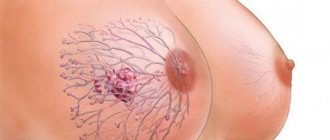
Fibroma (synonym - fibroblastoma) is a mature benign neoplasm arising from fibroblasts and connective tissue fibers.
It can be found in the skin, subcutaneous tissue or mucous membranes of any anatomical area. The most common fibroids are the uterus, skin, and mammary glands. There is no clear age association for this tumor (with the exception of fibroids of the uterine localization, it often debuts in women of middle age and does not occur after menopause).
Fibroma can be either single or multiple (fibromatosis). Its diameter varies from 0.01 to 20 cm.
Fibroma: origin and essence of the disease
The causes of dermatofibroma and other forms of this type of tumor are not known. Some researchers believe that fibroids can form as a localized tissue reaction after minor trauma. Sometimes fibroids can have a genetic component, especially in people of Northern European descent. Some medications, including beta blockers, have been reported to cause changes in fibrous tissue. In addition, some fibroids may be influenced by hormonal imbalances or pathologies of endocrine organs, including problems with the thyroid and pancreas.
Hyperhidrosis (increased sweating), inflammatory processes on the skin, especially chronic ones, as well as the influence of prolonged UV radiation, poor nutrition and bad habits can have a certain impact.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention that can eliminate the likelihood of fibroids. You can reduce the chance of neoplasms forming by carefully monitoring the health of your children.
- It is necessary to bring children regularly for preventive examinations.
- It is advisable to avoid prolonged exposure of children to direct sunlight, especially during the period of greatest sun activity.
- It is necessary to promptly and correctly treat infectious diseases, injuries, burns and other damage to the skin or internal organs.
You should not give children medications without the instructions of doctors, or try traditional and non-traditional treatment methods. It is also important to ensure that babies eat properly and get enough physical activity on a daily basis.
Fibroids do not always pose a danger to the body, however, they must be kept under control. Doctors at the SM-Doctor clinic will carefully examine the child and select the optimal method of treating the disease.
Signs and symptoms
Fibroids are classified as benign formations. They form a tumor-like growth of tissue, inside of which there is mainly fibrous (or connective) tissue. Signs of fibroids arise as a result of uncontrolled by the body, but slow and limited growth of a certain area of tissue. Rarely fibroids are malignant, and the reasons for this are trauma and malignancy of the formation. Different types of fibroids can develop anywhere, and if they are small in size, they require active monitoring or removal if they cause discomfort.
Some women with uterine fibroids have no or only mild symptoms, while other women have more severe, debilitating symptoms. Common symptoms of a tumor include:
- heavy or prolonged menstrual flow;
- abnormal bleeding between periods;
- pain in the pelvic area;
- frequent urination;
- lumbago;
- pain during intercourse;
- infertility.
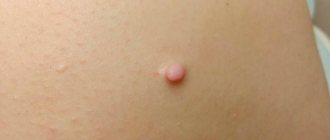
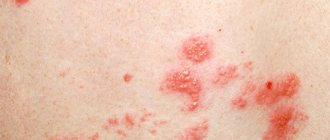
Common symptoms of dermatofibroma involve discomfort and may come and go. Symptoms of dermatofibroma are not severe and include:
- color change over time;
- itching;
- periodic swelling over the tumor;
- possible bleeding due to injury;
- sensitivity of dermatofibroma to touch;
- a small bump with a raised surface.
Symptoms of plantar fibroma are not severe and include:
- expansion of sizes over time;
- hard lump in the arch of the foot;
- pain when pressing, standing or walking;
- spread of additional fibroids over time.
Types, characteristics of fibroids
There are more than 10 different morphological variants. Pathologists give a description of what each form looks like and how it differs after histological examination - elastrophibroma, soft, dense fibroma.
- Dermatofibroma is a single or multiple formation of intradermal localization, mobile and painless when palpated with unchanged color.
- Desmoid fibroma has another name - aggressive fibrosis, refers to mesenchymal tumors originating from excess collagen fibers and differentiated fibroblasts. They often progress and recur, forming in soft tissues, the retroperitoneum or on the abdominal wall.
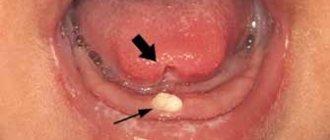
- Chondriomyxomas are rare tumors that affect bone tissue - the edges of long bones, pelvis, ribs, vertebrae, feet, metatarsus.
