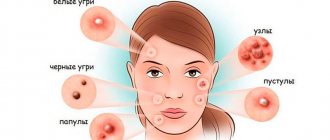
An allergy is an inadequate reaction of the immune system to various substances from the external environment - food, medications, pollen or household substances (dust, cosmetics, animal dander). The manifestations of allergic reactions are varied - these are digestive disorders, respiratory tract disorders (shortness of breath, coughing, sneezing), skin rash, itching, red eyes and lacrimation. One of the common localizations of allergic reactions is redness, swelling or rash on the face. Not only is this a pronounced cosmetic defect that attracts attention, it is also a serious threat to health, especially if it is an anaphylactic reaction - urticaria or angioedema.
Allergic manifestations on the face are especially unpleasant. They occur at the most inopportune times, can be very itchy, and lead to redness and flaking of the skin. In addition to these manifestations, swelling in the lips, severe runny nose or nasal congestion, redness of the eyes, and watery eyes are possible, which only aggravates the course of the disease. The most common triggers of facial allergies in adults are reactions to pollen and cosmetic products, and less often to food or medications.
It is important to immediately treat any skin reactions and, ideally, prevent any possible rashes or swelling by avoiding potential allergens. But why is the face the most sensitive? The thing is that the skin of the face is thinner and more sensitive, it is always open and more often comes into contact with various substances. In addition, many people use cosmetics and hygiene products, which can lead to negative reactions.
Types of facial allergies in adults
The most common types of allergic reactions in adults are:
- contact dermatitis, which occurs when various products are applied to the skin or come into contact with air or water;
- year-round allergies with skin rashes, lesions of the nasopharynx and eyes;
- seasonal allergies (hay fever) and urticaria;
- anaphylactic reactions;
- food allergies;
- reactions to medications;
- manifestations of atopic dermatitis (or eczema).
Each form has its own set of the most common allergens and typical external manifestations of reactions. Approaches to treatment, prevention and the degree of danger to well-being, general condition and even life may also differ.
Pharmacy ointments
Pharmacy ointments help remove irritation and flaking on the facial skin. The most popular means:
- Radevit. Restores skin, removes inflammation.
- Akriderm. Removes allergies, inflammation, redness, itching, and fights bacterial infections. Accelerates tissue regeneration.
- Triderm. It is a hormonal remedy that removes inflammation and allergies. Has bactericidal and antifungal effects.
- Sinaflan. An inexpensive drug for sunburn, allergies, dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis.
- Psilo-balm. Has a cooling effect. Helps with allergies, burns, insect bites.
- Gistan. Removes inflammation and itching, slows down the allergic reaction, accelerates skin restoration.
- Elidel. Most often, the product is used for atopic dermatitis. The drug eliminates inflammation and accelerates the recovery of affected areas of the skin.
- Elokom. The medicine eliminates inflammation and allergy symptoms.
- Fenistil. Removes itching (including from insect bites), relieves inflammation.
- Zinc ointment. Eliminates irritation, helps with acne, dermatitis, diaper rash and other skin defects.
In pharmacies you can buy vitamin complexes: Imedin, Supradin, Complivit, Revidox. They should be taken in courses. These products compensate for the lack of vitamins and other useful substances in the human body.
Causes of facial allergies in adults
Allergies are very common. In our country, more than 50 million people suffer from it every year. Allergic reactions occur in situations where the body's immune system mistakes harmless substances, such as food or pollen, as potentially dangerous compounds and tries to fight it off.
When the immune system detects an allergen, it produces an antibody called immunoglobulin. The formation of an allergen-antibody complex causes the body to release a chemical called histamine into skin cells and other parts of the body. Histamines cause most of the symptoms of an allergic reaction. Researchers don't fully understand why this happens or why the allergy gets worse with each subsequent exposure. One theory suggests that this may be due to the fact that you live in cleaner, more hygienic conditions, which prevent the immune system from actively working and fighting off the real enemies - germs, viruses or fungi.
Allergies on the face occur when an allergen comes into contact directly with the skin, when hazardous substances are inhaled or consumed. Depending on the type of reaction, the reasons may vary.
Contact dermatitis occurs when an allergen comes into direct contact with the skin. The face and hands are most often affected, and less often other parts of the body. The most common allergens are:
- various types of soap, shower gels, cleansers, shaving products;
- decorative cosmetics, creams, foams, gels, tonics;
- rubber and latex products in contact with the face (gloves, masks, protective shields);
- metal jewelry - earrings, piercings;
- chemicals, volatile compounds that come from the air, settling on the skin of the face;
- particles of soil, dust;
- juices, plant extracts.
