Due to their anatomical structure, the male genital organs are exposed to constant contact with the environment, which increases the risk of infection and spread of infection. Redness on the head and foreskin is a fairly common phenomenon and occurs in every tenth man. An unpleasant disease is called balanoposthitis and can appear at any age and has various causes.
Despite its apparent harmlessness, it can lead to very serious and dangerous consequences. An infection or fungus can cause a serious illness that requires long-term and expensive treatment if you do not seek medical help in time.
What are the causes of the disease, how is it treated and are there any preventive measures, explains urologist-andrologist Alexander Anatolyevich Tsybulin.
Phimosis, narrowing of the foreskin
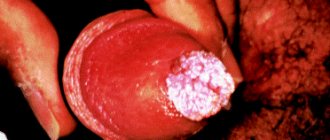
Phimosis is a terrible disease. A predisposing factor in the development of posthitis is congenital or acquired narrowing of the opening of the foreskin - phimosis . With a disease such as diabetes mellitus, or in the elderly and elderly, phimosis of the penis can develop even with regular high-quality washing of the glans. With balanitis, the foreskin is hyperemic and swollen, erosions and purulent plaque appear on its inner surface and head, a guy or a man is bothered by itching and pain when trying to have sexual intercourse. Sometimes the head is not exposed , the penis swells, becomes hyperemic, redness is noted, and lymphadenitis of the inguinal lymph nodes appears. A severe complication of phimosis is gangrene of the penis , which can result in complete tissue necrosis. The man is left without a penis. And this is already a difficult situation!
Treatment
Treatment of diseases accompanied by itching of the penis is conservative in the vast majority of cases. Corticosteroids and antihistamines are used to relieve itching. The list of other treatment measures depends on the type of pathology:
- Balanitis and balanoposthitis.
The patient is advised to strictly follow the rules of hygiene. Taking into account the nature of the pathogen, antibacterial, antifungal or antiviral agents of general and local action are prescribed. Antiseptic irrigation is used. - Dermatitis.
For common processes, detoxification therapy is carried out. Hormonal ointments are applied locally, the wet areas are treated with antiseptics, infusion of oak bark or chamomile. Pustules and vesicles are opened, the exposed surfaces are dried with aniline dyes. For severe itching, it is recommended to take sedatives. - Scabies.
Treatment of the entire body with special emulsions, creams or sprays is indicated in accordance with the established scheme. Then the underwear is changed, and after 2 days the course is repeated. After completion of treatment, clothing and furniture are wiped with an antiseptic or irradiated with a UV lamp.
Surgical interventions are required for patients with complicated balanoposthitis. For cicatricial phimosis, circumcision is performed. If there is a predisposing factor in the form of narrowing of the foreskin, preputioplasty may be recommended. With the development of precancerous and cancerous diseases, the scope of the operation is determined individually.
Postitis symptoms, signs in boys, guys and men
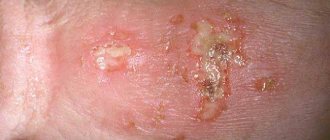
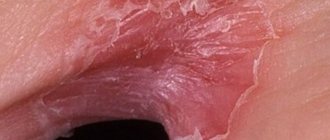
What are the main symptoms and signs of posthitis in men and boys? Which posthitis clinic ? Itching of the glans penis . Burning sensation on the head of the penis . Pain in the head of the penis. Swelling, redness of the head of the penis. Pain, pain, discomfort during sex in the area of the head of the penis. Difficulty opening the head. Decreased sensitivity of the head. Weakening of erection. Cracks in the foreskin. Ulcers and ulcers on the head.
How to treat?
Prevention of the disease is the best way to avoid serious consequences. And a significant role in this belongs to compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
If you notice the first signs, it is important to immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe the correct treatment. A paid urologist will conduct an examination and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The private medical clinic “Doctor Anna” has all the necessary equipment to diagnose the disease and invites you to undergo an examination. Experienced specialists will diagnose, identify the causes of the disease and select an effective course of therapy.
