01/03/2020 Many people believe that seborrhea occurs only on the scalp. But this is not true, since seborrheic dermatitis can affect any skin where there are sebaceous glands. According to statistics, 5% of the world's population is susceptible to this disease, and if we talk about its simpler form - dry dandruff - then it occurs in almost every 6th person.
What is atopic dermatitis?
IRINA Gubey
dermatologist, cosmetologist
– Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease with a complex multifactorial development mechanism.
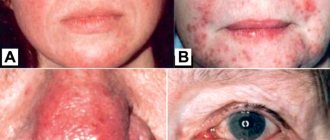
People with atopic dermatitis suffer from itching, dryness and flaking of the skin, rashes in the form of blisters (usually children) on certain parts of the body: the flexor surfaces of the knee and elbow joints, face, neck, earlobes, etc. And here it is important to note that this disease is not contagious.
Is seborrhea contagious?
In this case, the answer is clear - no! Therefore, there is no need to bypass such a person “by the tenth road”. Even if you shake hands with him, hug and kiss, everything will be fine with you if your immune system is fine and the sebaceous glands are working as expected. You don’t need to think that if pathogenic fungi get on your skin, you will immediately get sick. The fact is that such Malassezia fungi are already present on your skin, but do not form pathogenic flora.
Thus, we can absolutely say that even using the same comb, towel or hat with a person who has seborrheic dermatitis, nothing threatens you if you have a strong immune system and there are no aggravating diseases or prerequisites.
It is not transmitted by airborne droplets, so you should not limit communication with such a person because of his illness. People with this disease often limit their communication themselves, also believing that they can infect someone. Another question is that external manifestations cannot be called aesthetic. But these are not the Middle Ages, and making such people outcasts from society is only another blow to their psyche.
The earlier the better
any type of seborrhea can be defeated at the earliest stage
much easier. Modern medicine successfully copes with almost all types of seborrheic dermatitis at different stages.
What treatment your doctor prescribes depends on a number of factors. He has knowledge, experience and test results in his arsenal. Therefore, even if you found a detailed article on how to treat seborrhea, it is not a fact that you will succeed if you ignore the help of a specialist.
Without the participation of a doctor, you can only carry out preventive measures and follow general recommendations:
- Monitor your diet and lifestyle;
- To endure life's difficulties without falling into prolonged depression;
- Do not ignore basic rules of personal hygiene;
- Monitor the health of the entire body.
I wish you health and beautiful thick hair!
What causes atopic dermatitis?
– There are many factors. One of them is a defect in the gene responsible for the synthesis of filaggrin, a structural protein of the skin. Or, for example, immune inflammation of the skin, which increases its sensitivity. As a result, the formation of the normal stratum corneum (the top layer of skin) is disrupted, which is manifested by dryness, flaking, a weak barrier and itching. This is why transepidermal water loss occurs.
Studies have been conducted that reveal the fact: if both parents suffer from allergies, then the risk of atopic dermatitis in the baby reaches 80%. Often such people also have either bronchial asthma, or allergic rhinitis, or other allergic diseases.
Possible causes of irritant contact dermatitis
- detergents and soaps,
- preservatives and perfume,
- solvents,
- oils,
- acids and alkalis,
- cement powder,
- water (especially hard, calcareous or highly chlorinated),
- dust,
- fertilizers,
- some plants - anemone, mustard and others.
Often exposure to irritants is part of the job, so these workers are at risk of developing irritant KD. This type of work includes: cooking, house cleaning, hairdressing, agriculture and fishing, engineering, repair and construction, medicine, dentistry and veterinary medicine, drawing.
How does the disease manifest?
– The manifestation of the disease usually occurs in the first year of life and most often goes through 3 stages.
Infant: rash in the form of blisters, redness and severe itching. Localization of rashes is mainly on the face, less often on the legs and thighs.
