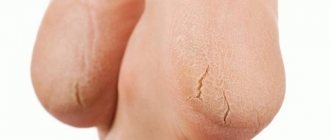
What is itchy skin like?
Itching of the skin can be of various types:
- Physiological and pathological itching. In the first case, the skin may itch due to some mechanical or chemical irritants, as well as insect bites. Pathological itching is a sign of a skin disease or other pathological condition, for example, neurological disorders or hormonal imbalance;
- Localized and generalized itching. Itching can be localized in a specific place, for example, under the hair on the head, in the genital area or anus, etc. As a rule, the symptom is paroxysmal in nature, often combined with other pathological manifestations of a particular disease. We are talking about generalized itching when literally the whole body itches. Often the symptom is associated with an allergic reaction or dry skin caused by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- Constant and paroxysmal itching. With constant itching, the symptom persists throughout the day, its intensity may increase at a specific time of day, often in the evening. Paroxysmal itching appears independently or under the influence of certain irritating factors.
Skin thickening, or hyperkeratosis
Diabetes mellitus
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Fungus
Menopause
Climax
17439 August 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Thickening of the skin: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Hyperkeratosis is an abnormal thickening of the top layer of skin (epidermis) as a result of excessive sun exposure, exposure to chemicals, frequent friction or pressure. In addition, hyperkeratosis can occur against the background of certain diseases.
Thickening of the skin occurs in the stratum corneum of the epidermis, which is the end point of the differentiation process of keratinocytes - cells containing the protein keratin. It is in the stratum corneum that keratinocytes lose water and their nucleus and turn into scales of the stratum corneum - corneocytes.
Normally, corneocytes are gradually exfoliated, due to which the skin is renewed.
With hyperkeratosis, accelerated differentiation of keratinocytes occurs, and the physiological exfoliation of horny scales from the skin surface, on the contrary, slows down.
Types of hyperkeratosis
Depending on the origin, acquired and hereditary hyperkeratosis are distinguished.
According to clinical manifestations.
- Calluses are a common type of hyperkeratosis. There are several types of calluses, but they all appear due to thickening of the skin in places most susceptible to mechanical stress. Moreover, such skin changes can be associated both with increased physical activity and with various chronic diseases, which is typical for elderly patients.
- Horny (tilotic) eczema manifests itself as hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles.
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune inflammatory disease in which hyperkeratotic scaly plaques form on the skin.
- Actinic keratosis usually appears as small, reddish, scaly bumps that appear after excessive sun exposure. Actinic keratosis is a serious condition with a high probability of malignancy and requires mandatory consultation with a doctor.
- Seborrheic keratosis is characterized by small brown or black patches, usually located on the face, neck, shoulders and back. This is one of the most common benign skin tumors in adults.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis (“goose bumps”) is characterized by blockage of the mouths of the follicles with keratinized epidermal cells.
- Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis is a rare hereditary disease that appears immediately at birth. Newborns have reddish skin, sometimes covered with small blisters.
Possible causes of skin thickening
Skin hyperkeratosis can occur in people who neglect regular skin care procedures, as a result of which dead cells of the stratum corneum accumulate and form keratomas - benign neoplasms.
Our skin is constantly exposed to adverse external factors, such as chlorinated water and detergents, and UV radiation. As a result, the protective lipid layer of the skin is damaged, and moisture begins to rapidly evaporate from its surface, and corneocytes lose their ability to physiologically exfoliate.
In diabetes mellitus, hyperkeratosis becomes a consequence of metabolic disorders and deterioration of skin microcirculation.
Wearing tight or uncomfortable shoes, especially with flat feet, congenital foot pathologies, and obesity, can cause thickening of the skin on the feet.
The development of cervical hyperkeratosis (leukoplakia) is promoted by the human papillomavirus.
The cause of hyperkeratosis can be chronic fungal infection, as well as herpes zoster.
It is believed that symptoms of thickened and dry skin may be caused by a deficiency of vitamins A, E, D and C.
Hyperkeratosis often results from a lack of the hormone estrogen in women during menopause.
Diseases and conditions in which hyperkeratosis develops
- Diabetes.
- Obesity.
- Flat feet.
- Ichthyosis.
