A lump under the arm can be a lipoma or atheroma, sometimes the lump is an enlarged lymph node. Lipoma is a benign neoplasm that grows in a capsule in layers of loose connective tissue. If the duct of the sebaceous gland in the armpit is blocked, a cyst (atheroma) is formed. An inflamed lymph node can reach 3-5 centimeters in diameter, visually it can be confused with a lipoma. Differential diagnosis is carried out by an oncologist or surgeon after examination, palpation, and ultrasound. With multiple compactions under the arm, other diagnostic measures will be required to determine the lesions and fusion with other tissues.
What does a wen in the armpit look like and feel like?
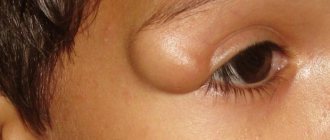
The wen looks like a rounded lump, painless on palpation. The size of the formation can be different, most often like a small tennis ball. If the tumor grows to 7-8 centimeters or more, the boundaries become less clear, the tumor protrudes above the surface of the body. The skin over the wen should not change, that is, turn red or peel. When pressed, the wen easily moves slightly to the side under the skin. It must grow in the capsule, without merging with the subcutaneous tissue and adjacent tissues of other organs.
The lipoma under the armpit cannot be felt for a long time; it begins to be palpated when its diameter is more than two centimeters. In cases where the wen reaches a large size, it compresses neighboring tissues. The patient constantly feels discomfort, it becomes difficult to move his hand.
Why do lipomas appear?
Fatty deposits in the armpit appear due to internal problems in the body and genetic predisposition.
The main reasons for the appearance of a wen in the armpit:
- Changes in genes on chromosome 12 that are responsible for fat lysis.
- Metabolic disorders in the layers of the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue.
- Disruptions in the production of thyroid hormones.
- Menopause, taking incorrect doses of estrogen.
- Eating unhealthy fatty foods and fast food.
- A sedentary lifestyle causes a slowdown in blood supply to small vessels, which can trigger the deposition of fat cells into the capsule.
- Wearing tight clothing that puts pressure under the armpit causes mechanical injuries in this area.
- Strong radioactive exposure of the body.
Harmful substances in food and polluted environment can indirectly cause wen. Toxins and heavy metal compounds suppress the immune system, so the body’s defenses do not recognize the emerging lipoma in time and do not destroy it.
Prevention measures
The main preventive measure is to strengthen the body's defenses. You should walk as much as possible, play sports and eat right. If there are signs of hormonal imbalances, you should make corrections and find the cause of the malfunction by consulting a specialist.
In addition to everything, it is recommended to monitor your weight. At the slightest skin manifestations, you should consult a doctor and under no circumstances self-medicate. It is recommended to avoid hypothermia and injury. If a small lipoma appears, you cannot squeeze it out or open it yourself, as this can cause infection and serious consequences.
Varieties
The first symptoms of a wen under the armpit are the appearance of a rounded lump, over which the skin easily moves. An axillary lipoma is primarily composed of fat cells, but other tissues may be added to its composition.
Depending on the presence of different types of tissue in the capsule, the following types of lipomas are distinguished:
- Lipofibroma. It is the most common among wen under the armpit. This tumor is 99% fat cells. In women with hormonal imbalance, a lipoma under the arm can grow to a very large size - 7-10 cm. It rarely degenerates into a malignant tumor.
- Fibrolipoma. It consists of about 70% fibrous (connective) tissue, the remaining 30% is occupied by fat accumulation. This type of lipoma grows slowly, but is more prone than others to malignancy, that is, degeneration into cancer.
- Angiolipoma. Half of its contents are represented by connective tissue, 45% are allocated to fat cells, and the remaining 5% are small blood vessels. Due to the direct blood supply, the tumor grows quite quickly. When removed, heavy bleeding often occurs. This type of lipoma is dangerous to injure or squeeze out on your own, as it is easy to provoke internal bleeding and the spread of pathological cells to neighboring organs.
- Myelolipoma. It rarely appears in women under the armpit; only isolated cases are known in men. Its growth can be provoked by hormonal changes in the body during menopause. This type of wen consists of muscle fibers. This type of lipoma is considered low-risk, never becomes malignant, and can go away without treatment.
Are wen dangerous?
