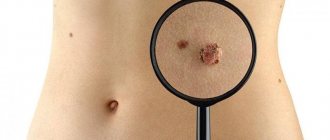
A melanoform nevus is one of the types of pigment spots (moles), a skin neoplasm that is formed from melanocytes (skin cells that produce melanin) and under certain conditions can become malignant.
Melanoform nevus can be located on any part of the body
Causes
Birthmarks, or nevi, are benign formations on the skin and mucous membranes that can appear in the prenatal period and have different sizes.
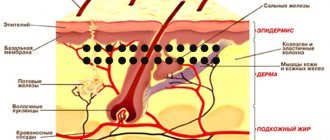
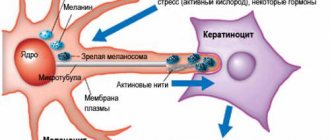
Melanocytes, from which a melanoform nevus is formed, are tree-like cells that perform a protective function by releasing melanin in response to exposure of the skin to UV radiation. Melanin protects the skin and is capable of coloring the skin, hair and eyes. Melanocytes are localized in the skin, retinal epithelium (pigmented part), vascular layer of the ocular analyzer, and inner ear.
All melanin-containing skin formations can be congenital or acquired. Melanoform nevi can be both, but congenital ones often appear only in adolescence.
The appearance of moles of this type depends on the person’s age, skin type, as well as hormonal changes. They are often of unspecified origin.
Risk factors include:
- diseases of the liver, pancreas;
- weakened immunity;
- papillomavirus infection;
- pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- heredity.
Children in the first years of life are practically not formed. About 90% of the population under the age of 15 have birthmarks. After 30 years, the number of moles that appear usually decreases. As you age, the number of birthmarks on your skin decreases.
Treatment of melanoma
For the treatment of local melanomas of stages I and II, the main method of treatment is radical excision of the tumor, involving healthy tissue from 0.5 to 2 cm, depending on the stage of the disease. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is performed in a specialized institution if the tumor thickness is more than 1.5 mm. For the treatment of stages III and IV, combined methods are used, including surgery, chemotherapy and, in some cases, radiation therapy. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy are also used (if mutations of the C-Kit and BRAF genes are detected).
How do melanoform nevi of the trunk and other parts of the body manifest?
Melanoform nevi form on the trunk, face, neck, limbs, and scalp. Have the following characteristics:
| Characteristic | Description |
| Variability | Throughout a person’s life, moles of this type may appear and disappear, their size and color may also change, and neoplasms may protrude more and more above the surface of the skin. If a mole changes quickly, for example, grows quickly, or if the changes are traumatic or inflammatory in nature, you should consult a doctor. |
| Color | Since melanocytes are the source of melanin in the body, melanoform nevi have a brown color of varying degrees of saturation. In some cases, such moles may have a bluish tint. |
| Hairs | Moles may grow hairs that are usually coarser and darker than elsewhere. When trying to remove hair from them, moles can become inflamed and painful. |
| Soreness | They are painless, pain can only appear when injured. |
Removal methods and common cases
To remove a nevus, several traditional and innovative methods are used, the decision on which one to choose is made by a dermatologist based on studying the diagnostic results and the general condition of the patient’s body:
Surgical removal of pigmented nevus is widespread. This reliable, repeatedly tested method is optimal for eliminating large-scale formations, “hanging” and other dangerous moles. Disadvantages are a long healing period and a high probability of scar formation, so the surgical procedure is used more often on areas of the body that are permanently covered by clothing;- Today, the cost of laser removal of a nevus on the eyelid, where the skin is especially thin and delicate, has become quite affordable. This method is also effective in most other situations, but the disadvantage is the burning of tissue, which does not allow for histological analysis;
- Cryodestruction is used only to remove flat moles that have captured only the upper layers of the epidermis. In other situations, this technique often leads to relapse and malignancy;
- removal of intradermal nevus of the scalp is performed mainly using advanced techniques - radioknife or laser, although other methods can be used depending on specific indications;
- Almost any method of removing Jadassohn's nevus (sebaceous nevus) is acceptable - surgical scalpel, electrocoagulation, laser, etc. The choice depends on the location and size of the pathological focus;
- Experts often come to the conclusion that there is a danger of a melanoform mole degenerating into a malignant tumor. The price for removing a melanoform nevus in Moscow depends on the chosen technique (any of the currently used ones can be used), the volume of work and its complexity, but it always remains profitable for clients of the MedBioSpectrum clinic.