- Psoriasis.
- Eczema.
- Menopause.
- Fungal skin infection.
- Shingles.
- Erythroderma.
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Seborrheic keratosis.
Which doctors to contact for hyperkeratosis
Most often, the first consultation regarding skin thickening is addressed to a dermatologist. After a thorough examination, collecting complaints, finding out the patient’s medical and family history, conducting laboratory and instrumental studies, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist may be required.
Diagnosis and examinations for thickening of the skin
A thorough history taking, taking into account all the patient’s complaints, examination and additional diagnostic methods will help determine the cause of hyperkeratosis.
- Clinical blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula to identify inflammatory processes in the body.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a dermatovenerologist if skin itching and peeling do not go away for a long time (more than two weeks), contribute to sleep disturbances and decreased performance during the day, spread throughout the body, and are combined with other pathological symptoms. These symptoms in combination with an inflammatory or infectious process require urgent contact with a specialist.
Itchy skin, as well as flaking of the skin, can indicate a serious illness, the absence of treatment of which will lead to serious complications. Experienced doctors at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy for the identified pathology in order to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and their cause.
How to deal with itching sensations
These methods and rules are recommended mainly for the elderly, for whom senile itching becomes a constant companion. But they can be successfully used to reduce the manifestations and prevent this phenomenon at any age.
Elderly itching may be caused by abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system.
In older people, itching of the back often causes more discomfort than in younger people, since due to general absent-mindedness it is difficult for them to concentrate on anything else. Not all older people can take anti-itch medications. Often this is not possible due to pathologies of the liver, kidneys or stomach. In addition, almost any medicine has a number of side effects that have a strong effect on a weakened elderly body and can negatively affect well-being and health.
Recommendations for eliminating itching
To minimize the sensation of itching, you must adhere to the recommendations given by therapists to combat this phenomenon:
- In the morning and before bed, wash in the shower with baby soap. This is not only hygiene, reducing the percentage of pathogenic microbes on the skin, but also improving blood circulation and moisturizing the skin.
- Wear clothes made of cotton or linen. Wool is allowed, but it is better if not in direct contact with the skin, since due to its rough texture it can cause additional skin irritation.
- Try not to scratch those spots on your back that constantly itch, and after a shower treat them with a cream that has a moisturizing property. This will preserve moisture in the epidermis and slow down drying.
- Do not be nervous. The advice to avoid stress is equally useful for patients of all ages, but older people need to especially monitor the situation and immediately take mild sedatives if it occurs.
Skin moisture loss
If you follow these rules every day, you can not only reduce the manifestations of senile itching, but also completely avoid it. And by starting to take care of preserving moisture in the skin until old age, you can significantly delay the onset of this phenomenon.
Advice. Do not scratch itchy areas under any circumstances. Ideally, you shouldn't itch at all. This will cause ulcers to appear, folliculitis to develop, and boils to form. You can use creams, ointments, and lotions to reduce itching topically, but only in consultation with your doctor.
Video - Itching in the elderly
What diseases cause itching and flaking of the skin?
There are quite a few diseases accompanied by itching and peeling of the skin of varying degrees of intensity and prevalence:
- allergies to food, medications;
- contact dermatitis;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- fungal skin diseases;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disorders;
- thyroid diseases;
- blood diseases;
- parasitic diseases (scabies, demodicosis, etc.).
Benefits of a private medical appointment
The result of seeking help from a dermatologist at a private specialized institution is the provision of not only advisory assistance at the appointed time, but also a full range of examinations with further implementation of the necessary treatment procedures. This fact greatly facilitates the implementation of all actions and provides comfortable conditions for completing the prescribed procedures.
And our Help Desk for private clinics in Moscow “Your Doctor” will help you find the right medical center that is convenient for visiting, which contains all the required data, allowing you to immediately make an appointment at a suitable time or arrange a call to a dermatologist at home.
Publication date: 2020-01-07
Useful information on the topic:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Treatment of skin diseases
- Dermatology - the science of skin diseases
- How to consult a dermatologist
- Prevention of skin diseases
- Dermatologist appointment
- Examination by a dermatologist
- Pediatric dermatologist
- Skin doctor
- Paid dermatologist
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.