Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
The Bartholin gland is located in the vestibule of the vagina, at the base of the labia majora. Its main function: moisturizing the vaginal and vulva area, producing lubrication during arousal. Pathogenic bacteria enter it quite often. This may be due to a general decrease in the body's resistance or changes in local immunity, wearing tight underwear made of synthetic materials, genital infections, poor hygiene, and much more.
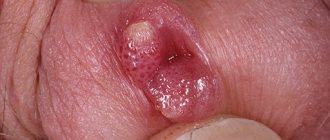
Inflammation of the Bartholin gland is called bartholinitis. Bartholinitis provokes tissue swelling, blockage of the gland and is fraught with the appearance of an abscess. This is a complication that is characterized by the appearance of purulent contents. Opening up bartholinitis or an abscess is perhaps the most effective way to quickly get rid of the disease and return the gland to normal function.
Why does an abscess occur?
The causes of bartholinitis are very extensive:
- Infection with pathogenic flora (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis or other STI);
- Reproduction of opportunistic microorganisms - streptococci, Candida fungi, E. coli, etc.;
- Factors that reduce resistance to infection are previous severe illnesses, allergic reactions, poor hygiene, swimming in open water, injuries (for example, due to too active sexual intercourse, medical procedures), hypothermia, vitamin deficiency, etc.;
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- Wearing tight underwear;
- Promiscuous sex life without the use of protection.
A combination of several pathogens at once is possible. It is worth noting that infection can enter the gland not only from the vagina, but also from the urethra, if cystitis or urethritis occurs. More rare routes of entry into the bloodstream and lymph from other foci of inflammation, for example, with tonsillitis, inflammation of the kidneys, etc.
2.When to see a doctor for a Bartholin gland cyst?
It is imperative to consult a doctor for a Bartholin gland cyst if the swelling continues to increase, and home treatment for several days does not produce results. In addition, if there is severe pain (and therefore a possible abscess), medical attention is also necessary. The cyst will have to be opened and treated. The same situation applies if a woman cannot walk or sit due to a cyst and pain.
Symptoms such as fever and abdominal pain are usually not associated with a Bartholin gland cyst. But their appearance is a reason to seek emergency medical help. If you have other symptoms - vaginal discharge, vomiting - be sure to call a doctor.
Visit our Gynecology page
Abscess symptoms
False and true abscess of the Bartholin gland are distinguished. If only the excretory duct is infected, and the glandular tissues are healthy, we are talking about a false abscess. The inflamed duct is filled with purulent contents, stretches, and its opening is blocked, while in the surrounding tissues, as a rule, there is no suppuration. A true abscess is characterized by suppuration of the gland itself.
A false abscess has an acute, rapid onset. A painful sensation appears in the area of the labrum major, depending on the side of the affected gland, increased pain with active movement, sitting and walking, during intimacy. On the side of inflammation, there is pronounced swelling and redness of the skin, while the skin easily moves to the sides. In addition to local symptoms, high body temperature is often noted - up to 38.5-39 C, fatigue, chills and loss of strength.
A true abscess has an even higher temperature - up to 40 C, and pronounced symptoms of intoxication. The pain is constant even at rest; there is a feeling of “pulsation” of the affected area. In this case, it is advisable to perform laboratory tests - there is an increase in the level of leukocytes and ESR. Swelling of the labia can reach 5 cm in diameter, the skin over the abscess becomes bright red, motionless when palpated. In some cases, there is an increase in the inguinal lymph nodes from the causative side.
1.What is a Bartholin gland cyst and its symptoms?
Bartholin glands
located at the entrance to the vagina in women, one on each side. They are small, and normally they are not noticeable and cannot be felt in any way. The function of the Bartholin glands is to secrete fluid onto the internal mucous membranes of the labia minora.
Bartholin gland cyst
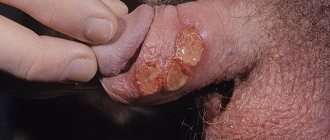
develops when the exit channel in the gland is blocked. This usually happens to only one of the two glands. The fluid that is produced in the gland begins to accumulate inside. As a result, the gland swells and forms cysts. If the cyst becomes infected, an abscess occurs.
Bartholin gland abscess
can be caused by almost any bacteria. Most often these are microorganisms that cause sexually transmitted diseases - chlamydia and gonorrhea, as well as bacteria that live in the gastrointestinal tract (Escherichia coli). Often, more than one type of microorganism is found in an abscess.
Cyst symptoms
Bartholin gland cyst causes swelling of the labia on one side
, near the entrance to the vagina. The cyst itself usually does not cause much pain. And if such pain appears, this may indicate the development of an abscess. Additionally, large cysts can be painful on their own due to their size.
A Bartholin's gland abscess causes severe pain in addition to swelling of the gland
. The swollen area becomes very sensitive and the skin turns red. Walking and sitting can be very painful. Vaginal discharge may also be present, especially if the infection is caused by sexually transmitted organisms. But there is usually no temperature with a Bartholin gland abscess.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Consequences and complications of an abscess
As a result of a chronic abscess of the Bartholin gland, a cyst can form - a cavity with dense walls and contents. This will also require the intervention of a doctor, so if the symptoms weaken, you should not refuse surgical treatment, that is, opening the Bartholin gland abscess. Even if the symptoms have gone away due to spontaneous opening, you should definitely consult a doctor: there is a high probability that the duct will become blocked again and the disease will become chronic. In addition, it is important to identify the causes of inflammation - diagnose STIs, receive treatment that corrects the function of immune forces, etc.
