Why does it hurt in the groin in men? The appearance of such painful symptoms is influenced by many factors. Unpleasant sensations bother the patient due to genetic problems. Pain in the groin on the right in men is a clear sign of infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted and appear in the body unexpectedly. In any case, it is worth contacting a specialist as soon as possible in order to diagnose abnormalities at the earliest stage.
The appearance of nagging pain in the groin in men indicates a disruption in the functioning of any of the body systems. It can have different frequency and cyclicity, character and duration. You should not self-medicate so as not to trigger the disease. At the KDS Clinic, diagnostics of the groin area of the body is carried out using modern equipment. In a matter of minutes, medical workers examine the patient’s body, study all indicators and tell about deviations.
Diseases and pathologies that cause lower back pain to radiate to the groin
If the pain in the lower back radiates strongly to the groin, inflammation or a degenerative process has probably begun in the spinal column or in the internal organs. It is worth familiarizing yourself with the main reasons why pain in the back may appear, radiating to the groin area.
Hard physical work
This is one of the common factors causing discomfort and pain. If you carry a lot of weights at work, you may experience severe pain while moving. However, when physical activity ends, the pain may gradually decrease and then disappear completely.
Injury
The causes of pain in the groin and lower back often lie in back injuries. This pain is different in that it manifests itself at the moment of exertion and is almost unbearable, very sharp. The area around the groin begins to swell, the skin becomes red and swollen. The pain may not go away for up to a day, and the patient is forced to take strong painkillers, and is also often in a forced position, since this somewhat reduces the pain syndrome.
Osteochondrosis
The occurrence of nagging pain in the lower back and groin is not uncommon if you have osteochondrosis in the lower back. This condition manifests itself in that the cartilage tissue becomes less dense, and the cartilage itself becomes thinner and cannot cope with its functions. The reasons may be low mobility, obesity, monotonous loads on the back, etc.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Due to arthrosis, pain in the groin and lower back most often occurs in women over the age of 45. The disease can affect both joints at once or just one. It is not easy to identify a disease; it disguises itself as a lot of others. The first manifestations may be an “ache” near the buttocks, and pain occurs with minimal exertion.
Intervertebral hernia
With a hernia, pain appears when the lower back is loaded. They have an acute “shooting” character, and only after a while the pain syndrome “descends” to the lower abdomen.
Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
Pain in the groin and lower back often occurs in men 30–50 years old, the pain syndrome is sudden and sharp. The condition is alleviated only by the use of prescription painkillers.
Intestinal pathology
The problem may lie in intestinal pathologies, examples are appendicitis, obstruction, or even oncology. Against the background of lower back pain radiating to the groin, vomiting, bloating and pain in the abdomen, and impaired bowel movements may occur.
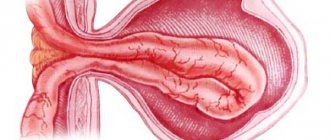
Classification of inguinal hernias
The disease is classified according to several factors.
By origin there are:
- Congenital, or embryonic - formed during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, clinically manifested immediately at birth or during the first year of life;
- Acquired are inguinal hernias in adults caused by unfavorable conditions.
According to the nature of the flow:
- Reducible - the protrusion in the lying position decreases, the hernia can be easily and painlessly reduced, the organs in the hernial sac are mobile and do not disturb;
- Irreducible - the protrusion does not reduce, the dimensions do not change with a change in body position, and complaints about deterioration of the condition appear;
- Uncomplicated - no problems with digestion, urination, no severe pain;
- Complicated – complications develop with obvious clinical symptoms that require emergency surgical care.
By location:
- Direct inguinal hernia - always acquired, typical for older patients, exits through the superficial inguinal ring, a rounded protrusion, disappears or noticeably decreases in size in the supine position;
- Oblique - can be congenital or acquired, passes through the inguinal canal, often descends into the cavity of the scrotum and labia majora, the protrusion is oblong, changes little when changing body position:
- Inguinoscrotal hernia;
- Funicular - the hernial contents are located inside the canal along the spermatic cord;
- Sliding - one of the walls of the hernial sac is an organ with a retroperitoneal location: the cecum, bladder, uterus with appendages; this is a difficult hernia to diagnose;
- Right-sided - occurs 2 times more often, because the right channel is shorter and wider than the left; congenital is formed when the testicle descends (inguinal hernia of the testicle);
- Left-sided inguinal hernia is a less common pathology;
- Bilateral – an extremely rare phenomenon, congenital in nature.
