The body reacts to environmental stimuli in completely different ways. The ambiguity and variety of effects can even confuse a person.
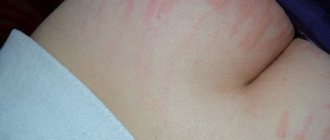
Urticaria is a large group of allergic diseases with similar symptoms. It is not contagious and affects a significant part of the world's population. Characterized by spontaneous eruption of blisters, redness, or angioedema1. symptoms of allergic urticaria and causes
Urticaria appears quickly and clearly, so it can be diagnosed using the following parameters:
- at the first manifestation of an allergy, the skin becomes blistered;
- the rash is accompanied by burning and itching;
- Externally, the affected area of the epithelium looks as if it were a burn from contact with nettles, hence the name.
The mechanism of allergy development is based on immediate hypersensitivity. Upon repeated contact with even a small dose of the allergen, the response appears quickly.
Experts identify several of the most common causes of the disease:
- stress;
- infections;
- use of medications;
- parasitic infestations;
- insect bites;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- ultra-violet rays;
- flower pollen;
- dust indoors and outdoors;
- some types of sweets;
- citrus.
There are two main types of illness:
- urticaria of an immune nature;
- non-immune urticaria.
In the acute form, fever always has an immunological basis for the manifestation of rashes. The chronic form is different and has a wider list of activation mechanisms:
- exogenous factors (influence of processes from outside);
- endogenous factors (the influence of processes occurring inside the body).
Food provocateurs, along with drugs and temperature, are considered exogenous factors. The second group is diseases of a somatic nature and associated with various internal pathological processes. These include:
- gout (a chronic disease characterized by metabolic disorders of certain substances);
- diabetes;
- lupus erythematosus;
- chronic cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder, which is characterized by a violation of its motor function, accompanied by changes in the physical and chemical properties of bile);
- pancreatitis (inflammatory processes in the pancreas), etc.2,3
The rapid spread of an itchy rash, which occurs at the slightest interaction with the substance that caused the allergy, is characteristic of acute urticaria. Externally, the rash looks like many bubbles of different sizes with a clear border of bright color. The rash is often local in nature. The rashes are concentrated on the skin, but there are cases when they appear on the mucous membranes. As usual, symptoms that appear up to 6 weeks characterize spontaneous urticaria; if the blisters do not go away for more than 6 weeks, we are talking about a chronic form of the disease4.
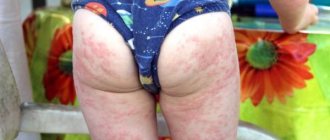
The recurrent (chronic) form of urticaria is an allergic-type disease, which is characterized by the appearance of a rash in the form of papules and itchy blisters. This allergic reaction lasts over 6 weeks. Occurs in 25% of patients. After a long period of remission, repeated manifestations of the rash are possible. Such symptoms are more common in women.
There are two types of chronic urticaria:
- persistent - there is a constant renewal of the rash;
- recurrent – periodic exacerbations of the disease occur.
Pseudo-form is a symptom indicating disorders in the digestive system. It appears when:
- hepatitis;
- helminthiasis;
- chronic gastritis;
- poisoning;
- infectious diseases.
However, there is no relationship between the immune system and the appearance of the pseudo-form5.
Causes
The main causes of allergic reactions on the hands:
- Hereditary predisposition. Characteristic of neurodermatitis, eczema, and other allergic dermatoses. If both parents have allergic diseases, the risk of developing neurodermatitis in a child is 70%2.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Biliary dyskinesia, chronic gastritis, and disruption of the pancreas can contribute to the development of allergies and their transition to a chronic form.
- Impaired skin barrier function.
- Regulation disorders of the central nervous system.
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
Allergy is a multifactorial disease that requires complex treatment. In some cases, it is not possible to determine the exact cause of the disease.
Allergic urticaria: recommendations to avoid
If the allergy trigger for hives is known, patients should avoid exposure to it as much as possible.
If you know that you are susceptible to spontaneous allergy symptoms due to hives, follow these guidelines:
- abstain from alcohol or reduce its consumption;
- do not prescribe any medications for yourself;
- avoid stress as much as possible;
- use anti-allergenic soaps, skin creams and cleansers;
- Avoid foods that trigger the production of histamine (they are listed in the “Causes of urticaria” section).