Child stage: from 2 to 12 years. There are fewer blistering rashes, but dry skin, pronounced skin patterns, and excessive peeling are added.
Adolescent stage: from age 12 and often continues into adulthood. It is characterized by predominant damage to the skin of the face and upper body, with a continuously relapsing course.
Also, with atopy, palmar hyperlinearity and increased pattern (“atopic” palms), nipple eczema, and recurrent conjunctivitis can be observed.
In adults, there is another interesting symptom: pigmentation in the area around the eyes in the form of dark circles. If you don't take care of the skin in this area, it will peel and age faster. Unfortunately, it is impossible to remove this “glasses effect” even with a cosmetologist.
Symptoms and stages of the disease
The clinical picture of contact dermatitis depends on the strength of exposure, its duration and frequency. At the very beginning, there is slight erythema, itching and pain, which may disappear after cessation of contact. Exposure to irritants causes pain, and itching is more common in allergic contact dermatitis. The skin itself thickens at the site of the lesion. As the erythema progresses, it increases and watery elements (vesicles) join. Elements can be located both at the point of contact and beyond. The rashes can be chaotic, or they can follow the contours of the object in contact. They appear within about a day. The swelling may increase, cracks and scabs form. This stage is dangerous due to the addition of a secondary infection. As healing progresses, a scar may appear. In connection with the described clinic, there are three main stages of contact dermatitis:
- erythematous;
- vesicular;
- necrotic.
Do I need to undergo any tests to diagnose atopic dermatitis?
– Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is based on clinical data: complaints, nature and localization of skin lesions, allergic history. But today there are no objective diagnostic tests that would confirm the diagnosis.
When making a diagnosis, it is recommended to determine allergen-specific IgE antibodies in the blood serum (mainly for children), conduct skin tests with standardized allergens, a general blood test, and consult an allergist and dermatologist.
How does the reaction occur?
How quickly an allergen can trigger an immune response depends on its ability to bind to the protein compounds contained in the skin.
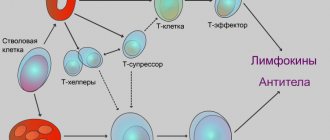
For example, dinitrochlorobenzene (a very strong allergen) binds to proteins containing the amino acids lysine and cysteine and forms an antigen. Macrophages (Langerhans cells), which respond to the penetration of foreign components into the body, begin to form an immune response, which leads to an inflammatory reaction. Some T-lymphocytes turn into memory cells during their work, which is why upon subsequent contact with the allergen, the reaction occurs again. Among medical drugs and products, allergic manifestations are most often caused by antiseptics, local anesthetics, and latex products.
How to treat atopic dermatitis and how to properly care for such skin?
– Treatment is prescribed by the attending dermatologist, pediatrician, or general practitioner. The basis is specialized skin care that will moisturize it and restore the barrier.
You always need to take care. During exacerbations, external hormonal (GCS) creams and ointments, calcineurin inhibitors, and oral antihistamines are prescribed. It is also necessary to carry out symptomatic therapy in the form of soothing, drying, antibacterial (for weeping rashes) and wound-healing drugs. In severe forms, systemic therapy may be prescribed.
Treatment and prognosis
First of all, it is necessary to find out the cause and get rid of its effects. During the treatment period, it is necessary to avoid water procedures at the affected area. Treatment is divided into external and internal. Cold compresses and bandages are applied externally.
The affected area can be treated with antiseptics and bandages with regenerating ointments and creams used. Glucocorticosteroids are used both internally and externally. Antihistamines will reduce further development of the allergic reaction and itching.
Treatment of contact dermatitis occurs on an outpatient basis, but in severe cases it can also be transferred to a hospital.
What other specialized care?
– Emollients are fats and fat-like substances included in cosmetic products created specifically for the care of dry, damaged skin. On the skin, emollient creates a thin film similar in structure to the natural lipid layer, which prevents moisture loss and protects the skin from the effects of traumatic factors (friction by clothing, sweat, tap water, soap, washing powder, low temperature).