Redness on the glans, glans in men, boys and itching of the foreskin
If you notice severe redness on the glans , slight redness of the glans in men and boys, incomprehensible redness of the head of the penis , noticeable redness of the head of the penis, redness on the glans and itching of the foreskin, redness around the head of the skin of the head of the penis, redness on the head of the penis, near the glans, under the head, on the head of a child boy, child, redness of the tip of the head after sex, white coating, slight redness, flaking of the head, under the head of the penis, around the head of the penis, edge of the head, skin, redness and dryness, rash, itching, burning, call doctor so that he can prescribe effective treatment.
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Shmeljov | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Balanitis, treatment of balanitis in Saratov, how to treat balanitis
Testicular orchitis, testicular inflammation, orchitis treatment
Epididymitis, acute, chronic: treatment, how to treat inflammation of the epididymis, pain in the testicles
Urethritis, treatment of urethritis, inflammation of the urethra
Cystitis, symptoms, treatment of cystitis in Saratov
Comments ()
Why does the penis itch?
Physiological reasons
The symptom develops briefly in connection with certain external influences. The manifestations do not reach a level requiring contact with a specialist and quickly disappear when the provoking factor is eliminated. Penis itching can occur in the following situations:
- Failure to maintain intimate hygiene.
Infrequent hygiene procedures and irregular changes of linen lead to the accumulation of dirt and irritation of the skin. Unpleasant sensations are especially disturbing after sexual intercourse, since seminal fluid remains on the penis. - Irrational choice of linen.
Underwear made from synthetic fabrics or too thick impedes heat transfer in the intimate area, causes discomfort and increased sweating, followed by itching and burning. - Mechanical impact.
Sexual intercourse with insufficient lubrication from the partner can lead to poor penile glide, excessive friction and skin irritation. Along with itching, quickly disappearing local hyperemia is often observed. - Stressful situations.
Psychogenic itching does not have an organic basis, occurs during nervous tension and intense experiences, and is not accompanied by external changes.
Inflammatory processes
The most common cause of itching in the penis area is considered to be balanitis and balanoposthitis of various etiologies. The pathology is nonspecific or is provoked by specific pathogens. May be observed with the following STIs:
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- chlamydia.
In addition, fungi and viruses act as sexually transmitted infectious agents. Balanitis is manifested by itching, pain, swelling and redness of the head, the appearance of plaque, plaques and ulcerations, problems with urination and erectile function. With balanoposthitis, swelling and accumulation of secretions in the preputial sac are added to the listed symptoms. The clinical picture depends on the nature of the pathogen and the characteristics of the process:
- Catarrhal form.
More often observed with nonspecific inflammation, occurs with STIs. The most favorable variant of the disease, accompanied by the most vivid subjective manifestations. Patients complain of intense pain, excruciating itching, and a burning sensation during urination. - Urogenital candidiasis.
Patients are bothered by burning and itching in the head area. The coronary groove, head and inner layer of the foreskin are swollen, inflamed, hyperemic, covered with whitish films. Possible erosion. The discharge is whitish, with the smell of kefir. Urination is normal. - Genital herpes.
Transparent bubbles appear in the affected area. After some time, the rashes become cloudy, open, and brownish crusts form in their place. General hyperthermia, regional lymphadenitis, and quite severe pain are possible.
Along with infectious lesions, inflammation and itching of the head can be non-infectious in nature and develop with diabetes mellitus, urological diseases and some other pathologies. A special form is xerotic balanitis obliterans, which often occurs in older people. Itching is moderate. Areas of atrophy, blisters and spots form on the inner leaf and head, which subsequently transform into sclerotic plaques.
Itching of the penis
Dermatitis
Itching of the penis is accompanied by dermatitis of the corresponding localization:
- Atopic dermatitis.
