Diagnostic technique
Correct identification of the main type of pathogen is carried out in a laboratory setting. When contacting a dermatologist, the initial examination involves a visual examination of the patient. Additional methods may be:
- study of epithelial scraping;
- examination of the scrotum under a Wood's lamp, which highlights hidden types of spots;
- Balzer test using iodine-based preparations;
- cultural method of sowing in an active medium.
A thorough and complete diagnosis is necessary to exclude sexual diseases with similar symptoms (syphilitic roseola or leucoderma).
Diagnostics
At first, it may seem that there is no particular point in diagnosis. “The first signs have appeared, which means it’s a fungus,” this is what most patients think, coming with advanced inguinal fungus and numerous consequences of self-medication, such as skin burns and others.
First, everyone must undergo a full diagnosis, during which the doctor will be able to determine the stage of development of the disease along with the optimal method of treatment. The doctor first conducts an examination (dermatologist), examining the skin infected with the fungus. After this, the specialist directs the patient to scrape the lesion, examine the damaged area using a Wood's lamp and the Balzer test.
During the penultimate manipulation, a special device is used to highlight hidden problem spots of the epithelium. It is important to understand that the outcome of treatment, as well as the expenses incurred by the patient, depend on a complete diagnosis.
The Balzer test is a procedure for applying an alcohol solution of iodine to a problem area. Instead of this solution, aniline dyes are often used, which also highlight problem areas. After applying a special composition, the affected skin begins to peel off, which makes it possible to determine the stage and stage of development of the disease. Pityriasis versicolor, when illuminated with a special lamp, stands out as brown spots, and pityriasis versicolor shows up as mesh spots.
Iodine test is a simple and accessible diagnostic method
Tinea versicolor
Lichen versicolor is often confused by patients during self-diagnosis with other diseases with similar symptoms. At the moment there are three stumbling blocks, namely:
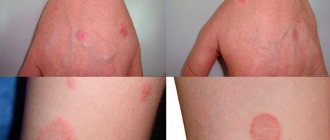
- leukoderma syphilitica - the spots are not brightly colored, have a network structure,
- roseola syphilitica - there is simply no peeling, the spots are pink in color and you just need to press on one spot and it disappears without the formation of frames, depressions, bubbles, pimples,
- imbricate mycosis - this disease is relevant in tropical climates, its spots are ring-shaped, the disease develops very quickly, affecting the entire area of the scrotum.
Possible fungal diseases
Skin peeling on testicles photo
All the pathogenic fungi listed above can cause various diseases that have a similar symptom in the form of peeling skin on the testicles. Among these keratomycosis:
- candidal inflammation in the groin;
- athlete's foot inguinal;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- complications of mycoses.
In addition to localization on the testicles, the disease can simultaneously or gradually appear on all genitals, inner thighs and in the inguinal folds. Several factors contribute directly or indirectly to the occurrence of these unpleasant problems:
- overweight men, which leads to sweating and even diabetes;
- improper hygiene of the genitals and the whole body;
- untreated or chronic forms of skin, foot or nail fungus;
- wearing underwear with a high synthetic content or a narrow cut.
Poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle and severe stressful situations greatly weaken the immune system and provoke an increase in fungi. At risk are residents of areas with high air humidity and hot climates. This is why most fungal diseases recur in the summer. Most often, the skin on the testicles peels off in the summer, during the holidays.
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory non-infectious skin disease that affects 0.5-1% of the world's population. Symptoms of LP typically include polygonal, flat, red-violet papules and plaques on the skin, as well as itching. At the same time, there is a wide variety of clinical forms of this disease, such as LLP of the oral mucosa, nail plates, linear, annular, atrophic, hypertrophic, inverse, eruptive, bullous, ulcerative, pigmented, palmoplantar, genital, bullous forms, as well as actinic LCP.
Involvement of the genital organs in LP is considered a relatively rare occurrence. However, in recent years, dermatosis of this localization has been increasingly observed, especially in Caucasian women in the perimenopausal period. Often this form of the disease is combined with damage to the oral mucosa. Thus, about 1% of the world's population suffers from LP of the oral cavity, while 20-25% of women and 3.7% of men with this localization of rashes have manifestations of the disease on the genitals [1, 2].
The nature of LP rashes on the genitals is characterized by a wide morphological diversity: papular rashes, erosions and ulcers, often accompanied by itching and pain; resolve with the formation of deforming scars.
