Like other parts of the body, there are sebaceous glands called Tyson glands on the head of the penis and the inside of the foreskin.
They produce a thick secretion - spegma - the purpose of which is to protect the penis from friction against the foreskin or other damage. Normally, this lubricant has a milky color, but some physiological reasons or pathological processes can provoke a change in its consistency and the formation of a white coating on the head of the penis.
Attempting to cope with this problem on your own is dangerous and can lead to the development of serious complications. Therefore, if this symptom occurs, you should immediately seek the help of a urologist.
Why does a white coating appear on the head of the penis?
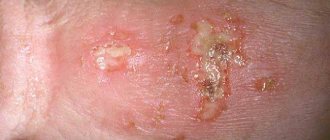
White plaque on the head of the penis may be a harmless accumulation of sebum, but microorganisms that multiply on it often provoke inflammation. The main reasons for the appearance of plaque are poor hygiene and candidiasis balanoposthitis. Sometimes this symptom accompanies more serious pathologies.
What everyone should know:
Simple tips for men's intimate hygiene.
Dermatovenerologist Sergey Gennadievich Lenkin talks about the possible reasons for the formation of white plaque on the head of the penis
Physiological reasons
The sebaceous glands of the foreskin constantly secrete smegma, an oily lubricant that protects the glans. The rate of its production depends on the amount of androgens. Smegma is secreted most intensely from the beginning of puberty until the age of 20-22. In older men, almost no smegma plaque forms on the head.
Photo of smegma around the head - https://prntscr.com/y5pvy5.
Fresh smegma is white. As bacteria multiply, the plaque acquires a yellowish or greenish tint, as well as an unpleasant odor. To avoid the development of inflammation, it is necessary to wash the head and fold of the foreskin 2 times a day. “Baby soap” will help completely remove greasy plaque.
Pathologies
White plaque on the head may be a sign of inflammation. Pathologies can be recognized by additional symptoms. Below are the main ones.
Candidiasis
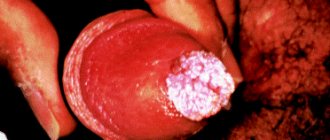
Candidiasis (thrush) is diagnosed with increased activity of the candida fungus. It is part of the normal flora, but in healthy people it does not reproduce, but is in a frozen state. When immunity decreases or due to stress, the fungus becomes active. A large colony of the pathogen can enter the body after sexual contact with an infected partner. A strong immune system will cope with the invasion, a weakened one will not.
White plaque with invasive candidiasis - https://prntscr.com/y5qcvl.
Photo of candida fungus under a microscope
First symptoms:
- Redness and swelling of the head.
- Itching.
- Small cracks, glossy shine of the affected area.
As Candida penetrates the epithelium, a white coating appears on the head and foreskin. When it is removed, erosions open, as in the photo - a red penis against the background of acute candidiasis.
Diabetes
Diabetic balanoposthitis is chronic. Increased sugar in the urine provokes constant irritation of the epithelium of the head and foreskin. As a result, the protective barrier weakens, and infections begin to actively multiply. Most often it is candida, which creates a white coating on the head.
Clinical features of diabetic candidiasis:
- The head and inner part of the foreskin are bright red.
- Characterized by mild bleeding, small ulcers covered with a yellowish coating.
- Frequent sharp relapses after treatment.
Diabetic balanoposthitis often provokes thinning, atrophy of the foreskin and the subsequent development of phimosis.
See also: All about the treatment of balanoposthitis in men.
Phimosis
Phimosis is a pathological narrowing of the foreskin, due to which it is impossible to fully open the head and wash out the accumulated smegma. In the stagnant secretion, bacteria multiply, causing inflammation of the head and foreskin. The result is redness, plaque, and an unpleasant odor.
Phimosis – https://prntscr.com/y5qqxu.
Genital herpes
The herpes virus, once in the body, periodically manifests itself as painful itchy rashes. First, a small lump is felt, which is both painful and itchy. Then a scattering of watery bubbles appears. After 2-3 days they burst, leaving ulcers that become infected and cause plaque to appear. A separate article is devoted to genital herpes in men.
- Herpes on the head of the penis: after opening the blisters, the foreskin and head became inflamed - https://prntscr.com/y5r8ip.
- Herpetic ulcerations and plaque on the head of the penis - https://prntscr.com/y5r9mv.
