What is eczema
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease that manifests itself as a rash, itching, and redness. The rashes can take a wide variety of forms, affecting different parts of the body. The disease is not contagious. Eczema is often recurrent.
The mechanism of inflammation developing in the dermis and epidermis is that a certain group of cells, when irritated, release substances that cause inflammation. The latter in turn causes itching. The patient itches - inflammation intensifies, microbes penetrate, which together leads to systemic disorders.
Eczema is a polyetiological disease, that is, it is not possible to name a reliable root cause of this pathology. As a rule, this is a combination of exogenous and endogenous factors, the main of which are:
- weakness of the immune system;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- nervous disorders;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- genetic predisposition.
According to statistics, this type of dermatitis most often occurs in women aged 30–40 years. This is probably due to high emotional lability (women are more often nervous), as well as frequent contacts with potential allergens: cleaning products, detergents, cosmetics.
Types of eczema:
Eczema is an idiopathic disease. The reasons why it appears are not fully understood. Doctors know several factors that, in combination or individually, can trigger a particular set of symptoms. For example, gastrointestinal pathologies, thyroid dysfunction, varicose veins, and psycho-emotional stress can lead to the development of eczema rash.
True eczema
True eczema is chronic, manifested by a cyclical development from exacerbations to relapses. A distinctive feature of the disease is the presence of symmetrical inflammation on the body. This diagnosis can be made based on the indicated symmetrical distribution of the rash, the presence of small vesicles (small pappulous rash), and polymorphism. By identifying an allergy to something and a history of stress, the accuracy of the diagnosis increases.
Stages:
- erythematous - the skin becomes noticeably red;
- papulovesicular - vesicles appear;
- weeping - the bubbles burst and microerosions form in their place;
- crusts appear.
As a rule, all stages are observed simultaneously.
Inflammations in this type are swollen, reddened, the surface becomes wet from the secreted exudate. A characteristic manifestation is the “serous well” syndrome, when the secretion lies in drops, resembling dew. Within the focus of inflammation there are vesicles with contents and crusts. In addition to foci of inflammation, there are scattered dry rashes on the body. If a person has been suffering from this disease for a long time, the quality of the skin gradually changes. Such patients are characterized by infiltration, hyperemia, and hyperpigmentation. The skin pattern becomes more pronounced, the skin thickens.
Microbial eczema
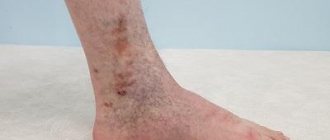
The causes of microbial eczema are factors associated with varicose veins (varicose eczema), trauma (paratraumatic), and fungal infections (mycotic). The cause of development is the basis for selecting treatment.
The lesions are asymmetrical, as is the case with the previous type. As a rule, foci of inflammation are located in the lower part of the body - in the projection of the veins. The second option is skin folds where intense sweating occurs. The basis for diagnosis is anamnesis, symptoms, microscopy, bacteriological, histological examination:
- microscopy reveals signs of mycosis in the form of mycotic cells;
- a bacteriological study determines the type of fungus and the drug to which it is sensitive;
- histology reveals widespread lymphoid infiltration with plasmacytic elements, epidermal localization of blisters, sclerotic changes in the skin (if microbial eczema has lasted for a long time).
The spots have uneven edges, the skin around them is thickened, red and blue. There are weeping crusts on the spots. Dry single rashes may form on the periphery. Often this type is complicated by additional diseases.
Seborrheic eczema
Eczema is localized in a characteristic way - on the head, in anatomical folds, behind the ears, on the folds. In the area of hair growth, dry skin and redness are noticeable, peeling marks separate from the spots, and the patient experiences itching. Inflamed spots have defined boundaries. They are dry, but sometimes serous-purulent or serous crusts appear, after removal of which eroded weeping spots appear.
With inflammation in the folds, deep cracks, swelling, and swelling appear. Sometimes lesions appear on the body, mainly in the lower part. They are clearly defined, yellowish-pink in color, flaky, and a rash is observed in the middle part. Some doctors consider seborrheic eczema to be seborrheic dermatitis or true complicated eczema. However, these diseases can be distinguished histologically.