It should be noted that the incidence of the genital form of LP is probably underestimated. Patients' anogenital area is not always examined, and LLP lesions on the genitals may be scanty and asymptomatic. The latter determines the absence of complaints from patients.
The variability of clinical manifestations of genital LP often causes misdiagnosis. The same patient may have different morphological elements, which significantly complicates diagnosis.
According to the classical ideas about LP, thin whitish lacy spots and papules appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, sometimes in the form of fern leaves, which can form both on an erythematous and unchanged background. This is the so-called reticular form of the disease. Such rashes are usually not accompanied by itching and are localized in women on the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina, in men - on the glans penis, in the coronary groove, on the inner layer of the foreskin.
In the erosive-ulcerative form of LLP on the genital organs, the rashes are often localized in fairly large areas of the mucous membrane (in women) and are accompanied by erosions and small ulcers, as well as whitish plaques and papules on a pronounced erythematous background. This form of the disease is usually accompanied by intense pain and burning.
The plaque form of LP localized on the genitals manifests itself in the form of edematous papules covered with a whitish coating.
The atrophic form of LP on the genital mucosa is characterized by the appearance of slightly sunken whitish spots.
Rashes with LP on the genitals can be located not only on the mucous membranes, but also on the smooth skin of the penis, the scalp of the scrotum, the labia majora, in the perineum, on the pubis, and also spread to the inner surface of the upper third of the thighs. In this case, the manifestations of the disease have signs of the classical form of LP and largely depend on the location and severity of the dermatosis. Typical symptoms of LP on the skin are red-purple polygonal papules and plaques with a dry, shiny surface on which a thread-like mesh is visualized, known as Wickham's mesh, a pathognomonic symptom of the classical form of the disease. This reticulation is caused by uneven granulosis. On the surface of the skin elements, whitish-opaline dots are clearly outlined, which intersect in the grid line.
The erosive form of LP is most common on the moist mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina. On the head of the penis, this form of the disease is much less common.
A characteristic feature of LP, including genital localization, is a chronic course with periods of exacerbations and remissions. During exacerbation, patients complain of irritation in the external genital area, itching, burning, soreness, and dyspareunia. If the vaginal mucosa is affected, these symptoms may be accompanied by discharge, often purulent. Upon examination, areas of inflammation, hyperemia, and erosion are found on the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina, which, upon epithelialization, become covered with a grayish-white coating.
Rash with LP on the vulva, especially with the erosive form, is usually associated with vaginitis. A whitish coating on the vaginal walls is rarely observed with LP. Upon examination, the vaginal walls are erythematized, sometimes with single erosions, which leads to the development of bleeding during sexual intercourse or gynecological examination. Microscopy of a vaginal smear visualizes immature parabasal and basal epithelial cells, small, flattened, cuboidal, with a relatively large nucleus, as well as accumulations of leukocytes. Lactobacilli are usually absent, and the vaginal pH is relatively high, at least 5-6.
The development of severe vulvovaginitis in patients with the genital form of LP can lead to the occurrence of cicatricial changes, synechiae, which disable the woman. In addition, the development of erosive LP on the external genitalia in individuals of both sexes is currently regarded as a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma of the corresponding localization [3, 4].
The vulvovaginal form of LP is often associated with lesions in the oral cavity. However, in patients with combined lesions of the mucous membranes of the genital organs and the oral cavity, atypical manifestations are often observed, such as diffuse erythema and superficial erosion of the gums, desquamative gingivitis. The triad of desquamative gingivitis and erosive vulvovaginitis is often referred to in the literature as “vulvo-vaginal-gingival syndrome” [5].
Differential diagnosis of LP of genital localization often causes certain difficulties due to the fact that this disease is sometimes almost indistinguishable from other pathologies of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. LLP papules may resemble genital warts when they occur on the glans penis; for psoriatic papules and plaques, intraepithelial neoplasia (eg, Bowen's disease, squamous cell carcinoma in situ
, as well as candidiasis).
Whitish lesions of LP are also often mistaken for lichen sclerosus, especially when the erythema is little noticeable, for example in patients with severe pigmentation. However, unlike LP, lichen sclerosus never affects the vaginal mucosa. However, differential diagnosis between these two dermatoses may be clinically infeasible and histologically difficult. In addition, lichen sclerosus and LP can occur in combination, and in recent years such an association has been observed more and more often.
