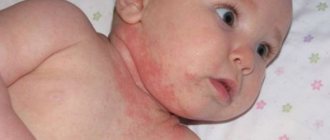
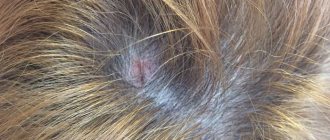
Main symptoms of the disease
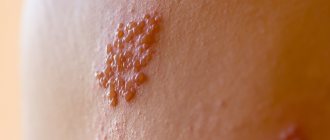
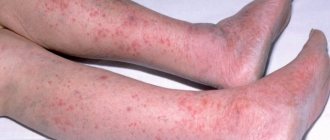
Herpes zoster mainly occurs on the body. At first it looks like pink spots. Soon they quickly become inflamed, turn red, and become covered with small blisters with transparent contents. Over time, the spots dry out and become crusty, and later they fall off.
The disease is characterized by severe attacks of pain, which can worsen at night.
Other signs of the disease:
- temperature rises to 39°C;
- painful rashes;
- headache;
- trembling and coldness in the body;
- runny nose (in children).
Types of herpes
Today, many types of infection are known, but only five are especially dangerous for humans.
Type name:
- Cytomegalovirus is a contagious type; due to its development, cytomegaloies are formed on the body. A healthy person who comes into contact with a sick person becomes infected immediately in more than 98% of cases.
- Chickenpox or varicella is an acute disease caused by Herpesviridae bacteria. The main route of transmission is airborne droplets. After infection, characteristic rashes appear on the body and body temperature rises. The disease most often affects children; in adults, the virus leads to the development of another pathology – herpes zoster.
- Epstein-Barr virus is the most common and dangerous virus. Because of the virus, cancer cells begin to develop in the body. There are no external symptoms, the course is hidden, because of this it is impossible to begin timely treatment. If the disease is not detected in time, the brain will malfunction.
- Herpes simplex type 1 is easy to get infected. Symptoms are common and may resemble colds. The genital herpes virus rarely provokes; the favorite localization of the rash is the face, eyelids, lips and neck.
- Herpes simplex type 2 is the cause of the development of genital herpes. For those people who have weakened immune systems, the pathology is especially dangerous.
Each type of infection is dangerous in its own way; only timely treatment can protect against consequences.
Disease in the cheek area
The video in this article explains in more detail what types of herpes there are.
Routes of infection
Different forms of infection require different methods of infection. In practice, the only way to get the virus is to come into direct contact with a sick person.
Infection can enter the body in different ways, namely:
- when kissing, coughing, during a conversation, in each case you can get saliva from a sick person;
- in case of close contact with a sick person, the danger most often increases in public places;
- pregnancy is another way in which the fetus becomes infected, but is only possible if the expectant mother is sick;
- sexual contact, as well as other close contacts;
- use of personal hygiene items for a sick person.
The herpes virus enters the body of a healthy person through mucous membranes or microtraumas on the skin and spreads throughout the body instantly. The lymph nodes are affected first, then the blood and internal organs.
The infection spreads along the nerve fibers and accumulates in the ganglia. After its establishment, the virus goes into so-called hibernation and waits for a favorable moment when it can become active and make itself known.
Formation of bubbles with liquid inside
After the virus degenerates into the active phase, the body begins to produce antibodies; the process lasts up to five weeks; they will be preserved for the rest of life. Once the virus is activated, external symptoms will begin to appear, namely, grouped rashes on the body.
The next stage of development is relapse. New outbreaks often cause health problems.
Every person can be affected by the infection process, but those whose immunity is weakened are primarily susceptible to the perception of the disease. Infection can occur anytime and anywhere, especially in places where there are large gatherings of people - public transport, hospitals, shops, etc.
Genital herpes can most often be contracted after sexual contact with a sick person, but the route of infection can be different. In medicine, there are many cases of self-infection. It is enough to touch the rash on some part of the body, and then touch another place with the same hands and that’s it, the infection will be transferred.
In the photo below you can see what one of the infection methods looks like.
One of the ways of infection is a kiss
Methods of treating the disease
Herpes zoster on the face and other areas is treated on an outpatient basis. Inpatient treatment is required only for the generalized form, as well as complications.
The peculiarity of therapy is its complexity - taking antiviral and immunostimulating medications.
Therapy involves relieving intoxication and pain, preventing the progression of infection. For secondary bacterial infections, antibiotics are used. To relieve rashes, use brilliant green and 5% dermatol ointment locally. If the process is sluggish, the doctor may prescribe metacil ointment or solcoseryl.
For herpes zoster on the neck or other areas, physiotherapeutic procedures are also sometimes prescribed.
Diet is important for the effectiveness of therapy. Exclude from the diet:
- fat meat;
- animal fats;
- spicy foods.
conclusions
Unlike other types of shingles, you can wash yourself if you have shingles. This is due to the fact that its causative agent is a virus, not a fungus.
For reference. However, when washing, you need to follow a number of rules: it is better to limit yourself to just a shower, do not rub with a washcloth, and minimize mechanical impact on sore spots.
In the later stages of the disease, in consultation with your doctor, you can take medicinal baths with extracts of medicinal plants. But it is better to avoid sunbathing and swimming at sea and in freshwater bodies - this can lead to adverse consequences.
Prevention
Disease prevention – strengthening the immune system:
- healthy lifestyle;
- hardening;
- regular physical activity;
- proper nutrition;
- proper rest, sleep.