The cause of occupational eczema is regular contact with irritating substances. The trigger for the onset of the disease can be microtraumas, chemical and aggressive drugs, and dust. In combination with existing allergies or impaired vascular permeability, this results in rashes. The clinical picture is similar to true eczema. Rashes are localized in areas of contact with the allergen, but can occur throughout the body.
The diagnosis is made taking into account the clinical picture and evidence that exacerbations occur upon contact with certain substances. This type may also be indicated by the fact that the symptoms disappear during the holidays.
Dyshidrotic eczema
The causes of dyshidrotic eczema are disturbances in the activity of the sweat glands. Additional causes include contact with substances that are known to be allergenic. Exacerbations are typical during summer time or periods of severe stress. As a rule, the first symptoms affect the fingers - rashes begin to appear on the sides, after which they spread to other areas.
The main types of eczema that can occur on the scalp
There are wet and dry forms of eczema. The latter most often manifests itself on the hands and fingers, and the ingress of water onto the affected areas significantly aggravates the condition. The weeping form is accompanied by a large amount of serous discharge with the resolution of small vesicular rashes, papules, and pustules.
The following types of eczema can be localized on the scalp:
- seborrheic;
- mycotic;
- true;
- microbial;
- sycosiform.
Let's take a closer look at what each variety is and how it manifests itself.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
The main cause of the development of seborrheic dermatitis is an infectious agent. It is believed that its cause is the yeast-like lipophilic fungus Pityrosporum. The fungi Pityrosporum ovale are present in the form of spores on the skin in 90% of people, but begin their active growth only with increased production of sebaceous secretions by the skin and a decrease in local or general immunity. For their vital activity and reproduction, fungi actively use sebum and can cause inflammation of the skin. Predisposing factors to active and excessive secretion of sebaceous secretions can be internal and external factors.
Internal factors:
- endocrine diseases
- diseases of the nervous system
- epilepsy
- Parkinson's disease
- immunity disorders (HIV, AIDS, congenital immunodeficiency, etc.)
External factors:
- hereditary predisposition to seborrhea
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating)
- cold air
- poor nutrition
- low zinc content in the diet
- vitamin deficiency PP
- stressful situations
- use of alkaline detergents in everyday life and for personal hygiene
Among the factors contributing to the hyperactivation of fungal microflora, the leading place belongs to changes in the composition of sebum, which significantly disrupts the barrier function of the skin. Among the reasons causing these changes, most leading dermatologists note neurogenic, hormonal, and immune.
It is well known that seborrhea and, in particular, diabetes are significantly aggravated by nervous stress. Patients with various diseases of the central nervous system and autonomic nervous system are significantly susceptible to the incidence of seborrhea, in various forms of its manifestation. Patients with cranial nerve palsies, trunk paralysis, Parkinson's disease, etc. have a huge predisposition to the incidence of diabetes; diabetes in this group of patients often takes a widespread course with a pronounced torpidity to the treatment.
Hormonal imbalance also underlies the development of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
The characteristic clinical symptoms of the disease are peeling and inflammation of the skin, accompanied by itching. The classic option is the symmetrical involvement in the pathological process of the skin of the scalp, the border of hair growth, eyebrows, eyelashes, the area of the beard and mustache. Small flour-like white scales appear on the scalp, or peeling can take on a large-plate character. This variant of the course of diabetes is characterized by the absence of changes in the skin and is considered as dry seborrhea. Many patients with dandruff (a mild form of diabetes) complain of itchy skin.
If patients rarely wash their hair, the process progresses, covers new areas of the skin, and peeling becomes more abundant. Inflammatory changes in this course may be slightly expressed. A more severe course of diabetes is characterized by erythematous spots and plaques covered with mealy or sebaceous scales, and in some cases, scale-crusts and hemorrhagic crusts. The skin of the forehead, behind-the-ear areas, and ear canal areas may also be involved in the process; patients may complain of a feeling of constant discomfort in the affected areas of the skin or intense itching. Often the severity of subjective sensations correlates with ANS disorders. If treatment is not carried out, papules and plaques may appear on the smooth skin of the face, back, chest and, in some cases, be complicated by a secondary bacterial infection.
