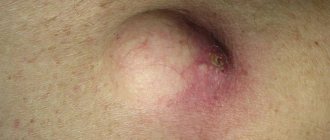
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that can cause small, raised papules to grow anywhere on the body, particularly on the genitals (lips, clitoral area, vaginal opening), as well as the perineum and anal area. There may be just one or a whole group, and although they are usually painless, they can become quite itchy.
Molluscum contagiosum papules on the labia are usually smooth and firm with a dimple in the center, but may be pink, white, or flesh-colored in appearance. The infection is spread through sexual or non-sexual skin-to-skin contact and is most common in children, sexually active adults, and immunocompromised people.
Causes
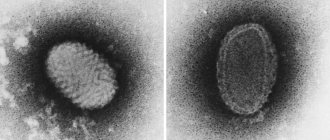
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus of the poxvirus family, close to the causative agents of smallpox. The rash on the genitals, buttocks and other parts of the body usually lasts for several months, but sometimes lingers for up to two years before disappearing spontaneously.
This skin condition can be spread from skin to skin or through close contact, shared towels, clothing, shaving equipment, swimming pools, or by scratching the affected area, etc. This skin condition can be sexually transmitted and occurs in the genital and anal areas. In this way they are similar to genital warts. Avoid self-contamination or passing the molluscum to a partner by practicing safe sex or abstaining from sexual contact altogether until the outbreak is treated or eliminated.
Relapses
Unlike the varicella zoster virus (chickenpox), which never truly goes away and can cause herpes zoster (shingles) years later, the molluscum contagiosum virus does not remain after recovery. However, if you come into contact with someone with molluscum contagiosum, you may become infected with the virus again. There is no immunity against molluscum contagiosum.
Prevention
Among adults, the most common method of transmission of shellfish is through sexual contact. Therefore, avoiding sex with someone infected with molluscum contagiosum is a good idea. It should be noted that molluscum contagiosum is considered a less severe sexually transmitted infection, but it is still an STI.
It is difficult to prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum among children, so this infection is much more common among children.
Prevention
Special complications usually do not arise. Prevention lies in following the rules of skin care. It is necessary that each family member has their own means of cleansing the body.
Most often, molluscum contagiosum affects children. Parents must take care of the child's hygiene. Swimming pools are especially dangerous. Often the virus is contained in the water in which a large number of people bathe.
Most modern pools are thoroughly disinfected, but there are exceptions.
It is important to wash your hands after using public transport. It is advisable to use an antiseptic.
Symptoms
Infection with the molluscum contagiosum virus causes fluid-filled bumps to appear on the skin.
These bumps range from the size of a pinhead to the size of a pencil eraser. They usually have a small dimple or dimple in the middle. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, may develop large bumps. They may grow to the size of a ruble coin, or they may have clusters of atypical bumps. In most people, lesions caused by molluscum contagiosum are painless. However, they may become itchy, irritated, swollen, or inflamed.
Photo of molluscum contagiosum
If you have molluscum contagiosum on your genitals or other intimate places, it is important to avoid injuring them. Scratching or scratching can spread the virus. Scratches can also make your skin susceptible to secondary infections caused by other bacteria. Molluscum contagiosum infections are usually easy to treat in people with healthy immune systems.
Because molluscum bumps are painless, you may not notice an infection. Visual examination of the genital area, perineum, buttocks and anus is the main way to identify signs of this disease. Molluscum contagiosum cannot be detected by smear or blood tests.
Main transmission options
The virus that causes the disease is transmitted from one person to another. Representatives of the animal world are not carriers of orthopoxvirus. There are 3 main infection options:
- Due to sexual intercourse with an already infected person;
- through water;
- contact-household method.
The last case occurs most often. You can become infected through tactile touch (hugs, travel on public transport, massage of a sick subject). This explains why children are often treated for this disease.
The indirect contact route is dangerous because a person cannot be sure that infection will not occur even in the absence of obvious signs (an incubation stage is possible).
You can simply walk into an unfamiliar room, sit on the sofa and become a carrier of the virus. After all, it is wonderfully preserved in various materials. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out thorough disinfection in residential premises and public places.
Another situation is frequent change of sexual partners. In this case, the person takes responsibility for his health. You need to understand that contraception cannot protect against all diseases.
In this case, even a hug will be enough to cause health problems. Although the virus foci are predominantly located in the genitals, so a condom can still protect against infection.
The waterway is often not classified as a separate group. In fact, infection occurs through water, but viral particles enter it from an infected subject. Therefore, many experts are inclined to believe that this is also a household contact route.
A similar outcome of events is possible when visiting swimming pools, saunas and public beaches.
