Tubular lichen (pityriasis versicolor) is a disease of the superficial part of the skin, expressed in the form of brown-yellow spots of different shades, and has a fungal origin. Due to the difference in shapes and shades of spots, this type of lichen is called “colored”, less often “multi-colored”. Due to the high probability of repeated manifestations provoked by visiting a solarium or excessive exposure to the sun, tubular lichen is called “solar”. The disease is not considered dangerous, but considerable discomfort is caused by frequent cases of renewed manifestations of tinea versicolor.
Varieties and atypical forms
Ringworm has a wide range of shades. The color of lichen is determined by the characteristics of the skin pigment, which leads to the following classification of tubular lichen:
- Black. Expressed in shades of gray.
- Achromic. It looks like a patch of skin devoid of pigments.
- Yellow, characterized by shades of pale yellow and cream.
In most cases (80%), tinea versicolor manifests itself in a standard form and proceeds without much discomfort or inflammation, but there are atypical manifestations:
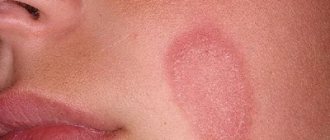
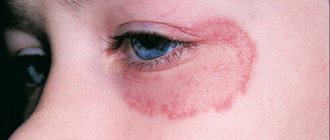
- Erythematous-squamous appearance, expressed in more intense peeling and redness of the skin.
- Urticaria-like appearance - similar to blisters formed after a nettle burn.
- Lichenoid type - in the form of a small rash scattered over the skin.
- Erythrasma - localization in the groin area, on the genitals, limbs, under the breasts. Diaper rash, discomfort and itching may occur.
- Diffuse form - penetration of affected cells into healthy ones.
- The vitiligo stage is a violation of pigmentation, loss of melanin in certain areas of the skin.
General characteristics of the disease
Tubular lichen is a dermatological pathology. It is caused by the yeast-like fungus Malassezia (mycelial form), Pityrosporum ovale (oval form), Pityrosporum orbiculare (round form). It affects the outer layer of the epidermis, hair follicles and appears on the surface of the skin in the form of pigmentation. The disease is infectious.
Tinea tubularis is not a contagious disease, as many people are carriers of the fungus that causes it. Excessive proliferation of pathogenic microflora with subsequent clinical manifestations is provoked by various factors.
Causes
The epithelium is infected by yeast fungi of the genus Pityrosporum or Malassezia, but under normal conditions they can go undetected on the skin for a long time. Typically, tubular lichen tends to appear between the ages of 16 and 45 years. The age when sweat is produced most intensely and creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of yeast fungi. At a younger age, the glands are not yet developed, and after the age of 45 their function already fades away, which significantly reduces the risk.
If certain conditions or diseases occur that affect the amount and composition of sweat, tinea versicolor may develop. Factors leading to its occurrence:
- The effect of UV rays, especially when visiting a solarium or staying in the open sun for a long time. The fungus on the skin receives a favorable environment: heat and humidity from sweating, which allows it to begin to reproduce and become parasitic. Therefore, the disease is usually seasonal and occurs in summer and spring.
- Genetic predisposition. The composition of sweat is different for each person, this is determined by the state of health and previous diseases, as well as often by the genetic structure of the body. The surface of the skin of some people is initially favorable for the development of fungi of this type.
- Endocrine disease. The course of the disease is long, and in addition to the main manifestations, it can lead to the development of tubular lichen. Thus, the endocrine disease is long-lasting and difficult to treat, which leads to repeated outbreaks of tinea versicolor at certain intervals.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases. This affects the composition of sweat and the intensity of its secretion, creating a favorable environment for tubular lichen.
- Hypothermia. Both during this process and after it, the composition of sweat temporarily changes and its quantity increases.
- Frequent wearing of tight synthetic clothing. It leads to a lack of oxygen in the skin, as a result it heats up and sweats, which affects the functionality of the sweat glands and the quality of the functions they perform, creating favorable conditions for the spread of infection.
- Antibacterial cosmetics. Depletes the protective layer of the epithelium, and protective functions deteriorate.
