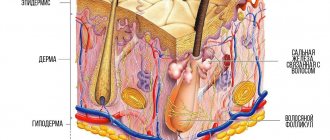
A furuncle is an inflammatory process that affects the hair follicles and surrounding tissues, characterized by a purulent-necrotic reaction and intoxication of the entire body. The main pathogens are ingested pyogenic bacteria, mainly Staphylococcus aureus. The main reasons for the occurrence of such a pathology can be: microscopic injuries to the skin (from shaving, depilation, ingrown hairs, dry skin, scratching, etc.), disruption of the metabolic response and immune defense of the surface layers, skin contamination and blockage of the ducts of the glands located next to the follicle , impaired sweating and sebum secretion, hypo- and avitaminosis, endocrine disorders.
A boil, as a skin disease, is characterized by a staged process:
- Development of infiltrate within 1-2 days (hyperemia of the skin, thickening, the skin stretches and becomes flattened, shiny over the area of formation of the pathological process, extremely painful);
- On the 3-4th day, suppuration of the follicular pustule occurs, with a necrotic center;
- Rejection of the necrotic core of the boil;
- The healing process with scarring lasts up to 10 days.
In addition to a local reaction, a boil is characterized by intoxication of the body. Often there is a temperature reaction to the infectious agent and pus, as well as general weakness.
A boil can be treated either conservatively or surgically. In the first stages, local anti-inflammatory drugs and antiseptics may be prescribed. The skin at the site of hyperemia is thoroughly cleaned (disinfected with iodine or alcohol solution), applications with ichthyol ointment are applied, dry heat and UHF are applied. After opening the boil during the process of discharge of purulent-necrotic masses, a wet-dry bandage and applications with a hypertonic solution are applied, this promotes better discharge of pus. After complete cleansing of the ulcer, antibacterial ointments are applied to the wound; levomekol is excellent. When the process is localized to the face, severe complications (purulent meningitis or sepsis) may occur, so systemic antibacterial drugs must be prescribed. In general terms, the medical impact for this pathology is the same for any location, although there are minor differences in the clinic and treatment methods. The surgical method is used when it is impossible to remove the purulent-necrotic rod on its own.
Why is bartholinitis dangerous during pregnancy?
Any disease of an infectious-inflammatory nature that appears during pregnancy negatively affects the growth and development of the unborn child. Pathologies that are accompanied by suppuration and intoxication pose a particular danger to the fetus. Bartholinitis in pregnant women is just such a disease, so even with minor symptoms it is necessary to consult a specialist and begin treatment as early as possible. Treatment of an infectious disease is carried out with antibiotics. The doctor determines the treatment regimen individually, taking into account the patient’s position. Sometimes conservative treatment does not bring results, then surgical removal of the abscess is performed under local anesthesia, which does not harm the health of the expectant mother and child.
Furuncle in the ear
A boil in the ear receives therapeutic treatment with minor differences. The opening and rejection of necrotic masses may be accompanied by their flow into the middle ear, which is very unfavorable and dangerous for the hearing organ, therefore the use of dry heat, which can also contribute to the occurrence of sepsis, is not recommended. It is recommended that the patient sleep on the affected side to prevent swelling. Be sure to contact an otolaryngologist. The specialist manages the patient conservatively throughout the entire period and only if necessary can perform minor surgery. Under no circumstances should you attempt to clean your ears at this time, squeeze out the boil, or carry out any other activities. The vascular network on the head is very well developed, so in this location it is necessary to approach treatment methods very carefully so as not to cause life-threatening complications. In addition to the local reaction, severe headache, loss of appetite, fever, and irritability often occur. When such a clinic develops, symptomatic additional treatment is prescribed: antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, analgesics.
How dangerous is the disease for a child?
Bartholin's glands are a paired organ whose ducts are located at the entrance to the vagina. It is through these ducts that the infection penetrates into the organ, causing an inflammatory complication.
The causative agents of bartholinitis can be the following microorganisms:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- enterococci;
- coli.
Inflammation of the glands may be a consequence of the progression of sexually transmitted diseases caused by trichomonas, chlamydia, and gonococci. Signs indicating inflammation of the Bartholin glands:
- swelling of the labia minora;
- formation of a tumor in the vaginal area, the size of which can vary from a small pea to a chicken egg;
- pain, discomfort in the area of the inflamed area, increasing during walking, intimacy;
- increase in body temperature;
- general intoxication, accompanied by weakness and nausea.