Emollients should be applied generously in a thick layer to the entire skin, even to those areas that have no visible damage. But if the product contains urea or a person has violations of the integrity of the skin, then this should not be done.
You need to apply emollient after each wash; during periods of exacerbation, the frequency can reach 5-6 times a day. Emollients do not need to be rubbed into the skin - we apply them gently. The goal is to create a protective film on the surface. There are no contraindications or addiction to long-term use of such drugs.
Aggravating factors
Very common seborrheic dermatitis
occurs as a consequence of other diseases, the most famous of which is HIV. About 75% of such patients also suffer from seborrheic dermatitis.
In this case, one should not be surprised, since our main defender - the immune system - can do practically nothing with the formed pathogenic flora. When a person’s immune functions decrease, all their weak points begin to “break down,” especially when there are aggravating factors.
Seborrhea and genetics
It should be immediately noted that the disease, as such, is not transmitted with genes either through the father or through the mother. But predisposition is a completely different matter. In this case, this is a predisposition of the sebaceous glands to increased secretion.
However, there is no need to panic here, even if every relative of yours suffered from this disease. If you pay attention to measures to strengthen your immune system in time, and also do not ignore your own mental health, you have nothing to fear.
Also, if you already know the “weak spot” in your genetics, regularly use special anti-seborrhea shampoos
. As a preventive measure, they are quite effective, since they not only gently cleanse hair and skin without drying them out, but also help maintain the proper functioning of the sebaceous glands. Even if everyone around you gets sick, it may not affect you at all.
FAQ
Is atopic dermatitis curable?
Atopic dermatitis is a systemic chronic disease that cannot be completely cured, but stable remission can be achieved with the right treatment - even if the disease is diagnosed as moderate or severe.
At the same time, atopic dermatitis is an insidious disease, and often therapy does not bring results. The disease can actively manifest itself over several decades and affect more than 50% of the skin surface. Sometimes, with severe exacerbations, the disease can occur up to 8–11 times during the year2, 3, 4.
At what age does atopic dermatitis appear?
Early onset of atopic dermatitis (between the ages of two and six months) is observed in 45% of patients, during the first year of life - in 60% of patients.
Spontaneous remission of the disease (the child outgrows the disease) is observed in 65% of children by the age of seven, and in 74% of children with atopic dermatitis by the age of 161.
Signs of atopic dermatitis
Typical symptoms of the disease: unbearable itching, skin rash and redness1.
Where do signs of atopic dermatitis usually appear?
In children - on the most exposed areas: on the forehead, cheeks and chin.
In adolescents - on the inner folds of the limbs: on the elbows, under the knees, on the arms, torso or neck.
In adults - on the face, neck and hands1.
Does atopic dermatitis only affect the skin?
Indeed, skin manifestations of AD are the most pronounced, but much more serious processes occur in the immune system. They are associated with disruption of its functioning, increased sensitivity to allergens and irritants. Atopic diseases are closely related. Often, with age, patients with AD consistently develop bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis and food allergies. This condition is called atopic march; The earlier the age at which AD begins and the more severe the course of the disease, the more likely the development of atopic march. Respiratory symptoms are observed in almost 85% of patients with AD under the age of 15 years, and allergic rhinitis in 82%14. Thus, AD is a systemic disease, that is, a disease of the whole organism1.
Should I be afraid of corticosteroids?
No, corticosteroids are one of the effective treatments for exacerbations of atopic dermatitis that a doctor can prescribe. When using them, you must follow the instructions of your doctor. Adhering to your treatment regimen will help reduce the likelihood of side effects1.
Is it true that a child can outgrow AD with age?
Indeed, the disease most often manifests itself in children, but it can persist into adulthood, and in some cases appear for the first time in adults, and also have a recurrent nature. In adults, relapses can occur after emotional stress, stressful situations, or exacerbation of other chronic diseases1,3.
