Types and varieties
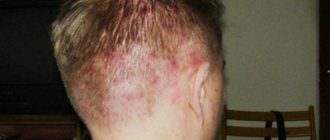
A formation that appears on any part of the head is called a fibroma. It is considered a benign tumor, not dangerous. In addition, its growth is very slow, which makes it possible to diagnose it at the initial stage before it reaches a large size. Fibroma of the head occurs in an adult or child, regardless of gender.
Depending on the location they distinguish:
Breast fibroma. The second name is fibroadenoma, which is a type of mastopathy.
Uterus. More often it is called fibroids, it forms in the body of the uterus, ranging in size from 1-2 mm to 20 cm. A woman can have single or multiple fibroids. The disease occurs without pronounced symptoms and is not prone to degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
Fibroma of the lower extremities. This type of swelling is divided into localization of the disease in any area of the lower limb or just the foot. In the first case, it is formed in any area of the limb, having a different color, but a round shape. In this case, it appears only on the foot.
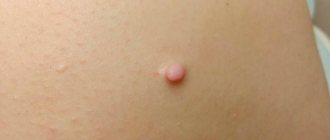
Skin. The size starts from 1-2 cm, with clearly defined boundaries, the fibroma is located under the scalp.
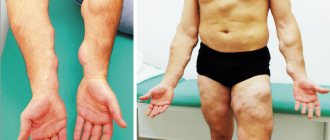
Skin fibroids are divided into hard and soft. Solids have a dense structure with limited mobility . When pressed, they go deep into the skin, leaving a concavity. Do not cause pain or physical discomfort. Most often they occur on the mucous membranes of the body and skin. Men and women are equally susceptible to them. Externally they can be convex or concave.
Soft fibroids look like a large mole or wart with varying color changes: from pale pink to purple. Most often they affect women over 40 years of age, as well as people suffering from excess weight. The location of fibroma is the armpits, chest and folds under it, scalp, ears, eyelids, and the front of the neck. Over time, multiple tumors appear in this area.
Even if a person notices the appearance of a mole or wart, it is worth consulting a dermatologist. Perhaps the formation is located in a place that is constantly exposed to mechanical damage, then the risk of its degeneration will increase.
Causes
Scientists have not identified the main causes of scalp fibromas, but have identified predisposing factors. These include:
- Heredity.
- Injuries received. At the site of the injury, scar tissue forms, which is the optimal environment for the emergence and growth of scalp fibroids.
- Hormonal imbalance. When hormone levels are disrupted, the body experiences a disruption in the proliferation of connective tissue cells.
- Diabetes. This disease causes systematic metabolic disorders throughout the body, causing pathological processes.
- Having bad habits. Harmful substances contained in alcohol and tobacco products promote mutations in fibrous tissue, resulting in active cell reproduction.
- Papillomavirus.
- Decrease in the body's defenses.
- Age. Elderly people are more often susceptible to this type of disease.
- In addition to these main factors, radiation exposure also plays an important role.
About diagnosing and treatment methods for fibrosarcoma abroad
Diagnosis of such tumors at the Meir Hospital in Israel involves pathomorphological studies of the tumor tissue area, histological examination of the tumor to determine the level of its malignancy. An accurate treatment plan is drawn up based on a set of data.
Diagnosis of fibrous tissue oncology is carried out using a number of methods, in particular:
- X-rays - using this technique, specialists determine the size of tumors, their area of location, and the level of tissue damage.
- CT - the procedure helps in conducting in-depth studies, and this allows for the development of metastasis to begin adequate treatment more quickly.
- MRI - diagnoses the localization of the process, the extent of tumor growth in blood vessels, soft tissues, nerve fibers, endings, as well as in the bone marrow.
- PET-CT allows you to evaluate the biological activity of formations. The procedure is carried out using expensive equipment, which is available only in leading foreign clinics.
- Biopsy is a microscopic examination of tissue to detect a tumor. A biopsy consists of a tissue incision or puncture.
The key approach used in the treatment of fibrosarcomas is its resection, along with the normal tissue surrounding the tumor. If the formation is located in the bones of the limbs, after its elimination, reconstructive surgery is used to restore the ability to move. If the tumor is located inside flat bones, the removed section of bone replaces the implant.
Absolute amputation of limbs in fibrosarcoma, as in the treatment of sarcoma in Israel, is practically not resorted to. It may be needed in situations where it is impossible to carry out a full-fledged reconstruction and when there is a high chance of infection due to malignancy of the soft tissues.
Symptoms
Fibroma of the soft tissues of the head does not have pronounced symptoms. The main sign of its manifestation is the appearance on the head of a rounded bulge measuring up to 1-2 cm in diameter. The initial stage of development does not cause pain, but scalp fibroids cause a change in appearance. If it is formed from cartilaginous and bone material, then it will not be visible visually.