Seborrheic dermatitis has nothing to do with sebum or any other fat. There are 2 forms of seborrheic dermatitis - adults and infants.
Adult seborrheic dermatitis
This is a chronic dermatitis with characteristic manifestations (inflamed, clearly defined red lesions covered with greasy scales). Typical localization is areas of the skin with a large number of sebaceous glands, namely the scalp (in combination with dandruff), face and upper torso.
Seborrheic dermatitis affects about 3-5% of young people, although mild dandruff is much more common. This condition is often seen in people living with HIV. The peak incidence occurs between the ages of 18 and 40, and the disease rarely develops before puberty. The figure shows the localization of seborrheic dermatitis rashes.
The yeast fungi Malasseriafuifur (synonym - Pityrosporum oviculare) are detected in increased quantities in dandruff flakes and foci of seborrheic dermatitis, which allows them to be considered causative factors. Perhaps for the same reason, seborrheic dermatitis is often observed in patients with immunodeficiency. The presence of mature sebaceous glands in the skin appears to be a necessary condition for the development of seborrheic dermatitis. Many young people with this condition have oily skin.
There are several variants of seborrheic dermatitis, which occur in various combinations with varying degrees of severity.
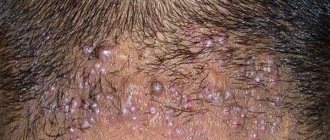
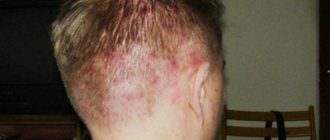
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
The earliest symptom is dandruff. Later, perifollicular redness and peeling of the skin develops with the formation of clearly demarcated plaques, isolated or merging with each other, occupying a large area and spreading to the skin of the forehead. In a chronic course, some hair may fall out with restoration of its growth after the severity of the inflammatory process decreases. Redness and flaking with greasy scales are often localized behind the ears, and cracks covered with crusts form in the folds. Persistent external otitis may be an isolated lesion or combined with manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis in other areas of the skin.
Face
With seborrheic dermatitis, rashes on the face are located in the area of the eyebrows, between the eyebrows and in the nasolabial folds, usually in combination with damage to the scalp.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is often observed, with the edges of the eyelids reddened, with a layer of small white scales and yellowish crusts. Sunlight causes a short-term exacerbation with gradual improvement as the tan develops.
Young women sometimes have paranasal erythema in combination with an easy blush on the cheeks. It is not always clear whether rosacea or mild seborrheic dermatitis is present, but overuse of potent topical corticosteroids may contribute to the development of this condition into a variant of rosacea called perioral dermatitis.
Torso
The most common localization of rashes on the body is the chest and interscapular area of the back, usually observed in men. Primary elements are represented by follicular papules of red-brown color, covered with greasy scales. When papules merge, multiple foci of irregular shape are formed, with the presence of larger scales along the edges.
FOLDS
When localized in the proximal folds, seborrheic dermatitis looks like diaper rash with the presence of clearly limited areas of diffuse erythema covered with greasy scales. Secondary cracks occur, and due to sweating, secondary infection or improper treatment, weeping dermatitis may develop and spread far beyond the initial lesions.
A combination of seborrheic dermatitis and seborrheic folliculitis is possible, more often in men. The rash consists of erythematous follicular papules and follicular pustules on the skin of the upper torso and shoulders, which are usually accompanied by itching. The absence of comedones, cysts and scars helps distinguish this condition from ordinary acne.
All of the above options tend to be chronic and recurrent. In rare cases, generalization of seborrheic dermatitis with the development of erythroderma is possible.
Equipment for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
Our clinic performs accurate diagnostics, allowing us to identify which factors contributed to the development of diabetes in a particular patient. And the use of hardware techniques makes it possible to achieve lasting treatment results based on increasing local immunity and eliminating disease-provoking factors.