- Angiofibriomas in the cheek and nose area, containing small tubercles with connective tissue fibers.
How to remove fibroids with a laser in Khimki Clinic No. 1
Laser fibroid removal is a completely non-contact method because... the tumor tissue is evaporated by a beam of light.
- the cavity is treated with a laser beam, which eliminates the possibility of re-inflammation.
- The operation is performed on an outpatient basis in 1 clinic visit.
- The patient's recovery period after surgery is very short.
- There are no side effects when removing fibroids with a laser.
Diagnostics
Initially, experienced specialists - oncologists or multidisciplinary surgeons - conduct a detailed examination of the patient, record all the complaints that exist, palpate the formation and make a preliminary diagnosis. Then you need to determine the nature of the tumor. After this, you need to conduct an ultrasound examination of the tissues where the tumor is located to determine its size, nature, and changes in the tissues. If necessary, an X-ray examination is performed. If questions remain, a biopsy of the suspicious area should be performed to rule out a malignant process.
Fibroids can be detected by palpation (feeling with fingers or hands) performed as part of a pelvic examination, or diagnosed through imaging procedures such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Fibroadenoma
| Make an appointment for surgery by phone. +79219453318 | Book an appointment and surgery online |
What is fibroadenoma?
Fibroadenoma is a benign tumor. Most often, fibroadenoma occurs in the mammary gland. Most often, fibroadenoma occurs between the ages of 20 and 30 and between the ages of 40 and 50.
What is the difference between fibroadenoma and fibroadenomatosis?
Fibroadenoma is a benign tumor, fibroadenomatosis is a dishormonal disease of the mammary glands. Most often, fibroadenomatosis is called mastopathy or fibrocystic disease. If the main treatment for fibroadenoma is surgery, then the main treatment for fibroadenomatosis is medication. Surgeries for fibroadenomatosis are performed only in cases of suspected breast cancer.
Can fibroadenoma develop into breast cancer?
| Phylloid fibroadenoma |
No. Fibroadenoma does not develop into breast cancer. This is a fact confirmed by vast experience summarized in world literature. But this does not mean that fibroadenoma cannot be confused with a malignant breast tumor. Often, a patient is taken for surgery with a diagnosis of fibroadenoma, and after surgery and histological examination it turns out that we are talking about a malignant tumor of the mammary gland. In this case, we are not talking about tumor degeneration, but about a diagnostic error, when the doctor before the operation assumed that it was a fibroadenoma, although in fact it was originally breast cancer. The only option for the degeneration of fibroadenoma into a malignant tumor is the degeneration of phyllodes fibroadenoma into sarcoma (not cancer, but classified as malignant tumors).
What is phyllodes fibroadenoma?
Phylloid fibrodenoma is a special type of fibroadenoma, which is characterized by rapid tumor growth and a tendency to disintegrate (due to impaired blood circulation in the tumor). If phyllodes fibroadenoma is detected, surgical intervention is necessary. If phyllodes fibroadenoma has degenerated into sarcoma, then removal of the mammary gland (amputation of the mammary gland) is necessary to achieve radical surgical intervention.
What examinations are performed for fibroadenoma?
| Mammography |
To establish a diagnosis of fibroadenoma, an examination by a specialist (surgeon, oncologist, mammologist, gynecologist), ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, mammography (in women over 35 years of age, puncture followed by cytological or histological examination) is necessary. A specialist can make a diagnosis only based on examination. An experienced specialist (working in an oncology institution and dealing with targeted treatment of breast diseases) can make a diagnosis only on the basis of an examination.
Why does fibroadenoma occur?
The causes of fibroadenoma are not clear. There is probably some defect in tissue development, which is subsequently realized in the development of a benign tumor. Oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy drugs, menstrual irregularities, pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding can stimulate the growth of fibroadenoma.
Does fibroadenoma affect pregnancy?
Fibroadenoma is not affected by pregnancy. Fibroadenoma does not affect fetal development.
Does pregnancy affect fibroadenoma?
During pregnancy, fibroadenoma may increase in size. This happens in approximately 15-20% of cases.
Is it possible to remove fibroadenoma during pregnancy?