- Increased air humidity. Frequent exposure to such climates by people with a predisposition to tinea versicolor makes them vulnerable to its attack.
- Hormonal changes. They may be influenced by the use of hormonal contraceptives or during pregnancy, when various changes occur, including hormonal levels.
- Violation of hygiene standards. Taking care of physical cleanliness is not only a pleasant necessity, it is also getting rid of pathogenic substances and sweat. When the sweat glands, especially during and after an illness, work intensively, along with the fluid, they secrete harmful substances, and if they are not washed off, this leads to the unpleasant consequences of tinea versicolor.
- Stress, weakened immunity. Both of these factors stimulate sweating, while weakening the body and depriving it of the strength to resist fungal diseases.
All reasons are associated with changes in the properties of sweat under the influence of genetic or acquired consequences of the disease, as well as the influence of external factors.
Prognosis, complications
The prognosis for tubular lichen is favorable. A correct diagnosis and competent and timely treatment ensure complete recovery.
Cosmetic defects of the skin are considered complications of tubular lichen. With properly organized treatment, this deficiency is completely corrected. There are no scar changes.
If treatment for tubular lichen is not started in a timely manner or the doctor’s instructions are not followed, then the rash may spread to a large area of the skin. Another possible complication is the duration of the pathology and the possibility of its relapse. This trouble can be avoided by following secondary prevention, which is based on eliminating risk factors for the development of tubular lichen.
Symptoms
The main manifestations of tubular lichen are colored spots, other accompanying symptoms: itching, burning - appear very rarely. There may be a slight desire to scratch the damaged area, but it is not intrusive and is rather psychological in nature. When the disease relapses, diagnosis is greatly simplified. The exception is atypical cases of diseases and those complicated by lack of treatment and poor hygiene.
Rarely, tinea versicolor manifests itself on the limbs and head; its location is the torso and large areas of the arms and legs.
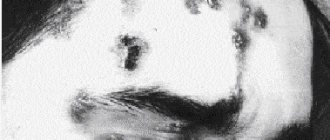
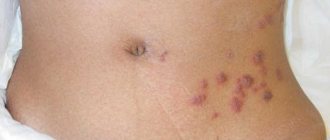
Photo of tubular lichen: what it looks like
Different colors of tubular lichen have the same structure and location.
Disturbance of skin pigmentation, achromic tinea versicolor.
A type of black tubular lichen.
The shavings are clearly visible on the body of a child with tinea versicolor.
Diagnostics
The initial examination will suggest the type of disease, but in order to establish it accurately, especially if the patient presented with such problems for the first time, a number of studies will be needed:
- Balzer iodine test. Despite the complex sound, the procedure is quite simple: a 5% iodine solution is taken and applied to the areas under study, the intensity of the staining of the loosened stratum corneum is analyzed.
- Dermatoscopy. The surface of the damage is lubricated with gel to eliminate glare of light, after which the surface is examined with a dermatoscope, pictures are taken, based on the results of the analysis of which a conclusion is drawn up.
- Test for Beignet's symptom. When the affected parts are scraped, the upper ones peel off, increasing peeling.
- Fluorescent examination, including Wood's lamp examination. Tissues fluoresce under the influence of a quartz lamp with a filter and UV rays, change color and make it possible to conduct a more accurate diagnosis.
- Scraping from the epithelium. Identifies the pathogen and prevents recurrent cases of the disease.
Diagnostic measures
Before you begin to treat tubular lichen, you should definitely go to the hospital for consultation with a specialist. The doctor will listen to the patient’s complaints and conduct an objective examination. Upon examination, a person’s skin is damaged in the form of multi-colored spots that merge and form rounded large areas of the lesion. Also, the examination confirms the positive symptom of “chips” - when the spot is scraped, a slight peeling appears and the patient complains of itching. If you illuminate the lesion with a Wood's lamp, it will change color to brown, green or red-yellow. After this, the specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis with other types of skin lesions and make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic methods:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- microscopy of stain scraping;
- sowing on a nutrient medium;
- immunogram;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- hormonal study.
