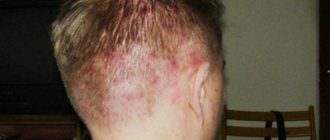
Pimples on the scalp in the hair are a very common occurrence. Unfortunately, it is usually not given importance, since the rashes are hidden behind the strands. As a rule, the patient turns to a specialist only when the problem becomes widespread. However, it should be remembered that treatment in this case turns out to be much more complex and lengthy.
Why do acne appear on the head?
The causes of acne on the head may be the following:
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- poor nutrition;
- insufficient or improper hair or skin care, as well as the wrong choice of care products;
- hormonal disturbances or physiological changes (for example, during puberty);
- increased sweating;
- folliculitis (its development may be indicated by purulent pimples on the head);
- constant wearing of hats made of synthetic materials;
- allergic reactions;
- frequent scratching, traumatic effects;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- dysfunction of the adrenal glands;
- decreased immunity;
- autoimmune disorders;
- hereditary predisposition;
- infectious diseases;
- taking certain medications (for example, corticosteroids).
Pimples on the scalp in men are most often caused by hormonal activity, stress, exposure to chemicals (for example, during industrial work), and skin reactions after shaving. In addition, breakouts can be a result of using dull trimmer blades while trimming. Acne on the head of women sometimes appears when using oral contraceptives.
Also, among other reasons, they can signal ovarian diseases, in particular polycystic disease. That is why, if the phenomenon is recurrent, a consultation with a gynecologist may be required.
How to get rid of a rash in an adult?
Acne elements, even hidden behind the hair on the temples, cause a lot of psychological discomfort, and therefore require high-quality elimination. By contacting a specialist, you can receive individual recommendations for comprehensive acne correction.
Facial care
Ensuring and maintaining the normal condition of facial skin is the main task of cosmetic care. And for acne, such measures have a number of features; among the most common recommendations you can hear the following:
Treatment of acne on the head
The course of therapy depends on the causes of the problem, however, as a rule, it includes:
- antimicrobials;
- enterosorbents;
- retinoids;
- means that dry out rashes.
In addition, clinical procedures such as mesotherapy, laser treatment, biocomplex, and plasma therapy are effective in this case.
When the rash spreads severely, it is sometimes necessary to take antibacterial drugs, as well as drugs to correct hormonal levels. To prevent the recurrence of acne on the scalp, the patient is advised to choose the right hygiene products, normalize nutrition, monitor the hormonal status of the body, take precautions when interacting with chemicals, take vitamins and microelements, and give up bad habits.
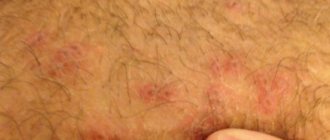
Symptoms of urticaria
The main manifestation is the appearance on the skin of red or pink spots of various shapes, and blisters, the size of which can reach several centimeters.
A slight swelling may appear, which gradually disappears over the course of a day, rarely two. If the swelling affects the deeper layers of the skin or mucous membranes, angioedema may result - a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical intervention.
The rash of allergic urticaria is always accompanied by unbearable itching, and some patients describe it as an unbearable burning sensation. Violent scratching of such areas can lead to infection of the epidermis with further complications in the form of pustules and wounds.
Minor manifestations of urticaria include:
- headache;
- elevated temperature;
- sleep disorder;
- anxiety;
- loss of appetite.
According to the nature of the course, allergic diseases are divided into two types.
Acute urticaria is diagnosed most often. Blisters and swelling of the skin in this form appear completely suddenly, sometimes against the background of a person’s excellent health. Most often caused by some external reasons, food. It also happens after using medications, especially when self-medicating. Symptoms go away on their own within a few days to several weeks.
Chronic urticaria is a condition in which symptoms continue to persist for more than 6 weeks after the first rash on the skin. This variant is characterized by a wave-like course, when periods of complete absence of symptoms (recovery) are abruptly replaced by exacerbations with the appearance of a new portion of spots and blisters. This is accompanied by unbearable itching and rapid development of Quincke's edema. The emerging elements of the rash can merge with each other, covering more and more new areas of the skin.
Sometimes periods of complete well-being without symptoms can last for a long time - up to 10 years.
Children's urticaria is an allergic skin disease, which most often develops against the background of an existing exudative diathesis and appears due to food products introduced as complementary foods.
It has been noticed that this type of allergy mainly develops in babies who are bottle-fed or eat foods that are not appropriate for their age.
Disorders of facial innervation
A neurotic face may develop due to damage to the nerves that innervate it. Most often these are the trigeminal and facial nerves.
The trigeminal nerve is the 5th pair of cranial nerves. It is the largest of all 12 pairs of these nerve fibers.
N. trigeminus arises symmetrically on both sides of the face and consists of 3 large branches: the ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular nerves. These three large processes innervate a fairly large area:
- skin of the forehead and temples;
- mucous membrane of the oral and nasal cavities, sinuses;
- tongue, teeth, conjunctiva;
- muscles - chewing, floor of the mouth, palatine, tympanic membrane.