According to our experts, the best solution in most cases is the removal of pigmented and other nevi with Surgitron. Radio wave technology has a minimum of contraindications, is atraumatic, and ensures rapid tissue healing.
You can get answers to questions, additional information and make an appointment at the MedBioSpectrum MC quickly and easily - right now dial our contact phone number in Moscow or Ramenskoye.
Complications
Moles, due to their specific anatomical location, can be subject to injury - for example, by seams or clothing fastenings. But the main danger is that moles can become malignant, that is, degenerate from a benign neoplasm into a malignant tumor - melanoma.
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm that is formed from melanocytes. The tumor is most often located on the skin, in more rare cases it is found on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, genitals, rectum, and on the retina of the eye.
Risk factors for malignancy of moles:
- genetic predisposition;
- history of melanoma;
- decreased immunity;
- the presence of a large neoplasm in a person (the larger the area the tumor occupies, the higher the risk of malignancy);
- the presence of more than 50 nevi on the body;
- regular exposure of the skin to direct sunlight and/or ultraviolet radiation from artificial sources;
- history of sunburn;
- exposure to ionizing radiation on the skin;
- the location of the mole in areas of skin friction (for example, if the neoplasm often comes into contact with clothing and underwear), its frequent injury;
- age over 50 years.
How dangerous are dysplastic nevi?
There are specific, proven figures here that it would be better for those who spread hysteria on the “Internet” to become familiar with.
- The annual risk of a dysplastic nevus turning into melanoma is 1 in 10,000. According to the authors [4], this is very low.
- About 70% of melanomas develop not against the background of nevi, but against the background of unchanged skin [5].
- A study examining the genetic profile of atypical nevi has challenged the hypothesis that they are precursors to melanoma [6].
- In two studies, the authors followed patients with incompletely removed, histologically confirmed dysplastic nevi for a long time (up to 17 years) [8,9]. Based on this, the very thesis about the increased risk of developing melanoma from a dysplastic nevus can be seriously questioned.
Treatment
Treatment for nevus usually involves its removal, which can be done using various methods.
| Method | Description |
| Cryodestruction | The neoplasm is exposed to low temperatures (liquid nitrogen, carbonic acid), there is no pain or discomfort, and after healing, usually no traces remain at the site of the mole. Several sessions may be required to completely remove the formation. |
| Electrocoagulation | The mole is exposed to high-frequency electric current. Since the procedure is quite painful, it is performed under local anesthesia. The method is not used to remove large moles. |
| Laser therapy | When the affected area is exposed to a laser, the patient usually does not experience pain and there is no scar left on the skin, however, the skin at the site of exposure may acquire a lighter shade. |
| Radiosurgical method | Non-contact excision of tissue is performed using a radio knife; the method can be used for benign and malignant neoplasms; it is not suitable for removing large moles |
| Surgery | It is used to remove large tumors located in hard-to-reach places that are malignant (in the latter case, the adjacent part of the skin is excised along with the formation). After the operation, a scar may remain, so it is used only in cases where other methods are contraindicated. |
Self-medication is strictly not recommended. When attempting to independently remove such tumors at home, the risk of malignant degeneration increases significantly.
Diagnosis of melanoma
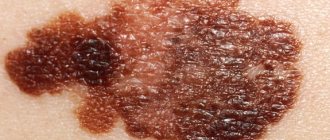
Dermatoscopy is carried out both using a simple magnifying glass and using a dermatoscope (epiluminescent microscope) which makes the stratum corneum of the epidermis transparent. In this case, it is possible to determine with high probability whether a nevus is dangerous or not based on the ABCDE system.
