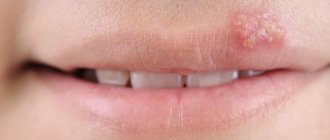
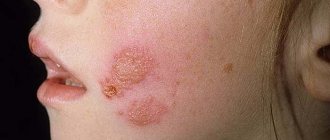
Almost everyone is familiar with a “cold” on the lips. As soon as you catch a runny nose or get nervous, an unpleasant harbinger immediately appears - a tingling sensation somewhere around the mouth.
The herpes simplex virus is present in the body of 95% of people. And only a few have immunity, the reasons for which are still unclear.
The virus enters the body in early childhood: at 3–4 years, when the antibodies against the herpes virus transmitted to the baby by the mother are depleted. Most often, infection occurs if a child is kissed by carriers of the infection. In addition to a kiss, the virus can enter the body, for example, with saliva. It penetrates the mucous membranes, reaches the nerve endings, rises into the cranial cavity, where it “hides” in a nerve plexus called the trigeminal ganglion and “sleeps” there until it is reactivated.
Herpes “wakes up” when immunity decreases
Causes of recurrence of herpes on the lips: stress or emotional distress; various other diseases, in particular colds, flu, diabetes, HIV; poisoning or intoxication; drinking alcohol, caffeine and smoking; excessive ultraviolet radiation; hypothermia or overheating; onset of menstruation; overwork and exhaustion; poor nutrition/diet or stomach upset; other factors individual to each person.
After “awakening,” the virus travels back to the skin. As the virus moves through a nerve, it causes inflammation of the nerve tissue.
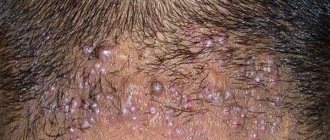
The development of herpes can be divided into several stages. At the first stage, the person feels unwell. At the site where the “fever” appears, there is pain, tingling, and the skin turns red. At the inflammation stage, a small painful blister filled with fluid forms. After some time, the bubble bursts and a colorless liquid containing billions of viral particles flows out of it. An ulcer appears in its place. At the final stage, the ulcer becomes covered with a crust.
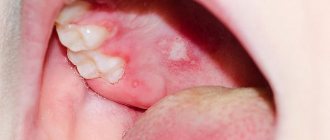
Most often, herpes appears on the lips, but lesions can also appear on the face, in the ears or in the mouth.
Herpes simplex - symptoms and treatment
The incubation period for the acquired form lasts 2-14 days. Most often, it cannot be installed due to lack of manifestation.
Herpes simplex in children usually occurs as stomatitis and gingivitis - the temperature rises, fever, general intoxication, focal hyperemia (redness) of all mucous formations of the oral cavity, pain when chewing, increased salivation. Small children refuse to eat due to pain. In a short period of time, small vesicular rashes appear at the site of hyperemia, which quickly open, leaving behind painful erosions - aphthae. Regional lymph nodes enlarge and become painful. Over time, the immune system strengthens and the symptoms gradually regress without any traces of damage. Relapses are rare.
When the skin is affected (mainly in adults), vesicular rashes often appear around the mouth, wings of the nose, and sometimes on the torso and buttocks. The rash consists of small vesicles with serous contents on a slightly hyperemic skin background. Subsequently, they open and dry out, after which crusts form without a trace.
Sometimes the bubbles merge into quite large bubbles. Often their contents fester, oozing forms, and a secondary streptococcal or staphylococcal infection (staphylo- and streptoderma) occurs.
General health, as a rule, does not change. Sometimes the regional lymph node may be slightly enlarged and painful. In general, the process rarely lasts more than a week.
With severe immunodeficiencies, the infection may take a more widespread (generalized) course. In this case, a syndrome of general infectious intoxication occurs and internal organs are affected: the liver and spleen are enlarged, the nervous system is affected (meningoencephalitis, encephalitis and meningitis), as well as the lungs, kidneys and other organs. With relapses of a chronic infection, patients sometimes feel mild discomfort and tingling in the area of future rashes.