Why is an inguinal hernia dangerous?
The main danger is an asymptomatic course at an early stage. The patient can walk for several years without paying attention to a small lump in the groin area. In this case, complications that threaten life and require emergency surgical intervention can arise at any time.
Inguinal hernia strangulation
Against the background of complete well-being, compression of the hernial contents in the area of the hernial orifice occurs. This is accompanied by sharp, intense pain in the area of the protrusion, followed by spreading throughout the abdomen. The state of health deteriorates sharply, symptoms of intoxication and pain increase, and body temperature rises.
Due to compression of the vessels supplying the strangulated organ, it can become dead. Toxins released during the breakdown of dead tissue lead to circulatory problems throughout the body, kidney problems, and changes in blood clotting.
The following dangerous conditions are diagnosed:
- Peritonitis – acute inflammation of the peritoneum;
- Gangrene, intestinal perforation;
- Sepsis, infectious-toxic shock;
- DIC syndrome;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Thrombosis of mesenteric arteries and veins;
- Acute renal failure;
- Bladder ischemia;
- Acute urinary retention;
- Multiple organ failure.
Inability to reduce the hernia
With a long-standing hernia, the organs in it become fused with the hernial sac and cease to be retracted into the abdomen. This is accompanied by dysfunction of the organs located in the hernial sac.
The patient is concerned about chronic abdominal or pelvic pain, pain in the protrusion itself, which intensifies with walking, exercise, difficulty urinating, defecating. In particularly advanced cases, phlegmon of the hernial sac, intestinal obstruction, acute urinary retention, and a clinical picture of an “acute” abdomen, indicating peritonitis, develop.
With forced reduction, perforation of the intestinal wall is possible.
Secondary infertility
In men, the spermatic cord passes through the inguinal canal, consisting of the vas deferens, vessels and nerves, and the levator testis muscle. An inguinal hernia leads to compression and disruption of blood circulation and innervation of the scrotum and testicles, changes in the functioning of the prostate gland, and inhibition of spermatogenesis. Problems with erection appear.
In half of the cases, an inguinal hernia in men turns into an inguinal-scrotal hernia, causing inflammation of the testicles - orchitis. Increases the risk of developing testicular torsion and malignant degeneration.
In a woman's body, the round ligament of the uterus passes through the inguinal canal . When a hernia forms, the fallopian tube with the ovary, and sometimes the uterus, is involved. This leads to menstrual dysfunction, chronic inflammation, the formation of adhesions, and intimate difficulties.
In the event of strangulation, removal of the affected organ may be necessary with subsequent loss of fertility.
Groin and lower back pain in men
In some cases, pain is detected in the groin and lower back, the causes of which are related to the functioning of the male reproductive system. There are several types of diseases that can cause pain in the groin and lower back.
Varicocele
It is a fairly common disease that occurs in approximately 15% of the stronger sex. Varicocele appears because the outflow of blood in the veins near the spermatic cord is disrupted. Men complain that the groin hurts and at the same time radiates to the lower back; pain occurs near the scrotum or testicle, most often the left one.
Prostate cancer
Lower back pain most often occurs during a long and chronic course of the disease, when the kidneys or urinary ducts are already affected. The pain has a different character: long aching, shooting or short sharp. At the same time, there is a burning sensation when urinating, stomach pain, erectile function is impaired, and discomfort appears during sexual intercourse.
Spermatic cord cyst
The reason why lower back pain radiates to the groin may be a funicocele, which means the development of a cyst - a cavity in the membrane filled with fluid. In this case, one side of the groin is noticeably painful, and the lesion may affect the left or right cord. Upon examination, the doctor reveals swelling of the scrotum, and the leg may swell on one side.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
ARS syndrome is inflammation and degeneration of tendons and ligaments attached to the pubic bone and symphysis. Athletes face this. Pain is observed in the lower abdomen and groin area, intensifying with hip abduction.