Rashes with LP localized on the mucous membrane of the genital organs may be similar to similar manifestations of cicatricial pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris. Making a correct diagnosis can be helped by extragenital detection of blisters and erosions in patients with blistering dermatoses, as well as microscopy of fingerprint smears.
Erythema multiforme exudative (EME) can also be similar in clinical picture to the genital manifestations of LP. A thorough history taking, assessment of the patient’s general condition and extragenital rashes during MEE can help in making the correct diagnosis.
Thus, almost any lesion of the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals must be differentiated from LP and a thorough additional examination of the oral mucosa, as well as the skin, must be carried out in order to detect morphological elements typical of LP. In difficult cases, a diagnostic biopsy is performed to make a diagnosis, which is very informative.
Taking into account the physiological characteristics of the anogenital area against the background of damage to the integrity of the skin (especially when erosive and ulcerative elements occur), therapy for LP localized on the genital organs is a difficult task. Erosive and ulcerative rashes of LLP in the anogenital area predispose to the addition of a secondary infection, both bacterial and mycotic, which creates additional difficulties in diagnosing the disease, aggravates its course, and complicates treatment.
Before starting therapy, patients should be informed that erosive LP is a disease that is difficult to treat. Adequate treatment is often determined by trial and error, can be lengthy, and the main goal is control of the disease.
An important aspect of therapy is also emotional support for the patient, since even papular LP in the genital area, which is not accompanied by itching and pain, can cause anxiety, a feeling of embarrassment or shame in the patient. Erosive LP often occurs with severe pain, which makes it difficult not only to sexual activity, physical exercise, but also to perform everyday activities and the ability to wear ordinary clothes.
Nonspecific methods of therapy for genital LP are aimed primarily at reducing discomfort in the genital area. In case of severe pain, short-term relief can be brought by cool compresses with clean water or non-alcoholic antiseptics. Using topical anesthetics and covering erosions with petroleum jelly or zinc paste before urinating or washing can reduce burning and pain.
To prevent vaginal synechiae for women who are not sexually active, daily insertion of dilators into the vagina is recommended. Men with uncircumcised foreskin should be warned about the possibility of developing phimosis, so it is extremely important for them to ensure daily and regular retraction of the foreskin with full exposure of the glans penis.
The first-line drugs for the treatment of the genital form of LP are topical glucocorticosteroids (GCS). In the absence of erosions, but in the presence of papules and itching, applications of 0.1% betamethasone valerate or triamcinolone once a day are recommended. Erosive forms of the disease require more powerful topical corticosteroids (0.05% fluocinonide or 0.05% clobetasol propionate). Applications of these medications are also carried out once a day.
Currently, there are no topical corticosteroids that are officially recommended for insertion into the vagina. Therefore, for the treatment of erosive lesions of the vaginal walls in patients with LP, suppositories with hydrocortisone acetate, approved for administration per rectum, or topical corticosteroids in the form of ointments are recommended.
The use of GCS in the genital area, as well as the anatomy and physiology of this area against the background of erosive changes in the mucosa, creates conditions for the addition of a secondary infection. Most often, the course of genital LP is complicated by the development of urogenital candidiasis. A bacterial infection is also possible. In such cases, it is advisable to use systemic antifungal or antibacterial drugs. Nevertheless, the use of topical forms of drugs remains a priority. Local azole antifungals in some cases have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane, and their use can aggravate local discomfort in patients.
In connection with the above, the use of combined topical corticosteroids is most optimal for the treatment of genital LP. One such medicine is Tetraderm
is a unique drug that is a combination of mometasone, econazole, gentamicin and dexpanthenol. Mometasone belongs to the class of strong topical corticosteroids with a high safety profile (according to the European classification Miller and Munro). Econazole is a modern, highly effective antifungal drug with a bactericidal effect, the basis of which is the suppression of the synthesis of ergosterol, which regulates the permeability of the cell wall of microorganisms. Gentamicin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. Dexpanthenol, which is provitamin B5, has an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect by stimulating the expression of IL-6, IL-8 and antioxidant genes, stimulating the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts to the site of dermal damage, as well as collagen formation. In addition, dexpanthenol helps reduce transcutaneous water loss, which reduces inflammation and moisturizes the skin. These properties of dexpanthenol justify its use as a means to accelerate epithelization. Dexpanthenol is used in gynecology, in particular for the treatment of cervical erosion, as well as for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, nose, larynx, respiratory tract (including after tonsillectomy), gastric mucosa, and urinary system organs.