Despite the fact that water procedures during the treatment of herpes zoster are contraindicated, the complication of the disease is caused by poor hygiene. Therefore, it is important:
- avoid taking hot baths - prefer a warm, short shower;
- exclude washcloths, cosmetics and anything that can irritate the skin;
- just blot the inflamed areas;
- use 2 towels - one for healthy skin, the other for infected skin (change daily).
If the disease progresses, you should limit yourself to wet wipes, and do not wet the damaged skin. When the ulcers turn into crusts, you can take a shower.
In any case, treatment is prescribed individually and exclusively by a doctor.
IMPORTANT:
Self-medication can aggravate the disease and provoke life-threatening consequences.
Other articles by the author
- Pyoderma
- Herpes zoster
- Pityriasis rosea
- Shingles
Rules for water procedures
- Take a shower rather than a bath to avoid spreading the infection to other areas of the skin.
- Wash once every two days to reduce irritation to areas of inflammation.
- The water should not be hot, and in no case should you create a “steam room” (by the way, visiting a sauna is also contraindicated).
- Do not rub yourself with a washcloth, do not use a scrub, because multiple damage to the bubbles can lead to bacterial complications.
- Detergents are needed with a neutral pH of 5.5 - they are gentle on the epidermis.
Fully or partially limited products
- For almost all skin diseases, highly extractive dishes (broths) are excluded.
- Fatty types of meat and poultry, and for some diseases, red meat and chicken.
- Fried foods, smoked meats, pickled vegetables, canned food (meat and fish), sausages, any semi-finished products (due to the content of preservatives). Sausages, sausages, ham, pates also contain preservatives and dyes.
- For all skin diseases, during the period of exacerbation, simple carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, jam, cakes, jams, sweet pastries, confectionery with cream) are excluded.
- Strong tea, coffee, cocoa.
- The use of hot sauces (vinegar, ketchup, mayonnaise), spices and alcohol is prohibited.
- If tolerance is poor, you should limit legumes and mushrooms, as foods that are difficult to digest and cause flatulence.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| pickled cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pickled tomatoes | 1,7 | 0,2 | 1,8 | 15 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| pineapples | 0,4 | 0,2 | 10,6 | 49 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| persimmon | 0,5 | 0,3 | 15,3 | 66 |
Berries | ||||
| blackberry | 2,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 31 |
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
| sea buckthorn | 1,2 | 5,4 | 5,7 | 82 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cake | 3,8 | 22,6 | 47,0 | 397 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| tonic | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,3 | 34 |
| Fanta | 0,0 | 0,0 | 11,7 | 48 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Authorized Products
- Bran bread, whole grain bread, bran bread.
- It is advisable to cook soups in vegetable broth with the addition of cereals and permitted vegetables. During an exacerbation, meat and fish broths should be excluded or secondary broth should be used.
- Second courses are prepared from veal, beef, chicken or turkey (meat according to permission and individual tolerance). They are prepared in pieces, boiled or baked. It is also better to bake minced meat products using a minimum amount of vegetable oil.
- Any fish is allowed (dietary and fatty - mackerel, cod, salmon, herring), if its consumption is approved by a doctor and it does not cause allergies. The fish is stewed, boiled or baked. If tolerated well, fish should be present in the diet daily, replacing meat.
- Any vegetables and herbs (as tolerated) up to 600 g per day. For some diseases, certain vegetables are excluded, but the list of them is sufficient to diversify the diet. Considering that the vitamin value of fresh vegetables is greater, most of them are consumed fresh with vegetable oils. Out-of-season greenhouse vegetables should be excluded or limited.
- Include allowed fruits in the menu daily (up to 500 g). Give preference to locally grown fruits.
- Eat foods high in dietary fiber: bran, prunes, gooseberries, dates, figs, raisins and dried apricots, unless they are prohibited due to your illness.
- Chicken eggs and quail eggs - boiled; they are excluded if you are allergic to chicken protein.
- Low-fat dairy products and cottage cheese. Give preference to natural kefir and yogurt with bifidobacteria (dyes and preservatives).
- All grains are allowed, but preference should be given to whole grains rather than processed flakes. Moreover, it is not permissible to consume instant porridges with preservatives and artificial flavor substitutes.
- Pasta products are allowed from durum wheat.
- Include vegetable oils, using them in prepared dishes and alternating.
- The preferred drinks are weak tea with milk, green tea, herbal infusions (in the absence of allergies to herbs), compotes, natural juices, and rosehip infusion.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| soybeans (sprouts) | 13,1 | 6,7 | 9,6 | 141 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| brown rice | 7,4 | 1,8 | 72,9 | 337 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
| sour cream sauce | 1,9 | 5,7 | 5,2 | 78 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| peasant unsalted butter | 1,0 | 72,5 | 1,4 | 662 |
| wheat germ oil | 0,0 | 100,0 | 0,0 | 884 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 9,2 | 40 |
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
What is lichen?
Ringworm is a group of dermatological polyetiological diseases, which is characterized by the appearance of a rash and itchy dry/weeping elements. There are several varieties of lichen, which differ from each other in:
- the type of rash present;
- pathogen;
- contagiousness;
- localization.
Among the most common types of lichen in humans:
- multi-colored (pityriasis);
- encircling;
- red flat;
- ringworm (trichophytosis);
- pink (pityriasis).
The course of the disease is long. There is always a danger of secondary infection.