Treatment of tubular lichen
Ringworm, like any type of lichen, is long-lasting and difficult to treat, but, unlike the same “pink lichen,” it is prone to recurrence.
This is a disease that is almost impossible to get rid of completely; you can only apply a set of measures to prevent its manifestations. The average duration of treatment with drugs is up to 2 weeks with breaks, with ointments - up to 4 weeks. Most often, the duration is 1 or 2 weeks, subject to the recommendations of the dermatologist. It happens that treatment lasts up to a year.
Ointments
The basis for the treatment of tinea versicolor is a local effect on the lesions; for this, ointments are used, which, depending on the active component in their composition, solve a specific problem. May be in the form of a spray, gel or cream.
A medicine based on the following substance:
- Naftifine - destroys fungal cells, helps destroy it. Preparations: “Exoderil”, “Mycoderil”.
- Ketoconazole - acts on synthesis in fungal formations, preventing neoplasms. Preparations: “Mycozoral”, “Nizoral”, “Sebozol”, “Mikoket”, “Dermazol”, “Dandrhotal”.
- Bifonazole - neutralizes the negative effects of the fungus and prevents its spread. Preparations: “Bifonazole”, “Mikospor”, “Bifasam”, “Bifosin”.
- Clotrimazole - impairs the penetrating properties of the fungus, which leads to preventing its spread and death. Preparations: “Candizol”, “Imidil”, “Candide”, “Funginal”, “Kanizon”, “Amiclon”, “Candibene”, “Clotrimazole”, “Fungitsip”, “Canesten”.
- Terbinafine - destroys the fungus, destroying its structure. Drugs: Exiter, Lamisil, Lamitel, Terbinox, Binafin, Lamisil Uno, Terbinafine, Terbizil, Ungusan, Tebikur, Termicon, Atifin , “Mikonorm”, “Terbifin”, “Terbized-Agio”, “Terbix”, “Fungotherbin”, “Exifin”.
- Sertaconazole - suitable for long-term use, actively fights tinea versicolor. Drugs: “Zalain”, “Sertamicol”, “Sertaconazole”.
- Isoconazole is a synthetic version of imidazole that actively acts on the fungus. Medicines: Travocort, Travogen.
- Miconazole does not allow fungi to multiply, inhibits their reproductive properties, leading to death. Preparations: “Mikozon”, “Daktarin”.
- Econazole - destroys the structure of fungal compounds. Preparations: Ecodax, Ifenek.
A number of ointments are aimed at accelerating exfoliation and getting rid of problem areas:
- Salicylic ointment, 5% is used.
- Salicylic alcohol, 3-5% is used.
- Glycolic acid, 5-10% is used.
- Resorcinol alcohol, 5-10% is used.
- Salicylic resorcinol alcohol.
Pills
To a greater extent, their use is due to the severe course of the disease or the neglect of the case.
The following groups of drugs are distinguished, depending on the active substance in their composition:
- Ketoconazole is a substance with complex effects that increases skin resistance to new growths of lichen colorus and destroys affected cells. Drugs: “Fungistab”, “Ketoconazole”, “Oronazole”, “Mikozoral”, “Nizoral”, “Funginok”, “Fungavis”.
- Itraconazole - inhibits the membranes of fungi, affecting them. Drugs: “Itrazol”, “Kanditral”, “Rumikoz”, “Orungamin”, “Irunin”, “Itraconazole”, “Mikonihol”, “Orungal”, “Orunit”, “Teknazol”.
- Fluconazole - acts on the fungus at the molecular level, destroying it. Preparations: “Funzol”, “Flucostat”, “Fluconorm”, “Flucoside”, “Fangiflu”, “Nofung”, “Fluzol”, Mikosist”, “Medoflukon”, “Diflazon”, “Difluzol”, “Disorel-Sanovel” , “Mikomax”, “Mycoflucan”, “Mikomax”, “Procanazol”, “Fluzol”, “Fluconazole”, “Flunol”, “Forkan”, “Tsiskan”, “Diflucan”.