Bartholinitis during pregnancy occurs in 4 stages:
1. Canaliculitis. At the initial stage, the ducts of the gland are affected. The woman is worried about redness of the mucous membrane, pain, which becomes more intense during walking, urination, physical activity, and sexual intercourse.
2. False abscess. The infectious-inflammatory process spreads to the gland, but the pus itself is not yet released.
3. Formation of a cavity with purulent contents. The gland gradually increases in size, pathological symptoms worsen, and the woman’s condition worsens.
4. Opening of the abscess and chronicization of the inflammatory process. If there is no treatment, the abscess ruptures or opens on its own. If the affected tissues are not cleared of pus, the pathogenic microflora remains in the gland, which leads to the development of chronic bartholinitis, characterized by periodic relapses.
Even at the initial stage of development, the disease poses a threat to the health of the unborn child. Bartholinitis during early pregnancy can disrupt the formation of the main organs and systems of the child and cause intrauterine death. In later stages, the risk of infection of the fetus during movement through the birth canal increases. During contractions, the purulent capsule that forms with progressive bartholinitis can rupture at any time, and its contents can enter the child’s body. This, in turn, leads to infectious damage to the organs of the visual, respiratory, and auditory digestive systems. Therefore, the disease must be treated as soon as possible, without allowing it to become chronic.
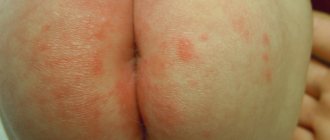
Furuncle on the leg
A boil on the leg or buttock often causes trouble when walking or sitting. Sometimes pain and inflammation significantly complicate the movement of the patient, who tries to spare the affected leg. Boils of the buttock are often complicated by the formation of phlegmon. This often leads to the formation of extensive necrosis, resulting in a scarring process. For this reason, a boil on the buttock is most often treated surgically with opening and drainage of the abscess. With this localization, the patient is recommended to spare the affected area, try to sit on the healthy side, and thoroughly disinfect the site of the pathological process. After rejection of the boil core, bandages with antibacterial ointments should be constantly changed to prevent infection of surrounding tissues with the formation of purulent streaks. After the formation of such ulcers, scars are formed that have an extremely negative cosmetic effect. A boil on the leg is treated conservatively, similar to that for other locations. In case of complications, minor operations are used to open the abscesses. In addition to local treatment, systemic antibacterial drugs are prescribed. With a single boil on the leg and careful handling of it, and with a favorable course of the disease, you can carry out conservative measures yourself. If the boil on the leg does not go away for a long time (more than two weeks) or is complicated by the appearance of a temperature reaction, then you should definitely consult a doctor.
Early stage therapy
To diagnose the disease at the initial stage, you need to pay attention to suspicious symptoms and contact a gynecologist as soon as possible. At the appointment, the specialist will conduct a gynecological examination of the internal and external genital organs, identifying swelling of the posterior or middle part of the labia, which displaces the vestibule of the vagina to the side. To confirm the diagnosis, additional diagnostics are carried out, including the following procedures:
- Laboratory examination of gland secretion. This diagnostic method will help identify the infectious pathogen that provoked inflammation of the Bartholin glands.
- Analysis of a vaginal smear to determine the nature of the microflora.
- Bartholinitis during pregnancy responds well to conservative treatment, but provided that the disease is not advanced and a purulent capsule has not yet formed. To stop the inflammatory process, applications with the Miramistin bactericidal solution are used. Decoctions of chamomile, calendula, oak bark, and sage are well suited for washing.
The following medications may be prescribed:
- "Polygynax". It has a bactericidal, fungicidal and anti-inflammatory effect. It is used in the form of suppositories according to the scheme: 1 suppository at night. The drug is safe for children.
- "Levomekol". Antibacterial ointment characterized by a pronounced antiseptic effect. It is used in the form of applications to the area of the inflamed gland.
- Vishnevsky ointment. The effect of use is the same as that of Levomekol. Used in the form of lotions.
Furuncle on the back
If you find a boil on your back, you should consult a doctor. This pathology can manifest itself either in a local clinic or in intense muscle pain. In case of complications and development of phlegmon (spread abscess), surgical intervention is necessary. The doctor carefully opens the cavity, cleans it of necrotic masses, and bluntly breaks off adhesions if they are present. The lesion is drained and a bandage with a hypertonic solution is applied (for better drainage of pus). A boil on the back is treated with local and systemic antibacterial therapy. If there is a fever and general weakness, antipyretic drugs are prescribed. Muscle pain is relieved with local and systemic analgesics. You should not try to remove a back boil yourself, comb it, or rip it off. Such actions can only lead to aggravation of the pathological process and the development of complications. Often with such localization there are not single, but multiple boils. A formation containing several necrotic rods is called a carbuncle. In case of multiple position of hair follicles, immunotherapy is recommended, and vitamin B complexes are also prescribed.