- Herpes on the shaft of the penis - https://prntscr.com/y5rbbq.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an inflammatory disease caused by gonococci. It is transmitted mainly through sexual contact. Main signs: white discharge and sharp pain after urination. With severe inflammation, drops of blood may appear from the urethra. The spread of white discharge on the head of the penis looks like plaque.
- Plaque and discharge from gonorrhea - https://prntscr.com/y5rhso.
- The chronic form of gonorrhea is characterized by sticking of the urethral sponges in the morning - https://prntscr.com/y5riy8.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is transmitted sexually, but can exist for a long time asymptomatically. Inflammation usually begins against a background of reduced immunity.
Symptoms:
- A small reddish rash on the head (in the circinar form).
- Discharge from the urethra.
- Pain during urination and ejaculation.
- Swelling of the urethral sponges.
Photo:
- Chlamydia discharge - https://prntscr.com/y5rvfe.
- Head lesion – https://prntscr.com/y5s6ot.
Urologist Sergei Gennadievich Lenkin learn more about the symptoms of chlamydia in men
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin. On the penis it occurs due to chafing, allergies to lubricants and medications, as well as infection. If, after using a condom or lubricant, the foreskin is swollen and the head becomes red, then an allergic reaction is obvious. Infections can easily take root in damaged skin. A decrease in local immunity provokes the development of candida and the appearance of plaque on the head.
Lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus, also known as lichen, lichen sclerosus is a chronic dermatosis, the exact causes of which are unknown. There is a version that the pathology occurs against the background of diseases of the endocrine, nervous, and immune systems. In men suffering from lichen, increased levels of androsterone and testosterone are recorded in the blood, and the amount of dihydrotestosterone is reduced. This indicates a deficiency or inactivity of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which is responsible for the transformation of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone. The disease affects men aged 35-40 years.
Provoking factors:
- Frequent allergies.
- Mechanical damage.
- Diabetes.
- Disorders of metabolic processes in the genital area.
Lichen can be caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which is carried by ixodid ticks. The infected person develops Lyme borreliosis.
Lichen sclerosus - https://prntscr.com/y5seqq.
The formation of plaque is preceded by thickening of the skin, a decrease in its elasticity, and the appearance of small gray nodules - scars from atrophied tissue. The latter gradually merge, forming light foci of atrophied skin, and the effect of a dry head occurs. They itch, hurt during sex, and when peeled off, erosions are exposed. When an infection occurs, inflammation occurs. Lichen is fraught with scarring and tissue deformation.
Dermatovenereologist, urologist-andrologist Evgeniy Aleksandrovich Volokhov tells what lichen sclerosus is and what symptoms it manifests
Syphilis
Syphilis is a tissue infection caused by Treponema pallidum. At the site of entry of the pathogen under the skin of the head, a compaction appears, which soon transforms into a purulent ulcer - syphiloma.
Primary syphilomas on the head and foreskin - https://prntscr.com/y5rl1p.
Syphilomas can be complicated by the addition of an additional infection. Complicated syphilomas, which are a source of white purulent plaque - https://prntscr.com/y5rrhl.
Read more about the symptoms and treatment of syphilis in men.
Keir's disease
Keir's erythroplasia is a rare precancerous lesion of the mucous membrane that can transform into squamous cell carcinoma. Occurs on the head of the penis in older men. Provoking factors: chronic balanoposthitis, frequent injuries, ultraviolet radiation, exposure to arsenic, tar, tar, infection by human papillomavirus types 33, 45, 35, 31, 18, 16 (more about HPV in men).
A characteristic feature is a single bright red, unevenly outlined spot. The surface is moist, velvety or shiny. There may be minor pain, which occurs mainly when the lesion is touched. The head of the penis becomes covered with a grayish coating, which is easily removed.
Keir's erythroplasia on the edge and under the head of the penis - https://prntscr.com/y5siz3.
Dermatovenerologist Lenkin Sergey Gennadievich tells more about Keir's disease
Normal discharge
Normally, discharge from the male genital organ appears during an erection and is characterized by a clear secretion. In medicine, the condition is called physiological urethrorrhea, and appears due to the work of the urethral glands during arousal. Other manifestations may be normal:
- A whitish odor of spermine with a viscous structure is a secretion of the prostate.
- The gray-white secretion with a mucous texture is ejaculate.
- Thick white lubricant, which after time changes to green or yellow - smegma from the preputial glands. It is constantly secreted and accumulates on the head of the penis, consists of bacteria and fats, the problem most often appears in young men of puberty. Accumulation occurs due to insufficient hygiene. A change in shade indicates the process of decay, after which an unpleasant odor appears. This phenomenon can cause inflammation and risks of tumor development.