Thus, Tetraderm
is a combined topical drug that is optimal for local treatment of the genital form of LP.
In addition to topical corticosteroids, cyclosporine for external use is used for the treatment of LP. The effectiveness of this drug has been demonstrated in the treatment of lesions of the oral mucosa in patients with LP [6]. One study demonstrated a significant reduction in erosions after 1 and 3 months of topical cyclosporine therapy [7]. This immunosuppressive drug is prescribed in cases where other drugs for external therapy are ineffective. For erosive vulvovaginitis in patients with LP, 1 ml of cyclosporine injection solution (contains 100 mg) is applied to the vulva or injected into the vagina 4 times a day daily until the rash resolves. However, vaginal administration of cyclosporine is limited due to its local irritant effect [7].
A remedy for topical therapy of LP with localization on the mucous membranes of both the genital organs and the oral cavity is tocrolimus ointment, which is used for lesions of the vulva 2 times a day, but its use, as well as in treatment with cyclosporine, is limited by the development of local irritation [8 ]. Topical use of tacrolimus for vaginal lesions is not recommended due to the high degree of penetration of the drug into the systemic circulation through the mucous membrane.
Systemic therapy for LP is indicated only after failure of local therapy. The only group of drugs with systemic action that are effective in the treatment of erosive forms of LP are GCS for oral administration. In some cases (for example, in severe cases of LP), systemic administration of GCS is used in initial therapy. Prednisolone in a daily dose of 40-60 mg is used for 2-4 weeks until the symptoms of the disease resolve. After the patient's condition improves, topical corticosteroids are used for further treatment.
As an alternative method of systemic therapy for torpid genital LP, hydroxychloroquine is used at a dose of 200 mg 2 times a day [9]. Also for LP, systemic retinoids are used, for example, isotretinoin at a dose of 1 mg/kg or acetretin at a dose of 25 mg once or twice a day, as well as oral cyclosporine, azathioprine, methotrexate at a dose of 10-20 mg once a week and dapsone [10-14].
In addition, to eliminate deforming scars and synechiae that develop in severe genital LP in the absence of adequate drug therapy, surgical treatment methods are used to restore sexual function.
Thus, LP with damage to the genital organs, especially in its erosive form, is painful, accompanied by cicatricial deformation, and, consequently, a sexually disabling disease. The prognosis for LP is favorable, but unpredictable. Nevertheless, adequate therapy with the use of topical corticosteroids as first-line drugs in the vast majority of cases can improve the course of the disease. Combined topical corticosteroids are the optimal drugs for the treatment and prevention of complications of the genital form of LP.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Information about authors
Dvoryankova E.V. — https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2458-419X
HOW TO QUOTE:
Dvoryankova E.V. Anogenital forms of lichen planus. Clinical dermatology and venereology
. 2019;18(6):762-766. https://doi.org/10.17116/klinderma201918061762
Corresponding author:
Dvoryankova E.V. — email
Corresponding author:
Svechnikova E.V. — email
Types of fungal infections
Peeling of the skin is a symptom of fungus on the scrotum.
There are several main forms of mycotic pathogens that provoke extensive lesions of the scrotum:
- Scrotal yeast or candida: leads to various forms of candidiasis. In addition to the scrotum area, the penis and genitourinary canal are involved in the inflammatory process.
- Epidermophytons: provoke the occurrence of dermatomycosis, which can manifest itself as lichen or inguinal athlete's foot. It is more often diagnosed in people leading an active or sports lifestyle.
- Pathogenic fungus of the Pityrosporum species: causes pityriasis versicolor on the scrotum. Among all cases, it is the least common due to the low survival rate. Often occurs during hormonal changes and problems with testosterone levels.
All species are part of the normal human microflora and have similar symptoms. Only a specialist will help determine their type and identify the cause.
Signs indicating the occurrence of a fungus
It is necessary to carefully examine this area of the body in men. The affected area becomes covered with pink spots, which later change color to yellow.
If timely treatment is not started, they will grow. The fungus can cover the entire scrotum, cover the groin and gradually affect the skin between the buttocks.
Can appear:
- Unbearable itching.
- Feeling pain.
- Peeling of the skin, which will cover the entire area and the egg as well.