Antibacterial therapy
If the disease is advanced and cannot be treated sparingly with the use of bactericidal ointments and solutions, then the doctor decides to use antibacterial drugs. The treatment regimen is determined individually, taking into account the duration of pregnancy, the stage of progression of bartholinitis, the presence of associated complications, and the type of pathogen that provoked the inflammation.
To destroy a bacterial infection, the following drugs are often prescribed:
- "Amoxiclav";
- "Augumentin".
The course of therapy and dosage are individual. Also safe for the fetus are drugs belonging to the group of cephalosporins:
- "Ceftriaxone" in the form of injections;
- "Cefexin" for oral administration.
If inflammation of the Bartholin glands occurs with complications, the pregnant woman is prescribed the antibiotic Sumamed. The course of therapy is carried out under the strict supervision of a specialist. The doctor monitors the condition of the unborn child, as well as the effectiveness of the drug used, and adjusts the regimen if necessary.
Furuncle under armpit
When the boil is localized in the armpit, movements of the upper limb are significantly hampered due to the sharp pain of the formation. It is difficult to adduct or abduct the arm. This condition worsens the patient’s life and makes it impossible to perform usual actions. A developed vascular network can contribute to the spread of infection throughout the body. Regional lymph nodes often become inflamed in response to local inflammation, making movement even more difficult. Fever is typical. A boil under the armpit is treated mainly conservatively. During the period of illness, shaving the armpit and using deodorants are prohibited. It is recommended to thoroughly wash the skin and disinfect the skin with alcohol or iodine solution. In general, conservative measures are carried out, as with boils of other locations. After opening the formation, applications with saline solution and antibacterial ointments are applied. Antibiotics and, if necessary, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. With proper conservative treatment and avoidance of trauma to the pathological focus, surgical treatment is extremely rarely resorted to.
Surgical intervention
If the abscess has reached a large size and general intoxication of the body is observed, the doctor discusses surgical treatment options with the pregnant woman. During the operation, local anesthesia is used, which does not harm the health of the woman and the fetus.
Having identified the source of inflammation, the surgeon opens the abscess, treats the cavity with an antiseptic solution, and installs a catheter to prevent the gland duct from being closed. This operation is called marsupialization. After a few days, the catheter is removed, and in order to prevent a bacterial complication, the doctor selects a course of antibiotics that are safe for the unborn child.
In case of relapse of the disease, a surgical extirpation procedure is prescribed. Its essence is to make a longitudinal incision on the labia minora with subsequent removal of the Bartholin glands.
These surgical methods can cure bartholinitis during pregnancy without harming the unborn child. After recovery, do not forget about preventive measures that will help prevent relapses. Main rules of prevention:
- strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene;
- for washing, use only special intimate products;
- treat foci of infection in a timely manner, preventing it from becoming chronic;
- have a protected sex life if your sexual partner is unstable;
- increase the body's immune defense;
- visit a gynecologist for a preventive medical examination, which will help identify any gynecological disease at an early stage.
Furuncle during pregnancy
Treatment for boils during pregnancy is the most gentle. Everything is carried out within the framework of conservative therapy; if possible, it is recommended to use only local antibacterial agents. Any pathological process, as well as excessive use of medications, can significantly disrupt the development of the fetus. Systemic antibacterial drugs are prescribed only in extremely severe cases: multiple furunculosis, often recurrent, severe condition of the mother (fever, diffuse cellulitis, sepsis). In extremely severe cases, there may be a question of termination of pregnancy and appropriate therapy. To prevent such life-threatening conditions from arising, you should not touch the developing boil or try to cut or squeeze it out yourself. During pregnancy, if a woman experiences even a single boil, it is imperative to consult a doctor for advice and periodic monitoring of the development of the pathological process. A pregnant woman must follow a diet. If a boil occurs, it is worth reducing the proportion of carbohydrates. B vitamins have a beneficial effect on the skin and its immune processes. Complex vitamin complexes are prescribed. Biological food additives with vitamins, yeast. The diet should be varied, balanced and regular. Walking in the fresh air and doing gymnastics are very useful for stimulating the immune system.
Treatment of a boil of any location is aimed at preventing the development of complications. With a favorable course of the process, the necrotic core is independently rejected and a small ulcer is formed at the site of the boil, which often heals without leaving a trace.
Be careful - strangers are in the body!