A - asymmetry, asymmetry of the mole
B - border irregularity, uneven edge
C - color, unequal color of different parts of the mole
D - diameter, the diameter of the mole is more than 6 millimeters
E - evolving, mole variability
There is also a Russian-language mnemonic way to remember alarming symptoms:
Shape – rising above the skin level AND change in size, accelerated growth Borders are irregular, edges are jagged A symmetry – one half of the tumor is different from the other Size large – the diameter of the tumor usually exceeds 5 mm O the color is uneven
Cytological examination is used in the presence of ulcerations; this method is not reliable and does not allow one to establish or refute the diagnosis of melanoma.
Radical removal of the formation followed by histological examination is a mandatory stage, the “gold standard” of diagnosis. Mandatory are:
— determination of the maximum tumor thickness in mm according to Breslow;
— determination of the level of invasion according to Clark;
— indication of the presence or absence of ulceration of the primary tumor;
— determination of the mitotic index (number of mitoses per 1 mm²) for tumor thickness up to 1 mm inclusive;
— presence of transient or satellite metastases;
— neurotropism;
- desmoplasia;
— assessment of resection margins for the presence of tumor cells
Molecular genetic testing of the tumor for the presence of BRAF mutation is recommended starting from stage III. Determination of BRAF V600 mutations in tumor tissue should only be performed in certified laboratories.
Prevention
In order to prevent malignancy of the tumor, it is recommended:
- Eat a complete and balanced diet.
- Avoid exposure to carcinogens.
- Avoid excessive sun exposure, especially for fair-skinned patients with a large number of moles on the body, use sunscreen.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Avoid drying out the skin.
- Avoid injury, especially chronic injury, to moles.
It is recommended to regularly examine skin formations for changes: pain, itching, cracks, bleeding. If any are detected, you should contact an oncodermatologist. Melanoform nevi that appear in a person 30-40 years of age or older should be monitored especially closely.
About intradermal nevus, as well as when to remove moles
Moles or “nevi,” which were once considered a piquant decoration, are more of a cause for concern in the modern world. It’s no longer a secret that they can be malignant or degenerate from benign to malignant. Therefore, the appearance of new moles on the body often causes not joy, but anxiety, and serves as a reason to consult a doctor. However, there is no need to worry about every mole you have! Today we will talk about which moles are best removed and which ones should not cause concern.
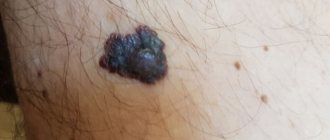
In the illustration for this article you see an intradermal nevus , which with age went deeper into the thickness of the skin and grew slowly, slowly. Its upper part was voluminous, and in this case, it was injured: because of this, the contours of the birthmark “floated”. We removed this nevus, sent it for histology (everything is fine), and now in place of the mole there is an almost imperceptible small scar.
Intradermal nevus is a benign skin neoplasm that occurs as a result of impaired development of melanocytes (cells that synthesize melanin and give color to the skin) when they penetrate into the deep layer of the skin. It is a common form of melancytic nevus. The shape of the mole is hemispherical, reminiscent of a wart or papule, with an average diameter of about 1 cm. The color can range from brownish to almost black. Most often develops during puberty. It is often located on the neck or head, less often on the torso.
Is intradermal nevus dangerous? This type of nevus rarely degenerates into melanoma and is not dangerous in itself. But just like with other moles, if your neoplasm begins to change, grow quickly, or cause discomfort (itching, pain, etc.), then you should consult a doctor and get diagnosed . Also, nevi located in areas of frequent trauma (in places where they are touched by clothing, a comb, jewelry, foreign objects, etc.) can become inflamed and lead to unpleasant consequences.
It is worth removing a mole if:
- The nevus is exposed to frequent mechanical stress, there is a risk of inflammation
- For aesthetic reasons (located in prominent places), i.e. cause psychological discomfort
- It has been established that the nevus is malignant
In other cases, if the mole does not cause concern or any discomfort, then it is not necessary to remove it . But do not forget that people at risk are those who:
- A large number of moles (more than 20)
- Bright skin
- Congenital giant pigmented nevus (a quarter of these children subsequently develop melonoma)
Therefore, do not forget to be examined by a dermatologist once a year! To make an appointment with the dermatologist of the Eurolaser clinics, Suleiman Louise-Michel, call +7 (495) 613-22-05. Clinic address: Moscow, st. Novaya Bashilovka, 3 (passage metro station Dynamo).