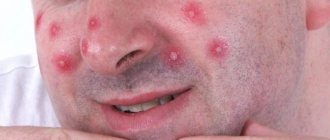
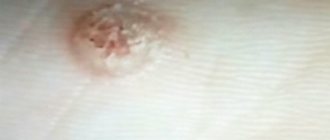
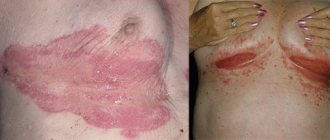
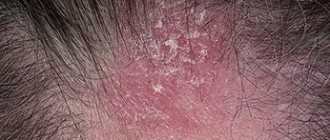
A boil on the head in the hair occurs due to infection with staphylococci, streptococci or fungi. It appears as a cone-shaped lump filled with pus.
Despite the fact that the problem is usually invisible to others, it usually causes significant discomfort: the patient feels throbbing pain, which intensifies when touching the affected area; in addition, severe headaches, dizziness, fever, weakness, and general deterioration of health often occur.
Causes
Boils or boils appear during a purulent-necrotic inflammatory process of hair follicles together with the tissues covering them. Sometimes inflammation affects deep-lying cells of the dermis. This is how abscesses differ from simple acne. But even visually the difference is clearly noticeable.
Boils appear for the following reasons:
- penetration of infectious agents (usually Staphylococcus aureus) into the body through microtraumas of the skin;
- excessive sebum secretion, hyperhidrosis;
- stress;
- weakened immune defense;
- hyperthermia or hypothermia;
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- long-term use of cytostatics;
- wearing synthetic clothing of the wrong size;
- metabolic disorder;
- hormonal imbalances.
The appearance of boils is possible with chronic diseases, for example, with diabetes or infectious lesions - bronchitis, hepatitis, tuberculosis.
The first reason is the main one, the rest are considered contributing factors.
Causes of boils on the head
The main risk factors for the appearance of boils on the scalp are:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules (rarely washing your hair, using someone else’s contaminated comb or towel);
- use of low-quality shampoos or other hair care products;
- violation of skin integrity;
- infection through dirty hands;
- hypothermia;
- deficiency of vitamins or microelements;
- decreased immunity.
Stages and symptoms
Boils can be external or internal. The difference is easy to notice by looking at photos on medical websites. In the first case, the site of the future abscess and accumulation of pus can be noticed immediately. In the second, the pus exit channel appears after maturation, which takes about a week and a half, and may not appear externally at all. This situation is the most dangerous - then the pus will break inside, which can cause blood poisoning.
Any type of boil has four stages of development:
| № | Stage | Period of occurrence | Symptoms |
| 1 | Infiltration | Four days | The appearance of a red bump, with an infected follicle in the middle. Its gradual growth, thickening, tingling, pain, swelling. |
| 2 | Suppuration | Two to three days | Formation of a necrotic core, increased pain, increased temperature, general weakness, loss of appetite. |
| 3 | Gap | One or two days | Isolation of pus and necrotic cells from the resulting wound. |
| 4 | Healing | Three to four days | The surface of the wound is filled with granulation tissue. Unpleasant sensations arise when touched, and a scar forms. |
If abscesses occur regularly and in large numbers, furunculosis is diagnosed. Metabolic and immune disorders contribute to the development of the disease. You need to contact an immunologist and donate blood for sugar.
Symptoms and manifestations of furunculosis.
The disease begins with the formation of a purulent-inflammatory infiltrate around the hair follicle. After a few days, the inflammatory process covers the entire hair follicle, after which the inflammation affects the adjacent sebaceous gland and connective tissue. Often, before the appearance of boils, a person experiences itching in the place where inflammation will subsequently develop. Externally, the boil is a cone-shaped node rising above the surface of the skin. At first, it may not be felt at all and may not cause any discomfort, but as a focus of inflammation forms, pain increases: a person may feel both swelling and pain of a pulsating or twitching nature. With furunculosis of the face and neck, extensive swelling usually occurs around the infiltrate.
On the third or fourth day, a fluctuation zone forms in the center of the infiltrate. If you press on it, you can feel the movement of purulent masses in the follicle cavity. In this case, a small focus of purulent tissue melting appears around the hair, and a fistula begins to form.
This disease does not have a clear localization in a specific area of the body, but it usually affects areas of problem skin that is prone to oiliness. Therefore, most often people encounter furunculosis under the armpit, on the face, forearms, back of the neck, buttocks and thighs.
Diagnostics
Often, an examination by an experienced dermatologist is enough to make a diagnosis .
Diagnosis of a boil includes:
- Visual inspection;
- Anamnesis;
- Dermatoscopy;
- Bacterial inoculation of the contents of the boil.
- General blood analysis;
- General urine analysis;
- Urine culture;
- Pharyngoscopy;
- Rhinoscopy;
- X-ray of the sinuses;
- Fluorography;
- Ultrasound;
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain.
Additional diagnostic methods may be:
How to get rid of a small external boil
You can cope with a small boil at home:
- Treat the abscess with an antiseptic composition.
- Lubricate with Levomekol, Vishnevsky liniment or ichthyol ointment.
