Breast lipoma is a mobile seal in the capsule, which mainly consists of adipose tissue. Lipoma refers to benign formations that can form in the meninges, bones, skin, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, mammary gland and other tissues. Lipoma is found in overweight and thin people; it can be small or large, single or multiple. Very rarely, a lipoma degenerates into liposarcoma. Large lipomas are subject to removal if there is a suspicion that a benign tumor has degenerated into a malignant tumor.
The Yusupov Hospital diagnoses benign and malignant breast formations in women and men. In the oncology hospital, patients will be able to undergo diagnostics using MRI, CT, ultrasound and other research methods. Based on the research results, the oncologist will prescribe effective treatment for the disease. The hospital treats tumors using innovative techniques used in leading clinics around the world, and offers patients a 24-hour hospital and a rehabilitation center.
General information
The term lipoma comes from the Latin word for fat.
This is a benign connective tissue tumor. It develops in a layer of loose connective tissue under the skin and can penetrate deep, developing between the muscles and bundles of blood vessels to the periosteum. The ICD-10 code for lipoma is D17. 9 (benign neoplasm of adipose tissue of unspecified location). Speaking about lipoma - what kind of disease it is, it should be noted that among the people, the disease, which is scientifically called lipoma, is often defined as a wen. This tumor grows slowly, has a soft consistency, is mobile and painless. Most often, this formation develops in places where there is little adipose tissue: on the shoulders, upper back, outside the thigh. In most cases, such a tumor does not pose a danger from the point of view of degeneration into malignant. But in rare cases, lipomas in the subcutaneous fat still degenerate into liposarcoma (malignant formations).
Lipoma develops from adipose tissue and is one of the most common soft tissue tumors. Often such formations are multiple, sometimes they appear symmetrically. There are many varieties of such tumors that have certain morphological and clinical features. Such tumors develop equally often in men and women. The average age of appearance of lipomas is 40-60 years.
This article will discuss what a lipoma looks like, why it appears, as well as how to distinguish a wen from a tumor and get rid of such a formation.
Kidney adenoma is a benign tumor
Adenoma is the most common benign tumor of the kidney. The etiology is unknown, but smokers have a higher risk of the disease. The histological structure of renal parenchymal adenoma is very similar to well-differentiated renal cell carcinoma, so there is a hypothesis that it is an early form of adenocarcinoma. Kidney adenoma does not manifest itself with any specific symptoms. The tumor grows slowly, does not metastasize, and does not invade neighboring organs. The most optimal diagnostic method is computed tomography, but preoperative differential diagnosis from other tumors of this localization is not possible. In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be used. Treatment of kidney adenoma consists of surgical removal of the tumor; preference is given to organ-preserving treatments (partial nephrectomy, laparoscopic partial nephrectomy). The prognosis for disease-free survival is favorable.
Pathogenesis
Currently, there is no consensus on the pathogenesis of lipoma. In some sources, this tumor is considered hypertrophied adipose tissue, in others – a true neoplasm. When tumors occur in areas where adipose tissue is absent, their development is associated with metaplastic transformation of connective tissue cells.
There is a theory that local accumulation of adipocytes occurs due to chromosomal abnormalities affecting the genes that are responsible for the synthesis of TAG lipase. This enzyme regulates the breakdown of fats and energy supply to the body.
There is also a theory that subcutaneous wen appears due to excessive deposition of lipids in adipose tissue cells. Certain prerequisites for the occurrence of such formations appear already during the period of embryonic development, when adipose tissue is just being formed. Subsequently, in adulthood, a wen may form on the arm under the skin or a tumor in other places.
Classification
Fatty tissue can grow in different places. Accordingly, different types of lipoma are formed. All types of wen are determined depending on a number of characteristics (location, structural features - what the formation looks like, histological features, etc.).
Depending on the location, the following types of wen are distinguished:
- Subcutaneous - develops in the subcutaneous fat layer of the skin.
- Retroperitoneal – formed in the fatty tissue of the abdomen.
- Perineural - such tumors surround the nerve trunks and compress them. In this case, the answer to the question of whether a lipoma can hurt is positive. If the wen is inflamed and hurts, you should consult a doctor. Most often, such lipomas develop at the site of the median nerve.
- Intraorgan - can develop in the myocardium, lung and bone tissue.
- Articular-synovial membrane and tendons - develop in the joint cavity, between the tendons.
- Intermuscular or intramuscular - may appear if the lipoma between the muscle fibers was removed, and the adipose tissue was not completely cleared. Such formation often recurs.