In most cases, lipoma is not life-threatening. For a long time it is not felt at all. The appearance of redness and pain indicates that the wen is inflamed. The cause of inflammation can be uncomfortable clothing, when the tumor under the arm is constantly injured. Infection through wounds on the skin also leads to an inflammatory reaction. In this case, surgery may be required.
If a wen that appears under the armpit reaches a large size, it begins to compress the blood vessels and affect the muscles. The patient experiences pain under the armpit and difficulty moving the arm. Such complications require immediate treatment.
A child may develop a lump under the armpit at an early age due to a genetic predisposition. The baby's hormonal background is aimed at the rapid growth of all organs and systems. This leads to a strong increase in lipoma. If lumps appear under the armpit of a child, you should not hesitate to contact a specialist. In most cases, the doctor removes the tumor so that it does not spread deeper into the mediastinal organs and does not interfere with the normal development of the baby.
The danger of a wen is that there is a possibility of its cells degenerating into atypical ones, which lead to the development of cancer. Therefore, it is necessary to observe the dynamics of the neoplasm. If the tumor quickly grows, hardens and becomes immobile, then a suspicion of a malignant oncological process arises. In this case, it is necessary to do a biopsy, that is, taking material from the tumor for examination.
Treatment prognosis and consequences
The prognosis for treatment is favorable in most cases. The main thing is to pay attention to education in time and undergo the necessary examination. It should be remembered that the armpit is often subject to friction, so the wen will often be injured, and this is dangerous due to the consequences of infection, because this area is favorable for the growth of bacteria, as it is equipped with sweat glands.
In addition, if you constantly touch a lipoma, then there is a risk of its malignant degeneration, which occurs due to constant trauma.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out by a surgeon or oncologist. He examines and palpates the pathological area under the arm, and, if necessary, prescribes ultrasound and MRI. These studies help determine the exact boundaries and size of the tumor, the presence of invasion into other tissues and organs.
A round lump that appears under the armpits can be a linden tumor, atheroma, or an inflamed lymph node. Atheroma is a cyst formed due to blockage of the sebaceous duct. It accumulates sebum, which is actively produced by the glands under the armpit.
Unlike lipoma, atheroma has a duct and can open on its own, with the contents coming out.
Lymphadenitis appears in the form of bumps under the arms and on the neck, similar to lipomas. Unlike lipomas, inflamed lymph nodes are painful on palpation, and the skin over them is hyperemic (red). As a rule, with proper treatment, lymphadenitis compactions decrease after 2 weeks from the start of therapy and completely disappear within six months.
Features in women and children
Lipomas in women often form under the influence of hormonal disorders. This may occur after an abortion, during pregnancy, or other similar conditions. The course of the disease is the same in men and women. In children, it is quite rare for a wen to form, but if such a phenomenon occurs, then quite often it goes away without a trace on its own. In this case, sometimes it is enough to apply an aloe leaf to speed up resorption.
If the formation does not go away for a long time, but does not change its size, then it is monitored. When the tumor site is frequently subjected to friction, the lipoma is removed using a laser.
How to get rid of wen under the armpit
You can cure a lipoma that appears under the arm, when its size is no more than 3 cm, using home medicine recipes. Self-medication can be done for no more than two weeks. If no significant positive dynamics are observed, you need to seek help from specialists. Doctors observe many types of wen for several years and are in no hurry to operate.
It is necessary to treat an inflamed wen under the supervision of a doctor. In cases where the tumor has grown (more than 5 cm) and interferes with the movement of the arm, radical surgical treatment will be required. The tumor under the arm is removed traditionally, using a scalpel or using hardware methods, such as a laser.
Surgical intervention
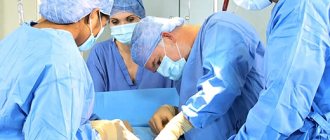
The removal of the wen is carried out by an oncologist or surgeon. Before the operation, blood clotting time tests and a number of other necessary studies are carried out to prevent complications.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. After preparing and treating the surgical field, the doctor injects the tumor with painkillers - novocaine or lidocaine.
After anesthesia, the doctor uses a scalpel to cut the skin over the wen. The lipoma grows in a capsule, so it is easily separated from the surrounding tissue and removed. Next, sutures are placed on the incision.
The extracted tumor is sent for histological examination. The conclusion provides information about the tissue composition of the neoplasm, the presence or absence of changes characteristic of the cancer process.