Year-round allergic reactions usually provoke rhinitis (runny nose), signs of conjunctivitis and dermatitis. They are similar to signs of hay fever, but occur at any time of the year, upon contact with an allergen. Most often this form of reaction is provoked by:
- dust mites that live in people’s homes (on carpet pile, books, mattresses, upholstery);
- mold spores that actively reproduce in damp and warm rooms;
- animal dander, bird feathers, particles of urine or saliva of domestic animals.
Food reactions on the face occur due to an inadequate reaction of the immune system to certain types of food or individual components (mainly of protein origin). Most often, such reactions occur in childhood, although rashes are also quite possible in adults.
The most common food allergens are:
- chicken eggs (less commonly, other birds);
- various varieties of nuts (especially peanuts);
- whole milk and its derivatives, where fermentation and protein breakdown do not occur;
- seafood.
However, allergic reactions can be caused by any food, including fresh fruits, even those classified as hypoallergenic.
On a note
Eczema on the hands: what it looks like
Drug reactions occur when taking certain medications, and it does not matter whether they are administered orally, injected, or applied topically or cutaneously. The most common drug allergens are:
- penicillin antibiotics and related groups;
- drugs from the NSAID group, especially ibuprofen and acetylsalicylic acid;
- anticonvulsant drugs;
- X-ray contrast compounds;
- serums and vaccines;
- drugs for the treatment of cancer and serious illnesses (chemotherapeutic).
Hay fever or hay fever occurs when the skin and mucous membranes come into contact with pollen. Moreover, these are not any plants or flowers, but only a wind-pollinated group. Facial lesions occur exclusively during the flowering and pollination period of a particular plant. It can be:
- trees and shrubs;
- weeds;
- cereals and cultivated plants cultivated in fields and gardens.
Atopic dermatitis or eczema is a chronic allergic reaction that is provoked by various types of allergens. The reactions have a clear hereditary predisposition, arise from early childhood and are provoked by:
- different types of food, including milk and soy;
- dust mites, mold;
- various hygiene products, cosmetics;
- contact with dyed fabrics, wool;
- changes in hormonal levels, especially in women during pregnancy or during PMS;
- weather changes - frosty, dry air, heat.
The severity of the manifestations varies greatly from person to person, but the common symptom for all is severe dry skin, flaking, and increased sensitivity to quite common external factors.
Folk remedies
In addition to creams, ointments and vitamins, various folk remedies are used at home in the form of masks, compresses, lotions, and applications.
Celery
Celery is used to make effective remedies for irritated skin:
| Means | Application |
| Petiole celery mask |
|
| Lotions from a decoction of celery leaves |
|
Herbal infusions
Effective herbal decoctions for different skin types and conditions:
| Skin type | Means |
| Irritated and inflamed | Use a decoction of calendula or string (1 tbsp of dried inflorescences per glass of boiling water). Use the product daily |
| Sensitive | Decoctions of rose, aloe, parsley, jasmine and cornflower are used. They are prepared in the same way: 1 tbsp. l. per glass of boiling water |
| Combined | Chamomile and nettle, linden and plantain are suitable. Herbs are brewed individually or in combination with each other, mixed in equal proportions. Recipe:
|
Compresses are made from herbal decoctions and infusions - they soak gauze with them and place them on the face. Hot compresses are recommended for dry and normal skin. To eliminate irritation on oily skin - cold.
Facial steam baths will be beneficial:
- Prepare 2 liters of any herbal decoction.
- They pour it into a basin and lean over it, closing their eyes.
- Cover with a thick towel.
- They wait 20 minutes.
Parsley
Parsley contains many vitamins, but the main ones are antioxidants - ascorbic acid and vitamin A, which relieve swelling and inflammation. The substances included in its composition soothe irritation, help get rid of acne and whiten the skin.
There are several types of parsley masks, they are chosen depending on skin type:
| Means | Recipe and application |
| Parsley mask for oily skin |
|
| Parsley and yoghurt for normal to oily skin |
|
| Parsley and ground oatmeal for oily skin |
|
| Acne mask |
|
Cosmetologists recommend wiping irritated or flaky skin with parsley juice or its decoction (2 tablespoons of the raw material is poured with a glass of boiling water, brought to a boil again, and then infused for 30-45 minutes).
If your face is very flaky, you can make a mask of parsley and fatty cottage cheese:
- The components are mixed in equal proportions.