After a certain time, the area affected by the fungal infection begins to turn red, and characteristic symptoms appear:
- Cracks form on the skin.
- These areas become dry and the protective properties are impaired.
- The skin begins to peel off not only in those places where there is a lesion, but also where healthy skin comes into contact with the affected area.
Signs of mycosis
Despite the fact that cutaneous mycosis is quite problematic in treatment, its manifestations are not long in coming. The problem is that the disease is prone to relapse after incorrect treatment. The disease can manifest itself in a variety of ways, but in the early stages the following occurs:
- small cracks appear on the skin in the scrotum area (on the inside of the thigh) (painful sensations depend directly on the characteristics of the body and the individuality of the case),
- the formation of bubbles is possible, due to which the skin becomes rougher and denser,
- over time, the pain may quickly go away, the skin will soften, return to its normal color and begin to peel off,
- under the condition of bacterial infection, in any case, the blisters will transform into ulcers.
All of the above signs are extremely general, but the following factors cannot be excluded: fungi on the testicles cause a feeling of itching, along with peeling off areas of the skin. Next, diaper rash appears, reddish spots appear, actively growing in size. Periodically, the spots begin to itch, causing discomfort, and all standard ointments for inflammation or disorder do not help. They only partially relieve inflammation and stress on the affected area, while the disease only temporarily stops progressing.
Read also: Herbs for fungus: effective recipes for internal and external use
If left untreated, the fungus spreads to neighboring areas
What is the lifespan of flies
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Annoying house flies have been annoying people since ancient times. They belong to a synanthropic species, that is, they are ecologically associated with human settlements and are not found in the wild. A long time ago, the ancestors of Tsokotukha began to live next door to people; their current relatives can no longer exist in any other way.
Flies have lived on almost the entire planet for millions of years. The oldest representative of the Diptera order was found in China; its age is 145 million years.
There are 2 subspecies of flies found in Russia:
- ordinary room;
- southern room.
The house fly poses a hidden threat to humans, being a carrier of helminths and pathogens of dangerous diseases: cholera, dysentery, tuberculosis, anthrax, diphtheria. By infecting food, insects make it dangerous to eat.
Annoying, ubiquitous insects greatly spoil the lives of humanity. Therefore, many are interested in the question: how long do flies live? The insect lives on average 3 weeks, but enemies and unfavorable natural conditions reduce the average life span of a fly to 6-10 days.
How does reproduction occur?
Flies have many enemies, but their colossal fertility saves the species from destruction. The speed of reproduction is amazing: during the summer season, a male and a female can produce offspring weighing 40 tons (in a comfortable habitat in the absence of enemies). Throughout the year, in a favorable climate, 20 generations of insects are replaced, and during the summer period - 7-8.
There are approximately 150 eggs in a clutch; in total, flies lay 600-2000 eggs in their entire life. For masonry, insects use rotting organic waste, manure, sewage, and food. After a day, larvae appear, resembling thin threads in appearance. They penetrate deep into organic waste, providing food, moisture, warmth, and protecting from harmful sun rays and enemies.
Stages of development
The life cycle of a fly has several stages:
- Egg – development lasts 8-50 hours.
- The larva, or maggot, develops in 3-25 days, undergoes 3 molts before becoming a pupa. In just a week, the size of the larva increases 800 times.
- Pupa – the period lasts 3-6 days. Lowering the temperature slows down pupation.
- An adult insect (imago) lives from 10 days to one or two months. 36 hours after emerging from the pupa, the adult is able to reproduce.
On average, development from egg to adult form of an insect lasts 20 days.
Lifespan of flies
It is impossible to answer unequivocally how long the common fly lives. Many factors influence the lifespan of a fly. For example, the state of the environment. Favorable temperature is 23-25°C with air humidity 80%. With an average lifespan of 3 weeks, a long-lived fly would live 8-9 weeks in such resort conditions.
The house fly population peaks in the fall. The parasitic fungus empusa saves from the dominance of insects, thanks to which the number of annoying insects sharply decreases. Harsh wintering conditions make a certain contribution to the extermination of the fly tribe.
Control measures and prevention
The presence of carriers of diseases dangerous to humans in the house cannot be ignored. Use available effective insect control methods:
- Equip windows with screens to prevent insects from entering the room.
- Do not leave food accessible; cover with lids, gauze, and napkins.
- Keep the kitchen clean, wash dirty dishes, remove trash, cover the trash can with a lid.