Hip sprain. May be caused by a fall or sudden abduction of the hip while performing any exercise.
Coxarthrosis, arthropathy, femoral neck fracture. These are diseases associated with damage or disease to the hip joint and the proximal part of the femur where it attaches to the joint.
Pain in the groin and lower back in women
Treatment for lower back pain that radiates to the groin is often required for women as well. The reasons may be the development or exacerbation of various diseases. It is worth understanding that self-diagnosis is impossible here, and you will need to promptly contact a qualified specialist who will carefully examine your health condition and prescribe medications.
Pelvic inflammatory disease
These include the uterus and ovarian appendages. The pain has no clear localization - the entire lower abdomen hurts, the lower back ache. There may be increased pain due to severe hypothermia, when the temperature rises, malaise and weakness appear. Vaginal discharge that is uncharacteristic of a healthy body often appears.
Exacerbation of chronic cystitis
If pain in the lower back on the right or left radiates to the groin, you have a frequent and painful urge to go to the toilet, and the process itself does not bring relief, going to the toilet is painful, you want to urinate even with an empty bladder, then the problem is probably an exacerbation of cystitis. In this case, the color and smell of urine can change significantly.
Ovarian cyst
Apoplexy of the right ovary is similar to appendicitis, as it is accompanied by nausea, severe pain, vomiting and decreased blood pressure. The situation is the same with the left ovary, only because of the localization of the pain, in this case it is impossible to confuse the cyst with appendicitis.
Trochanteritis
If the lower back hurts on the left or right and radiates to the groin, this may be a symptom of inflammation of the tendons of the thigh, which is otherwise called trochanteritis. This phenomenon is sometimes observed during menopause, when the level of sex hormones in a woman’s blood drops. The pain can radiate not only to the groin, but also to the inside of the thigh.
Causes, mechanism of formation of pathology
There are two fundamental elements in the formation of an inguinal hernia increased intra-abdominal pressure and weakness of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the inguinal canal .
Under the influence of high pressure in the abdominal cavity, movable organs are displaced from their usual place and protrude through weak spots in the abdominal wall. A hernial sac with a hilum in the area of the inguinal canal is visually identified. In women, the hernia may extend down into the labia majora. An inguinal hernia in men can spread into the scrotum.
The organs involved in hernia formation include the loops and mesentery of the small intestine, the cecum, the greater omentum, the ureters and bladder, the uterus, the fallopian tubes, and the ovaries.
Factors contributing to the formation of inguinal hernia in adults are the following:
- Burdened heredity;
- Exhausting physical activity with lifting heavy loads - professional weightlifting, loader profession, weight lifters;
- Multiple, multiple pregnancies, childbirth;
- Surgical treatment of prostate tumors, appendicitis;
- History of hernias of any localization;
- Loss of muscle strength and ligament elasticity with age;
- Chronic constipation;
- Prolonged paroxysmal cough;
- Anorexia, obesity 2-3 degrees.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of an inguinal hernia at the onset of the disease are not pronounced. For a long time, the pathology does not cause discomfort, does not reduce the quality of life, and progresses slowly. A small protrusion in the groin area is painless, softly elastic, and resembles an enlarged lymph node. Periodically, the swelling disappears.
As the hernial sac grows, complaints of pain when walking, physical activity, a feeling of fullness, and pressure in the lower abdomen appear. Dyspeptic symptoms are added - a feeling of heaviness, belching, nausea, vomiting; constipation, flatulence, difficulty urinating.
A characteristic sign is increased pain and discomfort when sneezing , coughing, or straining . In the case of an indirect hernia, asymmetry of the scrotum or labia majora is observed with an increase in the affected side. , a clinical picture of an “acute” abdomen appears : sharp pain in the area of the hernia, the hernia ceases to be reduced.
How to relieve pain
It is not always possible to see a doctor right away if your lower back hurts and radiates to the groin. Sometimes you have to look for a temporary solution to relieve pain in the lower body before visiting the clinic. Taking antispasmodics, which include no-spa and papaverine, can help. If you need to bring down the temperature, you can take Ibuprofen or Nurofen, but if the temperature is below 38 degrees, it is not recommended to bring it down. Under no circumstances should you heat or cool a sore spot without a doctor’s instructions. It is also worth providing the patient with bed rest.