- Apply to the skin in an even layer.
- They wait 20 minutes.
- Wash off with water.
A popular mask based on parsley and sour cream for any skin type:
- Chop greens.
- A couple of pinches are mixed with 2 tbsp. l. sour cream.
- Apply for 15 minutes.
- Wash off with water.
Peppermint based products
Mint contains not only essential oil and menthol, but also ascorbic acid, flavonoids, tannins, and other components. Thanks to this, it is a universal product that can be used for young and mature skin. Moisturizes, stimulates regeneration processes, eliminates irritation and redness, accelerates healing.
Effective peppermint-based products:
| Means | Recipe, application |
| Lotion |
The product helps relieve redness and inflammation after shaving, and also eliminates irritation caused by sun rays. |
| Tonic |
The tonic cleanses the skin well, helps relieve inflammation and redness, including after excessive tanning. |
Cosmetic ice cubes:
- Take a bunch of fresh mint leaves, one lemon, a glass of mineral water without gas.
- The leaves are thoroughly washed, crushed in a blender, mixed with lemon juice and added to a glass of mineral water.
- Stir.
- Pour into ice trays.
By rubbing the skin with such cubes, you can remove irritation and redness caused by any factors.
Masks
To quickly relieve redness and skin irritation, you can use homemade masks.
Cucumber
Cucumber mask is a classic of home cosmetology. It exists in several versions:
- For oily skin with irritation. Half a grated cucumber is mixed with egg white and applied to the face for 15 minutes and then washed off with cool water.
- For dry skin. The cucumber is peeled, chopped, mixed with 1 tbsp. l. sour cream and keep on the face for 15 minutes, then rinse with cool water.
Herbal
Preparation:
- Take 2 teaspoons of sage, the same amount of linden blossom.
- Brew in a glass of boiling water.
- Cover the container with them with a lid.
- After 10-15 minutes, filter the infusion through double-folded gauze.
- The resulting decoction is wiped over the face.
- A thin layer of herbal raw materials is applied to it.
- Cover the face with a terry towel.
- The wait time is 5-7 minutes.
Remove the remnants of the mask using a cotton pad and lubricate with regular nourishing cream.
Yeast based
For preparation:
- Take 10 g of dry yeast and mix with 1 tbsp. l. sour cream or kefir.
- Add the same amount of juice from any fruit.
The mask is applied to the face and washed off only after the composition has dried.
Oatmeal
Recipe:
- Mix equal amounts of oatmeal and hot milk.
- Add 1 chicken yolk, 1 tsp cottage cheese, 1 tsp. olive oil.
- The composition is cooled and kept on the face for 20 minutes.
With milk and olive oil
For preparation:
- Oatmeal is cooked in milk.
- 1 tbsp. l. the resulting product is mixed with 1 tsp. olive oil and honey.
The composition is kept on the face for 15 minutes.
Milk-vegetable
Cooking method:
- Grind the carrots on a grater.
- Mix 1 tbsp. l. product with the same amount of warm milk and oatmeal.
Keep the paste on your face for 15 minutes.
From egg yolk and honey
To prepare the mask:
- The beekeeping product is heated in a steam bath.
- Take 2 tsp. for 1 chicken yolk.
Apply the composition to the skin for 20 minutes.
From sea buckthorn
Take 1 tsp. sea buckthorn oil and 2 drops of lemon essential oil. Apply to skin for 20 minutes.
You can add mashed boiled potatoes.
From potatoes
For preparation:
- The root crop is washed, cooled and grated.
- Squeeze out the juice.
- A gauze pad is soaked in it and applied to the face.
Keep the mask on for 15 minutes.
From cottage cheese and fruits
Recipe and application:
- The fruits are crushed into puree and mixed with cottage cheese. Both components are taken in equal parts (any fruit is allowed).
- The composition is applied to the skin for 20 minutes.
With aloe juice
The pulp of the plant is crushed and mixed in equal quantities with honey. Keep the composition on the skin for 15 minutes.
Symptoms of facial allergies in adults
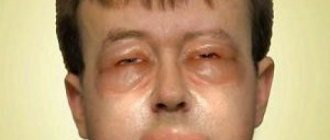
Manifestations of allergies on the face may vary depending on the type of reaction and age, the specific allergen. Anaphylactic reactions are the most striking and pronounced; they are characterized by swelling of the lips, lower part of the face and neck, as well as the eyelids, which dramatically change facial features.
