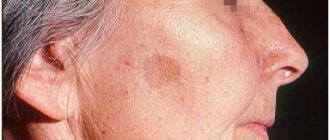
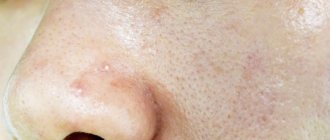
Dermatofibroma is a benign formation of the skin and connective tissue, similar in appearance to a mole. In most cases, they have a round shape and a smooth surface, much less often - keratinized or warty. Part of the dermatofibroma, a photo of which you can easily find, is located in the bulk of the skin, while the other rises above the surface of the dermis. If you touch such a mole, it seems that there is a small pebble stuck under the skin.
Dermafibroma of the skin occurs as a single formation; in rare cases, doctors diagnose several moles at once in one place. Dermafibromas themselves consist of fibrous tissue and contain a certain number of histiocytes and fibroblasts. As soon as a small grayish or pinkish dot appears on your skin, you need to consult a doctor. If treatment is not started in time, such a formation will turn black or dark brown and grow up to one centimeter. According to MBK-10, dermatofibroma is a response to any damage.
Causes of dermatofibroma
Modern specialists have still not been able to determine the exact reasons why dermatofibroma of the skin occurs. In most cases, doctors consider trauma to the skin of various etymologies as the main factor in the development of this disease: insect bites, frequent injections in one area, infectious diseases that affect the condition of the skin. The hereditary factor also plays a significant role here: if one of your relatives had problems of this kind, they will probably overtake you too. In addition, dermotofibroma on the leg or face often appears in individuals who suffer from acne and liver disease. The following causes of this disease are identified:
- Frequent skin injuries.
- Gender: statistics have shown that women suffer from such formations much more often than men.
- Negative environmental influences.
- Infectious diseases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Age – older people are more affected by dermotofibroma.
Knowing the cause of this disease will help determine the effective and correct treatment. It is highly not recommended to treat dermotofibroma using traditional methods, as there is a high probability of developing serious complications. Disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, in particular the gastrointestinal tract, can contribute to the development of the disease.
Modern types of treatment
One of the most technologically advanced methods of treating dermatofibroma today is treating the formation with liquid nitrogen. It is almost painless and does not imply the presence of postoperative scars. The only downside is the existing risk of reappearance.
If funds allow, you can get rid of dermatofibroma using laser removal. This is a more expensive but reliable type of removal. After such a procedure, no scar remains; at first, only a slight lightening of the skin at the site of removal will be noticeable.
Symptoms of dermatofibroma
Recognizing dermatofibroma of the skin, a photo of which you can easily find, is quite simple even by external signs. Such formations are round in shape, often smooth, protrude slightly beyond the skin, and are localized singly. Their diameter in rare cases exceeds 1 centimeter, most often varying from 0.5 to 0.7 millimeters. If several dermatofibromas appear on the body, they are scattered chaotically and are in no way tied to one particular part.
Dermatofibroma is a formation that can occur on any part of the body. In the vast majority of cases, it is located on the lower back, shoulders, back or lower leg. In rare cases, doctors diagnose such lesions on the palms and soles. The color of such formations varies from red-brown to grayish. In rare cases, dermatofibroma mimics the surrounding tissues and does not manifest itself in anything other than compaction. The edges of the formation are dark, becoming lighter towards the center. On palpation, a serious compaction is felt, there is a sensation of a foreign body under the skin.
Prevention
Due to the unclear etiology of the disease, it is difficult to formulate specific preventive measures. We only know what is needed:
- avoid damage to the skin;
- monitor your diet, get the required amount of vitamins and microelements from food;
- avoid overwork, decreased immunity;
- It is not recommended to expose the body to excessive sun exposure, as this leads to a decrease in immunity.
If you have the slightest doubt or discomfort, do not hesitate to contact a specialist - a dermatovenerologist. Only he will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. Any self-medication is always fraught with bad consequences.
Important points when contacting a dermatologist if you have a hair disease.How to care for braces
- ADVANTAGES OF TREATMENT ABROAD
Also, it is necessary to remember that this formation in itself does not pose a particular threat and you can calmly live with it all your life. So, the main thing is not to panic.
Treatment
Dermatofibroma rarely goes away on its own without some intervention. Many people live with such an education all their lives: once it appears, it may not manifest itself in any way and may not grow anymore. However, there is always a risk that the tumor will sooner or later become malignant, which is why it needs to be gotten rid of as quickly as possible. Removing dermatofibroma surgically can provoke relapses, which is why many doctors have long abandoned this method in favor of using a laser.
At the Healthy Skin Center, experienced specialists will provide you with a detailed consultation, thanks to which you will be able to determine how to treat dermatofibroma on your leg. Typically, doctors send their patients for a procedure using the Surgitron radio wave therapy device. Under the influence of high frequencies, the affected cells seem to evaporate, while the healthy ones remain in place. Using this method ensures that dermatofibroma will never appear on the treated area of the skin again.
