Skin inflammation is caused by various diseases. One of them is seborrheic dermatitis, which occurs in children and adults. It is also called seborrheic eczema, which most often appears at a young age, but can also occur after 40, and even in newborns. Men are most susceptible to the disease. The causes of dermatitis are varied and varied, depending on the geographic location of a person.
Seborrheic dermatitis occurs on the face (eyebrows, eyelids, nose, forehead, etc.), on the scalp, in the chest and interscapular areas. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus malassezia furfur, which chooses places with a large accumulation of sebaceous glands.
Seborrheic dermatitis in the photo
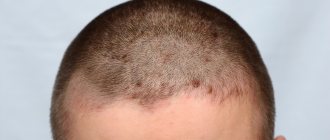
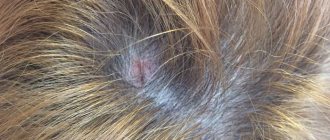
Photo 1. Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp.
Photo 2. Seborrheic dermatitis of the head.
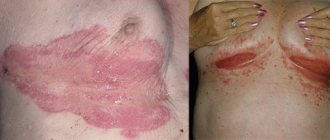
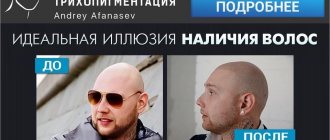
Photo 3. Photo of seborrheic dermatitis before treatment.
Photo 4. Photo of seborrheic dermatitis after treatment.
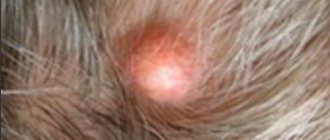
Photo 5. Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis: redness and peeling.
Photo 6. Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis: the appearance of crusts.
SKIN-CAP products
Modern clinical research [2] in the field of dermatology indicates the positive effect of products based on activated zinc pyrithione in the treatment of seborrhea - shampoo and aerosol SKIN-CAP.
The use of the products helped to eliminate the symptoms that bothered patients within 1-2 weeks of use [2].
The SKIN-CAP line includes medications in the form of cream, aerosol and shampoo; as well as skin care cosmetic product Skin-cap shower gel.
All forms of this drug are characterized by:
- High antimicrobial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory activity, due to which SKIN-CAP not only helps in relieving symptoms, but acts directly on the cause of these symptoms;
- High level of safety [4], thanks to which SKIN-CAP cream and aerosol are recommended for use by all categories of adults and children from 1 year of age [3];
- Wide choice of forms - the drug is available in 3 forms, which means that the doctor can easily select a flexible individual treatment regimen for a patient with any type of seborrhea in different parts of the body.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp and sebaceous glands
The secretion of the sebaceous glands is a mixture of lipids and is called sebum. It is necessary for the healthy functioning of the skin: moisturizing it, maintaining elasticity, creating an antimicrobial protective barrier.
The skin is covered unevenly with sebaceous glands; there can be from 4 to 380 ducts per 1 cm2. They lie in the middle layer of the skin - the dermis, between its papillary and reticular layers. The largest number of sebaceous glands are located in the so-called “seborrheic zones”: on the skin of the face and body (back, neck, scalp, pubis, chest, abdomen, shoulders, forearms, legs). There are no sebaceous glands on the skin of the soles and palms.
For the most part, the ducts of the sebaceous glands open at the mouths of the hair follicles. In smaller numbers, the excretory ducts open directly onto the surface of the epidermis - in the area of the eyelids, borders of the lips, external auditory canal, nipple halos, and anus.
The size of the glands and the amount of lipid secretion depends on various factors: the functioning of the endocrine, nervous, reproductive systems of the body, age. In young children, the sebaceous glands secrete very little secretion. By adolescence, their work increases sharply, but as they grow older, their activity decreases. In adult men, sebum is constantly secreted in approximately the same amount; in women, this process is often associated with the menstrual cycle. In old age, the amount of secretion released decreases.
Prevention
In order to never encounter oily seborrhea and dry seborrhea on the face and head, it is important to take basic preventive measures.
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the selection of shampoo. Experienced dermatologists and hairdressers recommend avoiding brands that use SLS (this component can be easily found in the description). If you have oily hair, do not take shampoos for this type of hair: the secretion may only increase.
Eat right, follow a routine and don’t worry. Carefully study the composition of the medications you are taking: if they contain unsafe hormones, it is better to find an alternative.
Treat combs and combs with care, do not give them to other people. This also applies to hats, especially summer ones.
Seborrheic dermatitis. Varieties
Oily seborrhea is the most common type of disease. It is characterized by increased secretion of sebum and changes in skin microflora. With oily seborrhea, redness of the skin or small reddish papules with an oily sheen and clearly defined boundaries are observed. Oily seborrhea, in turn, is divided into thick and liquid, depending on changes in the composition of the skin secretion (see photo of seborrheic dermatitis).
Oily seborrhea
Oily seborrhea
With liquid seborrhea, the level of free fatty acids in sebum increases. The skin of the face becomes shiny, rough, with enlarged pores. Comedones and acne easily form on it. If liquid seborrhea affects the scalp, the hair looks very dirty and sticks together in strands.
With thick seborrhea, there is a decrease in the level of lower fatty acids and an increase in higher fatty acids in the sebum. An imbalance in the composition of skin secretions reduces its protective properties and provokes the proliferation of microorganisms. Externally, thick seborrhea can manifest itself as pustular rashes, dilation of the mouths of the ducts of the sebaceous glands, comedones, and the separation of large yellowish scales glued together.