Common manifestations typical of allergic reactions on the face include:
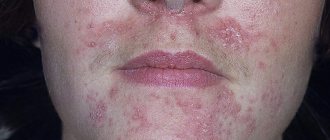
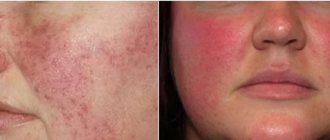
- small pinpoint rash or red spots all over the face or on the cheeks, forehead, chin;
- puffiness, prominence of individual parts of the face;
- burning or painful itching, feeling of heat, tingling;
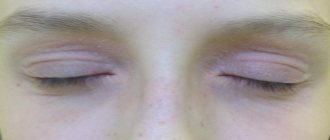
- swelling, redness of the eyelids, burning, crusts on the eyelashes;
- dryness, cracking, skin erosion.
Allergic reactions can occur abruptly, literally within a few minutes after contact with the allergen. In this case, they are considered anaphylactic and require especially close attention. Swelling of the lips, tongue, or neck can cause choking, so angioedema requires immediate medical attention.
Often reactions occur several hours or days after contact with the allergen and manifest themselves in dryness, peeling and redness of the skin, small rashes with itching.
If this is contact dermatitis, the key symptoms will be redness, itching, burning and swelling of the skin strictly at the site of contact with the allergen. Small blisters may form in the area of inflammation. Manifestations arise and intensify gradually, over the course of two days, and then also slowly disappear. The first contact with a dangerous substance may not cause a reaction - this is the stage of sensitization.
Food allergies usually present with signs of dermatitis or anaphylaxis. Typical symptoms include red itchy spots all over the face, swelling of the lips and eyelids, and swelling of the tongue and throat, which makes breathing difficult and leads to pale, bluish skin.
Hay fever usually provokes a runny nose and redness of the wings of the nose, lacrimation and conjunctivitis, itching of the facial skin, and red spots. With a severe runny nose, there may be a feeling of pressure in the projection of the sinuses, headache and malaise.
How to choose soothing creams
To eliminate dryness and irritation of the skin, products with a minimum content of preservatives and a maximum of beneficial herbal ingredients are used.
You should pay attention to the smell. Studies have shown that in 50% of cases, skin irritation is caused by fragrances of various products. It is more pleasant to use a scented cream, but if you have skin problems, it is better to give preference to an unscented product.
The following products can be purchased in pharmacies:
- Panthenol . Removes frostbite and burns, restores damaged skin, accelerates its regeneration.
- Bepanten . Removes peeling, irritation and inflammation.
- Rescuer . Accelerates skin regeneration, helps with insect bites, burns, frostbite.
- We see . Accelerates the process of tissue regeneration, fights eczema and dermatitis, and slows down skin aging.
- Pantoderm. Helps with severe peeling. Removes irritation, dryness, itching.
Helps relieve irritation with the “Protection and Moisturizing” day cream from the Natura Siberica brand, which is intended directly for sensitive skin. It contains extracts of Rhodiola rosea, Siberian rowan, chamomile, lemon balm, as well as components such as vitamin P and hyaluronic acid. The cream prevents allergic reactions and improves the skin's natural defenses against aggressive external factors.
Uriage “Roseliane” cream is recommended. for sensitive skin. Contains rose flower wax, glycerin, ginseng extract. The product moisturizes and soothes the skin.
The day cream “Day with buttercup extract” from Yves Rocher has proven itself well. It fights irritation and redness, improves blood microcirculation, and also increases skin protection from external influences.
Preventing facial allergies in adults at home
Most allergic reactions can be managed by either taking antihistamines before exposure to the allergen or avoiding the allergens entirely. Different types of reactions can be prevented in different ways.
- Food allergies. Always read labels and be careful when eating in restaurants, bakeries, delis and street stands. If a dish contains even a small dose of an allergen, avoid eating it.
- Reactions to animals. Avoid animals in the house, but if this is not possible, give them a separate place, do not allow them into the bedroom, constantly wash their fur during walks, and clean the house often.
- Hay fever. Stay indoors and avoid walking in forests and parks when pollen counts are high. If this is unavoidable, take antihistamines and wear sunglasses and a mask to keep pollen out of your eyes and skin.
- Allergy to dust mites. Always use bedding with hypoallergenic covers. If possible, remove carpets and install wood floors. Vacuum floors, ventilate and change bedding regularly.
This is interesting
Choosing the best allergy pills
What causes irritation: 5 common reasons
Flaky and itchy facial skin spoils a man’s appearance and causes discomfort. Dermatologists identify several common causes of irritation.