With prolonged development of the tumor, its size increases greatly and puts pressure on neighboring areas and organs. The person will also feel pain upon palpation.
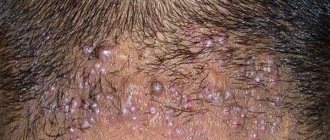
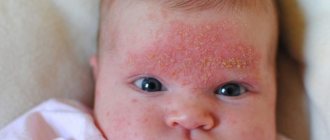
Fibroids on the head of a child are much less common than in adults. But in case of occurrence, its multiple occurrence is observed. Externally, fibroids on a child’s head resemble small round nodules and are pale or gray in color with a hard structure. Children have a fairly high risk of degeneration into a malignant disease. Therefore, doctors recommend removing fibroids from absolutely all neoplasms in children, preventing progression of the disease.
Kinds
Fibroma on the head is formed from various building materials. In this connection, it is divided according to its structure into the following types:
- Desmoid.
- Odontogenic.
- Ameloblastic.
- Lobular.
- Chondromyxoid.
- Non-ossifying.
Each of them is formed from certain tissues and has its own location and symptoms.
Desmoid
This type is considered the most dangerous among doctors due to the high percentage of malignancy and constant relapses. Formed from connective tissue of muscles, tendons and fascia. It is solid, outwardly flat in shape with almost perfectly smooth edges. In addition to the risk of degeneration, they quickly grow into the deep layers of the scalp and activate pathological processes in more and more new parts of the body. It most often occurs in women who have given birth between the ages of 20 and 30. Less common in men in childhood and adolescence.
Odontogenic
It is formed from the bone material of the jaw and is very similar to the pulp of a tooth. It is characterized by slow growth and localization at the root or not yet erupted tooth. It occurs more often in children than in adults. It is asymptomatic, but with a strong increase in its size, it deforms the jaw. X-ray examination shows clear boundaries and multiple formations. It is also possible that an infection and inflammatory process from a tooth or oral cavity affected by caries can occur.
Ameloblastic
This type is a type of odontogenic formation, but their difference lies in the composition. The dental epithelium does not participate in the formation of the tumor. Therefore the structure remains soft. It is most often diagnosed in boys in the area of the lower molars and premolars; it does not occur in persons over 20 years of age. Under a microscope it is gray-white in color.
Lobular
Most often observed in children and the elderly, resulting from trauma during eating. They are formed on the mucous membrane of the mouth of the upper jaw and are easily noticeable. They are soft, round-shaped seals with a bumpy surface.
How is it different from fibroids?
The main difference between fibroids of the scalp and fibroids is the material of their formation. The first is formed from the connective tissue of the body, the second from muscle tissue. The next difference is the location, since fibroids form only in the uterus, as a result of which only women are susceptible to it. In addition to the main factors of occurrence, the difference between fibroids lies in the reasons for their appearance:
- Multiple uterine curettages.
- Abortion.
- Not using contraception during sexual intercourse.
- Multiple changes of sexual partners.
- Pregnancy, childbirth after 35 years of age.
These reasons are not prerequisites for the development of fibroids on the head. Symptoms of the early stages of development do not appear in either case.
Why education is dangerous
The main danger is considered to be its degeneration from benign to malignant. This usually occurs as a result of its traumatization, and as a result of this, a concomitant infection may also occur. As a result of rapid growth, it puts pressure on nearby sections and can cause bleeding, spasms, and disrupt their functioning.
About the symptoms of fibrosarcoma
Clinical manifestations are related to the location of the tumor and the extent of the process. When placed in deep layers of soft tissue, fibrosarcoma can occur without symptoms for a long time. The formation is often accidentally discovered during diagnostic procedures for another disease. Many people go to the doctor when fibrosarcoma has reached large proportions, caused deformation of the affected areas, or caused contracture of a nearby joint. Fibrosarcoma of the proximal parts of the extremities can be detected earlier due to the presence of pain caused by compression of the nerves and involvement of the periosteum in the process.
The skin over the surface of the tumor is largely unchanged. With an rapidly growing large fibrosarcoma located on the surface, phenomena such as thinning of the skin, their bluish color, and an expanded network of veins under the skin at the site of the formation may be noted.
Palpation reveals a separate tumor-like neoplasm of an oval or round shape, with a dense consistency. A characteristic feature of all types of sarcomas, as noted by specialists in the treatment of fibrosarcoma in Israel, is a limited node, a “false capsule” or pseudocapsule, which consists of layers of fibrous tissue. As the disease progresses, the false outlines of the tumor become less pronounced.