Dry seborrhea - often observed in young children, as they produce an insufficient amount of skin secretion. In adults, the dry form of seborrheic dermatitis occurs less frequently. It is characterized by a decrease in sebum production, dryness, cracks and excessive flaking of the skin, a feeling of tightness that intensifies after contact with water. The hair on the head becomes thinner, brittle and split. In some cases, the scales layer on top of each other, forming crusts. Acne, pink and red spots appear on the skin.
Dry seborrhea
Severe seborrhea with infection
Mixed seborrhea - characterized by the simultaneous appearance of dry seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp and oily seborrheic dermatitis on the face.
Popular questions
1. Is it possible to dye your hair if you have dry seborrhea?
Dyeing your hair for dry seborrhea is not recommended, especially during an exacerbation. As a result of the disease, the hair is already weakened and prone to loss, and after dyeing with permanent dye, this process may worsen. Aggressive substances in hair dye can increase dryness and flaking of the scalp. It is better to first contact a trichologist and undergo treatment for dry seborrhea.
2. What to do if seborrhea does not go away?
Seborrhea is a chronic disease that cannot be completely cured. But proper therapy and compliance with doctor’s recommendations can prolong periods of remission. If exacerbations of seborrhea occur frequently, you need to consult a doctor (dermatologist or trichologist) to correct the treatment regimen.
3. Is seborrhea contagious?
The contagiousness of seborrhea is a myth. The disease develops under the influence of internal factors (immunological, neurological diseases, stress and others).
0
0
0
Article rating:
5 out of 5 based on 2 ratings
Author: Rozhkova Natalya Viktorovna
Dermatovenerologist, trichologist. Highest category. Work experience over 25 years.
Seborrheic dermatitis. Symptoms
Seborrheic dermatitis can develop both in the head and torso. Seborrhea of the scalp can manifest itself as inflammation of the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, hairline, nasolabial folds, external auditory canals and the area behind the ears. In men, it is often localized in the area of beard and mustache growth.
Seborrheic rash can also affect the chest and natural folds of the body: armpits, groin, abdomen, mammary glands. Seborrhea of the face and body manifests itself as red spots, accompanied by itching and peeling, a burning sensation and even the appearance of papules, merging into ring-shaped or garland-shaped plaques. The plaques have clear boundaries, the papules are covered with fatty yellowish scales. As the disease progresses, bright yellow crusts appear on the skin, inflammation grows over a large surface area of the skin, and a bacterial infection occurs.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is characterized by the detachment of whitish scales, which can be mistaken for large dandruff. However, unlike dandruff, seborrhea is accompanied by itchy skin, and the lesions are clearly visible. Many patients associate dry scalp with the appearance of “dandruff”, so they wash their hair less often. Unfortunately, such tactics, instead of the desired result, only lead to the accumulation of seborrheic scales, the formation of dense crusts and pathological inflammation of the scalp and sebaceous glands. Refusal of treatment leads to thinning hair and baldness.
Seborrhea of the scalp in infants usually appears at the age of 3 months. It consists of thick yellow crusts that can be easily removed with vegetable oil and does not bother children. However, the combination of skin rash with diarrhea and underweight in newborns requires urgent medical attention, as it may indicate the presence of such a serious disease as Leiner's erythroderma.
Diagnosis and treatment of seborrhea
To effectively treat the disease, correct diagnosis is necessary. A dermatologist may recommend that the patient undergo the following tests:
- blood chemistry;
- sebometry;
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
The MedicCity clinic employs doctors of the highest category who know how to help you! Diagnostics and treatment are carried out using modern equipment. In addition, neurologists will help you overcome depression, and endocrinologists and nutritionists will select proper and balanced nutrition.
Seborrheic dermatitis. Causes
The main reason for the development of seborrhea is the effect on the skin of opportunistic yeast-like lipophilic fungi Malassezia furfur, which are present in varying quantities in most people. The oval form of the fungus (Pityrosporum ovale) is responsible for the development of inflammation of the scalp. Lesions on the skin of the body are caused by the round form of Malassezia furfur – Pityrosporum orbiculare. Fungi create colonies around the ducts of the sebaceous glands, feeding on lipid secretions and actively multiplying.
However, seborrheic dermatitis does not affect everyone. Thanks to the immune system, a healthy body inhibits the growth of fungi. If the body's metabolism is disrupted, Malassezia furfur begins to multiply uncontrollably, which breaks down sebum into free fatty acids, which causes inflammation.
The development of pathology can occur due to the following factors:
- puberty - due to hormonal changes in adolescents, the composition of sebum changes, and the sebaceous glands begin to work with greater intensity. In this case, the disease goes away on its own as the patient grows older;
- hereditary predisposition explaining the hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal imbalance, in which there is an increase in the level of androgen and progesterone and a decrease in estrogen levels. Hormone-dependent seborrheic dermatitis is observed in women in menopause or with ovarian diseases, in men with testicular tumors, and in obesity;
- unhealthy diet with an abundance of spicy, salty and fatty foods;
- presence of bad habits (alcohol, tobacco smoking);
- infectious diseases, weakened immunity;
- stress and overwork;
- non-infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system and metabolism. Painful conditions are accompanied not only by increased work of the sebaceous glands, but also by excessive sweating and cardiac arrhythmia;
- psychological and mental diseases (for example, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, schizophrenia, epilepsy, manic-depressive disorder), in which the functions of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus are disrupted.
But despite the extensive list of possible reasons, none of them are absolute. The exact reason contributing to the excessively active activity of Malassezia fungi has not yet been identified.
How to prevent seborrhea
To prevent seborrhea you need:
- strengthen your immunity;
- eat properly and balanced;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- take vitamins “A” and “B”;
- spend more time walking outdoors and being in the sun;
- reduce consumption of sweet, fatty and spicy foods;
- pay great attention to the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract;
- strengthen your immunity;
- choose the right shampoos and creams for your skin type.