- In your garden or dacha, store garbage in containers with tightly closed lids.
- Regularly treat the cesspool with bleach.
- Use sticky tape and insect traps.
- If there are a large number of insects, use fumigators, repellents, and insecticides. When working with medications, follow the instructions.
Treatment of groin fungus in men
If a rash and ulcer appears in the groin, how to treat the disease? External fungal ointment helps in the fight against lichen. Treatment of inguinal dermatitis consists of several measures. In the early stages, antifungal and antibacterial ointments are sufficient, but if the disease is advanced, more serious measures will be required.
How to cure mycosis in the groin:
- Use antifungal ointment or cream. External remedies remove peeling, eliminate redness on the testicles and pubis, relieve itching, dry out the abscess and kill the fungus. The ointment is applied in a thin layer to thoroughly dried skin. The affected area is treated, including areas of healthy skin. This is necessary to avoid the spread of fungi.
- Take a course of antifungal drugs.
- Allergy medications will help with itching.
- Strengthen the immune system.
- Treat your pubic hair with an antifungal shampoo twice a day.
Antifungal ointments for the intimate area:
- Clotrimazole;
Clotrimazole - Miconazole;
- Monistat;
- Triderm;
- Mikatin;
- Zalain;
- Lotrimin;
- Lamisil;
- Terbinafine;
- Ketoconazole;
- Tinedol.
After applying the cream, the skin can be treated with zinc ointment. It will protect the skin from friction and excess moisture.
As prescribed by your doctor, you should take antimycotics in tablet form.
The doctor may prescribe:
- Fluconazole;
Fluconazole - Nystatin;
- Terbinafine;
- Griseofulvin;
- Intraconazole;
- Ketaconazole.
Inguinal athlete's foot causes unbearable itching, so you can take antihistamines:
- Suprastin;
- Zodak;
- Zyrtec;
- Diazolin.
Antifungal shampoos with the active ingredient ketoconazole are used to treat hair:
- Keto plus;
- Mycozoral;
- Nizoral;
- Sebozol;
- Akrikhin Mikozoral.
If the cause of tinea groin is a bacterium and not a fungus, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial drugs:
- Clindamycin;
- Erythromycin;
- Metronidazole;
- antibacterial soap Hibiclens, Lever 2000 and analogues.
For a serious bacterial infection, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics:
- Minocycline;
- Cephalexin;
- Doxycycline;
- Erythromycin;
- Dicloxacillin.
Treatment of scrotal fungus
The treatment period for a disease such as inguinal fungus is two months, but it is possible to completely safely speed up this process. Recommendations:
- purchase and wear loose underwear, changing it daily,
- use medicinal ointments only after taking a bath and washing the genitals with baby soap,
- treat infected and near-infected areas of skin with ointments,
- to avoid genital friction, use special talcum powder,
- shave your groin hair,
- avoid sexual intercourse during therapy (this is not only to protect yourself, but also your sexual partner).
Read also: Drug Creolin for nail fungus
Usually effective therapy is prescribed by doctors. It includes medication and the use of special ointments. The ointment is selected solely based on the type of disease and stage of development (volume of affected tissue).
Some people decide to use folk recipes to combat groin fungus, which, in principle, only gives the desired result in 20% of cases, especially if you have not consulted a doctor.
Traditional medicine involves the use of alcohol tincture of iodine for two weeks. You need to lubricate the affected area once a day, preferably before bed after a shower. The product has proven itself effectively in the fight against fungus; the main thing in the process is not to overdo it with the dosage.
Why does the disease appear?
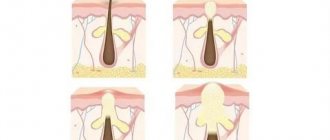
The fungus, which has not shown itself in any way for a long time and “lives” on the testicles, feeding on dead skin cells, begins its active activity only if there are factors that provoke the disease.
We list the main reasons for the development of infection:
- a humid environment has been created in the scrotum area, which is caused by intense sweating, violation of personal hygiene rules or specific working conditions;
- increased air temperature - this is why in the hot season the disease begins to manifest itself or worsens;
- excess body weight;
- metabolic disorder or hormonal imbalance;
- other types of fungal diseases that have not been completely cured;
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- long-term stressful conditions;
- hard physical labor;
- cardiovascular diseases.
All these causes of infection in men are provoked by the structural features of their genital organs. The disease begins to develop on them because ideal conditions for its life have been created there: comfortable temperature and humidity.
