1. Lipomas
Formations on the genitals come in several varieties. The reasons, patterns, mechanisms of their occurrence in some cases are known and understandable, in others they remain not entirely clear. Different types of formations affect specific tissues. The following types of formations on the external genitalia are divided: lipoma, atheroma, bartholinitis, papilloma.
Lipomas
most often form in the subcutaneous fat layer. It is impossible to clearly identify the reasons for their occurrence, but a certain statistical connection with hereditary predisposition has been established. Moreover, the growth of lipomas has nothing to do with fat consumption or a tendency to develop subcutaneous fat deposits. The incidence of lipomas in thin and overweight people is the same. Lipomas can range in size from 1 to 15 cm and are usually not painful or itchy, presenting only a cosmetic problem. Cases of malignant degeneration of lipomas are very rare; More often, mechanical damage carries the threat of suppuration and infection. Lipomas up to 3 cm are treated non-surgically - by injecting them with a drug, the action of which leads to the resorption of the formation. Large lipomas are removed surgically: with laser, electrocoagulation or radioknife.
As a rule, a new lipoma does not appear at the site of a well-performed operation. However, it is not uncommon for new lipomas to form in nearby tissues.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Diagnostics of education
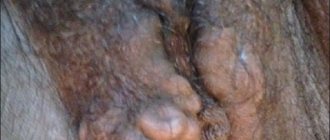
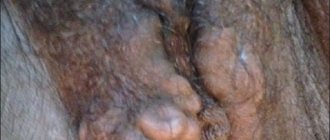
In appearance, Fordyce papules are small - no more than 2 mm, and most often smaller, granules of white, yellowish or dirty yellow color. Cysts are painless and do not increase in size. If you open the tumor, a thick white-yellow mass will be released. In this case, a small hematoma forms and pinpoint drip bleeding occurs.
Doctors distinguish 2 types of Fordyce papules:
- pearlescent papules - affect the male genitals, do not occur in women;
- Fox-Fordyce disease - papules are located on the labia of women, the pubis, and around the nipples. Not painful, but there may be some slight itching before menstrual bleeding.
A cosmetic defect should be differentiated from the following pathologies of the skin and genital mucosa:
- molluscum contagiosum;
- neurodermatitis of various etiologies;
- lichen planus;
- eczema.
Diagnostic measures consist of a visual examination, analysis of the patient’s complaints, and exclusion of other pathological processes on the skin. Additional studies - neither clinical tests nor ultrasound - are not carried out for this aesthetic defect.
2.Atheromas
Atheroma
is a cyst filled with a yellowish fluid formed by fat cells, epidermis and sebum. Since all this in the cyst is in a state of stagnation, when opened, the substance that is usually removed has an unpleasant odor. Causes of atheroma: increased oily skin, acne, poor cleanliness, hormonal changes, heredity. Atheromas form where there are many sebaceous and sweat glands. When they grow to a size of 5 cm, tension occurs on the surface of the skin and even internal inflammation is possible. It is always recommended to remove atheromas without waiting for complications, although they also degenerate extremely rarely.
The atheroma is completely removed by isolating it from the tissue. At the same time, they try not to disrupt its integrity and make sure that no particles of the cyst shell remain, otherwise this may cause a relapse in the same place.
Visit our Gynecology page
Why can’t tumors on the genitals be ignored?
Class Clinic
Practicing gynecologist-oncologist Irina Vladimirovna Shekhovtsova spoke about what neoplasms on the external genitalia are dangerous, what to do if they appear and how to easily remove them.
What neoplasms on the female genital organs do you most often encounter?
Due to the specifics of my work, these are most often diseases of the vulva, anal area, and cervix. One of the most dangerous and scary diseases that you have to deal with is vulvar cancer. Fortunately, such localization of cancer is a fairly rare case, accounting for 2-8% of all diseases affecting the external genitalia. The main thing is that its development can be easily prevented by consulting a doctor in time - when the first signs appear, and this can be almost any neoplasm on the vulva.
What signs of vulvar cancer can a woman detect herself?
I would like to immediately note that it is impossible to suspect vulvar cancer on your own; for this you need to visit a doctor. Symptoms of vulvar cancer, especially in the initial stages, are similar to viral and bacterial inflammation - itching, burning of the external genitalia. The appearance of condylomas is typical, the woman believes that it is a “skin horn”, a dense nodule, “just a compaction”, it happens that such symptoms do not cause concern. It happens that a woman comes to a gynecologist, but he is not alert for cancer and does not diagnose cancer. Next, a dense tumor develops, against the background of the tumor a bleeding ulcer appears, it is very specific, it has uneven dense edges, a necrotic bottom. Women try to treat these ulcers on their own and also do not turn to a specialist, since at this stage of the disease there is no pain. In our country, women go to the gynecologist when something hurts.
What happens if you don’t see a doctor in the initial stages, what are the later signs of the disease?
