells located underneath them from negative environmental factors.
With the development of hyperkeratosis as a pathological condition of the skin
- on the one hand, there is an active accelerated division of epidermal cells that produce keratin;
- on the other hand, there is a delay in the process of normal physiological exfoliation of horny scales from the surface layer of the skin.
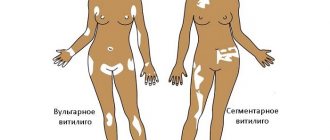
Distinctive signs of vitiligo
The affected areas and healthy epidermis are clearly demarcated.
A characteristic symptom of the disease is the absence of scales in areas of spotting. The lesions themselves do not have elements protruding above the surface of the skin. Upon closer examination, you will notice that the pigment shifts to the edges of the spots, and the skin in these places has a more intense color. The hairs growing on areas of vitiligo are also discolored, like the skin. The patient has no pain or itching or other unpleasant sensations. Recently, it has been found that skin covered with vitiligo patches is highly sensitive to ultraviolet rays. After irradiation, the skin in the area of pathology does not become tanned, and the surrounding hyperpigmented areas become even darker.
The sweat glands contained in the affected skin do not function fully. This provokes disturbances in the sweating process.
TYPES OF KERATOSIS
Most often, the phenomena of hyperkeratosis are localized on the legs (heels, feet, knees) and arms (palms, elbows), less often - on the scalp, face in the area of the nose, cheeks, forehead. Basically, this pathology is formed in areas of irritation by any external mechanical or environmental factors. However, hormonal imbalances, heredity and improper skin care can also provoke hyperkeratosis.
The most common types of manifestations of hyperkeratosis are:
- Actinic (solar) keratosis on the face and body (keratomas). It develops due to excessive exposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays and photodamage. Appears as flat, rough yellow or brown spots;
- Palmar and plantar keratoderma - calluses, corns on the soles of the feet and palms, heel cracks. Formed in areas exposed to prolonged friction or pressure, during infectious and fungal diseases;
- Follicular or pilaris keratosis (“goose bumps”). Dermatosis occurs as a result of both accelerated keratinization and disruption of the physiological desquamation of horny scales. Against this background, the normal secretion of sebum is disrupted and local inflammation of the hair follicles on the body occurs. It looks like a rash of small multiple nodules of bright pink and gray color on the face, shoulders, legs, buttocks;
- Seborrheic keratosis is the most common form of hyperkeratosis. It is a hyperpigmented “plaque” with clear boundaries from light to dark brown, covered with keratinized skin. It can be either single or multiple.
- Actinic keratosis - develops in old age in the form of beige-brown spots and is localized on the face, shoulders, back, and back of the hands.
White spots on the skin: photodermatitis
04.10.2021
What to do if white spots appear legs , chest Will this really stay forever?
White spots on the body, especially in the indicated places, are a manifestation, that is, a symptom of a particular disease. Very rarely, in individual cases, spots are an independent disease. It is important to know whether pigmentation appeared on its own, or whether it is a consequence of past rashes, vesicles, papules, pimples , etc. This is a very important point, one might say that it is key in making a diagnosis. A correct diagnosis guarantees correct treatment.
In most cases, the described spots on the skin are a manifestation of the so-called “sun allergy”, or more precisely, photodermatitis. This allergy does not mean that if you go out into the sun you will always get spots. Photodermatitis is caused by the fact that ultraviolet rays react with certain substances on the skin or in the skin, forming spots. Very often, the spots are preceded by a rash, or “pimples,” but it happens that just spots appear, which can be either white or any other color.
Photodermatitis is divided into exogenous and endogenous. Accordingly, exogenous dermatitis is a reaction of ultraviolet radiation with carcinogenic substances on the surface of the skin. Such substances include cosmetics (deodorants, creams, ointments, perfumes, lipsticks, etc.), pollen, and other substances released by the environment.
As a remark, you can make the following: The most carcinogenic substances found in perfumes and most often causing photodermatitis include: Eosin, para-aminebenzoic acid, retinoids, essential oils, salicylic acid, mercury preparations, phenol. Also, spots of this type can appear after cosmetic procedures ( peeling , tattooing, etc.)
Endogenous photodermatitis is caused by an ultraviolet reaction, or by ultraviolet reaction products in the skin itself. Especially often, photodermatitis manifests itself in diseases of the liver , gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system .
You need to understand whatever dermatitis or other disease is, it is primarily an allergic reaction , against the background of decreased immunity .
If your problem appeared in the spring, when the sun begins to shine more and warmer, and all the plants begin to turn green and bloom, then we can assume that this is an allergic reaction . Moreover, the stains appeared in those places that are covered with clothing in winter, and become exposed with the arrival of warm weather.