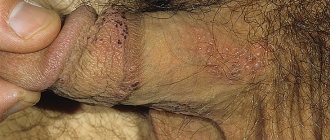
With genital herpes, rashes appear on the skin and mucous membranes in the genital area and perineum. They are usually accompanied by soreness, hyperemia of the surrounding tissue, enlargement and tenderness of the inguinal lymph nodes. The frequency of relapse depends on the individual characteristics of the immune system.
With ophthalmoherpes - eye herpes - unilateral lesions are more often observed due to the transition of the primary process to the organ of vision, i.e., a secondary lesion occurs. Keratitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, iridocyclitis, uveitis, chorioretinitis, optic neuritis and other manifestations may be observed.
A very unusual form of manifestation of herpes simplex is known as Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis - eczema herpeticum. As a rule, it occurs in people who have any skin disease or predisposition to it (dermatosis or “problem skin”). In this case, intoxication and high body temperature are observed, herpetic blisters appear everywhere, quite abundant and closely spaced, periodically merging, sometimes with hemorrhagic impregnation. In some cases, they suppurate, then they open, dry out and form a solid crust. When the rash is completely treated with green paint, the patient’s skin takes on the appearance of crocodile skin. The disease is often quite severe and can lead to death.
During pregnancy, the child becomes infected:
- before birth - in 5% of cases (primary infection and ascending infection during this period are rare);
- during childbirth, i.e. when passing through the natural birth canal - in 95% of cases.
With primary infection of a pregnant woman in the first trimester or with ascending infection of the fetus, malformations often develop that are incompatible with life, or a miscarriage occurs, especially when infected with type II herpes virus, which is the infecting agent most often - up to 80% of cases.
When a pregnant woman is infected in the second and third trimesters, the risk of injury to the child is about 50%. At the same time, the liver and spleen enlarge, specific inflammation of the lungs, jaundice, metabolic disorders, malnutrition, meningoencephalitis, anemia and more occur. After birth, it can occur either in an asymptomatic subclinical form or have severe disabling consequences - blindness, severe damage to the central nervous system, deafness [1][2][6][8][11].
What to do if you have a “cold” on your lips
At the moment, no drugs or treatment methods have been developed that would completely destroy the herpes simplex virus in the human body. But we can give some advice to those suffering from herpes.
- Strictly follow the rules of personal hygiene! Since herpes is contagious, it is necessary to wash your hands with soap and use separate utensils and towels.
- Don't put your hands near your eyes! And do not wet your lenses with saliva! Herpes can affect the mucous membrane of the eye.
- It is not recommended to touch the viral rash or kiss. The virus can be transmitted by wearing one lipstick or smoking one cigarette.
- If you try to remove a blister or scab over a sore, the virus can spread to other parts of the body.
- Avoid oral sex! The virus from the affected lips can cause genital herpes in a partner.
- A young mother must also take certain precautions to protect her baby from contracting herpes. If you have herpetic rashes, you must wash your hands with soap and water every time before touching your child. And under no circumstances should the affected surface come into contact with the child’s skin.
Herpes is a virus
The source of the disease is the so-called herpes viruses. These are DNA-containing microorganisms that are causative agents of various types of infections.
The initial entry of the virus into the body usually occurs through the mucous membranes (although entry through damaged skin is not excluded). Having overcome tissue barriers, harmful microorganisms enter the blood and lymph and spread throughout the body. They are able to penetrate the cells of internal organs and nerve endings. The peculiarity and danger of herpes is that it is genetically introduced into the nucleus of nerve cells, after which it remains in the body forever.
Many people do not even realize that they are carriers of the virus, since the pathology in most cases is asymptomatic, not showing itself in any way (this is called a latent state).
The human immune system is capable of suppressing the development of the virus, but if it is weakened, the infection “awakens.”
Herpes Virus
How to minimize discomfort
You should start using antiherpes medications as soon as you feel a tingling sensation. Medicines will not get rid of the virus, but they will stop its development and speed up recovery. There are drugs that prevent the development of the virus: tablets, ointments for external use, which help heal blisters and ulcers and reduce discomfort.
When applying the ointment, use cotton swabs to avoid transferring the virus from your lips to the skin of your fingers.
Herpes requires the attention of specialists! A “cold” on the lips can be a symptom of serious diseases: a sharp decrease in immunity, cancer, HIV infection.