Accordingly, when it is damaged, pathological sensations arise in these elements.
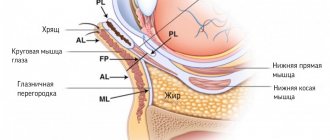
Facial nerve – 7th pair of cranial nerves. Its branches surround the temporal and ocular region, the zygomatic arch, and descend to and behind the lower jaw. They innervate all facial muscles: auricular, orbicularis and zygomatic, chewing, upper lip and corners of the mouth, cheek. As well as the muscles of the lower lip and chin, around the mouth, the muscles of the nose and laughter, and the neck.
N. facialis is also paired, and is located on both sides of the face.
In 94% of cases, the damage to these nerve fibers is unilateral, and only 6% is a bilateral process.
Disruption of innervation can also be primary or secondary.
Primary is the lesion that initially involves the nerve. This could be hypothermia or strangulation.
Secondary damage develops as a consequence of other diseases.
Another reason for the development of facial neurosis is neurogenic and mental disorders. When unpleasant sensations in the face and head occur against the background of psycho-emotional arousal, shock, or as a result of stressful situations.
Dermatillomania
Neurosis of the face and scalp can manifest itself in a behavioral disorder such as dermatillomania.
Its main manifestation is scratching the skin of the face and head, not because of itching, but because of dissatisfaction with its appearance. This also includes an obsessive zeal to squeeze out pimples, scratch off scabs, and pull out hair. Self-injurious actions cause a short-term feeling of pleasure, followed by feelings of shame, frustration, and dissatisfaction.
The face of such patients is covered with scars and scars due to constant trauma to the skin. This process is uncontrollable and can occur at any time of the day. But most often traumatic actions are carried out in front of a mirror.
Symptoms of the disorder also include the habit of biting the lips and mucous membranes of the cheeks. Patients are not deterred by the prospect of redness, bleeding, and scarring of the skin. They repeat the ritual day after day. It lasts from a few minutes to an hour.
Such actions can be provoked by feelings of fear, anxiety, and close examination of one’s skin because there is nothing to do.
Dermatillomania has been described as a state of addiction. It begins with concentrating on what the patient thinks is a skin defect. Gradually, attention is increasingly focused on this detail. A person begins to think that he is sick with something serious. This provokes irritability and nervousness in him, leading to obsessive actions.
The root cause of the disease is rooted in the psychological state of a person and lies in self-dissatisfaction, anger, feelings of shame and malice. Traumatic rituals are a way of punishment, self-flagellation.
Treatment of this pathology requires the intervention of a psychotherapist and a dermatologist.
The main method of treating addiction is psychotherapy, in particular cognitive behavioral therapy.
Yoga, physical exercise, relaxation procedures, as well as any hobby that absorbs a person and helps redirect attention will help reduce anxiety, distract and relax.
The help of a dermatologist is necessary to eliminate skin lesions in order to prevent infection and reduce the degree of dermatological defect.
Trigeminal neuralgia
This is another lesion of the nerve fiber structure, which is often chronic and accompanied by periods of exacerbation and remission.
It has several causes, which are divided into idiopathic - when a nerve is pinched, and symptomatic.
The main symptom of neuralgia is paroxysmal sensations in the form of pain on the face and in the mouth.
Pain sensations have characteristic differences. They are “shooting” and resemble an electric shock; they arise in those parts that are innervated by the n.trigeminus. Having appeared once in one place, they do not change localization, but spread to other areas, each time following a clear, monotonous trajectory.
The nature of the pain is paroxysmal, lasting up to 2 minutes. At its height, a muscle tic is observed, that is, small twitching of the facial muscles. At this moment, the patient has a peculiar appearance: he seems to freeze, but does not cry, does not scream, and his face is not distorted from pain. He tries to make a minimum of movements, since any of them increases the pain. After the attack there is a period of calm.
Such a person performs the act of chewing only with the healthy side, at any time. Because of this, compaction or muscle atrophy develops in the affected area.
The symptoms of the disease are quite specific, and its diagnosis is not difficult.
Therapy for neuralgia begins with taking anticonvulsants, which form its basis. Their dose is subject to strict regulation and is prescribed according to a specific scheme. Representatives of this pharmacological group can reduce agitation and the degree of sensitivity to painful stimuli. And, therefore, reduce pain. Thanks to this, patients have the opportunity to freely eat and talk.
Physiotherapy is also used. If this treatment does not give the desired result, proceed to surgery.
Disease prevention
Doctors recommend eliminating effects on the body that cause inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Here are some recommendations to help avoid illness:
- Avoid drafts and hypothermia
- Keep your head warm during the cold season
- Monitor your blood pressure
- Timely treatment of infectious and bacterial diseases
- Have a routine check-up with an oncologist
- Avoid skull and head injuries
You can sign up for an individual consultation, take tests or undergo treatment at the Medunion private clinic. You can easily make an appointment with us by calling 202-95-54 or online, directly on the website, by clicking on the “Online booking” button.
We have been working in Krasnoyarsk since 2006 and provide high-quality medical services to the population. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors of broad and narrow specialization.