From this article you will learn:
- why does an abscess appear on the gum,
- what to do when the gums fester.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
A prerequisite for the appearance of gum suppuration is the presence of a source of infection. Most often, this source is an infection in the root canals of the tooth, which develops there either due to poorly performed root canal filling, or due to the patient’s untimely treatment of dental caries or pulpitis. And in this case, the dentist will diagnose you: “Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.”
The second main cause of gum suppuration is the formation of deep periodontal pockets during periodontitis. Such pockets contain a large amount of infection and can cause the formation of a purulent abscess in the gum. The choice of treatment method will depend on the cause of gum suppuration in your case. Therefore, you first need to determine why pus appeared in the gums, and only then begin treatment.
How can a fistula on the gum be cured?
Of course, we treat it, we deal with it, we work for it. In order to cure a fistula on the gum, first of all, we should eliminate the reason due to which the fistula occurred. We should not
fight the pimple itself, smear it with various ointments and lotions, but must eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
We must
eliminate the chronic inflammation itself that led to this fistula.
The first treatment option for a fistula is endodontic
For such treatment, we provide the patient with high-quality endodontic treatment under a microscope when:
- the tooth canal itself is visible,
- its branches are visible
- and you can see if there are cracks in the tooth canal.
Our doctors perform minimally invasive treatment procedures under a microscope at a high level. Treatment of processes that led to a fistula, to a fistulous tract on the gum, to complications of various periodontitis. In the video - endodontist of the Scientific Research Center, winner of many international competitions in endodontics and dental restoration Melikov Azer:
In the clinics of the German Implantology Center, special materials are used that seal the apical part very well and for a long period, which are biocompatible with the tissues surrounding the tooth and which give a very good result.
That is, we have a therapeutic method of treatment - this time
. When highly qualified endodontists, using microscopes, special equipment and special materials, carry out canal therapy and eliminate the cause of the fistula.
The second treatment option for fistula is mixed
Second method
- This is a mixed treatment, when treatment is carried out jointly by a therapist and a surgeon. If the lesion is already quite strong, lysis of a certain part of the root apex has occurred, when the process has already been going on for quite a long time, then the therapist cleans the canals:
seals the apical part of the root with a special material, and the surgeon opens, makes surgical access and polishes the apical part of the tooth root.
We do not perform dental resections when the tooth is cut down in half. You often think, I often have patients come to me who have had a resection and you think the person has had ⅔ of the root cut off and this tooth is no longer tenable, it can barely hold on, and why did it have to be done? We do it minimally invasively. We polish the apical part of the root with special ultrasonic tips after the therapist has carried out the treatment, and we get very good long-term results.
The third treatment option is surgery.
There is also a surgical method - this is the third method
treatment when the inflammation is already chronic according to the principle “No tooth - no caries, no periodontitis, no nothing.”
That is, the tooth is removed
, the source of inflammation is removed:
and an implant is placed
:
Subsequent rehabilitation of the patient takes place on the implant.
The fourth treatment option is autotransplantation.
Autotransplantation is a type of third, surgical treatment option. But the patient’s own donor tooth acts as an implant. As a rule, wisdom teeth, which are not involved in the process of chewing food and are actually the body’s reserve for such cases, are excellent for this role. Wisdom teeth transplantation is suitable for posterior teeth and premolars (fourth, fifth, sixth and seventh teeth).
Advantage
This method of treatment is that the patient’s own tooth is transplanted, the patient’s own tissue, which is not foreign to the body, even in conditions of the inflammatory process with a fistula, significantly reduces the risk of tooth-implant rejection.