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
Atopic dermatitis
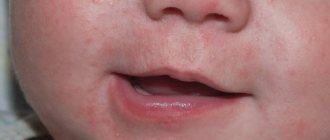
Neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that first appears in early childhood. Neurodermatitis on the hands is accompanied by severe itching, which can interfere with sleep at night. Rashes can occur on the scalp, face, neck, upper and lower extremities. Visually, during the acute period of the disease, redness, swelling of the skin, itchy spots of various shapes and sizes, exudation with subsequent formation of crusts are noted. When transitioning to the chronic stage, the skin becomes dry, flaky, and areas of thickening of the skin appear with an intensification of the skin pattern.
There are three age periods of atopic dermatitis:
- infant (up to 2 years);
- children (from 2 to 13 years);
- teenage and adult (13 years and older).
The disease lasts a long time, and other allergic diseases (seasonal rhinitis, bronchial asthma) may occur. In adolescents, rashes may be accompanied by symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia (weakness, mood swings, headaches, discomfort in the heart area).
Hives
An allergic rash on the hands of an adult can be a symptom of urticaria. Urticaria is characterized by redness, swelling of the skin, and the appearance of itchy blisters. Local edema develops due to increased vascular permeability upon contact with allergens. The rash is accompanied by intense itching and can appear on any area of the skin. Symptoms of acute urticaria completely disappear within a day (usually a few hours after stopping contact with the allergen).
Forms of the disease:
- Immunological urticaria (the development is based on a hypersensitivity reaction).
- Physical urticaria (reaction to high or low temperatures, sun, pressure, other physical factors).
- Drug-induced urticaria.
- Idiopathic urticaria (when the cause of the rash cannot be determined)3.
A dangerous complication of the disease is angioedema. It is accompanied by swelling of the deep layers of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, submucosal layer of the upper respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, and urogenital tract3. When the first signs of Quincke's edema appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Drug allergy
Signs of allergies on the body can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
The most common pharmacological substance that causes allergies is penicillin.
Other triggers that may cause reactions (that are not related to IgE antibodies) include the following:
- Sulfate preparations
- Anticonvulsants
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Some types of food coloring (usually red and yellow)
- Chemotherapy drugs
Clinical signs of allergic reactions may be accompanied by mild itching of the skin, redness, and rash.
When identifying allergies to certain medications, it is important not to confuse them with side effects.
They may be accompanied by hives, rashes, and stomach upset.
Particular attention should be paid to cases where drug allergies on the body develop in pregnant women.
It is necessary to stop signs of the reaction as soon as possible.
Allergists often make a diagnosis based only on medical history and associated symptoms.
This is what in practice is called a “clinical diagnosis”.
In many cases, patients may have an allergic reaction when taking multiple medications at the same time.
In these cases, if the doctor cannot identify the true allergen, a comprehensive examination is additionally prescribed.
During the diagnostic process, your doctor will recommend stopping all medications.
Contact dermatitis
A common allergic skin disease that occurs due to skin contact with allergens. It can occur in acute or chronic form. During an exacerbation, it manifests itself as redness of the skin and the formation of itchy blisters. In the chronic version, the skin becomes dry and the skin pattern intensifies2.
Allergens that can cause rashes include:
- metals (nickel, cobalt, chromium, aluminum);
- rubber and rubber products (balloons, latex gloves, condoms);
- cosmetics and perfumes (containing flavors, stabilizers, preservatives);
- local medications (anaesthetics, glucocorticosteroids, antibiotic ointments);
- Hair Dye;
- synthetic glue, adhesives;
- plants (primrose, poison ivy and others).
The development of dermatosis can occur through allergic or non-allergic pathways (irritant contact dermatitis). It is important to identify the substance causing the rash in time and avoid contact with it.
Dangerous symptoms of an allergic reaction on the body
The most dangerous symptoms and complications of an allergic reaction are Quincke's edema and Lyell's syndrome.
Quincke's edema is a skin reaction characterized by rapid swelling of the skin involving the mucous membrane.
Edema is often accompanied by swelling of the tongue and larynx, which can be life-threatening.
Quincke's edema got its name thanks to the doctor who first described this clinical sign in 1882.
In allergology, the symptom is found under the medical term angioedema or angioedema.
Doctors distinguish two forms of angioedema:
- Histamine-mediated angioedema. This form includes allergic angioedema and drug-induced angioedema.
- Angioedema due to hereditary C1 inhibitor deficiency (HAE). The C1 inhibitor is a protein in the blood that aims to protect the body from angioedema. In addition, there is also angioedema due to acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency (AAE).