In addition, a person who has previously suffered from molluscum contagiosum may become self-infected again. This happens when the skin rubs. But regardless of the method of infection, the clinical symptoms are very similar.
Some people are immune to this infection.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
There is no cure, but molluscum contagiosum growths from the labia will eventually go away on their own. In most people, the lesions or growths usually disappear between 6 and 12 months of age. However, sometimes the infection can take years to clear up and this is the main reason why people get treatment.
Growths from the intimate area can be removed by a doctor. In fact, your doctor may recommend removal of the molluscum contagiosum to limit its spread to other people. Remember that molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious!
Cryotherapy and radiosurgery are considered among the most effective treatments, although they have received some criticism due to the risk of blistering, scarring, or hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin). A type of non-invasive surgical curettage, otherwise known as molluscum contagiosum “plucking,” is also effective in physically removing papules from the labia and other private parts of women, although it can also cause scarring. Two other ways your doctor can remove lesions secondary to molluscum contagiosum are scraping and laser.
Prevention of infection
Molluscum contagiosum of the genitals is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. It can also be spread by contact of the labia with objects, such as clothing or towels, that have been contaminated with the virus. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid sharing clothing, towels and sex toys with infected people. Finally, wash your hands after touching any of your own molluscum contagiosum rashes. This may help you avoid spreading the virus to other areas of the skin.
Because labia molluscum is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, safe sex cannot completely prevent transmission. However, reliable condom use can reduce transmission of the virus. Additionally, there is some evidence that having pubic hair may reduce the risk of shellfish transmission. At least two studies have found evidence of more infections in people who shave or epilate their pubic hair.
Where to go in Moscow
Two different types of medications can be used to treat molluscum contagiosum.
First, topical medications containing retinoids can be applied to the lesions. Second, irritants containing salicylic acid can be applied to the lesions to dissolve them over time. Immunomodulatory and antiviral methods, in particular oxolinic ointment and other drugs, can also be considered. As always, treatment for molluscum contagiosum should be prescribed by a doctor. Clarification:
✔ If you want to get rid of this problem, sign up for a preliminary consultation with a leading specialist at our Moscow clinic!
Diagnostics
The symptoms are quite specific, so once symptoms appear, diagnosis is not difficult. For example, a rash with an umbilical depression and crust-like contents is typical of molluscum contagiosum.
After examining the nodules, a dermatologist can immediately make the correct diagnosis.
Additional examinations are extremely rarely required. To do this, a small amount of skin is taken from the neoplasm. Next, it is studied under a microscope.
Such a biopsy of the biopsy thoroughly shows all the features of the disease. Molluscum contagiosum nodules are often confused with similar formations, which happens with certain diseases.
Among them are the following formations:
- Flat warts. They usually appear on the face or the back of the hands. They are small in diameter and smooth.
- Keratoacanthomas are convex-shaped formations. They are usually hemispherical in shape and slightly reddish in color.
- Milia are small white dots located in the sebaceous glands of the skin. They occur when excessive amounts of dense sebum are produced. It is not completely released from the layers of the skin and the pores begin to clog.
- With scabies, small pink papules appear on the skin.
- Basal cell carcinoma actually resembles a clam on the skin. They are also lightly pearlescent in color and protrude above the surface of the skin. The main difference is the single location. But the “contagious mollusk” appears in plural quantities. Moreover, these rashes are nearby.
But the risk of confusing this disease with warts or lichen ruber is minimal.
Recommendations for caring for a child during illness
To avoid spreading the infection to other parts of the body, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Cover the lesions with tiny bandages.
- Wash your hands often.
- Wash clothes in hot water and iron with a hot iron.
- Clean your child's skin with a hydrogen peroxide solution.
Rice. 15. If you have molluscum contagiosum, you should constantly clean and lubricate the skin with antiseptics.
How to be treated
Only the doctor explains how to treat molluscs on the face after making a diagnosis. Typically, specialists do not resort to drug therapy if the body as a whole is strong and the immune system is in order.
Over time, all symptoms gradually disappear. If immunity is reduced, then without taking certain measures there is a high probability of transformation of the initial stage into a chronic one.
If the body is extremely weakened due to any diseases or for other reasons, it is vitally important to constantly take measures to strengthen the immune system.
In such a situation, medications are prescribed depending on a number of indications: the patient’s age, general well-being, and the stage of the disease.
List of commonly prescribed medications:
- Cycloferon.
- Amexin.
- Antibiotics: Metacycline, Tetracycline.
For external treatment of the affected areas, ointments are used - oxolinic, Acyclovir.