The specialists of the German Implantology Center have accumulated many years of clinical experience in such operations. You can see how the autotransplantation operation takes place in the following video. There, at the end of the film, the patient shares his impressions of the dental transplant (this is a review 1 year after
the transplant operation):
Why gums fester: reasons
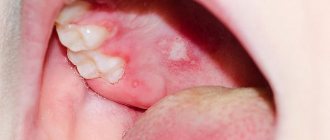
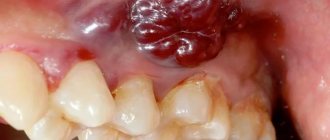
1) With an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis , infection in the root canals leads to the formation of a focus of purulent inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. Depending on the type and size of such lesions, dentists call them by terms: granuloma, cyst or granulating periodontitis. You may not be aware of the presence of such foci for years, but sooner or later an exacerbation of chronic inflammation occurs, and then pus-filled abscesses form in the projection of these foci on the gums (Fig. 1-2).
2) Against the background of inflammation of the gums (with periodontitis) - in slightly less than half of all cases when the patient's gums near the tooth fester - the cause is a local or generalized form of periodontitis. Despite the fact that the causes of these two forms of periodontitis are different, the common thing is that the formation of a purulent abscess occurs in a deep periodontal pocket formed between the gum and the surface of the tooth root. Below you can see what an abscess on the gum looks like during periodontitis (Fig. 3).
The causes and treatment of an abscess on the gum will always be interconnected, and therefore, depending on the background of what disease (periodontitis or periodontitis) the suppuration occurred, either treatment of the root canals and the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root will be indicated, or treatment of the periodontal pocket using anti-inflammatory therapy , curettage and other methods. Below we will discuss in detail the treatment of gum suppuration in both cases.
Features of treatment of fistula with concomitant diseases
Are there any particularities in the treatment of fistula if the process is accompanied by other diseases in the oral cavity, such as periodontitis? No, in fact there is no particular connection. Periodontitis is an inflammation of the periodontium of a tooth, while periodontitis is an inflammation of the apical tissues surrounding the tooth. Of course, in some very severe forms, periodontitis can lead to the formation of fistulas, but often these are all unrelated, and one should be treated separately. First, cure periodontitis, if the tooth is healthy, if it does not wobble and can be preserved, and then treat periodontitis.
How long does it take for a patient to recover after fistula treatment?
The treatment of chronic periodontitis itself is not quick, since the patient must first open the tooth canal, clean it, disinfect it with special antimicrobial drugs, and only after that the tooth canal is sealed. If we talk about rehabilitation, when the results are visible, the fistula “goes away” almost immediately, and the bone takes a long time to recover.
If we talk about the surgical method
treatment of periodontitis, when the apical part of the tooth is opened according to the type of resection, but the apical part of the root is polished, the mucous membrane is restored quite quickly - this is
3-5 days
.
Types of dental abscess
- Osteomyelitis
- Phlegmon
- Tooth loss
Osteomyelitis
When pus remains in the soft tissues, complications arise. Dense formations with pus form in the bone tissues, and swelling of the lymph nodes also occurs.
Phlegmon
A life-threatening complication occurs when the infection spreads into the soft tissues of the gums. The growth of pus leads to chronic pathologies.
Tooth loss
If the infected fluid spreads to the base of the tooth, painful swelling appears, which may lead to tooth extraction.
Recommendations after fistula treatment
After treatment of the fistula, no special recommendations need to be followed. If the treatment was related to surgery and was carried out jointly with a therapist, then yes:
- baths with antimicrobial agents must be done carefully,
- eat soft food
- Do not put your tongue into the area of the healing wound.
If we are simply talking about therapeutic treatment, then there are no special restrictions at all.
How to avoid the appearance of a fistula on the gum
Are there any prevention methods to avoid the development of periodontitis? Of course, you can avoid the appearance of a fistula on the gums, and the prevention of these fistulas is a regular visit to the dentist in order to avoid these fistulas, not to lead to chronic periodontitis, and to keep your teeth healthy, beautiful and functional.
Therefore, once every six months
You need to come to the dentist for an examination and early diagnosis of any diseases, diagnosis of caries. It is better to cure caries at an early stage than to treat canals later, or to re-treat canals that can lead to the formation of a sinus tract and a fistula on the gum.
Can a fistula on the gum go away on its own?