Shampoos (including lotions, oils)
This method is rather auxiliary; some people use it as a preventive measure, but this approach is very expensive and does not justify itself.
The active components are:
- Selenium sulfide. Preparations: "Sulsen Mite" - can be shampoo or paste, "Sulsen Forte" - shampoo, "Sulsena" - lotion, shampoo, oil.
- Sodium thiosulfate solution. Drug: sodium thiosulfate.
- Zinc pyrithione. Preparations: “Keto Plus” - usually shampoo, “Skin-cap” - can be shampoo, cream, aerosol, “Zinocap” - cream, aerosol.
- Ketoconazole. Preparations: “Keto Plus” - usually shampoo, “Dandrhotal”, “Mikozoral”, “Nizoral”, “Mikanisal”, “Sebozol”.
Diet
To speed up recovery, you need to eat right:
- avoid alcoholic beverages, they neutralize the effect of medications;
- reduce the amount of sweets in your diet: sugar, flour products;
- limiting or avoiding carbohydrate foods;
- choose bread with bran, from wholemeal flour;
- take fortified foods: vegetables, fruits, natural juices;
- natural fermented milk products, without heat treatment.
Treatment with folk remedies at home
Popular recipes:
- St. John's wort, infusion. Place several branches of St. John's wort in a container, pour boiling water over it and drain, re-fill with hot water, and leave to steep for half an hour. Moisten a tampon with the decoction and apply to the areas of the disease for half an hour or 40 minutes.
- Celandine and peppermint. To make the infusion, you need to take equal quantities of both types of herbs, rinse with water, place in a container for the stove and add hot water. Keep on the stove at low temperature for 5 minutes. After cooling, apply with tampons or gauze to the affected areas for 20 minutes to 40 minutes.
Recommendations
You can and should:
- wear light, breathable, loose cotton clothing;
- more careful care of the patient’s clothes: washing at high temperatures, if possible, steam treatment in a washing machine, ironing clothes and linen on both sides;
- carry out wet cleaning at least once a day;
- take a shower with baby soap or special shampoo, do not allow sweat on the body.
It is forbidden:
- wear tight synthetic clothing;
- share a towel, dishes, and bedding with the patient;
- solariums, tanning;
- use cosmetics;
- allow hypothermia, stress, sleep disturbances;
- physical exercise.
Prevention
After recovery, the main task is to prevent recurrence of tinea versicolor.
What you need to do for this:
- Strengthen the immune system: hardening, walks in the fresh air, physical activity, timely treatment, avoiding complications. The body's natural defenses are the best way to prevent it.
- Hygiene. If a case of tubular lichen has already occurred, you need to be more careful about personal hygiene: frequent showers, avoiding excessive sweating, especially after illness, using natural gels and shampoos, frequently changing towels and bed linen.
- A course of antifungal therapy. Carried out on the recommendation of a dermatologist.
- Avoid UV rays, overheating in summer and late spring.
Is it contagious and how is it transmitted?
Theoretically, it is possible to become infected with tinea versicolor, but in fact this is only possible if the environment is favorable for its development. When one of the family members falls ill, it is necessary to comply with sanitary standards, rules of personal hygiene and monitoring the health of those in the same apartment. This does not mean that someone will definitely become infected from a patient: the fungus can get on the skin on the street, in a supermarket, or in the gym.
Without receiving the desired favorable conditions, the fungus can remain in a passive state without presenting any danger, like other microorganisms that inhabit the surface of the outer layer of the skin.
1.What is pityriasis versicolor?
Pityriasis versicolor
Also called “lichen versicolor” or “sun fungus”. This type of fungal disease is not as common in our climate as in countries with hot, humid climates. However, dermatologists in Russia detect pityriasis versicolor in 5% of the population.
Especially often, the fungus colonizes on the body of people prone to excessive sweating and seborrheic diathesis, which creates a favorable environment for the introduction and development of this skin infection. Pityriasis versicolor lasts for years without treatment, practically without affecting the general condition of a person, but creating psychological discomfort due to cosmetic defects of the skin. Manifestations of the disease are reduced in winter and worsen in the hot season.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!