Drug therapy
To date, there are no pharmaceutical products that can completely get rid of lipoma. The adipose tissue in the tumor is not susceptible to the action of enzymes and drugs that lyse lipid substances.
Lipoma cannot be completely cured with medication, but its size can be reduced.
Injections of fat-dissolving medications are made into the base of the wen under the armpit. Medicines help reduce fat cells and prevent capsule growth.
Warming solutions are applied to the inflamed wen under the armpit. Dimexide can reduce signs of inflammation. This drug must be diluted in half with warm boiled water. The resulting solution is used as a compress twice a day and at night.
Treatment at home
Traditional methods of treatment are indicated for the first symptoms of a wen under the arm, when the size of the tumor is no more than 2 cm. Onions are often used in home medicine recipes, but they can cause irritation and inflammation. At the first painful symptoms, you should consult a doctor for help.
Traditional medicine for the treatment of lipoma:
- Golden mustache. This product helps to dissolve small lumps under the skin. It is necessary to finely chop the golden mustache leaf with a knife or grind it with a blender. The resulting pulp is spread on a gauze napkin and applied to the skin in the projection of the tumor. You need to put a bag or oilcloth on top of the napkin. The compress is fixed with a bandage and left overnight. The procedures are repeated for about 10 days.
- Onions and laundry soap. It is recommended to bake the onion in the oven and grind it in a meat grinder. Laundry soap, previously grated on a fine grater, is added to the resulting slurry in the same quantity. A compress with this remedy must be done every day for 4-5 hours.
Treatment with folk remedies is carried out only on the entire skin. Do not apply compresses if there are abrasions, scratches or ulcers under the armpit.
Alternative lipoma removal methods
A lipoma in the armpit can be removed using a laser. This method is considered the most effective, since relapses at the site of the operated tumor rarely appear. Patients do not experience pain during laser removal, but only a slight feeling of discomfort. There is no scar deformation left at the operation site.
Another alternative way to remove lipomas up to 5 centimeters is electrocoagulation. An electric knife carefully cuts through the skin and immediately coagulates damaged blood vessels. After peeling the wen, an inconspicuous scar remains.
Lipoma. Diagnosis and treatment
Lipoma, or wen , or lipoblastoma is a benign tumor that develops from adipose tissue . Most often, lipoma occurs in women 30-50 years old. Lipoma can form in the place of the body where adipose tissue is located, i.e. the tumor can develop in the subcutaneous tissue, retroperitoneal tissue, perinephric tissue, mediastinum, lungs, mammary gland, etc. There are cases when a symmetrical lipoma develops, caused, according to some authors, by neurotrophic changes, and multiple lipoma also occurs.
The growth of tumors does not depend on the general condition of the body, so fat accumulates in them even in an exhausted body, which proves their autonomy. In some cases, the lipoma grows to a significant size, at which the tumor begins to sag. The base of the lipoma turns into a thin leathery stalk (lipoma pendulum), which leads to stagnation of blood, swelling, and, as a result, necrosis and ulceration.
The macroscopic structure of the lipoma is a node surrounded by a capsule and having a lobular structure. In rare cases, you can find a diffuse lipoma that does not have a connective tissue capsule with adipose tissue. From a microscopic point of view, a lipoma has a structure similar to that of adipose tissue, but unlike it, fat cells and lipoma lobules can be either very small or gigantic. In addition to ordinary fat cells, a lipoma also contains multilocular cells - groups of cells with several fat vacuoles. Multilocular cells are cambial. Depending on which tissue predominates in the lipoma: adipose or fibrous, lipofibroma and fibrolipoma are distinguished. If the tumor has abundantly developed blood vessels, it is called angiolipoma. If mucus tissue is found in the lipoma, then it is a myxolipoma, if smooth muscle fibers are found, then it is a myolipoma.
In appearance, a subcutaneous lipoma is a painless, round, mobile formation, not fused with the skin and nearby tissues. If you stretch the skin over the lipoma, you can see retractions on it, which are formed due to the fact that the tumor has a lobular structure. Lipoma can reach different sizes: most often it is 1.5 – 5 cm, but there are tumors the size of a child’s head. In its normal state, a lipoma is a soft formation with an elastic consistency (lipoma molle). In case of development of connective tissues, the consistency of the lipoma thickens (lipoma durum).