Yes, it can only go away on its own if the causative tooth is removed, then it will go away on its own. It's a joke! In fact, the fistula cannot go away on its own as long as there is a chronic process that occurs in the gums, in the hard tissues of the upper or lower jaw. This chronic process is ongoing, and through this fistula there is an outflow, all purulent masses are drained along with exudate. And all this goes into the body, the body is certainly poisoned. There is a constant infection - these are staphylococci, which can then provoke all sorts of sore throats and various other diseases in the oral cavity. This is unhealthy flora that is constantly in your mouth, which constantly oozes, flows out and poisons you from the inside.
The fistula itself cannot go away
. It must be treated either therapeutically or surgically.
Available Dental Treatment Options
Self-medication is strictly prohibited. The help of an experienced dentist is required. Treatment in a clinical setting involves:
- Clinical examination and surgery. An x-ray is taken to make a diagnosis. Under local anesthesia, the wound cavity is opened and drained. After removing the drainage, the cavity is disinfected and sutured.
- Drug therapy. To speed up tissue healing, doctors prescribe rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions and applications with dental gels. In rare cases, antibiotic therapy is required. For pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are allowed. To strengthen the immune system, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed.
- To prevent recurrence of the abscess, the diseased tooth is treated. The dentist eliminates carious lesions, treats pulpitis, periodontitis and other inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. At an advanced stage of the inflammatory process, the diseased element is extracted. Cystectomy and cystotomy are performed according to indications.
If an abscess occurs in a child, you should immediately consult a dentist. In children, any pathology occurs more rapidly and causes complications. When an abscess occurs on the milk units, there is a risk of infection of the buds of permanent teeth.
Treatment at home
Self-medication is dangerous to health. Resorting to folk remedies is allowed only to relieve symptoms when it is not possible to immediately consult a doctor. It is allowed to rinse the mouth with a decoction of sage or chamomile, or a soda solution, which has an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect.
When the abscess breaks through, the patient may experience temporary relief. But even in this case, competent treatment in a clinical setting is required. Without treatment, the pathological process inside the tooth will progress.
You should not try to squeeze pus out of the gums. There is a risk of infection in the wound and causing the condition to worsen.
It is forbidden to heat the painful area. When exposed to heat, the pain will intensify and inflammation will worsen. The flow of blood to the sore spot will cause the infection to spread to nearby tissues.
Consequences of ignoring the problem
Patients who ignore the disease risk losing their teeth. An advanced purulent process can provoke the development of serious complications. There is a risk of abscess of the maxillofacial area, osteomyelitis or phlegmon. These are dangerous conditions not only for health, but also for life.
You should be attentive to your health and if any alarming symptoms occur, consult a doctor. Regular dental examinations and oral hygiene will help you avoid gum suppuration.
What happens if the fistula is not treated?
If the fistula is not treated, then nothing good will end. The tooth will need to be removed, and what’s more, the bone surrounding the tooth suffers greatly, and the vestibular cortical plate suffers. When the tooth is not treated, when the cause of the fistula is not dealt with, the cortical plate is quite destroyed. Large cavities are formed in the bone, as exudate is formed, all this rots and the bone decomposes, softens and becomes infected, lyses, and exits through the fistulous tract.
Therefore, in addition to, as I said earlier, there is a fairly strong load on the body, since a fistula is a constant open source of infection in the oral cavity.
Clinical symptoms
When an abscess forms, a person experiences acute throbbing pain. The tissue adjacent to the diseased tooth turns red and swells. Increased sensitivity to mechanical stress and temperature changes. A white abscess is visible on the affected area. When pressure is applied, pus comes out of the abscess.
An unpleasant odor appears from the oral cavity, hyperthermia, and general health worsens. As the pathology progresses, the swelling spreads to the soft tissues of the face.
Complications that a gum abscess can cause
Without treatment of the disease and inadequate medical care, complications may develop. Adverse consequences arise due to the spread of inflammation to neighboring organs and tissues, as well as the spread of infection throughout the body with the formation of secondary septic foci. The most common pathological conditions that occur are:
- lymphadenitis - infection of the lymph nodes;
- sinusitis - infection in the maxillary sinuses;
- periostitis of the jaw (inflammation of the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis of the jaw bones (destruction of bone tissue due to purulent-necrotic melting of osteocytes);
- phlegmon - diffuse odontogenic inflammation of soft tissues, accompanied by progressive swelling of the face;
- destruction of the alveolar processes with significant loosening of teeth or their loss;
- peri-implantitis with implant rejection;
- sepsis.