It most often occurs in childhood, but can also manifest itself in old age. Pale pink lesions with increased dryness and roughening of the skin, cracks, papules, and peeling appear on the face, neck, in the folds of the skin, on the flexor surfaces of the joints and in the groin area. The penis is not a typical location, but it can be affected. The pathology is often complicated by secondary infection with the formation of balanitis. - Simple contact dermatitis.
Develops under the direct action of irritating substances (cosmetics, powder residues on linen). Itching and pain are not intense. The skin is dry, sometimes with cracks. It is possible to form bullae with their subsequent opening and formation of erosions. With constant contact with the irritant and the occurrence of chronic dermatitis, the symptoms are smoothed out, there is little or no itching. - Allergic contact dermatitis.
It is observed in case of an allergic reaction to washing powders, care products, synthetics, and clothing dyes. In the acute form, the affected area has clear boundaries and corresponds to skin contact with the allergen. Against the background of severe itching, swelling and hyperemia, papules appear, which quickly transform into blisters, open and heal with the formation of crusts. With chronicity, changes spread beyond the contact area. Scratching occurs due to constant itching. - Orthogenic contact eczema.
It is detected in men who abuse hygiene procedures and use irritating care products. Itching and discomfort in the projection of the penis are complemented by erythema and the formation of scabs. With prolonged exposure, lichenification and hyperkeratosis may develop.
Scabies
Typical localizations of itching and rashes due to scabies are the abdomen, the anterior inner thighs, interdigital folds, and the lateral surfaces of the fingers. In men, the scrotum and penis may be involved in the pathological process. Upon examination, traces of scratching and scabies are found in the form of lines 5-7 mm long with a vesicle or papule at the end.
Other dermatological pathologies
In the listed diseases, damage to the skin of the penis is not a specific symptom, but one of the possible (and often not the most common) localizations:
- Psoriasis.
A single lesion in the penis area is found extremely rarely; changes in several zones are more common. Small psoriatic plaques and papules are detected on the skin of the penis, accompanied by mild itching. Bright red plaques are often detected in the groin, axillary areas, and other places. - Lichen planus.
Characterized by intense itching and possible burning. The skin changes appear as small, smooth, purple bumps that often spread from the periphery to the center. The rash may also appear on the ankles and wrists. After resolution, areas of hyperpigmentation remain. - Lichen scleroderma.
A rare disease. Uncircumcised men of mature age are more often affected. As a rule, the head is involved in the process, often with a transition to the foreskin. Flat white papules transform over time into sclerotic and atrophic plaques. Itching, burning, and difficulty urinating are noted. Bleeding is possible.
Consultation with a urologist
A comprehensive examination by a urologist/sexologist includes:
- Inspection (palpation);
- Hardware diagnostics: ultrasound of the prostate gland;
- Ultrasound of the bladder;
- Doppler examination of blood vessels (Dopplerography);
If the doctor deems it necessary, the following may also be prescribed:
- Additional laboratory tests (blood tests, urine tests, prostate secretions, spermogram);
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Needle biopsy;
- X-ray;
- Scintigraphy;
- Urethroscopy;
- Cystoscopy.
What tests should I take if I suspect chlamydia?
Chlamydia trachomatis has some complications because the pathogen is intracellular.
It is difficult to culture and serological tests will not provide meaningful results.
Thus, chlamydia culture and ELISA will indicate the presence of chlamydia with an accuracy of only 60-70%.
The only informative method that can detect infection with 100% accuracy is PCR.
Chlamydia in men can be effectively treated with antibiotics.
The most common treatment consists of Azithromycin therapy.
Patients who have been infected through anal intercourse are prescribed Doxycycline.
The drugs are taken daily for 5-7 days.
Possible side effects of treatment: nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
In case of infection with chlamydia, treatment is also prescribed to the sexual partner.
During the entire course of therapy, it is recommended to abstain from intimacy.
What is the most effective prevention of chlamydia?
There is only one truly effective preventive measure.
This includes regular condom use and annual STI testing.