Any change in skin tone, if it did not occur under the influence of sunlight, is a serious signal about a disruption in the functioning of internal organs.
So, for example, if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, the shade of the face may change from healthy to gray; it may turn blue if there is impaired blood circulation, diseases of the cardiovascular system or respiratory failure; in addition, a purple tint indicates congenital heart disease, and a yellow hue indicates liver diseases.
Gray facial skin - a disease or a consequence of bad habits
A sharp and noticeable change in complexion from natural and healthy to gray is most often a sign of a malfunction of the digestive system . At best, your face may turn gray due to banal constipation or poor nutrition, at worst, due to gastritis or the development of a stomach ulcer. It is hardly possible to independently diagnose the disease on the basis of dyschrony alone, so in this situation it is better to go to an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
In addition, gray facial skin does not always portend illness. Often, against the background of smoking, sedentary work and constant stress, people's blood circulation is impaired and blood vessels narrow, which is also manifested by a deterioration in complexion.
Grey
See a doctor urgently!
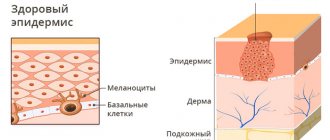
Dull, grayish skin is a sign of thickening of the outer (horny) layer of the epidermis. In medicine, this condition is called hyperkeratosis. This problem can be caused by various skin diseases (ichthyosis, keratoderma, etc.) and internal diseases - diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus. This condition can also develop with hypovitaminosis, especially with a lack of vitamin A.
Or to a cosmetologist?
Exposure to aggressive factors on the skin - strong wind, frost, direct sunlight - can also give the skin a dull hue. In addition, a grayish complexion can be caused by improper skin care and stress. A cosmetologist's solution to this problem is aimed at normalizing home skin care - serums that even out skin texture, scrubs and exfoliating masks, as well as surface peelings, including enzyme peeling, hydropeeling, and carbon peeling will be used.
Winter is not suitable. How to cope with seasonal appearance problems Read more
Earthy tint and sharp darkening of the skin - pancreatic disease or oncology
Changes of this kind indicate more serious illnesses. Often, of course, an earthy tint appears due to diseases of the pancreas, adrenal glands, or against the background of long-term use of antibiotics, but if such options are excluded, then the best recommendation in this case would be to turn to modern medicine. Diagnosis of the disease by the skin and on the basis of examinations will allow you to correctly and accurately determine the cause of the change in complexion, as well as timely diagnose the disease that provoked it.
Pale complexion
The main objective reason is age. In addition to facial wrinkles and age-related wrinkles, skin aging also involves a change in its shade. It turns from healthy pink to light yellow, which indicates a lack of moisture in the dermis. Its retention is entrusted to collagen fibers, which, as the body ages, begins to be produced in ever smaller quantities and ceases to fully perform its function. The skin loses moisture, dries out, and becomes vulnerable to external influences. This is facilitated by poor tissue nutrition, which occurs during less active work of the cardiovascular system. Subjective reasons are presented in several aspects at once:
- A person’s lifestyle determines the state of his body, in particular, poor nutrition, constant stress and lack of sleep lead to premature aging of the skin, which first of all becomes noticeable on the face. In addition to this, there is an environmental situation in which the oxygen content in the blood is insufficient for adequate nutrition of the tissues.
- Pale facial skin also appears with anemia and is the result of a lack of iron in the blood. This element is very important, as it acts as a conductor for oxygen. In patients of the younger age group, the presence of anemia is indicated by insufficient body weight and stunting.
- Another, no less common cause of pale skin color is vegetative-vascular dystonia. A characteristic sign of pathology will be a pronounced vascular pattern, which is especially noticeable on white skin. The clinical picture of the disease is supplemented by pressure changes, heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmia), pain in the heart, dizziness and cyanosis of the hands.
- Diseases of the excretory system that affect the kidneys can also lead to pale skin. In such cases, the skin acquires a yellowish tint, and the mucous membranes of the oral cavity are involved in the process. The patient's condition is aggravated by weight loss, swelling and dark circles under the eyes. Pain in the abdominal area can be severe.