This makes it possible to refuse the use of corticosteroid drugs externally and systemic drugs orally, or to significantly reduce the indications for use and doses of these drugs.
Excimer laser XTRAC
One of the types of phototherapy, the distinctive feature of which is excimer light therapy with a wavelength of 308 nm.
The excimer laser is included in the list of mandatory equipment for health care facilities in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 151N dated March 16, 2010.
Our clinic introduced excimer lase in the Russian Federation and was one of the first in the world to substantiate its pathogenetic effectiveness.
Benefits of excimer laser treatment:
- high duration of remissions of a year or more;
- has no side effects on the body;
- Possibility of use for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp;
- the procedure is absolutely painless.
Before the procedure, a preliminary examination is required to rule out an allergy to ultraviolet rays in the patient and to determine the degree of damage to the skin surface.
The principle of operation of an excimer laser is to produce ultraviolet radiation, which is transmitted through a fiber optic cable and exits at its end in the form of a compressed beam of laser light. The energy source in the laser is a gas mixture consisting of xenon and halogen.
Excimer system Derma GmbH
The world's first excimer system in which there is no light guide, which allows more precise delivery of energy to the lesion.
The excimer system is included in the list of mandatory equipment for health care facilities in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 151N dated March 16, 2010.
A unique balance between the effectiveness and safety of therapy.
The world's first development in which there is no light guide, which allows energy to be delivered to the lesion without loss. At the same time, excimer systems and lasers make it possible to direct the laser to damaged areas of the skin. Thus, the effect does not affect the entire body (healthy skin is not exposed to UV radiation).
The Quantel Derma GmbH device was developed by the Quantel Group (formerly Wavelight Aesthetic GmbH) in Erlagen, Germany. Also part of the company is located in France. Quantel Group has been in the laser business since 1970 and has since built a strong reputation as a leader in the field.
JET PEEL
The most modern gas-liquid treatment
The operating principle of Jet Peel is based on non-contact jet treatment of the skin. The equipment of the Israeli manufacturer of cosmetology equipment TavTech is an innovative device, the only gas-liquid device that can be used for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Jet Peel operates using a patented technology that delivers a mixture of tiny droplets of liquid and air under pressure.
The use of this device for seborrheic dermatitis allows you to:
- lymphatic drainage to stimulate microcirculation in tissues;
- hardware introduction of medicinal solutions into the skin.
MULTICLEAR
It is a revolutionary technology designed to safely and effectively treat many common skin lesions.
MultiClear™ is a product of CureLight, the world leader in selective phototherapy.
- An easy-to-use, fast expert system allows the doctor to accurately select the optimal phototherapy method.
- Generates a minimally effective targeted narrow-band beam of UV-B and UVA radiation without affecting healthy tissue.
The operating principle of the device is based on selective exposure of biological tissues to a light stream in the range of 280-320 nm. with a peak power of 314 nm, without damaging the skin and surrounding tissues.
Ultraviolet cabin UV Waldmann
Along with pronounced repigmentation, it leads to restoration in the skin of patients with seborrheic dermatitis.
New! UV cabin manufactured by Herbert Waldmann GmbH & Co. KG (Germany)
The cabin is equipped with 26 low-pressure fluorescent lamps, which are generally recognized as the most efficient and provide a guaranteed optimal level of light exposure.
Creates an ideal, uniform photoload and is most effective both for the treatment of various forms of seborrheic dermatitis and for maintenance therapy of seborrheic dermatitis.
Narrowband mid-wave ultraviolet therapy with a wavelength of 311 nm (Herbert Waldmann GmbH & Co. KG (Germany) is an effective treatment method for patients with vulgar, segmental, focal and acrofacial forms of vitiligo. The effectiveness of treatment increases as the course number of procedures increases. Due to the lack of need taking photosensitizers, is safe and highly effective. Along with pronounced repigmentation, it leads to recovery in the skin of patients with seborrheic dermatitis. After a course of narrow-band (311 nm) phototherapy, in most cases, partial or complete normalization of cellular immune reactions is observed, which indicates the pathogenetic mechanism of this phototherapy method.