- If the pain is severe, take a No-shpy or Analgin tablet.
- Until the boil matures, keep it covered with a sterile bandage.
- After opening, re-treat the affected area with an antiseptic and cover with a sterile bandage.
Protection is necessary to prevent infection and the wound from being injured by friction against the other thigh or clothing.
Treatment under medical supervision
If a subcutaneous boil has formed on the inside of the thigh, immediately go to the clinic to identify the stage of development of the disease and get medical help. A doctor should treat such a boil on the thigh. But even with the external option, medical consultation is necessary if:
- reddish stripes appeared, running away from the boil (a sign of the development of lymphangitis);
- temperature rises;
- a lot of pus has formed;
- the pain prevents active movement.
The doctor will prescribe applying bandages with ointments that draw out pus, warming the boil with dry heat, and UHF. If the disease is severe, you will need to take antibiotics (Tetracycline, Amoxiclava).
During the entire period of treatment of the boil, the skin surface around the source of inflammation must be treated with antiseptic medications - hydrogen peroxide, Miramistin, salicylic alcohol. To strengthen the defense system, vitamins and immunostimulants are prescribed.
Treatment of furunculosis.
In order to cope with the disease, be sure to contact a specialist and follow all his instructions.
During the treatment of furunculosis, the patient will have to limit water procedures or even completely abandon them. The exception is extensive furunculosis: in this case, warm baths with potassium permanganate are recommended to disinfect the skin. Instead of washing and taking a bath, visiting a bathhouse, or taking a shower, you will need to wipe healthy skin with non-aggressive antiseptic solutions, for example, salicylic alcohol or furatsilin solution.
Personal hygiene during the treatment of furunculosis is extremely important - it was already mentioned above that microtraumas of the skin can lead to the further development of this disease. Therefore, it is necessary to frequently change underwear and bed linen, and treat any, even the smallest, cuts and scratches with a solution of brilliant green.
At the stage of boils maturation, the skin around them must be treated with antiseptics.
Antibiotics for furunculosis are also used as prescribed by the attending physician - in cases of abscesses and in the chronic course of the disease. If general diseases are diagnosed, the patient is exhausted, or has a decreased immune status, a specialist may prescribe antibiotics in the form of intramuscular injections.
To prevent complications such as cellulitis or abscess, experts recommend electrophoresis in combination with antimicrobial drugs.
If an abscess develops as a result of the disease, then the boil is opened under local anesthesia, and the purulent-necrotic masses are removed.
Prescription of general strengthening drugs and vitamins.
Regardless of the stage of furunculosis, it is necessary to correct the concomitant pathology: sanitize chronic infectious foci, treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, and so on.
During treatment, it is necessary to exclude spicy and fatty foods from the diet, and eat more food rich in vitamins and protein, which promote tissue regeneration. Products with a high fiber content promote good gastric emptying, which helps avoid dysbiosis, and this is very important for furunculosis. Instead of tea and coffee, it is better to drink rosehip infusion, compote or fruit drink.
Surgery
If the boil is large and the patient feels unwell, he is hospitalized and undergoes surgery:
- The body of the boil is cut or punctured, the purulent crater is cleaned of inflammatory fluid and remnants of necrotic tissue.
- Wash the surface of the wound with antiseptic compounds and apply a bandage with an antibacterial drug.
- Drainage is installed in the wound for five days to facilitate the release of purulent contents.
- The drainage is removed, after which the wound heals on its own.
The operation is performed under the influence of painkillers.
Additionally, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and immunostimulants, and vitamin therapy.
For faster relief, laser therapy is used. The operation is performed in one session with absolute cleansing of the wound from pus and necrotic core.
Possible complications
Lack of proper treatment, a late visit to the doctor and weakened immune defense are the main causes of complications. These include:
- lymphangitis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- phlegmon;
- sepsis;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- abscess;
- lymphadenitis.
To avoid them, squeezing out the boil or simply ignoring it is prohibited. During treatment, you should not visit the sauna, swimming pool, or allow clothing to rub the abscess.
Preventive measures
To prevent the occurrence of boils or the disease becoming chronic, it is recommended:
- do water procedures at least once a day;
- change bed and underwear regularly;
- wear loose clothing made from natural fibers;
- treat hyperhidrosis, skin ailments;
- get rid of bad habits;
- drink vitamins;
- use personal hygiene products - razors, towels, washcloths;
- eat a balanced diet;
- control body weight;
- train stress resistance.
Preventive measures prevent the infection from spreading, normalize metabolic processes, and prevent the occurrence of severe complications.
Boils on the thigh and near the groin are especially dangerous: in these areas there are large blood vessels, lymph nodes, and nerve fibers. That is why getting rid of an abscess should be under medical supervision.
Causes of furunculosis
Most often, purulent abscesses occur in areas of the skin where there is hair - on the head, face, neck. Often, boils also form in areas where clothing rubs the skin - on the neck, lower back, under the arms, in the groin area. The disease is more often observed in male patients.
Doctors associate the formation of boils with the following reasons:
- Increased activity of sebaceous and sweat glands.
- Neglect of personal hygiene rules.
- Hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorder.
- Weak immunity.
- Microtraumas received during shaving.