- Shaving with a dull razor.
Even the most expensive five-blade machine can damage thinning skin. It is especially dangerous to remove stubble with a dull razor. Instead of shaving hairs with one movement of his hand, a man has to go over the same place 3-4 times. As a result, the skin begins to turn red and itch.
- Using a dirty razor.
Every time a man runs the machine across his face, microparticles of skin, hairs, and natural fat fall on the blades. If biological debris is not removed, then any cut can result in infection.
- Pathological dry skin.
If a man has overdried dermis, then even careful shaving can lead to itching and flaking. Each movement of the machine will remove a thin layer of dead epithelial cells, which will lead to redness.
- Shave against the direction of hair growth.
If you move the machine against hair growth, you can achieve ideal results. But such shaving is considered stressful, since every movement of the razor increases the risk of irritation.
- Shaving dirty skin.
It is necessary to wash your face thoroughly before each shave. Otherwise, sebum and dirt may enter the bloodstream through cuts.
But even the correct use of a perfectly clean machine with sharp blades can lead to irritation of the facial skin. It is important to be able to independently eliminate the negative consequences of shaving.
What should you not do if irritation occurs?
Dermatologists do not recommend that men with irritated skin use cosmetics containing fragrances, synthetic dyes and acids. Alcohol solutions prevent blood infection and the appearance of ulcers, but at the same time contribute to further drying and thinning of the skin. If there are no cuts, but red spots constantly appear in place of the stubble, then you should stop using chemical foam and shaving gel. It is better to use organic soap. It is also forbidden to cover your irritated face with a snood or scarf.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a dermatovenerologist if skin itching and peeling do not go away for a long time (more than two weeks), contribute to sleep disturbances and decreased performance during the day, spread throughout the body, and are combined with other pathological symptoms. These symptoms in combination with an inflammatory or infectious process require urgent contact with a specialist.
Itchy skin, as well as flaking of the skin, can indicate a serious illness, the absence of treatment of which will lead to serious complications. Experienced doctors at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy for the identified pathology in order to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and their cause.
Peeling skin
Measles
Scarlet fever
Fungus
Syphilis
Allergy
23685 December 14
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Peeling of the skin: causes, diagnosis, what diseases it occurs with, methods of treatment.
Definition
Peeling of the skin occurs as a result of the death of cells (keratinocytes) of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Normally, the process of rejection of keratinized epithelium occurs constantly, but the scales and their number are small enough to be visible to the naked eye. When the processes of keratinization and death of keratinocytes are disrupted, the number of scales increases significantly; they can fall off the skin in tiny particles or merge to form large plates.
Types of peeling skin
The skin consists of several layers, the structure and role of each of them provides it with a barrier function.
Disruption of physiological processes in the skin leads to increased keratinization processes and the appearance of an excessive number of dead cells.
The color of the flaky scales can vary from gray-white to dark gray. With hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands, the scales stick together into large and fatty-looking plates. With hypofunction, the scales resemble tiny dust.
The location of peeling may depend on the disease that caused it. Increased peeling is usually observed on the scalp, in the folds of skin behind the ears, between the fingers, and on the flexor and extension surfaces of the limbs.
Possible causes of peeling skin
Peeling skin can occur in any skin type, but dry skin is most susceptible to it. Loss of skin moisture can be caused by improper selection of cosmetics (especially a passion for peeling, as well as alcohol-containing cleansing lotions and tonics), prolonged exposure to the wind, sun, dry indoor air, constitutional characteristics and age-related changes (lack of female sex hormones).
Peeling of the skin occurs due to a deficiency of vitamins (vitamin A and group B) and microelements (for example, iron).
What diseases cause skin peeling?
Atopic dermatitis
. This disease is one of the common allergic pathologies caused by immune disorders. It manifests itself as itching and rashes on the skin in the form of pink plaques or blisters with their subsequent pigmentation and peeling. In young children, an erythematosquamous form of dermatitis with redness of the skin and peeling is observed; in children 2–13 years of age, thickening of the skin with folds and scaly plaques predominates; in adolescents and adults, dryness and peeling of the skin mainly on the face and upper torso.
Psoriasis
. Psoriasis is one of the autoimmune diseases. Hereditary predisposition, immune, endocrine disorders, environmental factors and the state of the human nervous system play a significant role in its development. The disease can be provoked by stress, infectious diseases, injuries, and medications. As a rule, psoriasis begins with the appearance of pink itchy plaques on the skin, which, merging, form spots of various shapes, covered with silvery-white scales.