In such cases, pain begins and is difficult to ignore. The tumor moves from one labia to another, so-called “kissing ulcers” appear. The lymph nodes are affected, the tumor can spread to the vagina, urethra, etc. As a rule, in such cases a diagnosis of vulvar cancer is made.
Any tumor, including this one, begins with an underlying disease and has a precancerous form. There is no cancer without precancer and underlying disease. And our task is to diagnose as early as possible.
Are there any predisposing factors for developing vulvar cancer?
Yes, of course - this is low immunity and diabetes, often insulin-dependent. A risk factor is infection with the human papillomavirus (types 16, 18 and others, there are more than 70 of them, which can provoke the development of cancer). In addition, obesity, tobacco smoking is a very serious factor, promiscuity in sexual relations, non-compliance with personal hygiene standards, crourosis (wrinkling of the labia majora and minora, itching, skin resembles parchment paper) and leukoplakia (signs are the same as crourosis). Dark spots – pigmented nevi – should also alert you. If a dark spot appears on the vulva, which the patient may call a mole, this is an alarm bell, in such cases it is necessary to immediately contact a gynecologist.
Are women who smoke at risk?
Yes, definitely. Women often think that smoking can only cause lung cancer, but this is not true. One of the most powerful factors contributing to the development of both vulvar and cervical cancer is the carcinogens contained in tobacco mixtures. In addition to nicotine, tobacco smoke contains ions of radioactive metals such as cesium, polonium, radium-226 and radium-228, and more than 50 other compounds that can cause cancer. Through the lungs, these substances penetrate the circulatory system and slowly affect the entire body, including the female genital organs.
What diagnostic methods are used to distinguish vulvar cancer from other diseases?
To conduct the study, a small piece of tissue is taken and sent to a morphologist, and the morphologist, in turn, gives a conclusion whether there are malignant cells or not. I would like to note that diseases of the vulva cannot be treated without a preliminary histological examination, without establishing the true causes of the neoplasm and nosology.
In women of what age is this disease more common?
It is cancer that occurs more often in older women, 70 years and older. For some time I worked with this particular age group: women in deep menopause who do not take care of themselves, do not take care of their health and ignore recommendations for the prevention of this disease. There have been a few cases in younger women, over 50 years of age. But in such cases it was about early diagnosis. Such women visit the gynecologist more often, and the gynecologist may diagnose vulvar cancer earlier.
How good is the prognosis with early diagnosis?
In such cases, we can talk about radical and more effective treatment; it is clear that in such a situation a favorable outcome is more likely.
Accordingly, any neoplasms should alert a woman, and in such cases it makes sense to consult a doctor?
Oncological vigilance has never harmed anyone. Even when I was studying, teachers said that a doctor should always look for something bad. It is better to overdiagnose and scare the patient than to miss the disease. I would like to note that in my practice, women with vulvar cancer come late when there is metastasis to the regional lymph nodes, and in such cases the treatment is very difficult, often patients die within a few months. For this disease, surgical treatment involves severe mutilating operations, and reconstructive plastic surgery cannot offer anything, since a huge flap of skin with lymph nodes and subcutaneous fat is removed.
Tell us about tumors that are not malignant.
We have already touched on this topic a little. Condylomas, small papillary growths of the mucous membranes of the genital organs, and papillomas are very common. The main signs are typical for almost all neoplasms: compaction, swelling, inflammation, itching and burning. This applies to both the vulva and vagina.
How are these tumors removed?
Very easy to remove. One of the most effective methods is radio wave. With a special device “Surgitron”, which is equipped in our clinic, it is possible to remove condylomas without the formation of a scar and a weeping surface. The device actually dries out the tumor. Previously, we used electrocoagulators, but this was complicated by a lot of unpleasant sensations; healing took several weeks. There is also laser removal, but with this method histological examination of the tissue is impossible. In addition, it is still possible to remove it using the classical surgical method, but in such cases cosmetic stitches are applied and a slight scar is likely to form.
Make an appointment with Irina Vladimirovna Shekhovtsova on the website or by phone (4012) 33-44-55.
3.Bartholinitis
Bartholinitis
- This is a consequence of blockage of the Bartholin gland. It is located at the entrance to the vagina and is involved in lubrication (moistening) of the external genitalia. During moments of sexual arousal, this process is especially intense. When a blockage of the gland duct occurs, a cyst is formed in which the produced secretion accumulates. If therapeutic measures are not taken, infection and cyst rupture often occur. This gives relief because the cavity is freed from accumulated secretory masses. However, the consequences of such spontaneous opening against the background of an abscess can be very dangerous. You should definitely consult a doctor at the first sign of a lump at the entrance to the vagina. If treatment is not carried out or the cyst does not open spontaneously, general malaise begins: the temperature rises, pain is felt when walking, and signs of acute infection appear. In the most difficult cases, the abscess can spread to the internal genital organs: the uterus, appendages.