Diet after hernia repair
A proper diet will speed up recovery. For the first few days, it is better to eat only liquid and pureed food in small portions. On day 4-5 you can go back to your normal diet.
You need to eat as many foods rich in protein and fiber as possible. The diet should include:
- lean boiled meat (chicken, beef);
- seasonal vegetables (raw or steamed);
- dairy products, especially cottage cheese;
- fruits and berries;
- various porridges (buckwheat, millet, oatmeal, pearl barley);
- Fish and seafood;
- nuts and dried fruits.
It is better to exclude alcohol and coffee from your diet, as well as smoking.
Which doctor should I contact?
As has already become clear, there are many reasons why pain appears in the groin and left or right lower back. Determine independently whether in this case it is necessary to be treated by a urologist-andrologist
or
a gynecologist
, a
neurologist
or a surgeon, it is not possible. The best solution in such a situation is to make an appointment with a general practitioner. After the specialist performs an examination, he will draw preliminary conclusions about your state of health and prescribe the necessary types of diagnostics. Based on the results of a more detailed examination, it will become clear which specialist you need to be redirected to, and whether this will be necessary at all. Then you will be prescribed adequate treatment tactics that will allow you to improve your health.
Operations
The inguinal region is of great interest in surgery from the point of view of choosing the safest surgical approaches to the iliac blood vessels, abscesses and phlegmons located in the subperitoneal section of the small pelvis (see Pirogov incision). In addition, through P. o. operational access is made to the contents of the inguinal canal (see) for inguinal hernias (see) and for funiculocele (see Spermatic cord).
Bibliography:
Venglovsky R.I. About the descent of the testicle, in the book: Works of the hospital. hir. clinics, ed. P. I. Dyakonova, vol. 1, p. 7, M., 1903; aka, Development and “structure of the inguinal region, their relation to the etiology of inguinal hernias,” M., 1903; 3olotareva T.V. Surgical anatomy of the anterolateral abdominal wall, in the book: Surgeon. Anat, belly, ed. A. N. Maksimenkova, p. 23, L., 1972; Kukudzhanov N.I. Inguinal hernias, M., 1969; Lubotsky D. N. Fundamentals of topographic anatomy, p. 458, M., 1953; Ostroverkhov G. E. Lubotsky D. N. and Bomash Yu. M. Operative surgery and topographic anatomy, M., 1972.
G. E. Ostroverkhov, A. A. Travin.
General information about male disease
Cystitis in men is an infectious disease. The prevalence of this disease in men is much less than in women. This is explained by the fact that it is more difficult for bacteria that cause the disease to enter the male body. The male urethra is longer, so the infection does not reach the internal organs of men as often as in women.
Cystitis is a disease that affects the genitourinary system, regardless of the person’s gender. The course and symptoms of the disease differ somewhat among representatives of different sexes, although there are common signs. Cystitis in men is a process of inflammation of the urinary system. With this disease, the mucous tissue of the bladder is affected, as a result of which the man experiences discomfort and cannot live a full life.
Manifestations of abnormal bladder activity: painful and frequent urination, the appearance of mucus and blood in the urine, repeated urges to visit the toilet at night. The patient may not immediately see a doctor; this is dangerous because of its consequences. Cystitis can become chronic and lead to other complications. In order not to progress the disease, try to contact experienced specialists at the Global Clinic Center in a timely manner.
Prevention
The disease can be prevented by avoiding excessive physical activity and lifting heavy weights. It is important to take care of the stable functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, because constipation provokes hernias. You need to lose excess weight and do physical therapy. You should strengthen your abdominal wall by performing abdominal exercises and “bicycle” exercises. Therapeutic gymnastics should be given at least 20-30 minutes a day.
It should be noted the importance of maintaining a competent diet. You need to eat often, but little by little, and no alcohol. Instead of fatty and spicy foods, flour and confectionery products, you need to eat vegetables, fish and meat, boiled or steamed.