Phototherapy panel Dermalight 1000
Used for maintenance therapy of seborrheic dermatitis.
Dermalight 1000 is used for the maintenance treatment of seborrheic dermatitis.
Considering the lack of a generator for energy control and light scattering due to the open circuit, it cannot be used as an independent method of treating seborrheic dermatitis.
It does not create the proper uniform photoload and can be used as maintenance therapy for seborrheic dermatitis.
Narrowband mid-wave ultraviolet therapy with a wavelength of 311 nm. is an effective method of treating patients with vulgar, segmental, focal and acrofacial forms of vitiligo. The effectiveness of treatment increases as the course number of procedures increases. Due to the absence of the need to take photosensitizers, it is safe and highly effective. Along with pronounced repigmentation, it leads to restoration in the skin of patients with seborrheic dermatitis. After a course of narrowband (311 nm) phototherapy, in most cases, partial or complete normalization of cellular immune reactions is observed, which indicates the pathogenetic mechanism of this method of phototherapy.
Photos before and after treatment
Cost of treatment
| Initial-repeated consultation with a dermatovenerologist | 2500 |
| Primary consultation with a dermatovenerologist - repeated after 20.00. | 3500 |
| Consultation with a dermatovenerologist, doctor of medical sciences/professor | 6000 |
| Primary consultation | 6000 |
| Repeated consultation | 3000 |
| Comprehensive 3D skin diagnostics | 5000 |
| 3D skin scanning | 3500 |
See the full price list
* The cost is indicated in the comprehensive procedure
*** The final cost of the procedure will be determined only after consultation with the specialists of our clinic.
"PresidentMed" guarantees its patients the best price-quality ratio!
Doctors Clinics
Nezgovorova Oksana Ivanovna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2006.
Skorodumova Olga Evgenievna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2000.
Kirilyuk Tatyana Igorevna
Graduated from the Medical Academy named after S.I. Georgievsky Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education “KFU named after. IN AND. Vernadsky" (Medicine). Red diploma.
Grishanova Natalia Alexandrovna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2003.
Oleynikova (Alekseeva) Svetlana Mikhailovna
Doctor - cosmetologist, doctor - dermatovenerologist. Experience in the field of medical cosmetology and dermatology since 2004.
Patient reviews
Natalya Ivanova, 04/28/17 The clinic has modern equipment and medications. I am very pleased with the work of the doctors. Thank you! Best regards, Natalia
True eczema
It is developing rapidly. Small scattered bubbles appear, which soon, sometimes within several hours, open. A serous secretion is released, foci of weeping are formed, crusts, peeling, peeling of crusts, and open wounds appear. Each of the stages of eczema is rapidly replaced by the next: erythematous - papulovesicular - weeping - cortical.
In parallel, fresh vesicles and papules with serous content may appear in another area, since the process is rarely limited to one area. Characteristic is the symmetry of the rashes and the tendency of the rash from the scalp to the skin of the upper, lower extremities, and torso. There are no clearly defined lesions.
True eczema is accompanied by severe itching, which can cause neurosis and insomnia.
Treatment of scalp eczema
Curing eczema on the scalp is quite difficult. Firstly, eczematous wounds are difficult to treat. Secondly, patients most often consult a doctor when the disease has already taken on a complex form and a secondary infection occurs. The reason for this lies in the same “insidiousness” of the disease, especially when it comes to eczema of the scalp: localized in the crown area, such lesions are difficult to detect. Simply put, the disease goes unnoticed for some time: itching is considered an accident, flaking is considered dandruff.
Mycotic infections can complicate the course. In this case, treatment will not bring results; preliminary antimycotic therapy is necessary. To do this, you need to determine the type of fungus that has settled. If the fungal component of the process was not excluded before starting treatment, then hormonal ointments and antibiotic-based ointments, which are used to combat eczema, will lead to active reproduction and mutation of fungi, if present. Therefore, in the treatment of eczema, you cannot do without consulting a dermatologist or trichologist.