In most cases, angioedema is a symptom of a severe allergic reaction.
Requires immediate medical attention.
Allergic angioedema can be treated with anti-inflammatory drugs.
For example, a doctor may give intravenous cortisone, epinephrine, antihistamines (anti-allergy medications), sodium thiosulfate, and calcium gluconate to quickly relieve symptoms.
As a result of swelling of the tongue, eyelids, lips and larynx, various complications can occur.
The root of a swollen tongue, expanding, narrows the airways, which threatens asphyxia.
Lyell's syndrome is the most severe form of allergic dermatitis and is also known as toxic epidermal necrolysis.
They are characterized by the appearance of blisters, followed by their opening and the formation of erosive lesions of the skin epithelium. More than 30% of the body surface area may be affected.
As a rule, it is a consequence of exposure to certain groups of medications, most often antibiotics and NSAIDs.
If such a symptom develops, patients should be hospitalized in the intensive care unit or burn department.
The mortality rate for Leila syndrome reaches 20-25%, sometimes reaching 50%.
Eczema
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by the appearance of a polymorphic rash and severe itching. True eczema is manifested by redness and limited swelling of the skin, on which small blisters appear filled with transparent contents2. After opening the bubbles, erosions remain, which eventually become covered with crusts. In the chronic form of the disease, the skin thickens. The rashes are symmetrical, most often occurring on the upper, lower extremities and torso.
Cetrin for hand allergies
Cetrin is a second generation antihistamine whose active ingredient is cetirizine hydrochloride. It blocks H1-histamine receptors, helping to reduce swelling, redness, and itching of the skin. Cetrin is used for the following diseases: hay fever, urticaria, neurodermatitis, allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis.
Advantages of the product:
- The effect of use and relief of symptoms begins 20 minutes after taking the tablet.
- Convenient method of use (one tablet is enough to maintain the effect for 24 hours4).
- Suitable for long-term treatment, non-addictive.
- Practically does not cause drowsiness5.
- Eliminates symptoms regardless of the factor that caused the allergy.
Cetrin can be taken regardless of meals; the therapeutic effect lasts for three days after the end of the course of treatment4.
Treatment of an allergic reaction on the body
Most cases of allergic reactions can be successfully treated with antihistamines.
Antihistamines are the first choice for mild to moderate symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Drugs are prescribed if the patient has the following symptoms:
- Allergic rhinitis (runny nose), hay fever, lacrimation, redness of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
- Hives, which is accompanied by itching and the formation of bright spots on the skin.
- Angioedema (swelling of the dermis and/or swelling of the mucous membrane).
- Drug allergies that appear within an hour.
- With severe itching, a sign of eczema, dermatitis and other inflammatory skin reactions.
Antihistamines can be used locally (nasal spray, eye drops, ointments) and orally in tablet form.
Separately, antihistamines for intravenous administration, as well as hormonal creams and ointments, can be prescribed.
Dermatologists usually recommend using antihistamines in tablet form.
Because they are more effective than topical creams or cooling gels.
As a rule, one dose of the drug is enough to relieve signs of allergies on the body in the form of urticaria or dermatitis.
However, in the case of tablets (and other systemic forms of administration, such as injections or infusions), side effects such as fatigue and drowsiness cannot be ruled out.
Nowadays they more often resort to the use of non-selective second generation antihistamines.
They are better tolerated and have a smaller range of adverse reactions.
Glucocorticoid hormones from the adrenal cortex (cortisone) may also be prescribed.
Medicines containing cortisone are primarily prescribed and used when antihistamines do not satisfactorily relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction.
For example, with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and bronchi.
Therapeutic effectiveness from cortisol medications is usually observed within 24-48 hours.
Literature:
- Werfel T., Breuer K., Rueff F et. Al. Usefulness of specific immunotherapy in patients with atopic dermatitis and allergic sensitization to house dust mites: a multi-centre, randomized, dose-response study. Allergy, 2006. - V. 61. - Issue 2. - P. 202-205.
- Clinical allergology. Guide for practicing doctors / ed. R.M. Khaitova. - M., 2002. - 624 p.
- Russian national conciliation document. Urticaria and angioedema. Recommendations for practicing physicians. — Ed. I.S. Gushchina, N.I. Ilyina. - M.: Farmarus Print Media, 2007. - 128 p.
- Instructions for medical use of the drug Cetrin®.
- Kareva E.N. Choosing an antihistamine: a pharmacologist’s view // RMJ. 2016. No. 12. pp. 811–816.