- A small amount of transparent mucus with grayish inclusions is prostatorrhea. Appears as a result of tension in the abdominal muscles.
If a secretion develops that is white, green, yellow or foamy, then a pathological process or inflammation is occurring in the body, and the color, smell and consistency will indicate an infection.
More often than not, an unusual secretion indicates sexually transmitted diseases or sexually transmitted infections. After infection, the incubation period is about 4-15 days, and additional symptoms may include itching, burning or redness of the glans. If the infection moves to the urethra, pain begins, disruption of urine outflow occurs, and the frequency of urination increases.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact: a dermatologist, urologist.
At least 3 days before visiting a doctor, you do not need to smear your penis with antibacterial ointments, take baths or treat it with antiseptics. You should also not take broad-spectrum antibiotics. All this will distort the test results. It is also not recommended to urinate 1.5 hours before taking a smear. During your consultation with a doctor, you must tell about all the medications you are taking, possible injuries to the groin area, chronic diseases, and allergic reactions.
Diagnostic methods:
- Plaque scraping for fungal analysis. Antifungal agents cannot be prescribed without analysis. Inflammation may worsen and become chronic.
- Urethral swab.
- Analysis of biomaterial using PCR methods using bacterial culture.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Blood test for Borrelia burgdorferi, syphilis.
- Allergy tests.
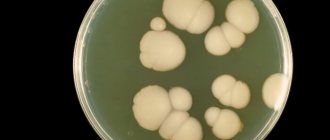
Colonies of Candida fungus as a result of bacterial culture
If a cancerous lesion is suspected, a part of the epithelium is taken for cellular analysis. Often this study is prescribed only after classical anti-inflammatory therapy has not produced positive dynamics. Pigmented erythraplasia of Queyrat may be similar in appearance to the following lesions of the glans penis:
- Seborrheic keratosis.
- Solar lentigo.
- Melanocytic nevus.
- Basal cell carcinoma.
The doctor should differentiate the usual form of erythroplasia from psoriasis, candidiasis, lichen planus, and xerotic balanoposthitis obliterans.
How to treat
If the head is covered with a white coating, and a lot of cheesy lumps have accumulated under the foreskin, then the reason is poor hygiene. It's easy to get rid of excess smegma. To do this, just wash your penis with a delicate cleanser in the morning and evening. If the glans becomes red, you need to completely retract the foreskin 2-3 times a day and treat it with miramistine or chlorhexidine.
Pills
Table 1. Tablets to eliminate various causes of plaque on the head
| Pathology | Name of the drug |
| Candidiasis | Antifungal: Fluconazole, Flucostat. Polyene antibiotics: Nystatin, Pimafucin. |
| Chlamydia | Doxycycline, azithromycin. |
| Syphilis | Penicillin preparations: “Retarpen”, “Extencillin”, “Bicillin-1”, combined “Bicillin-3”, “Bicillin-5”. |
| Herpes | Acyclovir |
| Gonorrhea | "Ciprofloxacin", "Tsiprolet". |
For reactive inflammation of the head caused by urethritis, tablets are prescribed according to the results of a smear analysis.
Ointments
Ointments are prescribed in cases where plaque on the head is caused by an infection that has not yet penetrated the blood. External agents are also used as adjuvant therapy to relieve inflammation.
Table 2. Ointments prescribed to eliminate the causes of white plaque on the head
| Pathology | Ointment |
| Candidiasis | "Clotrimazole", "Itraconazole", "Pimafucin". Combined ointments: “Clomegel”, “Metrogil plus”. |
| Allergic dermatitis, inflammation | “La-Cri”, “Zinc ointment”, “Advantan”, “Hydrocortisone”, “Dex-gentamicin”. |
| Erythroplasia Keira | Cytostatics: 5% Imicvomide cream, 5% 5-fluorouracil cream, prospidine ointment. Combine with corticosteroid ointments: Lokoid, Advantan, Afloderm. |
| Lichen sclerosus | Steroid drugs, ointments with 0.1% tacrolimus. |
| Ulcerative lesions, peeling | "Solcoseryl" |
| Balanoposthitis | "Levomekol", tetracycline ointment. |
| Herpes | "Acyclovir", "Zovirax" |
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is used in cases where conservative therapy does not produce positive dynamics.