Types of gynecological abscesses
Gynecological abscess is classified according to several criteria. Firstly, purulent capsules are divided according to the nature of their formation:
- acute purulent process - develops rapidly, symptoms quickly intensify, and the patient’s general well-being worsens;
- chronic abscess - practically not accompanied by symptoms, characterized by frequent relapses of suppuration and the formation of fistulas at the site of the purulent cavity.
Secondly, the disease is classified according to the place of formation of ulcers:
- bartholinitis or abscess of the Bartholin gland, which is located near the entrance to the genital tract;
- suppuration in the area of the pelvic cells with damage to the uterine ligaments;
- a mammary abscess develops as a consequence of advanced mastitis and can be located in the nipple area (subareolar purulent cavity);
- pelvic abscess - occurs during inflammatory processes in the fallopian tubes and ovaries (the pathology is characterized by a large volume of purulent discharge);
- paraurethral abscess is located in the area of the urethra, labia and vagina;
- a retrouterine purulent capsule forms between the walls of the uterus and rectum;
- tubo-ovarian abscess is formed as a result of the development of adnexitis;
- Ovarian abscess usually occurs with unsuccessful abortions or advanced gynecological diseases.
Features of intervention for Bartholin gland abscess
If acute bartholinitis can be cured using conservative methods, then when an abscess forms, the only reliable and effective method of therapy is an autopsy. It lasts no more than 15-20 minutes and is carried out as follows:
1. The doctor treats the surface of the genital organs with antiseptic solutions and performs local anesthesia. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, but such a decision will require careful preliminary preparation - examination to ensure there are no contraindications, restrictions on food and drink intake.
2. The abscess of the Bartholin glands is opened, the contents are evacuated, and washed.
3. A drainage is installed - a thin tube that will prevent the hole from closing prematurely and will ensure the outflow of the resulting fluid. Usually it is installed for a period of no more than 5-6 days.
The doctor will also recommend the use of antibacterial agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, solutions for local compresses; will explain the features of the rehabilitation period and give recommendations for accelerating healing during the first time after the intervention.
Diagnosis of gynecological abscesses
The diagnostic process begins with identifying the patient's disturbing symptoms and complaints. After the interview, the doctor conducts a gynecological examination by palpation and using gynecological speculum. Some genital abscesses (for example, bartholinitis) can be diagnosed during a gynecological examination. Others require more in-depth diagnostics - laboratory and instrumental studies.
The doctor gives a referral to donate blood and urine for general and specific laboratory tests (CBC, OAM, tests for sexually transmitted infections), which can identify various viruses and inflammatory processes. Hardware research methods include computed tomography and transvaginal ultrasound.
Recommendations after surgery
After opening the abscess, it is important to carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- Avoid sexual intercourse during the recovery period;
- Do not visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, ponds;
- Washing in the shower instead of lying in baths;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- Give preference to loose cotton underwear.
As a rule, recovery occurs quite quickly. At first, it is preferable to remain in bed to prevent stress on the perineal tissue.
3. Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Diagnostics
A medical examination is necessary to diagnose a Bartholin gland cyst or Bartholin gland abscess.
. In most cases, no additional medical tests are required.
Sometimes analysis
, which allows you to determine the type of bacteria that caused the infection and check whether the patient has sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea or chlamydia). For analysis, a smear is simply taken using a cotton swab from the contents of an opened abscess or other area (cervix, for example). The result of such tests may indicate the need for antibiotic treatment.
Treatment
The main treatment for Bartholin gland cyst at home and treatment for Bartholin gland abscess is sitz baths
, which help drainage. The water should not be scalding hot, but still warm enough. These “compresses” should be done 3-4 times a day for 10-150 minutes. Often this procedure alone is sufficient to treat the cyst. An abscess may require drainage from a doctor. If cysts recur and bacterial infections occur, a course of antibiotics may be required.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
4. Surgical treatment of cysts
Abscesses and large, painful cysts often require surgical treatment - drainage
. An abscess is an infection in a confined space, and antibiotics may not have the desired effect. Therefore, treating a Bartholin's gland abscess almost always requires draining the fluid inside it (opening the Bartholin's gland abscess).
When draining an abscess
local anesthesia is used. Then, when opening the Bartholin gland abscess, an incision is made through which the affected contents of the abscess are drained. Gauze or a small catheter may be inserted into the cavity. This helps keep it open and promotes further drainage. The gauze pad is removed after 24-48 hours. And if a catheter is used, it can remain in place for up to several weeks to minimize the chance of recurrence.
Draining an abscess can be inconvenient because local anesthetics do not always work well in inflamed tissue and mucous membranes. Therefore, depending on the individual situation, additional pain relief may be given.
Once a Bartholin's gland abscess has been opened, antibiotic treatment is usually not required. But if a sexually transmitted infection is suspected, or if a vaginal or genitourinary infection is confirmed, an antibiotic may be prescribed.
Postoperative period after opening the abscess
For 5-7 days, the drainage should remain in the cavity of the emptied abscess. It is necessary for the timely evacuation of contents and to prevent the development of a repeated episode of inflammation. Premature removal of drainage and infection of the wound can lead to relapse of inflammation and the formation of a Bartholin gland cyst. And then opening the abscess will be required again. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and daily wound care procedures. Care consists of washing the abscess cavity with a solution of peroxide or furatsilin, introducing tampons with medications (most often with levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment).
An abscess is painful and unpleasant. The opening of an abscess in our center is performed by qualified surgeons. Delicacy and accuracy are especially important during this operation. By contacting us, you can always count on competent and careful assistance.