If you are suffering from relapses of herpes, consult a doctor. A specialist will not only save you from unnecessary worries and eliminate health hazards, but will also help you choose a comprehensive program for the prevention and treatment of herpes.
In order to make an appointment with an immunologist or dermatologist for a program for the diagnosis and treatment of herpes, call the Family Doctor clinic (clinic hours: Mon-Fri from 8.00 to 21.00, Sat-Sun from 9.00 to 20.00), or sign up for reception and diagnostics via online registration form
How to find out if there is a virus?
Already during the initial examination of the patient, the doctor can determine the presence of herpes (often people who have visual manifestations of the disease seek medical help). But in order to confirm the diagnosis and determine the degree of development of the infection, laboratory tests are prescribed.
Tests are important when planning pregnancy, since the virus is dangerous to the fetus. Tests are also required for patients preparing for transplantation.
There are several diagnostic methods - which one will be optimal in a particular case, the doctor will tell you. The presence of the herpes virus and its type can be determined by blood tests (enzyme immunoassay, PCR analysis, immunofluorescence reaction) and scrapings (culture method, immunofluorescence reaction). The most accurate, but also the most time-consuming and expensive method is the cultural method, which involves “growing” a virus obtained from a patient’s biomaterial in laboratory conditions.
Diagnosis of herpes
conclusions
1. Standard treatment regimen with Valvir
is effective for the treatment of recurrent genital GVI.
2. During treatment with Valvir
in patients with CHRGVI, there is a reduction in the duration of local symptoms of relapse.
3. Valvir's
in the first 6 hours from the onset of exacerbation of GVI significantly improves the quality of life of patients.
4. Drug Valvir
It is well tolerated and safe in both young and older patients.
Factors that provoke recurrence of herpetic infection
- Colds viral and bacterial infections
- Hypothermia of the body
- Stress and overwork
- Immunodeficiency conditions
- Nonspecific endocrine disorders
- Fasting, hypovitaminosis, general exhaustion
- Excessive tan
If the herpes virus gets on the skin or mucous membranes from the outside, then a herpes infection develops regardless of the virus carrier. The main route of transmission of the virus from a sick person to a healthy person in this case is through household contact, through kissing, a shared towel, dishes, household items or sexual contact.
Causes
There are many provoking factors leading to exacerbation of the disease. In addition to the weakening of immune forces, there are a number of other reasons:
- Emotional stress, physical fatigue, stressful situations.
- Long-term insolation.
- Surgical interventions.
- Taking immunosuppressive drugs.
- Hormonal imbalances.
In addition, there may be a combination of several negative factors leading to the activation of infection in the body. During illness, it is important to isolate yourself from others.
Material and methods
The study was conducted on patients who applied to the clinic of the Institute of Immunology of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia in 2014. The main group included immunocompetent patients (without established primary immunodeficiency and HIV infection), men and women over 18 years of age with a clinical picture of exacerbation of genital herpetic infection . Exclusion criteria were: pregnancy, lactation, use of other antiviral or immunotropic therapy, presence of decompensated diseases or acute conditions that could significantly affect the results of the study.
At the screening visit, specialists collected an anamnesis of the disease, noting the frequency and duration of exacerbations of infection, and previously used treatment. All patients were given recommendations for timely initiation of the drug valacyclovir ( Valvir
) during the first 6 hours from the onset of symptoms of exacerbation or during the period of prodromal symptoms.
In the process of monitoring patients who received therapy at the time of exacerbation of genital herpes, attention was paid to the duration and severity of local symptoms (itching, pain, burning at the site of the lesion), the nature of the elements of the rash, the area of the lesion, healing time and the duration of symptoms of intoxication.
The severity of subjective symptoms (itching, pain, burning) during an exacerbation was assessed in points on the following scale: 0 points - no complaints, 1 point - slight sensations of itching, burning or pain at the site of the rash that do not interfere with everyday life, 2 points - moderately severe symptoms that create daily discomfort, 3 points - complaints of pronounced subjective sensations in the area of the rash with irradiation to other anatomical areas (hips, sacrum, perineum, etc.).
