He underwent a routine examination. I was unpleasantly upset and amazed because the doctor discovered a tumor in the mediastinum. A detailed study revealed the type of tumor - lipoma.
One thing is good. This tumor is benign. But you still have to remove it from the body. What is mediastinal lipomatosis? What are the treatment options for the disease and the prognosis for the patient?
What is mediastinal lipomatosis and its symptoms
In order to clearly understand what kind of pathology this is, you need to understand the medical terminology.
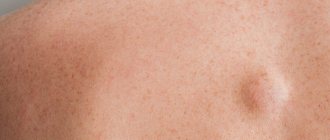
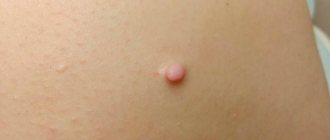
Lipoma is a benign neoplasm formed from mature fat cells separated from each other by connective tissue. Tumors of this type can be encapsulated - that is, they have clear boundaries, and the contents are enclosed in a capsule of connective tissue - and diffuse - that is, the fatty growth does not have clear boundaries and the cords can intertwine with muscle fibers.
The mediastinum is the area of the body bounded by the spine at the back and the sternum at the front. This cavity contains the lungs, heart, aorta, trachea, bronchi, large nerve nodes, and esophagus.
That is, if the diagnosis is mediastinal lipomatosis, this means that a benign fatty tumor was discovered in the retrosternal space. Wen.
The symptoms of this pathological process at the initial stage do not bother the patient. When fatty strands grow, syndromes associated with compression of internal organs develop.
Symptoms of mediastinal lipomatosis:
- the appearance of shortness of breath after minor exertion;
- cyanosis of lips and nails;
- swelling on the face;
- chest pain;
- heart rhythm disturbances, both increased and decreased contraction speed;
- pleurisy;
- weakness;
- weight loss without changing eating habits;
- decreased performance;
- signs of cerebral vasospasm - migraines, headaches;
- cough, wheezing breathing due to compression of the trachea or bronchi;
- when nerve nodes are damaged, hyperemia of the skin, ptosis of the eyelids, impaired sweating, and pathological constriction of the pupil appear;
- feeling of a lump in the throat.
The causes of this pathology have not yet been identified. Hereditary factors, diseases of the endocrine system, and cases of toxic damage to the body play a certain role. Excess weight does not provoke the development of this disease, just as losing weight does not contribute to the resorption of these tumors.
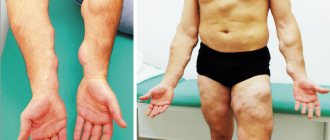
Lipomas in the chest space are somewhat more common in women than in representatives of the stronger sex.
Lipoma symptoms
When a neoplasm develops directly in the brain, it will be accompanied by significant headaches, as well as slightly increased blood pressure. Unpleasant symptoms are caused by neoplasms in the esophagus - the patient will always feel as if there are foreign bodies in the throat area, which is often accompanied by a strong cough, which can even lead to gagging. Mediastinal lipoma is usually accompanied by a hoarse voice and noticeable facial swelling.
Kidney lipoma does not cause any discomfort, but tends to develop into a malignant tumor - liposarcoma.
A tumor in the stomach is also found. In this case, lipoma causes severe pain, loss of appetite, and vomiting.
What are the possible consequences of pulmonary mediastinal lipomatosis?
Lipomas grow slowly, do not metastasize, and do not penetrate healthy cells. In the area of the anterior mediastinum, the organs of the respiratory system are located, and fatty growths begin to compress the lung tissue and bronchi.
Consequences of lipomatosis in this area of the body:
- disruption of the outflow of mucus from the bronchi;
- lung ventilation is difficult;
- shortness of breath;
- the appearance of sputum with blood due to compression of the vessels of the respiratory organs;
- stenosis – narrowing – of the lumen of the bronchi;
- Inflammatory processes develop in the trachea, lungs, and bronchi. Bronchial bleeding is possible.
In severe cases, atelectasis may develop. This is the collapse of an area or lung in its entirety.
Important! Lipomas themselves do not pose a threat to human life. They do not degenerate into malignant neoplasms. The danger is the size of the tumor and the possibility of compression and injury to nearby organs and tissues!
What it is?
Mediastinal lipomatosis is the formation of a benign tumor in this area (between the heart, aorta and bronchi). The basis of formation is mature cells of adipose tissue. Such formations are located in the subcutaneous layer of fatty tissue. Development into a malignant tumor is very rare. Tumor growth is possible, which causes pressure on nearby tissues and organs, reducing their functionality. Changing a person’s weight does not in any way affect its reduction; therefore, diets are not a panacea for the disease. The tumor is asymptomatic, and its growth rate is slow.
Features of diffuse mediastinal lipomatosis
A distinctive feature of this type of fatty tumors is the absence of clear boundaries of the tumor. Wen tissues are distributed around the organs, do not have a clearly defined capsule, and can be intertwined with healthy muscle fibers.
Diagnosis of such growth is possible only with the help of x-ray examination. Fat tissue in the images is defined as a uniform expansion of the median shadow.
Diffuse nodular lipomas are distinguished separately. These neoplasms are characterized by the presence of an extensive vascular network connecting individual fat capsules.
Structure and size of mediastinal lipoma
Most lipomas of the chest do not reach large sizes, although medicine knows exceptions to this rule. Forming as many local cells - wen, they are able to grow together. They are held together by connective tissue, the amount of which determines the hardness or softness of the tumor. The boundaries of education are fuzzy and blurred. It has a lobular structure or a node structure. In the lobules, when cut, you can see cystic neoplasms surrounded by mucus. The wen itself is surrounded by a capsule.