- Lumbosacral (epidural) - develop in the spinal canal, near the vertebrae. May appear in patients with Cushing's syndrome , with benign tumors in the pituitary gland .
- Angiolipoma is a lipoma of the kidney.
- Adenolipoma - localized near the sweat glands.
- Myolipoma - forms between muscles and tendon fibers.
Depending on the characteristics of the structure, the following are determined:
- Classic - formed exclusively from adipose tissue.
- Ring-shaped cervical - develop in the subcutaneous fat tissue, forming a kind of “necklace” around the neck.
- Tree-like - appear against the background of inflammation around the joints. They grow inside large joints.
- Capsulated - grow in internal organs on the skin-fatty tissue of their internal surfaces.
- Cavernous (angiolipomas) are formations through which blood vessels penetrate.
- Petrified (ossified) - appear when calcium salts are deposited.
- Lipofibromas (soft) - in the cavity of such formations there is adipose tissue and fluid.
- Fibrolipomas (dense) - the formation contains adipose and connective tissue.
- Pedicled - formations that have detached from the epithelium and formed a stalk
- Myxolipomas develop when mucous and fatty tissues mix.
- Myelolipomas - such formations include hematopoietic elements. They are formed in the pelvis, retroperitoneum and adrenal glands.
- Hibernomas are atypical formations that appear when metabolic processes are disrupted and brown fat is actively formed in the body.
Depending on the histological structure, the following types of lipomas are distinguished:
- Nodular - formations inside the capsule are divided into lobules of different sizes. In most cases, lipomas of this type are formed.
- Diffuse - develop mainly in systemic diseases associated with impaired fat metabolism.
What are the dangers of wen under the skin and appearance?
Lipomas located on the surface, that is, near the skin, are absolutely safe. The exception is diffuse type formations that can exert pressure and create compression on blood vessels and nerves. In this case, the patient complains of pain and discomfort.
Subcutaneous wen is benign and cannot develop into cancer. The growth does not destroy surrounding tissue. Rarely transforms into liposarcoma. The cause of degeneration is the long course of the disease and regular trauma. But there is a risk of missing a malignant tumor due to its external similarity to a lipoma. In the initial stages, some forms of cancer appear as small to medium-sized lumps under the skin. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a doctor.
Features of the clinical picture:
- location on different parts of the body and in internal organs;
- has clearly defined boundaries;
- soft consistency;
- shape – round;
- there is mobility;
- diameter – 1-4 cm, but can increase to large sizes;
- color – yellowish;
- does not decrease or, on the contrary, increases in size when losing weight;
- There is no pain upon palpation, but when a large diameter is reached, discomfort may be felt.
To determine the nature of the wen, an ultrasound, MRI, x-ray, and biopsy are required. After diagnosis, you can accurately answer the question of whether a lipoma is dangerous.
Causes of lipoma
The reasons for the appearance of wen on the body can be different. Lipoma can be either an independent formation or appear against the background of other diseases. The main causes of lipoma are the growth and compaction of subcutaneous fat. The following factors can provoke this process:
- Hereditary disposition - lipomatosis is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. If the disease was diagnosed in parents, then the probability of such formation in children is 75%.
- Disturbances at the stage of embryonic development - the cause of the formation of wen in uncharacteristic places is associated with dystopia of embryonic fat cells.
- A number of diseases and syndromes - the answer to the question of why lipomas appear may be the presence of certain pathological processes in the body. These are Madelung's disease, Dercum's disease, Cowden's syndrome, etc.
- Endocrine disorders - the risk of developing wen increases the hypofunction of the pituitary gland, thyroid and pancreas. Lipomatosis may also be associated with changes in estrogen , diseases of the genital area, and malignant tumors of the upper respiratory tract.
- An insufficiently active lifestyle leads to stagnation, which leads to the formation of fat deposits and blockage of the gland duct.
- Impaired tissue trophism – due to impaired nutrition of nerve tissue, free fat accumulates in the subcutaneous fat layer.
- Injuries – after injury, cell nutrition and metabolic processes are disrupted. As a result, the sebaceous glands can become clogged. The causes of wen on the face may be associated with injuries.
- Improper skin care - this factor is sometimes an explanation for why white wen appears on the face. This can be caused by the use of very oily creams or poor quality cleansing of the skin after cosmetics. White lumps are often the result of blocked gland ducts.