Whatever the reason, be sure to consult a dermatologist and allergist . It is rare to achieve a quick positive result by simply adjusting your lifestyle, although this is extremely important.
You need to take a number of antihistamines, use special ointments, creams or gels, and apply special cosmetic procedures.
We hope our answer helped you and you will soon solve your problem. We wish you and your loved ones all the best.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic
REASONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF KERATOSIS
Factors causing the development of hyperkeratosis are divided into external and internal.
External factors that provoke hyperkeratosis include chronic inflammatory processes on the skin, infections, ultraviolet radiation, exposure to aggressive chemicals, as well as strong pressure, for example, tight shoes, a tight hat, hairpins, headbands, improper skin care and incorrectly selected cosmetics, which causes dry skin, as well as a lack of vitamins A, C, D, etc.
If the pathology has formed without prior irritation or injury, then skin hyperkeratosis is probably caused by internal factors. In this case, it may be hereditary diseases, dry skin due to metabolic disorders, liver disease, gall bladder, thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus, congenital pathologies. In addition, manifestations of hyperkeratosis occur and accompany some chronic skin diseases - eczema, psoriasis, lichen planus, seborrhea, erythroderma, keratoderma.
Methods of treating the disease of the chosen ones
Is there a method today that guarantees a 100% recovery? We asked Tatyana Sukhova, a dermatologist,
highest category of Moscow clinic.
Cuban doctors have achieved the best results in treating the disease. The method involves administering intramuscular injections of vitamins into depigmented areas. But even he cannot cope with the disease completely. Vitiligo treatment at the Dead Sea is now being actively advertised. Israeli doctors were able to obtain pigment on a white spot, but this, alas, does not always look beautiful and, again, does not guarantee complete healing. In our country, the most effective method in the treatment of vitiligo is considered to be a combination of UV and PUVA therapy with the use of photosensitizing drugs. As a result, it is possible to “revive” the white spots, but, unfortunately, it will not be possible to get rid of them completely.
Folk remedies for spots
Among practicing doctors there is also the following opinion: vitiligo is not a disease, but only a cosmetic skin defect. This means that you need to treat it as normal pigmentation, using herbal medicine, as well as masking the spots with regular foundation. If you choose a shade similar in color to a healthy area of skin, then no one will notice vitiligo. Only on condition that this product is approved by a doctor, since many foundations contain microsubstances that affect pigmentation and can enhance the development of the disease.
HOW TO TREAT HYPERKERATOSIS
Symptoms of hyperkeratosis usually do not cause pain and are considered a cosmetic defect. The exception is calluses and corns on the feet, which cause discomfort when walking. In this case, you should immediately seek qualified help, especially if the manifestations of hyperkeratosis cause pain, discomfort, there are symptoms of infection (redness, swelling, accumulation of pus) or if you have diabetes.
Hyperkeratosis will not go away on its own; in any case, it is necessary to start treatment.
The method of treating hyperkeratosis is chosen by the doctor, taking into account the cause, location, prevalence and shape of the thickenings, as well as compensation for the underlying chronic disease as a result of which the pathological process was formed.
To treat hyperkeratosis, the following are most often used:
- ointments, creams with a softening effect; creams rich in fat;
- taking acitretin;
- Daivonex ointment (calcipotriol);
- medical hardware manicure (if the process is localized on the palms, feet, arms and legs);
- creams with urea;
- peeling, including chemical and laser peeling (face and body);
- radiosurgical removal (keratomas);
- surgical cutting (calluses, corns).
You cannot remove calluses, corns or warts on your own, as there is a risk of infection and other complications.
Localization and size of spots
The disease is not characterized by a specific localization. Spotting can appear in any places:
- on the head;
- in the eyebrows;
- in the groin area.
It is not typical for vitiligo to be localized in the area of the palms, feet or mucous membranes. Most often, the spots cover the external genitalia, which is why the pathology can be mistaken for signs of sexually transmitted infections. The disease also tends to affect the back of the hands and the skin between the buttocks. Sometimes the signs of vitiligo take on a peculiar form - small white spots alternating with areas of healthy skin.
In rare cases, small spots with increased pigmentation are present inside the lesions. At the very beginning of formation, the foci are small in size. Gradually, the affected area can increase due to the combination of pathological elements, covering a larger surface of the skin. In this way, large spots with irregular outlines are formed. At the same time, the characteristic clinic of the pathology is preserved - increased coloration of the skin along the edges of the spotty formations. In some patients, the spots can become gigantic, covering the entire buttock area, back or abdomen. In isolated cases, the lesion can cover the entire skin of the body.
In many situations, the disease does not occur in isolation, but in combination with various disorders - scleroderma, baldness, Satten's nevus, porphyrin disease. Specific signs of vitiligo, by which it can be distinguished from other pathologies, are the absence of peeling and skin atrophy in any form of the disease.