Is AD contagious?
No, AD is not a contagious disease. Children with AD have the opportunity to play normally with their friends, attend kindergarten and school. With the right treatment, adults can lead a normal lifestyle, work, relax, and play sports1, 5, 6.
Should you see a psychologist if you have AD?
Although AD is not a psychological disease, sometimes the severity of the pathology affects the quality of life of the patient and his loved ones, so psychological help may be required 7, 8.
Is it possible to get vaccinated for AD?
There are no contraindications for vaccination during remission, but before vaccination it is necessary to consult with your doctor. Vaccination is not carried out during the period of exacerbation of the disease1.
Is it possible to play sports and go to the pool if you have AD?
With the right treatment for AD, you can live a full life. But regardless of your activity, you should pay special attention to skin care1.
Can certain foods make AD worse?
The allergic component is not the only and main cause of atopic dermatitis, since AD is a multifactorial disease. The triggers that trigger the disease or its exacerbation can be completely different factors. Food allergens provoke exacerbation of AD in only 35% of cases.
It is also incorrect to assume that AD has multiple food allergies, since most patients with AD combined with food allergies react to only one or two food allergens15.
If you suspect a food allergy, you should always consult your doctor1, 9, 10.
Should all AD patients use emollients?
Moisturizers and emollients (emollients) should be used by all patients with atopic dermatitis, regardless of severity.
Special medicinal and cosmetic products that soften and moisturize the skin in AD are called emollients. These products are able to retain moisture in the skin, forming a film on its surface, and restore the epithelial skin barrier.
Moisturizers can help reduce symptoms of AD, such as itching and redness.
Emollients are available in different forms: milk, cream, gel. The choice of the drug and its form is carried out individually, taking into account the patient’s preferences, individual skin characteristics, season, and climatic conditions1.
Emollients should be applied to the skin not only after bathing, but throughout the day. Emollients are applied to the entire skin, except for wet areas. Special medications that can be prescribed by your doctor should be applied to these areas. The consumption of emollients recommended by doctors for children is 200 grams per week (for adults - up to 500 grams).
Regular use of emollients is an important part of skin care that can prevent flare-ups and speed up remission1, 14, 15.
Do natural creams help with AD?
Many people often incorrectly associate the terms “natural” and “safe”. Therefore, we advise you to stick exclusively to licensed products (they are called medicinal and cosmetic). And before using any “natural”, “natural” remedies, be sure to consult a doctor11.
What causes an exacerbation of AD?
It is often difficult to determine the cause of exacerbations. It should be remembered that AD is a multifactorial disease that affects not only the skin.
As a rule, there are many factors that provoke exacerbations, some even mutually enhance the effect on the body. These are allergens and dust, food, climate change and stress. Therefore, joint work between the doctor and the patient, knowledge and understanding of their disease is extremely important1, 2, 12.
How to cope with itching in AD?
“Just stop scratching your skin” is bad advice for people with AD.
60% of adults with severe AD experience intense or unbearable itching, which brings not only discomfort, but also suffering and disrupts sleep.
The cause of itching is inflammatory mediators secreted by cells of the immune system, and not just external irritants.
Therefore, itching should be dealt with under the guidance of a doctor who can prescribe modern medications not only for local, but also for systemic action1, 14, 15.
How can I find a doctor in my area who knows how to properly treat AD?
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist or allergist in your area. You can also visit our Find a Doctor page to find a center where you can choose a specialist.
Allergic
Allergic dermatitis is the body’s reaction to a specific allergen: food product, household detergent. Knowing what exactly caused the reaction, you can cope with an outbreak of the disease: it is enough to eliminate the irritant. In the case of food products, everything is simple: the allergen must be removed from the diet and avoided in the future. If the cause was external irritants (aggressive chemicals, alkalis, acids, UV radiation), it will be more difficult to identify, let alone avoid contact. In this case, you will have to seek medical help.