Purulent lesions of soft periodontal tissues are always accompanied by general intoxication of the body. The temperature rises and chills appear. There is a headache, tachycardia, and the pulse quickens. Pain relief with medications brings short-term relief, but symptoms return after the medication wears off.
Is it possible to cure an abscess at home?
Doctors do not allow you to open a flux tumor on your own. This may lead to the addition of a secondary infection. If you are unable to visit a dental clinic in the coming days, you can alleviate the uncomfortable symptoms with the help of:
- Therapeutic and prophylactic rinses. When performing them, you need to use water at room temperature, salt and soda, and pharmaceutical antiseptics.
- Apply cold compresses to the sore cheek.
Under no circumstances should you heat the inflamed area. This will lead to activation of purulent-necrotic processes and the spread of infection, which is very dangerous.
Signs indicating a problem
A purulent neoplasm is difficult to miss. A person complains about:
- discomfort in the affected area, which intensifies with palpation, pressure, chewing food, and talking;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth (caused by periodic discharge of blood and necrotic masses from the abscess);
- tissue swelling;
- swelling of the cheek (indicates that the inflammation has gone very far and emergency dental care is required).
If the patient continues to ignore the symptoms, his health will worsen. His body temperature will rise, headaches and weakness will appear.
A violent inflammatory process will disrupt the dentogingival apparatus. Then the unit will become mobile and can fall out at any moment.
How do dentists treat pus in gums?
Typically therapy includes the following steps:
- Survey. The doctor finds out when the purulent neoplasm appeared, how quickly it grows in size, and how it manifests itself.
- Examination of the oral cavity. The doctor studies the location of the abscess, its color, shape. If necessary, gives a referral for an x-ray of the affected side of the jaw. X-rays are needed to understand the condition of the internal structures.
- Removing food debris, stone and soft plaque from teeth and gums. Sanitation of the oral cavity before treatment of an abscess.
- Opening of a purulent neoplasm. Performed under local anesthesia. First, the patient is given an injection of anesthetic, and then the affected area is carefully dissected. As a result, purulent masses come out.
- Installation of drainage. To prevent exudate from beginning to accumulate in the gums again, a small drainage tube is installed into the incision. You need to walk with her for several days.
A mandatory stage of treatment is anti-inflammatory therapy. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and mouth rinses to prevent the recurrence of a purulent lesion.
It happens that pus is released when pressing on the tooth. In this case, there is no “bump” on the surface of the gum. In this case, the above scheme will be ineffective. The doctor removes the filling (if it was installed), cleans the dental canals and washes out all purulent accumulations. Places a special medicine and closes it with a temporary filling.
On the appointed day, the patient must come for a follow-up appointment. Then the doctor will assess whether the inflammation was removed. If yes, then he will replace the temporary filling with a permanent one; if not, he will re-place the anti-inflammatory composition in the canals and re-install the temporary filling material.
Causes of gum abscess
The human oral cavity contains about 30 strains of microorganisms, represented by more than 700 species of bacteria. Under normal conditions, microbiocenosis does not harm its owner. A dental abscess occurs only in the presence of certain factors:
- traumatic disruption of the periodontal junction;
- infectious dentogingival pathologies;
- transmission of microorganisms through the bloodstream from other infectious foci (meningitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, etc.);
- gum damage during segment therapy;
- trauma to the crown or root of the unit;
- peri-implantitis (inflammation around the implanted tooth root).
The likelihood of developing the disease increases with poor oral care, hypothermia, accumulation of tartar inside deep periodontal pockets, and smoking. Professional hygiene and gum treatment in Moscow is carried out by doctors of the North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1. A timely visit to the clinic will reduce the risk of the formation of a purulent formation.