August 16, 2020
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that can occur due to a variety of irritants: allergens, aggressive chemicals, fungi, and adverse weather factors. Chronic inflammation of the skin also occurs with psoriasis, but in this case the condition is distinguished as a separate disease, and dermatitis is a collective concept, a syndrome that may not relate to any specific disease, occurring periodically.
Types of dermatitis
Dermatitis is classified depending on the cause of its occurrence. The following types are distinguished:
- atopic - caused by excessive sensitivity of the skin to environmental factors, the genetic nature of atopy is assumed;
- traumatic - appears as a result of mechanical trauma to the skin;
- medicinal - adverse reaction to any pharmaceutical drugs;
- thermal - burns or frostbite;
- allergic - skin reaction to any factor that leads to an increase in histamine levels;
- seborrheic - occurs in those areas of the skin that are actively supplied with sebaceous glands, manifested by the occurrence of dandruff and acne;
- herpetic dermatitis - associated with damage to the body by herpes;
- infectious, for example, scabies or lichen;
- contact - a reaction to an external irritating factor.
You may have already heard the term “contact dermatitis”. This is not a separate type, but a type of dermatitis that is caused by direct contact of the skin with a damaging factor. For example, allergic dermatitis may be contact dermatitis if you used a detergent to which your skin reacted, or it may be non-contact if the allergen was in the air or food.
Contact dermatitis - symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of simple contact dermatitis:
- soreness;
- redness;
- burning;
- edema;
- itching (less pronounced).
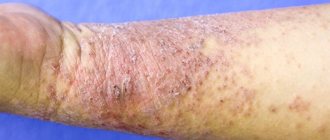
Sometimes blisters with clear serous fluid appear, which can burst. As a result, weeping occurs in the area of dermatitis - fluid separation. If an infection is added to the irritation, pustules appear.
Symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis:
- severe itching;
- edema;
- redness;
- blisters with serous fluid, which then dry out and form scales and crusts;
- pain as a result of scratching and secondary infection.
When dermatitis becomes chronic, peeling and thickening of the skin may occur in areas of inflammation [3]. If the patient does not begin treatment in a timely manner, the disease progresses, and allergens appear - rashes on other parts of the body, far from the primary focus.
Dermatitis can affect various areas of the body: scalp, face, eyelids, mouth, lips, neck, hands, feet, limbs.
Scalp
On the scalp, dermatitis develops with increased sensitivity to certain metals, in particular nickel. Products made from it (for example, curlers, hair straighteners) can cause redness and itching. Hair washing products can lead to the development of “washing dermatitis”, which appears as strip-like lesions on the face and neck. Other causes of dermatitis are accessories with rubber or leather parts: hat band, cap lining, wig patch [5].
Face
Dermatitis can be caused by the use of cosmetics: moisturizers and sunscreens, hair care products, perfumes. Mobile phone use can cause dermatitis in the form of a unilateral rash on the cheek [6][7].
Eyelids
Sensitivity of the skin in the eyelid area often causes the appearance of dermatitis in this area. Dermatitis can be caused by the prescription of eye drops and the use of objects containing rubber, such as swimming goggles and microscope eyepieces. [8]. If you rub your eyes with your hands, “accidental” allergens can get on your eyelids.
Mouth, lips
The causes of damage to the oral cavity are dentures, crowns, and hygiene products. Nickel, cobalt, mercury, and gold are used to make dentures. These substances can cause burning and tingling sensations in the mouth [8][9]. An allergic reaction occurs to chemicals, flavorings contained in toothpastes and other oral care products. Sodium lauryl sulfate, which is part of toothpastes, often causes irritation.
Lip dermatitis is associated with the application of lipstick, which contains dyes, flavors, and preservatives. Another cause of lip dermatitis is the habit of putting metal objects in the mouth, in particular pens and pencils. Chronic dermatitis in the form of a plaque on the lower lip can develop in musicians who play wind instruments.
Neck
The use of cologne and perfume leads to rashes on the front surface of the neck. Photoallergic dermatitis of the face and neck can be caused by sunscreen agents. A rash in the form of a strip around the neck appears from contact with the collar of a shirt or coat if the allergen is part of paints and resins. Allergic dermatitis develops from contact with metal, which is part of jewelry - chains, necklaces. The lesion will correspond to the location of the decoration [13][14].
Hands, feet, limbs
Dermatitis can develop through daily contact with water, detergents, and the use of rubber gloves. There is palmar grip dermatitis, which affects the central part of the palm in contact with the allergen. The causes of such dermatitis are a mobile phone, a gear shift in a car, gripping a cane and other objects [2].
Hairdressers experience rashes due to the use of shampoos, hair dyes, and nickel-plated scissors [15]. If the periungual ridges on the fingers become inflamed, exposure to formaldehyde resin or acrylate in nail polish and artificial nails can be suspected.