Table 3. Surgical methods to eliminate the causes of plaque on the glans
| Pathology | Type of intervention |
| Chronic candidiasis balanoposthitis against the background of diabetes mellitus and other systemic diseases, phimosis | Circumcision. The doctor excises the skin of the foreskin and stitches the remainder around the glans. |
| Penile cancer, Queyra's erythroplasia | Excision of the lesion with a laser (ablation) or burning out using the cryodestruction method + local therapy described above and intravenous infusion of bleomycin (chemotherapy). |
| Lichen sclerosus | Surgical intervention in the form of urethroplasty is used in cases where the lesion prevents urination. |
At home
Home recipes can only be used after visiting a doctor and with his permission.
For herpes, the head of the penis can be lubricated with aloe or Kalanchoe pinnate juice. It is applied to the head pre-treated with chlorhexidine 4-5 times a day.
For candidiasis, soda baths help get rid of the white film. The solution is prepared at the rate of a tablespoon of soda per liter of warm water. The procedure is carried out at night for a week. The penis is dipped for 2-3 minutes, then removed, dried and antifungal ointment is applied.
Preparation of soda solution
A good remedy for intermediate treatments, including for lichen, are baths with infusions of chamomile, oak bark, sage, and calendula. Recipe: pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of boiling water, leave until the temperature drops to 30˚C. The penis should be kept in the bath for 10-15 minutes, while it is important to move the foreskin away from the head. Repeat the procedures 2-3 times a day.
Nutrition
For any type of inflammation of the head of the penis, spicy, smoked, salty foods, and alcohol should be excluded from the menu. Compliance with a diet is also required for candidiasis.
Diet for candidiasis
Deviations from the norm
In addition to physiological discharge, which is considered normal, there are deviations. They can be easily identified by the structure of the secretion, color or smell:
- Bloody manifestations from the urethra indicate hemorrhea, a non-inflammatory disease that often develops due to trauma, for example, during a medical examination using an instrument.
- Spermatorea – the appearance of sperm without intercourse indicates a decrease in the tone of the vas deferens. The disease develops due to constant inflammation.
- White discharge in men on the head with a purulent-mucous structure is a sign of urethritis, which appears with chlamydia, mycoplasmosis and other infections. The problem is not accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, itching or stinging.
- A white foamy secretion appears during inflammation, which develops against the background of trichomoniasis. In addition, patients experience pain and burning, discomfort in the pelvic area.
- Yellow, green or brown manifestations of a thick consistency are a sign of gonorrhea. In addition, the patient has a number of other symptoms that cause discomfort.
- White or yellow mucus appears with prostatitis, inflammatory processes and other diseases occurring in the acute phase.
In addition to the described deviations, the shape of the urethral opening may change in patients, and the intensity of the transformation depends on the severity of the course and type of disease. Often the tissues swell and the color of the head changes.
Complications
Syphilis can lead to tissue necrosis of the penis and amputation. Any advanced inflammation with erosive foci can provoke deformation of the genital organ, melting and fibrosis of the cavernous bodies.
A complication of Keir's erythroplasia is the degeneration of lesions into squamous cell carcinoma. In this case, the prognosis worsens significantly.
White plaque on the head is most often caused by candida. With timely, competent therapy, the prognosis is favorable, but in an advanced form, the infection spreads throughout the body. The fungus affects the prostate, testicles and other organs. Candidal balanoposthitis often provokes thinning of the foreskin and phimosis.
Urologist and dermatovenereologist Lenkin Sergey Gennadievich explains why candidiasis is dangerous for men
Transparent discharge in men
The transparent secretion released from the urethra due to sexual arousal is a type of non-pathological discharge - libidinal urethrorrhea. The source of discharge in this case is the urethral glands. The level of the amount of such discharge varies depending on the period of sexual abstinence and on the individual physiological characteristics of each man separately. Rarely, physiological urethrorrhea occurs at the time of defecation.
This type of discharge implies the secretion of spermatozoa capable of fertilizing an egg if they enter the woman’s genital organ during coitus. Sometimes, discharge that visually resembles physiological discharge is a symptom of a disease of the genitourinary system. If the quantity or nature of discharge deviates from the norm, the man should immediately consult a doctor.
Prevention
General preventive measures:
- Maintain personal hygiene, rinsing the penis in the morning, evening and after sex, including protected sex.
- Careful handling of the foreskin during masturbation. Microcracks can lead to phimosis.
- Using a condom with untested partners for any type of sex.
- Maintaining immunity.
For frequent balanoposthitis, it is better to undergo circumcision to avoid the development of erythroplasia or cicatricial deformity.