Types of cutaneous dermatofibroma
Depending on the cellular composition of dermatofibroma, there are several types:
- cellular – formed by loose connective tissue, as well as collagen and fibroblasts;
- sclerosing - its peculiarity is that it contains a large number of small vessels;
- fibrous – consists of fibroblasts and collagen, due to which it is not prone to enlargement and growth;
- fibroxanthoma - formed by cells with several nuclei.
If a growth appears on the skin, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible. Under no circumstances should you damage or try to remove the tumor yourself, because only a specialist can determine its type and the likelihood of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Removal of dermatofibroma
- Dermatofibroma
Dermatofibroma is a deep-lying benign tumor of dark brown connective tissue, has the appearance of a retracted or hemispherical protruding formation, up to 1-2 cm in diameter, with a dense consistency.
As a rule, it is located on the skin of the upper and lower extremities. Not to be confused with botryomycoma and atheroma. Diagnosis of dermatofibroma: ultrasound of the skin, advanced dermatoscopy.
Causes and symptoms
Cutaneous fibroma is most often diagnosed in women. The disease practically does not occur in children and adolescents. The exact cause of the development of dermatofibroma has not been established. The following factors can trigger its development:
- microtraumas;
- dermatological diseases of an infectious nature;
- insect bites;
- acne;
- age-related changes in the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- liver pathologies.
Symptoms of the disease are accompanied by the appearance of a small convex formation in the shape of a hemisphere. It has a dense consistency and a smooth surface. Most often the growths are located on the feet.
Treatment of dermatofibroma
Removal using radiosurgery.
In our center, tumor removal is performed by a dermato-oncologist using radio wave surgery under local anesthesia.
In order to remove the formation more efficiently, the doctor uses a dermato-oncological magnifying glass, which allows for more detailed and complete removal of skin tumors without leaving pathological cells in the wound. Therefore, after removal, we can say with complete confidence that the formation has been completely removed and you will no longer have it. Read more about tumor removal in our center...
The cost of removing dermatofibroma is from 2300 rubles.
Consequences of surgical treatment
After surgery to remove dermatofibroma, a scar will always remain; this must be realized. However, modern medicine and cosmetology, in particular, have the necessary arsenal of tools to completely get rid of a postoperative scar. First, you can try to get by with a special gel.
If this does not help, or a faster result is needed, an experienced cosmetologist will excise the scar with a laser. For concomitant therapy, hormonal drugs can be used to reduce inflammatory manifestations.
Recommendations
- ^ a b c d e
Rapini, Ronald P.;
Bologna, Jean L.; Iorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-volume set
.
St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.[ page needed
] - ^ a b c
Friedberg;
and others. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine
(6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. item 668. ISBN 978-0-07-138076-8. - "benign fibrous histiocytoma" in Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- "Dermatofibroma | Genetic and Rare Diseases Clearinghouse (GARD) - NCATS Program.” rarediseases.info.nih.gov
. Retrieved 2018-04-17. - "dermatofibroma" in Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ a b c Dermatofibroma
at eMedicine - Jung, Kyu Dong; Lee, Dong-Yun; Lee, Joo-Heung; Yang, Jun-Mo; Lee, Eil-Soo (2011). "Subcutaneous dermatofibroma." Annals of Dermatology
.
23
(2): 254–7. Doi:10.5021/ad.2011.23.2.254. PMC 3130878. PMID 21747634. - Hanly, A. J.; Jorda, M; Elgart, G. W.; Badiawas, E; Nasiri, M; Najee, M (2006). "High proliferative activity excludes dermatofibroma: a report on the utility of MIB-1 in the differential diagnosis of selected fibrohistiocytic tumors." Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
.
130
(6):831–4. Doi:10.1043/1543-2165 (2006) 130 [831: HPAEDR] 2.0.CO; 2 (inactive 09/10/2020). PMID 16740036.CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of September 2022 (link) - Boursicot, Catherine (24 January 2013). Oxford Assess and Progress: Clinical Specialties
. Oxford University Press. p. 249. ISBN 9780199657582. - Kim, H. J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, Y. J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, M.H.; Cinn, Y. W.; Cho, K. H.; Yoon, T. (2007). "Stromelysin-3 expression in the differential diagnosis of dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: comparison with factor XIIIa and CD34." British Journal of Dermatology
.
157
(2):319–24. Doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08033.x. PMID 17596171. S2CID 7049937.
List of sources
- Kurbanova A.A., Skin diseases: a guide for doctors and students of medical universities / A.A. Kurbanova. - M.: GEOTAR-Medicine, 1998;
- Skripkin Yu.K., Skin and venereal diseases: a guide for doctors and students of medical universities / Yu.K. Skripkin. - M.: Triada-farm, 2001;
- Paltsev M.A., Potekaev N.N., Kazantseva I.A., Lysenko A.I., Lysenko L.V., Chervonnaya L.V. Clinical and morphological diagnosis of skin diseases: Atlas. M.: Medicine; 2004;
- Fitzpatrick T., Elling D.L. Secrets of dermatology. Per. with English-M.S-Pb-Bean, Nevsky dialect.-1999.