Treatment of bartholinitis in uncomplicated cases by opening the cyst is not difficult. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. In more severe cases or when a postoperative relapse is established, a decision is made on bartholinectomy (complete removal of the Bartholin gland). This is a rather complicated operation, but in some cases it cannot be avoided.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Treatment and removal methods
If the tumors do not bother the woman, it is recommended not to touch them. By the age of 30, wen goes away on its own. During this period, hormonal statuses stabilize. By the age of 40, hormone activity begins to decline. Doctors associate the disappearance of Fordyce granules with a decrease in the production of androgens and estrogens in the body.
If a cosmetic defect causes aesthetic distress, it is recommended to remove fatty papules.
What absolutely cannot be done? Squeeze out the wen yourself. It is not possible to completely remove the fat capsule. And the risk of getting a bacterial infection is huge. In addition, a hematoma forms at the site of the papule.
We recommend reading:
- Why do Fordyce granules appear on the nipples?
- How to treat gastric lipoma
- How to effectively treat HPV in women
What doctors offer:
- Lubricate the wen with Retin-A cream.
The drug is applied to the affected area 2 times a day. Under the influence of the active components of the ointment, sebaceous plugs dissolve. Users note that the first signs of improvement appear after 3–5 procedures.
- Treat the affected area with an alcohol solution of calendula.
A tampon soaked in tincture is applied to the affected area for 20 minutes. But ethyl alcohol dries the skin and instead of healing, you can get dry skin and extensive chemical burns of tissue.
This method is unacceptable when Fordyce granules are located on the reproductive organs, and especially on the mucous membrane of the labia. Ethyl alcohol will cause a burn to the delicate area and destroy the beneficial microflora of the genitals. What can cause an inflammatory process due to an imbalance of beneficial and opportunistic flora.
- Cryotherapy.
Papules are treated with liquid nitrogen. Under the influence of low temperatures, fat formation is burned out. The risk of infection and bleeding is minimal, since there is no contact with the skin during the procedure.
- Electrocoagulation.
High frequency currents are used to remove wen. The procedure is painful, so anesthesia is required. Although the manipulation is minimally invasive, after healing, scars may remain on the skin. Therefore, it is not recommended to use this technique to remove tumors on the lips.
- Laser therapy.
The procedure is similar to electrocoagulation. Instead of electric current, a laser beam is used. After exposure to light quanta, a crust forms on the mucous membrane. In a few days it will disappear. There will be clean, healthy skin underneath.
Classical surgery is not used in the treatment of Fordyce papules. The procedure is invasive and there is a risk of bleeding and scar tissue at the site of the cyst.
All treatments are temporary measures. In 85% of cases, a relapse of the disease develops within 1–2 years after removal of the sebaceous cysts.
- Treatment with Darsonval apparatus.
This is more of a physiotherapeutic procedure than a method of treating neoplasms. Under the influence of weak alternating current pulses, microcirculation in skin tissues improves and sebum production decreases. To obtain a sustainable effect, a minimum of 10 procedures will be required.
The use of this treatment method for papules located on the labia should be discussed with a gynecologist. In addition, darsonvalization has a number of contraindications, such as pathologies of the thyroid gland, rosacea, and the presence of heart rate stimulants in the body.
4. Papillomas
Papillomas
external genitalia - this is the growth of the epidermis of the labia. By their appearance, papillomas are easily differentiated from other formations. They are usually located on a stalk, resembling the shape of a mushroom. Unlike other uncomplicated formations, papillomas may itch or hurt; They are often injured. The reason for their appearance is HPV, the human papillomavirus, which is activated under favorable conditions (decreased immunity, stress, hormonal changes). HPV infection occurs through sexual contact or from the mother at birth. The latent period of this virus (without any formations on the skin) can last indefinitely. The actual growth of the epidermis on the genitals can be provoked by a number of factors, mainly associated with a decrease or depletion of the body's protective resources.
Papillomas are always treated comprehensively: formations on the skin are surgically removed, and the human papillomavirus itself is subjected to systemic therapy aimed at increasing immunity, restoring hormonal balance and balanced metabolism.
It is necessary to treat papillomas. Not only can they grow to large sizes, but they also carry the risk of infecting a sexual partner.
Causes of occurrence on the labia
Medicine does not name the exact reason for the appearance of Fordyce granules. These growths are sebaceous cysts. The favorite location is the corners of the mouth, the genital area in women and men, sometimes on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
Science knows that Fordyce granules:
- are not a skin disease;
- are not transmitted either sexually or by any other means;
- do not become inflamed;
- do not fester;
- don't itch;
- no changes occur in the epithelial tissues. The skin works normally, biological mechanisms are not affected.
Such neoplasms appear during puberty during sudden hormonal changes in the body. In the area of the lips, labia minora, directly under the upper layer of the epidermis, there are many sebaceous ducts. This location is determined genetically. Therefore, it makes sense to consider this a congenital cosmetic defect that does not appear immediately.
What can affect the development of sebaceous cysts? Doctors identify a number of provoking factors:
- injury to the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal imbalance;
- bad habits have some influence;
- ignoring personal hygiene requirements.