Yes. The operation is safe both when performed under local anesthesia and when using general anesthesia.
| Make an appointment for surgery by phone. +79219453318 | Book an appointment and surgery online |
What are the indications for fibroadenoma removal?
1. Suspicion of breast cancer (when, according to any examination, a specialist cannot exclude breast cancer).
2. Large size fibroadenoma (more than 5 cm), which may raise suspicion of the presence of phyllodes fibroadenoma
3. Cosmetic defect
4. Cancerophobia (fear of cancer) in a patient.
Tactics against fibroadenoma, which first appeared in women over 40 years of age, are usually active. Often at this age it is not possible to clearly say whether it is a fibroadenoma or a tumor suspicious for breast cancer.
When planning pregnancy or IVF, it is also optimal to discuss the issue of fibroadenoma removal.
Can fibroadenoma be cured with medications or nutritional supplements?
No. Neither dietary supplements nor medications help with fibroadenoma.
Under what anesthesia is the operation performed?
Surgery to remove fibroadenoma is usually performed under local anesthesia. This type of anesthesia involves the administration of a local anesthetic (lidocaine, novocaine) using a syringe or cannula for infiltration anesthesia. I usually add a solution of epinephrine (a vasoconstrictor) to the anesthesia to reduce tissue bleeding and enhance the effectiveness of the local anesthesia. General anesthesia is performed, as a rule, in case of intolerance to drugs for local anesthesia, as well as if the tumor cannot be palpated. Local anesthesia can be used even when it is necessary to remove a fibroadenoma from an incision in an inconspicuous place, for example, when removing a fibroadenoma in the central zone of the breast from an incision in the axillary region.
How is the operation performed?
Before the operation, the patient takes sedatives; an injection that reduces vegetative reactions (atropine) and relieves excitability (tramadol) can be given. The patient is placed on the operating table and covered with sterile surgical linen. The surgeon makes an injection into the skin and injects an anesthetic solution (in the case of local anesthesia). In the case of general anesthesia, drugs are administered intravenously. The surgeon makes a skin incision and removes the section of the breast with the tumor. After removal, hemostasis is performed (stopping bleeding from small bleeding vessels). The surgical procedure can be performed either with a scalpel or with a power tool (use of an electrician). Sutures are placed on the wound, usually made of absorbable material (Vicryl threads). The operation takes 15-30 minutes. The removed fibroadenoma is sent for urgent histological examination. In this study, a morphologist (pathologist) gives a conclusion on the benignity of the tumor or otherwise if we are talking about a malignant tumor. For more details, see the article on fibroadenoma removal.
What sutures are used after fibroadenoma removal?
Usually cosmetic stitches are applied. I do this 100% of the time. If another surgeon is planning an operation for you, then before the operation it is necessary to clarify what sutures will be applied.
How long does hospitalization last for fibroadenoma treatment?
When treated under compulsory medical insurance (compulsory health insurance), hospitalization lasts 7 days (at the Leningrad Regional Oncology Dispensary). In fact, surgery can be performed on an outpatient basis.
When can I bathe after surgery?
If a cosmetic suture is applied, you can wash 2-3 days after the operation. You must wipe the seam carefully; it is advisable not to use a washcloth or steam while washing your breasts.
How to reduce the scar after fibroadenoma removal?
I usually prescribe Contractubex gel (Merz company). This gel contains substances that lead to the resorption of scar tissue and prevent the development of a rough scar. I usually prescribe the gel from the moment the scabs fall off the stitches (1-2 weeks after surgery). It is optimal to use the gel within 1-2 months after surgery.
If Dermabond is used during the operation, then there is no need to use Contractubex. Dermabond is a medical glue, the use of which, firstly, allows you to wash the very next day after surgery, and, secondly, the use of this product leads to the formation of a really unnoticeable scar.
Can fibroadenoma reoccur?
Yes. This happens in 15-20% of cases.
Is it possible to sunbathe/go to a solarium with fibroadenoma or after its removal?
Yes, both in the presence of fibroadenoma and after its removal. Ultraviolet light does not affect the growth of fibroadenoma, although the myth about the dangers of the sun and solarium for breast diseases is quite common among doctors. It is important to remember that exposure to ultraviolet light may increase the risk of skin cancer and melanoma. Exposure to the sun or solarium should be dosed and selected according to your skin type. Everything is good in moderation and this must be remembered.
| Make an appointment for surgery by phone. +79219453318 | Book an appointment and surgery online |
Is it possible to do fitness/physical exercise with fibroadenoma or after its removal?