Typical allergens that cause foot dermatitis are rubber vulcanizers in rubber, tanning agents, rosin, chromates, such as potassium biochromate in leather [16][17].
The upper and lower extremities are exposed to irritants and allergens [2]. Dermatitis is localized on the wrists, thighs, and calf muscles.
Torso
Dermatitis of the trunk is common, but it is not always possible to determine the source of the allergens. Rash on the abdomen and back occurs when wearing belts with buckles and bras with clasps containing nickel. Nickel can cause dermatitis on the left side of the chest if a man carries a lighter or other item containing this metal in his chest pocket.
In the armpits, dermatitis appears when using deodorants that contain fragrances, essential oils, propylene glycol, and parabens.
Clothing can be a source of allergens. Rashes occur during intense sweating and are located in areas of friction between the skin and clothing. The causes of contact dermatitis are both the fabric itself and the dyes used in its production [20]. In recent years, it has been associated with dimethyl fumarate. The substance is used as a biocide to prevent the growth of mold and is found in fabrics covering sofas [21]. This type of dermatitis is severe and affects the back, buttocks, and lower limbs.
Causes
Patients with allergies always have a hereditary predisposition to its occurrence. Among relatives there will definitely be allergy sufferers, and their allergies can manifest themselves in different ways: skin, food, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma - the form does not matter.
To develop the clinical picture, exposure to a sensitizing substance—an allergen—is necessary. They can be dust, pollen, chemicals in detergents, clothing, hazardous industries, some food products, medicines, etc., as well as substances formed in the body itself under the influence of cold or sunlight, metabolic products of parasites.
Classification
The classification is based on the clinical symptoms (course) of the skin process, according to which the following are distinguished:
- An acute course, manifested by pronounced bright red hyperemia with predominantly exudative morphological elements (spots, papules, blisters, erosions, weeping). Dermographism (local change in skin color due to mechanical irritation) is persistent, red.
- Subacute course. Hyperemia is less pronounced, pinkish-red in color. In addition to exudative elements, scales, crusts, and infiltration may be present on the skin, mainly at the base of the morphological elements. There is no weeping. Dermographism is not persistent, red.
- Chronic course. Hyperemia of a bluish-reddish color. Exudative elements are practically absent, in places there are scales, crusts, and lichenification. There is no weeping. Dermographism is mixed - red with a transition to white.
What happens to the human body before skin symptoms appear?
Allergic skin diseases are based on changes in the reactions of the immune and nervous systems. After initial contact with an allergen, the immune system remembers information about it, i.e. the body enters a state of heightened readiness to quickly react to the re-entry of the same antigen (sensitization). During this time, the person is not bothered by any symptoms. And when this allergen is reintroduced, a pathological immune process begins with damage to the skin and sometimes other organs.
General symptoms
Characteristic signs for all dermatitis are hyperemia (redness) of the skin, swelling, local increase in temperature, feeling of heat and itching at the site of the lesion. After prolonged contact with the provoking factor or as the disease develops, a vesicular rash, blisters of various types, skin cracks, scabs, and areas of necrosis appear.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods help relieve exacerbation of allergic dermatitis, itching and weeping, and also contribute to the speedy restoration of the skin:
- Baths and rubbing from infusions of string, chamomile, viburnum bark, elecampane root.
- A cream made from sea buckthorn oil mixed with goose fat in equal proportions heals and softens the skin well.
- Grind 5 plantain leaves in a meat grinder, pour 70 ml of the pulp. dry white wine, leave for a day. Lubricate manifestations of dermatitis 2 times a day.
- Fresh basil leaves are crushed into a paste and then applied under a gauze bandage to the affected areas of the skin.
- Gruel from crushed celery is an effective remedy for weeping processes on the skin.
However, in some cases, folk remedies can only aggravate the situation, so such treatment should be undertaken with caution.
Can a patient self-diagnose and manage the symptoms of allergic dermatitis?
No and no again!
How and how to treat allergic dermatosis should only be determined by a doctor, since incorrectly diagnosed and incorrectly selected independent treatment can lead not only to the spread and worsening of the disease with chronicity of the process, but also to subdepressive and behavioral disorders.
- Treatment needs to be comprehensive, but primarily aimed at eliminating repeated contact of the patient with the allergen. To find out the type of allergen, the presence of cross-allergic reactions and the severity of pathological immunity disorders, an immunological examination is prescribed.
- Do not forget that these diseases, as a rule, occur against the background of abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, mineral and carbohydrate metabolism, endocrinopathies, and hereditary disorders, therefore, symptoms of concomitant disorders must be identified and eliminated. Therapy consists of systemic and external treatment that suppresses allergic inflammation and eliminates the effects of triggering factors.
- The complex uses hypoallergenic diet therapy, hyposensitizing treatment, eliminates harm associated with professional duties, and avoids household contacts with sensitizers. In addition, physiotherapeutic treatment methods are prescribed.