- Also, pale facial skin can be explained by angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, or myocarditis.
If small bruises appear on the skin and the mucous membrane of the mouth becomes covered with wounds, this may indicate the development of leukemia. At the initial stage, the disease often has signs of a common acute respiratory viral infection. The patient feels weakness, drowsiness, lethargy, which occurs against the background of elevated body temperature. However, seemingly harmless signs indicate a serious disease of the hematopoietic system, which requires the intervention of a qualified specialist.
In any case, if pale facial skin causes concern or is accompanied by other specific symptoms, you should contact a medical facility for examination.
Vasculitis is a disease of blood vessels in the skin.
This disease involves damage to the blood vessels and tissues of the damaged organ. If the skin vessels are affected, the main symptoms of the disease will be redness, rash and itching. Vasculitis can also affect the circulatory system of the brain, which causes a stroke, the heart, which increases the risk of heart attack, etc., quite often small hemorrhages under the skin are a sign of vasculitis of other organs.
The main symptoms of this disease include: general weakness, fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, rash and itching, joint pain.
A similar syndrome can also occur with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases characterized by damage to connective tissue.
Peripheral (cold, venous) cyanosis
Peripheral (cold, venous) cyanosis is a condition in which the blood in the arterioles of the cutaneous vascular plexuses has a normal oxygen content, warming the skin is accompanied by redness, and after pressing, a pink spot first appears, which later acquires a bluish tint. It is observed with a decrease in minute blood volume (heart failure, pericarditis, armored heart), local stasis in the final sections of the bloodstream (cooling, collapse and shock of various origins, arterial embolism, polycythemia, etc.).
In case of carbon monoxide poisoning (carbon monoxide, CO), carbon monoxide, entering the blood, combines with the iron of hemoglobin, converting it into carboxyhemoglobin, whose concentration in the blood is more than 35 g/l, hemic hypoxia, respiratory failure and neurological disorders occur (children's neurologist - polyclinic "Markushka"). Typically, patients have a bright red (cherry-red) face, acrocyanosis, and in a later stage severe cyanosis develops.
Cuperosis is a vascular skin disease
Couperosis appears in the form of a small red vascular network or so-called on the cheeks, chin and nose when the blood vessels dilate against the background of increased blood circulation. At the same time, the connective tissue squeezes the vessels from the outside, which makes them more visible on the face. This disease occurs among older people, as well as among those with thin and sensitive skin.
Couperosis can be treated either in a cosmetology salon or using traditional methods. Although the first method allows you to get rid of the signs of rosacea in the shortest possible time. But in case of lack of funds or opportunities - facial massage. This way you can normalize blood circulation and tone the blood vessels and muscles of the face. In addition, supplement your diet with foods or dietary supplements rich in vitamins C, P, K, antioxidants, Omega 3 and 6 fatty acids - they strengthen the walls of blood vessels and help normalize blood circulation.
There are total and regional cyanosis
There are total and regional cyanosis (perioral - around the mouth, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, cyanosis of the distal parts of the body (acrocyanosis) - the tip of the nose, earlobes, lips, tip of the tongue, hands, feet). More often, cyanosis is observed in diseases of the respiratory system and cardiovascular system. In lung diseases, cyanosis occurs as a result of blood passing through poorly ventilated areas of the lungs, while the amount of unsaturated hemoglobin increases as a result of a mismatch between ventilation and perfusion. In congenital heart defects, cyanosis is caused by intracardiac mixing of venous and arterial blood. Peripheral cyanosis can occur as a result of a decrease in peripheral blood flow; the amount of unsaturated hemoglobin in the capillary bed increases due to increased extraction of oxygen by tissues. Cyanosis in a healthy child can develop at high altitudes, where the partial pressure of oxygen in the inspired air is reduced.
Yellow skin – liver disease
Most often, yellowing of the face and body is accompanied by a change in the shade of the eye sclera, mucous membranes, especially under the tongue, feet and palms. At the same time, the color of the urine changes - it acquires a rich dark shade.