Patients of the main group (20 men and women with genital CHVI) received the drug valacyclovir ( Valvir
) according to the regimen of 500 mg 2 times a day for 5 days. To assess the effectiveness and safety of therapy, patients were examined in the clinic on the 1st, 3rd, 5th day of treatment, as well as 14 days after completion of therapy. If new rashes appeared, the patient came to the clinic for an unscheduled visit. The comparison group included 20 patients who received therapy with acyclovir (manufactured in Russia) according to the standard regimen - 400 mg 3 times a day for 5 days.
All patients underwent an objective examination during each visit, including registration of the following parameters: localization of the lesion; area of the lesion (cm2); characteristics of the elements of the rash indicating the time of appearance (hyperemia, vesicles, erosions, beginning of epithelization, complete re-epithelialization).
The effectiveness of the study drug was assessed based on the following criteria:
— reducing the severity of the clinical course of relapse;
- duration of local symptoms (itching, pain, burning in the affected area);
— time required for epithelialization to begin;
— time to achieve complete recovery (complete epithelization).
In addition to objective data, the effectiveness of therapy was assessed according to the patient’s subjective feelings in points: 5 points - very good; 4 points – good; 3 points - satisfactory; 2 points - unsatisfactory; 1 point – extremely unsatisfactory.
Adverse reactions from taking the drug were assessed according to objective data and subjective feelings of the patient. The severity of adverse reactions of the study drug was assessed on the following scale in points: 5 points - no side effects noted; 4 points - minor side effects are observed that do not cause serious problems for the patient and do not require discontinuation of the drug; 3 points - side effects are noted that affect the patient’s condition, but do not require discontinuation of the drug; 2 points - there is an undesirable side effect that has a significant negative impact on the patient’s condition, requiring discontinuation of the drug; 1 point - side effect requiring discontinuation of the drug and the use of additional medical measures.
Tolerability of the drug was assessed both by the attending physician and by the patients themselves according to the following scale: 5 - very good, 4 - good, 3 - satisfactory, 2 - bad, 1 - very bad.
The results obtained were statistically processed by methods of variation statistics using Student's tests and presented in the form of tables.
Causes of oral herpes infection
Herpes that affects the oral cavity develops when infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1, which not only provokes the appearance of a blistering rash, but can also cause complications in 10% of cases. The second type of herpes virus (genital) also causes a rash in the mouth, but does not cause serious disruption to the body and differs in its mode of transmission (through sexual contact).
Most often, primary infection with a herpes virus occurs in childhood, after which it is introduced into the genome and remains in an inactive form for life.
The main routes of infection with a viral agent are close conversation, skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and the use of shared hygiene products or utensils. However, the entry of viral particles into the body does not guarantee that the disease will develop, since the immune system can suppress the action of the pathogen. In this case, situations that worsen the overall health of the body, on the contrary, provoke a clear manifestation of infection:
- surgical interventions;
- emotional and physical stress;
- lack of sleep, overwork;
- colds;
- chronic pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- periods of menstruation, pregnancy or lactation;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- AIDS;
- abuse of nicotine or alcohol;
- the appearance of microtraumas from excessive exposure to the sun or frost.
Possible complications
The herpes virus should not be perceived as an unpleasant but harmless “sore.” This is a rather insidious disease that poses a particular danger to pregnant women, infants and people with weakened immune systems (patients with cancer, people with HIV and AIDS).
The virus is not limited to superficial tissues - it easily penetrates into internal ones. The main targets of herpes are the mucous membranes, skin, eyes (conjunctivitis can also be a consequence of herpes), as well as the central nervous system and brain. Lymph nodes and internal organs can be affected by the virus. Due to the fault of the pathogenic microorganism, the functioning of the liver, lungs, intestines and kidneys can be disrupted.
The consequences of herpes can be stomatitis, infertility, miscarriage, congenital deformities in children, encephalitis, inflammation in the joints, prostatitis, benign and malignant tumors. Scientists, based on research, associate the development of multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease with herpes.
If a person’s immune system is weakened, other infections, both viral and bacterial, can “join” herpes, and this, in turn, puts an increased burden on the heart.