- To consolidate the treatment, daily skin care is necessary. A prerequisite is to moisturize the skin with special products, especially after bathing, and avoid hot baths with detergents that alkalize the skin.
Thus, timely contact with a dermatologist will provide a modern, rational approach to treatment, without the development of adverse reactions, and will allow you to combat exacerbations at the early stage of the disease, long-term controlling the course of allergic dermatosis.
Diet for allergic dermatitis
Hypoallergenic diet
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21-40 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1300-1400 rubles. in Week
The duration of the elimination diet is at least 6-8 months. It is dietary nutrition that can reduce the general state of hyperreactivity. In this case, the diet menu should correspond to the age/gender needs for basic nutrients and calorie content. The nutritional menu for adults should exclude to the maximum all foods that have high allergenic activity (coffee, chocolate, cow's milk, strawberries, cheeses, etc.). Also, nutrition provides for the exclusion/limitation of products containing food additives (antioxidants, flavorings, preservatives, dyes).
Nutrition rules
Compliance with nutritional rules for dermatitis is included in the treatment of the disease and allows you to achieve stable remission. A specially developed diet for allergic dermatitis in adults with a daily rational menu eliminates allergens and speeds up the process of getting rid of the disease.
Highly likely irritant foods include:
- nuts;
- coffee;
- sauerkraut;
- seafood;
- citrus;
- legumes;
- chocolates;
- strawberry.
Also, the presence of foods containing preservatives, emulsifiers and dyes should not be allowed in the diet. Dangerous foods for allergy sufferers are rich broths, all fried, salty and spicy foods, which increase the permeability of the gastrointestinal tract to the absorption of irritating substances.
When preparing dishes, it is important to follow the technology and not use expired products. Vegetables and fruits should be purchased from those that were grown without fertilizers. If dishes are prepared from cereals, they must be soaked in water for at least 10 hours. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of sugar and salt by 2 times. As for meat, it is recommended to boil it twice.
Facial dermatitis: causes
Statistics say that today every 8th person in the world suffers from facial dermatitis in one form or another, and adults and children suffer equally. And half a century ago, this disease occurred exclusively in children, and quite rarely. What changed?
It is not known exactly what exactly provokes the development of the disease: each case is individual. The main risk factors include heredity and poor lifestyle.
If you have a weakened immune system due to illness, you smoke, experience stress, do not take enough care of your facial skin, use low-quality cosmetics, neglect a healthy diet and vitamins, then sooner or later all this can affect your health and lead to dermatitis on the face.
Pathogenesis of ACD
Allergens with low molecular weight (less than 500 d) penetrate the stratum corneum of the skin and bind to tissue proteins, forming a new antigen as a result of the pathological process - an immunogenic neoantigen. This process is called haptenization. Haptens can penetrate even intact skin, but if the skin barrier is compromised, the risk of sensitization to topical medications and other allergens increases.
Many patients with ACD, which develops as a result of nickel allergy, have a mutation in the filaggrin FLG gene. Filaggrin is involved in the aggregation of cytoskeletal proteins that form the keratinized layer of cells. Mutations in the filaggrin gene lead to disruption of the skin barrier.
Haptens activate toll-like receptors, which leads to the activation of resident dendritic cells, including Langerhans cells, which bind the antigen and transport it to regional lymph nodes. There, Langerhans cells present the antigen to naïve T cells (cells not yet exposed to the antigen) and memory T cells. In the final stage, T lymphocytes proliferate, accompanied by the release of proinflammatory cytokines such as interferon-gamma. In addition, effector T cells promote the death of hapten-bearing cells, resulting in the development of the classic inflammatory rash characteristic of ACD.
Initial sensitization usually takes 10–14 days, starting with the first exposure to a strong allergen (eg, nickel).
List of sources
- Ivanov, O. L. Allergic contact dermatitis and associated allergic dermatoses: modern ideas about etiology, pathogenesis and diagnosis / O. L. Ivanov, E. S. Fedenko // Ros. magazine leather and venereal diseases. 2010. -No. 4. - P. 47-51.
- Korsunskaya, I. M. Therapy of contact dermatitis in adults and children / I. M. Korsunskaya, O. B. Tamrazova, T. A. Shashkova // Vestn. dermatology and venereology. 2006. - No. 4. - P. 46-46.
- Yu. Ilyina, N. I. Allergic skin diseases in clinical practice / N. I. Ilyina, E. S. Fedenko // Ros. allergol. magazine 2005. -№3.-S. 55-67.
- Luss L.V., Erokhina S.M., Uspenskaya K.S. New possibilities for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis // Russian Journal of Allergology. 2008. No. 2. P. 28-35.
- Immunological mechanisms of development of allergic dermatoses / R.T. Kazanbaev, V.I. Prokhorenkov, T.A. Yakovleva, E.Yu. Vasilyeva // Siberian Medical Review. - 2013. - No. 4. — P.9-13.