The level of fibrosarcoma mobility determines the prevalence of the process. Minor local neoplasms may shift (most often in a transverse direction). In the case of germination of nearby structures, fibrosarcoma becomes immobile. When the formation is placed in the space between the muscles, the nodes are perfectly palpable during relaxation, but lose their contours and mobility during muscle tension. The initial stages of fibrosarcomas are painless. If nerves are compressed, tenderness may be noted during palpation. If the bones are affected, the pain becomes constant.
Late phases of fibrosarcomas are characterized by signs of general intoxication. A person’s weight decreases and their appetite deteriorates. In addition, the following manifestations of the disease were noted:
- heat;
- anemia;
- increasing weakness;
- instability of emotional state;
- depression or subdepression.
When metastasizing to distant parts of the body, there are signs of involvement of the corresponding parts of the body in the process. If bone metastasis occurs, persistent pain is characteristic, which cannot be eliminated with painkillers. With metastasis to the lungs, coughing, shortness of breath, and spitting up blood appear; and with liver cancer - jaundice, growth of this organ.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by primary palpation to determine its structure, mobility, and diameter. Exclusionary diagnostics are also carried out, which are necessary to exclude the presence of skin cancer. Since these two diseases are very similar at an early stage of development.
The next stage of diagnosis is research using:
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- x-ray;
- histological examination.
Histological examination is carried out if the malignancy of the neoplasm is suspected. In this case, the doctor takes a small fragment of the formation for analysis. After collecting all the results obtained, the most suitable treatment is prescribed. It is worth noting that folk remedies for cancer treatment are ineffective and can only aggravate the disease.
Fibroma treatment
Fibroma of the scalp requires mandatory therapy, as it can grow into the skull with increasing size, causing pathologies in the functioning of the brain. In addition, the risk of degeneration is very high, in general, as is the risk of traumatization.
The main methods of treating scalp fibroids are:
Exposure to liquid nitrogen. When exposed to cold, necrosis occurs, and then it dies painlessly.
Surgically. It is used to remove a fibroid tumor with a diameter of more than 5 cm. It is performed using local anesthesia; during the operation, the tumor is cut off using a scalpel. This method is considered radical; the main disadvantage is the large scar on the head after the operation.
Electrocoagulation. The operation is performed using electric current. It is not used when the tumor is localized on the head, or in children.
Removal using laser. It is considered a popular method for removing fibroids on the head, as it does not leave scars. Used to treat fibroids of the skin of the face and head.
In each individual case, the treatment method is selected only by the attending physician, based on the type, size, and location of the disease.
All about skin fibroids with photos
Fibroma: symptoms
The symptoms of cutaneous fibroma have been described above. Symptoms of fibroids localized in different areas are as follows:
- fibroid . A painless neoplasm, the only symptom of which is bleeding or prolonged menstruation;
- breast fibroma A spherical lump localized on the chest. No pain is observed on palpation, however, patients sometimes complain of a bursting sensation in the chest before menstruation.
Diagnosis of fibroma
fibroids are suspected .
Basic diagnostic methods for fibroma :
- histological examination of fibroma . As a rule, biomaterial for histology is taken during the process of removing the formation;
- Ultrasound. Makes it possible to determine the depth of tumor growth in the tissue and its consistency;
- dermatoscopy. Used for skin fibromas , it is considered the “gold standard” for diagnosing skin tumors. Using a dermatoscope, the doctor can carefully examine the tumor and, if necessary, take pictures of it for further study.
Fibroma treatment
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the clinical picture and location of the fibroma .
- Drug therapy. Possible for small tumors and if there are contraindications for removal.
- Surgical treatment of fibroma . Prescribed for uterine fibroids depends on the size of the tumor. For small fibroids, laparoscopy is used; for large fibroids, hysterectomy and complete removal of the uterus are used. fibroids
fibroma on the leg under the skin photo
Hardware removal of fibroids
Modern dermato-oncology has several effective non-invasive techniques for removing fibroids: laser removal, electrocoagulation, and radio wave surgery.
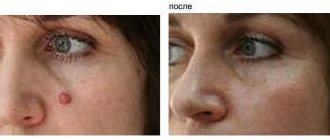
The peculiarity of the high-frequency radio wave surgery method is the possibility of non-contact excision with simultaneous tissue coagulation. The procedure is carried out using the Surgitron apparatus using local anesthetics. The radioknife not only removes fibroids, but also disinfects the wound tissue, after which a crust forms on it, preventing infection.
Another reason to choose this method is the possibility of completely removing the tumor and taking a full section of fibroma for histological examination. After removing the fibroma in this way, the wound heals quickly without leaving scars.
Treatment of fibroids is the field of activity of experienced dermato-oncologists. Under no circumstances should you try self-medication advice on yourself. Tying with a thread or, what sounds even worse, cutting the fibroma with scissors means injury and infection of the tumor, which can provoke malignant degeneration of the fibroma.