Herbal treatment
Additionally, herbal remedies can be used in the treatment of inguinal athlete's foot. Herbs are used in complex therapy.
Herbal medicinal preparations help relieve itching on the testicles and the front of the thighs. Herbs have an anti-inflammatory and healing effect, so they are used if the skin is cracking and inflammation appears in the skin folds.
In the treatment of inguinal epidermophytosis, herbal decoctions are used:
- strings,
- violets,
- eucalyptus leaves,
- birch trees
- oak bark,
- poplar buds,
- chamomile flowers,
- yarrow,
- St. John's wort.
Herbs are used in the form of baths or lotions. After using the herb, you need to let the skin dry.
Nail fungus. Vinegar, egg as treatment methods
Onychomycosis is a disease that causes a person a large number of problems and troubles. The disease mainly affects the feet, and therefore if you have nail fungus, vinegar and eggs will become your helpers in the fight against the disease. Today in the pantry of traditional medicine recipes there are many that are based on the use of eggs and vinegar.
Treatment of onychomycosis with vinegar
Standard methods of treating nail fungus may not always bring the patient the desired result. In addition, the disease is simply insensitive to many medications, and therefore all efforts may be in vain. Meanwhile, the nail will remain the same and will not look aesthetically pleasing. Another important fact is that medications are allowed to be used for a certain amount of time so as not to cause harm to health.
The main recipes against nail fungus based on the use of vinegar include:
- Foot baths - 0.5 liters of 9% vinegar should be heated, poured into a basin and lowered the feet there. To ensure that the damaged area is completely covered with liquid, place the basin on a slope. Keep your limbs in vinegar for at least 15 minutes. You can wear socks at night, or better yet, if they are soaked in wine vinegar.
- Apple cider vinegar mixed in equal proportions with iodine has a good effect in the fight against onychomycosis. This mixture should be applied to the damaged area twice a day until healthy nails grow back.
- Apple cider vinegar with vegetable oil - these two components are mixed in equal parts and a cotton swab is soaked in the resulting product. Then it is applied to the affected nail plate and sealed with an adhesive plaster. All this is secured with a sock and left overnight. Repeat sessions until complete recovery.
- Vinegar with carrots - mix carrot juice and vinegar essence and smear the skin and nail plate. Vinegar has a destructive effect on the fungus, and carrots restore the epidermis.
- Vinegar with egg - take 2 tbsp. vodka and vinegar essence, as well as 3 proteins. Everything is thoroughly mixed in order to lubricate the nails with fungus twice a day until the plate is renewed.
- Vinegar with dimethyl phthalate - mix 1 tbsp. dimethyl phthalate with the same amount of vegetable oil, 1 egg. The resulting mixture is added to 2 tbsp. essences. The product should be lubricated on the affected areas in the evening. After the mixture is applied to the nail, a bag and socks are put on top.
I would like to note that therapy using vinegar is allowed only if there are no abrasions, open wounds or lesions of the epidermis. If acid penetrates the wound, it will be at least unpleasant.
In this case, slight tingling and tingling is allowed, which will mean that the vinegar is working and the infection is dying. In addition, different skin reacts to these components in its own way - sometimes it peels and turns red (especially when using concentrated acid solutions).
Preventive measures
To prevent infection with onychomycosis, you need to pay attention to some rules of prevention:
- actively combating sweating of the feet;
- daily change of socks and tights;
- washing hands and feet every day with soap (preferably laundry soap);
- having light, replaceable shoes at home and at work;
- going to public baths, swimming pools and beaches only with your own slippers;
- After taking a shower, you need to dry your feet/hands well.
If you notice the first symptoms of the disease, immediately begin its treatment, since it poses a danger not only for you, but also for others.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=3gBSQBxbi3c
Prevention of inguinal mycosis
As with every disease, prevention of this disease involves eliminating all underlying factors. Thus, the patient is obliged:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules (including the fight against sweating),
- restore metabolism (consultation with a specialist is required),
- taking a shower at the end of the working day upon returning home and after physical activity,
- change of underwear daily,
- using powder to combat excessive sweating,
- use of strictly individual personal hygiene items (do not trust or lend your own personal hygiene products),
If you have been in contact with an infected person or things they use, you should wash your hands well with soap and preferably take a shower. This measure will significantly reduce the risk of disease.