Such changes most often occur against the background of increased levels of carotene or bilirubin. In the first case, the skin can become yellow if you follow a diet consisting of oranges or carrots for a long time. If these did not occur, then most likely the matter is an increase in the content of bilirubin - a bile pigment that appears as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin. The latter is responsible for saturating the blood with oxygen and transporting nutrients not only to skin cells, but throughout the body. When there is a decrease in hemoglobin and an increase in bilirubin, changes occur not only in the layers of the dermis, but also in the liver. Then there is a risk of jaundice. In addition, yellowness may indicate diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, the formation of cysts, as well as disorders of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
Red
See a doctor urgently!
Redness of the face can be either an independent disease - rosacea (it is characterized not only by redness, but also by a rush of blood to the face), or a symptom of various internal problems: arterial hypertension, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular the liver, infectious diseases. In addition, redness can develop as an allergic reaction. In this case, you must first eliminate the allergen, and then treat the skin with anti-inflammatory drugs, and, according to indications, prescribe hyposensitizing therapy.
Or to a cosmetologist?
If your face turns red periodically, it is necessary to choose care aimed at protecting the skin from aggressive factors. These are usually products for sensitive skin. Also in the arsenal of cosmetologists there are injectable drugs that reduce vascular reactivity - mesobotox; mesotherapy and biorevitalizing preparations that restore and protect the skin.
Sallow complexion and acne. 8 signs that it’s time for you to see a doctor Read more
Diagnostics
To identify jaundice and determine what kind of disease a person has, you need to carry out the following diagnostics:
- CBC, where hemoglobin is determined;
- Blood biochemistry, which shows total bilirubin and its secretions;
- Lipid profile study;
- Test for thyroid hormones;
- Testing for tumor markers;
- Test for roundworms;
- TAM, which determines the level of bilirubin and its secretions;
- Immunological analysis to detect antibodies to viral hepatitis;
- PCR research;
- Antiglobulin test (for newborns);
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy, which shows inflammation, neoplasia and bile duct stones.
Dyspnea
Diagnostic procedures for each patient are selected individually by the doctor.
Norm
Jaundice occurs due to disruption of bilirubin metabolism, its excretion and accumulation.
Bilirubin tends to form due to cytochromes, red blood cells and myoglobin, which have broken down.
Bilirubin comes in two forms:
- Incoherent. It is toxic, interacts with the protein albumin, and is transported to the liver area through the bloodstream;
- Connected. Cells that are in the liver area combine bilirubin and glucuronic acid, changing it into direct or conjugated bilirubin. Next, the liver produces bile, where bilirubin will be located, and it enters the intestines with it. Next, bilirubin is removed from the feces.
“Gray” syndrome is a form of cyanosis in children in the first months of life associated with the use of chloramphenicol
“Gray” syndrome is a form of cyanosis in children in the first months of life associated with the use of chloramphenicol. In children, regardless of age (especially with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency), sulfonamides in high doses can cause sulfhemoglobinemia, and for clinical signs of cyanosis to appear, a blood level of 5 g/l of sulfhemoglobin is sufficient. Ingestion of 100-300 mg of methylene blue per day restores the oxygen transport function of the blood in all forms of methemoglobinemia, while ascorbic acid in a dose of 100 to 500 mg is effective in congenital methemoglobinemia. Sulfhemoglobin is a strong compound, and methylene blue has no effect on the restoration of the oxygen-containing space of the blood.
The light blue coloration of the skin in argyria may resemble cyanosis, but abnormal skin pigmentation due to skin color can occur in Addison's disease or hemochromatosis.
What you need to know
Yellow skin color also occurs due to carotene oversaturation. This happens if a person often eats vegetables and fruits that contain it in large quantities.
How to distinguish such yellowing from jaundice? With it, only the skin is stained, but not the mucous membranes.
It happens that the skin turns yellow due to taking medications containing acryquine or picric acid.
Further, the skin turns yellow. If you consume excessive amounts of spices, spicy foods, fast for a long time, or frequently use alcohol or drugs.