Yes. Both in the presence of fibroadenoma and after surgery, fitness and physical education are not contraindicated. After surgery, you should refrain from physical activity for 1 week (this time is enough for complete healing to occur).
Is it possible to go to the sauna with fibroadenoma or after its removal?
Yes. Both in the presence of fibroadenoma and after its removal, you can visit the sauna. After surgery, you must refrain from visiting the sauna for 2 weeks.
How can I get an operation to remove fibroadenoma from Dmitry Andreevich Krasnozhon?
It’s easy to get to me for treatment. You need to download the patient instruction sheet and follow the recommendations. I can perform operations to remove fibroadenoma both under the compulsory medical insurance policy (hospitalization for 4 days, a referral is required, form 059/u from the health care facility at the place of registration, and in a paid mode (hospitalization for 1 day, a referral is not required). The cost of the operation under local anesthesia is 25 thousand rubles, the cost of the operation under general anesthesia is 45 thousand rubles.
Dmitry Andreevich Krasnozhon , February 08, 2010, last edition August 08, 2022.
Treatment methods
Dermatofibromas are harmless and treatment is not required unless there are warning signs or cosmetic concerns. If the patient wishes to remove dermatofibroma, surgical treatment is possible - surgery . It is important to evaluate its consequences: the scarring and tissue changes that occur after surgical excision may look worse than the original lump.
For plantar fibroids, non-surgical treatment options are preferred because the surgical procedure requires a long recovery period and can lead to complications that may be worse than the plantar fibroids themselves. Non-invasive treatments for plantar fibroids include:
- extreme cold or cryodestruction to reduce fibroids.
- pads or insoles to relieve discomfort when wearing shoes.
- stretching.
Most doctors agree that for severe cases of plantar fibroma, the smartest option is to resort to invasive treatments and surgery. Invasive treatments for plantar fibroids include:
- injections of corticosteroids into fibroids.
- surgical removal of the entire plantar fascia (which is associated with a long recovery period and a high risk of developing other foot problems).
- surgical removal of fibroids (with a high recurrence rate).
Treatment is indicated when dermatofibromas are bothersome or persistently irritated. In these cases, surgical removal and freezing with liquid nitrogen can be performed.
Treatment for uterine fibroids depends on the size, symptoms, and other factors. Asymptomatic fibroids may not require treatment. A myomectomy (surgical removal of uterine fibroids) may be performed to remove fibroids that are interfering with fertility in women who want to become pregnant. Hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) is also commonly performed on patients with severe symptoms of uterine fibroids, but is not an option for women planning a pregnancy. Non-surgical treatment for uterine fibroids includes medications, uterine artery embolization and targeted ultrasound treatment.
Causes
The exact culprit behind the development of fibroids in children has not yet been determined. Experts have identified a number of factors contributing to the appearance of tumors. These include:
- unfavorable environmental living conditions (proximity to chemical and cement plants, landfills, contaminated areas);
- frequent injuries, bruises and falls;
- various infectious diseases of acute and chronic form;
- irrational use of potent drugs;
- endocrine pathologies;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Predictions of why fibroids are dangerous
Dermatofibroma has no serious complications. Complications of plantar fibroids usually occur as a result of surgical interventions. These include flattening of the arch of the foot, postoperative nerve entrapment, and postoperative growth of larger and recurrent fibromas.
Article sources:
- Desmoid fibroma. Staged, organ-preserving surgical treatment. Khvastunov R.A., Mozgovoy P.V., Lukovskova A.A., Yusifova A.A. Volgograd scientific and medical journal No. 2, 2022. p. 54-57
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2927520/ Central odontogenic fibroma: a case report with long-term follow-up. Marco T Brazão-Silva, Alexandre V Fernandes, Antônio F Durighetto-Júnior, Sérgio V Cardoso, Adriano M Loyolacorresponding
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3351722/ Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of cardiac fibroma. SuguruTorimitsu, Tetsuo Nemoto, Megumi Wakayama, Yoichiro Okubo, Tomoyuki Yokose, Kanako Kitahara, Tsukasa Ozawa, Haruo Nakayama, Minoru Shinozaki, Daisuke Sasai, Takao Ishiwatari, Kensuke Takuma, Kazutoshi Shibuya
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.