Inflammation of the female genital organs is quite easy to suspect. Sudden pain in the lower abdomen, menstrual cycle disorder, itching and strange (in color and smell) vaginal discharge - all this indicates the presence of inflammation. If, in addition, the temperature rises and weakness appears, most likely the inflammatory process is in the acute phase. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the female genital organs in two ways: through the blood and through the vagina, and the latter route is much shorter than the first. After all, the internal genital organs of a woman are an open system by nature; it communicates with the environment through the vagina and cervix. An inflammatory disease can be caused by sex without a condom, trauma to the genital organs of any origin, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, abortion and childbirth. When the infection circulates in the blood, for example, with influenza and scarlet fever, it can also reach the female genital organs. A similar situation is observed when somewhere in the body there is already a focus of inflammation: caries, chronic sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc. A dormant infection can “wake up” at any moment, “swim” through the bloodstream to the genitals and “arrange” inflammation. It is impossible to talk about all inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs in one article; we will focus on one of them - bartholinitis.
What it looks like and where it appears
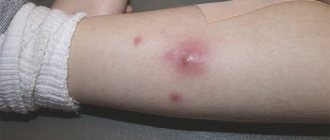
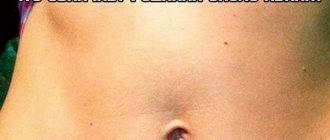
A furuncle is formed during purulent-necrotic inflammation in the hair follicle, which is provoked by certain strains of staphylococci. The first signs of an abscess are:
- the skin turns red and swells a little;
- on the surface of the skin you can clearly see how it is filled with pus;
- the location of the boil is usually very painful;
- if the boil is large or there are several of them (we are talking about a carbuncle), the body temperature can rise significantly.
A boil in a pregnant woman can occur on any area of the skin where sebaceous glands and hair are present. Most often, staphylococcus affects the skin near the ears and the area between the nose and upper lip. Other locations:
- skin on the thighs and buttocks;
- in the genital area;
- armpits;
- on the back of the neck, in the collar area;
- on the scalp.
What not to do
Independent opening of inflamed ulcers, both during pregnancy and for all other patients suffering from furunculosis, is prohibited. Another number of taboos:
- In no case should you heat the location of the chiria;
- Direct contact with water of an inflamed, mature abscess, which can burst at any moment, should be avoided;
- It would be a huge mistake to make compresses on the site of the abscess - moisture can cause it to loosen and allow the infection to enter the bloodstream, causing serious complications.
If the boil suddenly bursts, remove the leaked purulent contents with a sterile gauze swab. Sterile material should be purchased in advance and always available. The edges of the wound are carefully treated with hydrogen peroxide (iodine is not recommended).
The wound should be covered with a sterile bandage, fixed and seek help from a doctor. The specialist will remove the remaining pus and the core, completely clean and disinfect the wound, preparing it for healing.
Preventive measures
Prevention of skin diseases, including furunculosis, includes a number of principles. It is important to adjust your diet. During pregnancy, the diet should contain a sufficient amount of simple and easily digestible dishes from vegetables, meat and fish, as well as whole grains. You need to exclude foods that are too fatty, fried, smoked, as well as dishes prepared with preservatives.
It is important to follow the carbohydrate limit. If it is exceeded (abuse of confectionery products with rich cream, puff pastry, fresh baked goods, chocolate with caramel), the risk of skin rashes increases.
It is equally important to monitor your water balance, which is very important during pregnancy. With a lack of fluid, metabolic processes in the body are quickly disrupted, which also provokes skin problems.
Vitamin complexes prescribed by a doctor will help support a pregnant woman’s immunity. It is not recommended to take such drugs on your own, since in the case of vitamins, their excess is just as fraught with health complications as their deficiency.
Three more important components of prevention are moderate physical activity (regular walks in the fresh air, light exercise), strict adherence to personal hygiene rules and timely treatment of any skin injuries.
Possible consequences for the pregnant woman and fetus
Furunculosis is a dangerous disease for both a pregnant woman and her unborn baby. In women, the pathogen, in addition to skin problems, can cause mastitis. Infection in the mother's body has a direct effect on the fetus.
This can lead to sad consequences throughout the course of pregnancy. But the expectant mother needs to be especially careful in the first weeks after conception, when infection of the membranes may occur.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, exposure to the pathogen increases the risk of developmental defects in the child. In the second, it promises to undermine the child’s health after childbirth, in particular, it threatens serious disruption of the respiratory system, cardiovascular system and brain. With the development of furunculosis, the risk of spontaneous termination of pregnancy ahead of schedule cannot be ruled out.