As a rule, complex therapy is prescribed and may include the use of:
- hormonal ointments;
- antibiotic-based ointments;
- antihistamines;
- sedatives;
- desensitizing drugs;
- diet.
During treatment, it is also important to visit a specialist who will monitor the progress of the disease. In no case should you independently extend the prescribed course of treatment - corticosteroid hormones can cause serious side effects if used uncontrolled.
Is it possible to use folk remedies for eczema?
Some folk remedies, composed of natural products of plant origin, have proven to be very effective drugs for seborrheic eczema. However, it should be remembered that different types of plants and compositions based on them may not be suitable for all people. These are not universal recipes, and their choice should be approached with maximum responsibility. At a minimum, they can cause an allergic reaction, not help, or worse, worsen the symptoms of eczema. For this reason, using folk remedies on your own is strictly not recommended. Before using a traditional medicine recipe, you should consult your doctor.
Experts recognize most traditional methods of treating this type of eczema, and therefore they themselves can prescribe a number of measures from this category. In any case, consultation with a dermatologist is mandatory. Folk remedies can be a good addition to the main course.
As an additional therapy, decoctions of birch buds and oak bark are used. They are used to apply lotions to areas of skin affected by eczema or to take medicinal baths.
A mixture of olive oil, baby cream and golden mustache juice with valerian tincture for treating the scalp has a good effect. The composition is applied to the surface of the skin and hair 2 hours before washing to speed up healing and give the skin nourishment. A mixture of garlic and nettle, washed off with chamomile decoction, has a similar effect. Any means of general strengthening and calming action are useful, which should be given the greatest preference.
Tips for those suffering from eczema
If you have a genetic predisposition or have already experienced eczema, you should be extremely careful by following these recommendations:
- avoid wearing clothes made of synthetic, wool or flannel fabric;
- include in your diet more vegetable dishes, boiled meat, fermented milk products, fruits (except for those that can provoke allergies: oranges, strawberries, raspberries, tangerines);
- avoid gastronomic experiments, alcohol, too spicy, salty and fatty foods, marinades;
- take vitamin complexes, in particular vitamins A and B are important;
- avoid contact with suspected allergens in everyday life (powders, detergents, etc.);
- in case of a history of varicose veins, wear rubber stockings and bandage the legs with medicinal bandages;
- be as nervous as possible;
- Visit a dermatologist periodically.
At the MediLife clinic in St. Petersburg, highly qualified experienced dermatologists and trichologists receive treatment. You can make an appointment online. Prices for services are presented on the website. You can clarify any details by phone. Friendly staff, the ability to choose a convenient time to visit and complete anonymity are pleasant and significant additions to the qualified consultation that will be provided at MediLife.
Diet and lifestyle for seborrheic eczema
Since eczema can also be the result of an allergic reaction, its treatment is associated with eliminating the likelihood of allergies. To prevent the signs of eczema from worsening, you should follow a diet that does not contain allergens, since allergic reactions will add unpleasant symptoms, even if there was another reason for them. As with any skin disease, following a hypoallergenic nutrition plan for the pathology in question is mandatory. It will not only speed up recovery, but will also have a positive effect on the condition of internal organs.
You need to especially carefully monitor your diet in winter, when the body is already weakened. It is necessary to avoid citrus fruits, seafood, nuts, honey and whole milk. You should also exclude canned food, homemade preparations, spices, salted and smoked foods. It is better to avoid red berries and fruits, as well as fried and fatty foods in your diet.
Foods that are useful for seborrheic eczema are boiled and baked foods, soups and cereals, green apples, bananas and other fruits, light-colored vegetables.
During the entire period of therapy for eczema, exposure to sunlight on the skin, exposure to heat and a humid microclimate should be avoided. For this reason, visiting baths and saunas is strictly contraindicated for patients. You should take baths and showers only at medium temperatures without steaming or exposure to hot water and steam.