Plaques are localized mainly on the scalp, the extensor surface of the elbow and knee joints, and on the lower back.
When the rash is scraped, small scales give the plaque the appearance of a greasy stain, and after removing the scales, the surface of the plaque may bleed. With exudative psoriasis, the scales, under the influence of the oozing contents of the plaques, form crusts and are difficult to tear off. It is possible to localize the rashes only in areas with oilier skin (on the scalp, in the nasolabial and behind-the-ear folds, in the chest area and between the shoulder blades). In such patients, the peeling border goes down below the hairline to the skin of the forehead. With an exacerbation of the disease, psoriatic erythroderma can develop, when the process spreads to almost the entire skin, leading to swelling, redness and peeling of the skin.
Severe psoriasis is accompanied by damage to the joints, including their deformation and limited mobility.
Seborrheic dermatitis
. The disease is characterized by excess or insufficient function of the sebaceous glands. With increased sebum secretion, the stratum corneum of the skin thickens, and it becomes oily and flaky. With insufficient production of sebaceous secretion, small scales or large dry plates are formed, which are easily separated from the skin. Seborrhea affects areas with a large number of sebaceous glands (scalp, forehead, nasolabial triangle, ear area). With seborrhea of the scalp, the hair thins and falls out.
Children's infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever)
. The rashes that appear with measles gradually become pigmented, acquiring a brown color. Their surface is covered with small scales. With scarlet fever, the skin begins to peel off after the rash disappears, small scales may cover the face, and patches of skin on the palms and soles may come off in patches.
Demodicosis
.
The disease is caused by mites of the genus Demodex
, which can also be present in small quantities on healthy skin. They are found in hair follicles and sebaceous gland ducts on the face and scalp, as well as eyebrows and eyelashes. As the colony of mites grows, pinkish spots form on the skin around the hair follicles, covered with small or large scales. Papules (nodules) and pustules sometimes form, similar to acne. In advanced cases, the skin thickens and loses elasticity. Peeling, itching, oily skin and hair loss are characteristic symptoms of the disease.
Pityriasis versicolor (lichen versicolor)
. This type of keratomycosis is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Pityrosporum, affecting the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Pityriasis versicolor is not contagious, but a genetic predisposition to pityriasis versicolor has been identified in persons who are consanguineously related.
Most often, the lesion is noted at the age of puberty, since intensive proliferation of fungi correlates with hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands. Fungi form colonies in the form of yellowish-brown dots around the sebaceous glands. Merging, the colonies form pink-yellow spots, which gradually become brown-yellow. The surface of the spots is covered with pityriasis scales; they are easily scraped off, revealing lighter areas of the skin.
Pink lichen of Zhiber
. To date, the cause of the disease has not been established, but the prevailing opinion is that the lesion is viral in nature (presumably, these are herpes viruses). The disease begins with a prodromal period, which is characterized by muscle weakness, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. Then pink plaques up to 5 cm in diameter with raised edges appear on the skin, which lighten after a week. Over the course of several months, the plaques gradually disappear, becoming pigmented and peeling off. The disease develops mainly in adolescents and young adults.
Syphilis
. Syphilitic rash (papular syphilide), which is accompanied by peeling of the skin, is more common with secondary syphilis. Yellowish or bluish-red rounded papules, slightly protruding above the surface of the skin, have a dense consistency and a smooth shiny surface. Peeling of papules leads to the formation of a rim around them.
Ichthyosis
. This name combines a group of diseases, the characteristic feature of which is diffuse keratinization of the skin of the “fish scale” type. All variants of the disease (vulgar, X-linked, lamellar ichthyosis, congenital bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma) are hereditary in nature. Areas of hyperkeratosis and peeling can be localized in various parts of the body. Thus, with vulgar ichthyosis, peeling is more pronounced on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, but is also present on the skin of the thighs, forearms and buttocks, and deep folds can be seen on the palms and soles. In X-linked ichthyosis, the skin of the palms and face is not affected by hyperkeratosis. The color of the scales varies from light to dark brown. With lamellar ichthyosis, peeling affects all parts of the body.
Which doctors should I contact if my skin is peeling?
If foci of peeling appear in children, you should first contact a doctor who can refer the child to a dermatologist. Adult patients should immediately visit a dermatologist and, if necessary, an allergist-immunologist.
Diagnostics and examinations for peeling skin
To diagnose a disease characterized by peeling skin, it is necessary to do a number of laboratory tests:
- clinical blood test;