In the thickness of the muscles, an intramural or infiltrating lipoma may develop, which does not have definite boundaries. If multiple small lipomas are located on the nerve trunks, they can be very painful, as they put pressure on the nerve. Deep-lying lipomas are diagnosed only by histological examination. For a long time, the tumor may either not change at all or grow very slowly. A lipoma can develop into a malignant tumor with damage to adjacent tissues either as a result of injury or without a specific reason.
Clinical picture of lipoma
As an additional method used to diagnose the disease, X-ray and ultrasound examinations are used. To diagnose soft tissue lipoma using the X-ray method, long-wave X-ray (“soft”) radiation is used to evaluate the structure of the soft tissue. To recognize lipomas that lie deep in muscle tissue, “harder” X-rays are used. On x-rays, the lipoma looks like a smooth-defined clearing, most often having a regular shape. Lipoma usually forms a homogeneous clearing, in which small areas of calcification may often appear. The clearing has a shape depending on the density of the organs between which the lipoma is located. If a nodular lipoma is located under the skin, then the formation will have a clearly defined round shape, and the intensity of its shadow will be the same as the surrounding adipose tissue. In the case of the formation of large lipomas that exist for a long time, they can displace the surrounding tissues.
The most accurate radiation method for recognizing this type of tumor is computed tomography, which quite clearly distinguishes adipose tissue with a low X-ray absorption rate from tissues with denser soft tissue structures.
During ultrasound examination, the lipoma looks like hypoechoic formations with a delicate capsule located inside the adipose tissue.
To confirm that the detected tumor is benign, fine needle aspiration biopsy with cytological examination is used. To do this, a tumor fragment is taken with a thin needle for further examination under a microscope.
Lipoma can only be cured with surgery. No “folk remedies” will help in this case.
The following indications exist for surgical treatment of lipoma:
- rapid increase in tumor size;
- large size lipoma;
- compression of organs and tissues surrounding the lipoma, its pain, disruption of the normal functioning of the organ;
- cosmetic defect.
If the lipoma is small in size and located in an accessible location, then surgery to remove it is performed on an outpatient basis using local infiltration anesthesia. In the case of a large lipoma or a lipoma formed in areas that are difficult from an anatomical point of view, for example, on the neck or in the armpit, it is recommended to hospitalize the patient and perform the operation in an inpatient setting.
Three types of surgery are used to remove a lipoma:
1. Classical excision of the lipoma along with the capsule is the most radical method of treatment. First, a wide skin incision is made under local anesthesia, and then the lipoma is enucleated and removed along with the capsule. Next, sutures are placed on the subcutaneous tissue and incised skin. If the tumor is large, then drainage should be left for 1-2 days. The advantages of this method are a high degree of radicalism and the absence of recurrence of lipoma. Disadvantage: low cosmetic effect.
2. Minimally invasive lipoma removal . First, a small incision, up to 1 cm long, is made in the skin, through which the lipoma is destroyed and removed inside the capsule. The completeness of removal is controlled using a mini-endoscope. The advantages of this method are an excellent cosmetic effect. The downside is that it is not radical enough.
3. Liposuction of lipoma. First, an incision up to 0.5 cm long is made, through which the lipoma is removed using a lipoaspirator inside the capsule. Subsequent monitoring of tumor removal is not carried out. The advantages of this method are the best cosmetic effect. The downside is a high degree of possibility of relapse.
Classic lipoma excision
What not to do
When a wen is discovered, some people try to get rid of it as quickly as possible. As a result, they make a number of mistakes that lead to the enlargement and proliferation of the tumor.
Involuntary injury to the seal can have serious consequences. Therefore, you need to be careful and wear comfortable, loose clothing.
Absolutely forbidden:
- Try to squeeze out the wen under the arm yourself. A small tumor after compression can increase significantly, as its vessels are damaged.
- Scratch, independently cut the skin over the wen or try to pierce it. All these actions will lead to infection of the tumor, which will provoke painful inflammation under the armpit.
- Get involved in self-medication when there is no positive dynamics already after 1-2 weeks of using various means.
- Warm and massage the armpit where the lipoma is. These actions will lead to the spread of pathological cells to neighboring lymph nodes and underlying tissues. The tumor can develop into cancer.