As the lipoma of the anterior mediastinum grows, the blood supply and functionality of the lungs are disrupted, and breathing becomes difficult. Occurring in peripheral zones, lipoma is not dangerous (due to the formation of a pseudocapsule) and does not produce symptoms. With development and growth, it can affect the diaphragm, making breathing difficult. Deformation of blood vessels in the lungs is possible. A lipoma can clog the bronchi if it appears in the central zone and grows (causing coughing up blood).
Treatment methods
Initially, diagnostic measures are carried out. Lipomas should be differentiated from retrosternal goiter, cysts and other mediastinal neoplasms. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor determines further tactics for managing the patient.
Diagnostic measures include:
- Inspection and palpation of the mediastinum area. The doctor notes the mobility, softness and painlessness of the tumor.
- Diagnostic imaging methods are indicated - ultrasound, CT or MRI, x-ray studies.
- To exclude the malignant nature of the neoplasm, it is recommended to perform a tissue biopsy.
After making a diagnosis, specifying the type and location of the lipoma, the doctor chooses a method of managing the patient.
Treatment options for lipomatosis
There are 2 tactics for managing the patient - watchful waiting - if the wen is small and if it does not compress nearby organs and surgical removal of the tumor.
The operation is indicated for:
- significant size of the wen;
- diffuse or diffuse nodular tumor;
- Compression of neighboring organs with corresponding symptoms was detected.
Surgical interventions on the mediastinal organs are performed only in a hospital setting. Outpatient removal of tumors of this type and location is not provided for by WHO protocols. The operation is performed under full anesthesia; local anesthesia is technically impossible.
Types of surgical intervention for mediastinal lipomatosis:
- through open access;
- Thoracoscopy – performed endoscopically through a puncture in the projection of the tumor. This method is indicated for unilateral location of the wen;
- longitudinal sternotomy is an open method of access to the mediastinal organs. Indicated for bilateral lipomatosis and retrosternal location of the tumor.
Wen in the mediastinum with timely treatment does not have a pathological effect on the patient. The prognosis for surgical intervention is favorable and relapses of the disease are rare.
Don't start the disease. And also carry out surgical intervention in the volumes provided for by WHO methods and protocols. If fat capsules remain in the mediastinum area, the risk of relapse and degeneration of the tumor increases.
Preventive actions
If there have been cases of mediastinal lipomatosis in your family, then once a year you should undergo a comprehensive examination at a medical institution.
Prevention methods:
- fluorography or chest x-ray;
- self-examination for foreign growths;
- supporting the body's defenses.
Mediastinal lipoma is not a death sentence.
But surgical interventions on the chest organs are classified as complex surgical procedures. Therefore, if you have a lump in this area, you should not wait until it reaches a significant size and requires surgery with full access to the chest. The article has been verified by the editors
Lipoma treatment
Many people are interested in the question of how to treat lipoma. There are a lot of folk remedies, but their effectiveness is practically zero. If the patient wants to get rid of the tumor for sure, he will need the help of an experienced surgeon, who will most likely suggest going under the knife. And this is the most effective method, since a tumor that has already formed is difficult to treat with tablets, ointments or herbal infusions. The speed of the operation depends on the size of the tumor; for example, a lipoma of the mammary gland is removed within 20 minutes under local or general anesthesia.
Prevention measures
This disease is rare, and when the tumor is removed, the risk of recurrence is very low (with incomplete excision, reappearance is possible). If there were people in the family with lipomatosis, it is necessary to undergo systematic observation by a doctor with fluorography. An important factor is self-checking symptoms, palpation and recording changes in the body. Such data can help in the future. You should not neglect and ignore other ailments, as they can cause the development of wen in the chest. Maintaining immunity is the main preventive measure in the fight against the problem.
Causes of tumor
Diabetes, problems in internal organs, and nervous disorders can provoke the growth of mediastinal lipoma.
It is impossible to name a clear cause of lipoma in the mediastinum. Doctors point to a number of factors influencing education. Main reasons:
- neurotrophic processes (nerves do not receive sufficient nutrition);
- failure of the thyroid gland;
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- pituitary dysfunction;
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- autoimmune diseases;
- diabetes.
A possible reason for the development of such a lipoma is a genetic predisposition. Women are more predisposed to this disease than men.
Symptoms of the disease
In the initial stages, a lump in the breast is very difficult to diagnose; the patient does not feel any painful or unpleasant symptoms. In this case, pathology can only be identified through a series of medical tests. With the development of mediastinal lipomatosis:
- swelling appears;
- there are difficulties in performing physical activity;
- breathing disturbances and difficulties are observed;
- lips and fingers turn blue;
- there may be a feeling of pain in the sternum, neck, shoulder blades and shoulder girdle;
- pleurisy is likely to occur;
- body temperature rises;
- the patient is shivering;
- there is general fatigue and weakness;
- aches in bones and joints;
- cough and shortness of breath appear;
- Horner's symptom develops;
- there is a feeling of stuck food after swallowing.
Mediastinal lipoma is manifested by swelling, temperature fluctuations, difficulty breathing, and loss of strength.
The occurrence of symptoms depends on the duration of the disease, the patient’s health status, age and attentiveness to one’s health. The larger the tumor, the stronger the shortness of breath and pain. Symptoms may occur suddenly and not subside for some time, or they may disappear spontaneously. It is important to urgently contact a surgeon for consultation and diagnosis. Timely assistance will protect a person.