- Age factor - despite the fact that subcutaneous wen can appear at any age. However, after 30-40 years, metabolic processes slow down, and the body’s defense mechanisms decrease. Therefore, after this age, lipomas appear more often.
- Improper nutrition - the appearance of wen can provoke a prolonged insufficient supply of nutrients to the body.
- Bad habits - they lead to a deterioration in the function of the immune system and disruption of metabolic processes.
- General diseases - diseases of the liver, digestive system, urinary system, diabetes and other diseases associated with metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance.
Benign tumor oncocytoma of the kidney
Oncocytoma is a benign kidney tumor that develops from the epithelium of the proximal collecting ducts. The etiology of this disease is unknown, but patients with a family history of oncocytoma have an increased risk of developing this tumor. Also, with Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome, there is an increased risk of kidney tumors (15-30%). This syndrome is also associated with the frequent occurrence of benign tumors of the hair follicles and lung cysts. The clinical picture is similar to kidney cancer, i.e. may manifest as pain, a palpable mass, and blood in the urine. The presence of clinical signs is directly related to the size of the tumor. Diagnosis - on computed tomography, a specific symptom is the presence of a zone of reduced density in the center of the tumor, resembling the spokes of a wheel or a star. Treatment – the best option is resection of the kidney with the tumor. The prognosis is favorable.
Symptoms
Symptoms of lipoma, photo
Wen on the body is not difficult to recognize, since the clinical picture of lipoma is characteristic.
- The consistency of the tumor is soft, it is surrounded by a pronounced capsule, mobile relative to the tissues that surround it. If you put a little pressure on the formation, it will move to the side. In places where the tumor is constantly compressed, it can grow together with tissues and become less mobile.
- The consistency of wen on the body resembles jelly or dough. If the lipoma is deep, it may have a denser consistency.
- As a rule, people with such formations do not experience pain. But sometimes, if the nerve endings are affected, a person may feel pain. When a lipoma develops in places where there is constant friction, contact with clothing or injury (under the armpit, on the nipple, under the breast, etc.), abrasions and suppuration may appear.
- Pain may be observed in the following cases: if the lipoma borders on nerve endings (perineural lipoma); if the formation compresses nerve tissue; if the contents of the tumor are inflamed or infected.
- On the body, wen look like a small tubercle. Initially, their size is no larger than a pea, so often a person may not notice such formations. Over time, the formations may increase in size.
- Most often, such formations appear in the upper part of the body - on the chest, shoulder, back, elbow, face, arms. Less commonly, they form on the stomach, groin, butt, and legs. Wen does not form on the palms and soles, since there is no subcutaneous fat in these places.
- Sometimes it is possible to develop multiple lipomas. If a person has a lot of wen on his body, what this means is determined by the doctor during the research process.
Wen on the face
Photo of a wen on the face
Speaking about what a lipoma looks like on the face, it should be noted that, as a rule, it is perceived as a cosmetic defect. If white wen or subcutaneous lipoma appears on the forehead, cheek, chin or nose, this leads, first of all, to psychological discomfort and the appearance of complexes. Therefore, it is very important to determine the causes of such manifestations and carry out the treatment prescribed by the doctor. Sometimes a lipoma appears behind the ear or on the earlobe.
In a child, wen may appear on the face immediately after birth. However, in a newborn this condition is physiological. Wen on the cheeks, near the eyes and lips are formed due to underdevelopment of the sebaceous glands. But, as a rule, such formations go away on their own within three months.
Wen on the eyelid
Most often, white wen appears on the eyelids, which develop on the lower eyelid, near the eye. As a rule, wen under the eye looks like small yellow-white nodules. Dense subcutaneous lipoma in these areas is a relatively rare occurrence. Despite the fact that they do not cause pain or particular discomfort, people strive to get rid of wen in such places. It is important to consider that removing such formations on your own can aggravate the situation. Therefore, if a wen appears on the eye, you need to contact a specialist who will suggest the best method to remove such a formation. It should be noted that such a formation developing on the white of the eye is not a wen.
Wen on the neck
Wen on the neck, photo
A lipoma on the neck, as a rule, also does not cause pain and is a cosmetic drawback. However, if such a formation occurs on the back or front of the neck, it is often injured and compressed. As a result, frequent injury and compression occurs, and this provokes compaction and calcification of the formation. Some sources note that a lipoma on the neck in a child and an adult may be a sign of Madelung's disease, in which deformation of bone tissue occurs.
Wen on the head
Photo of a wen on the head
It happens that a lipoma on the head is formed in the hairy part (on the crown, on the back of the head), since these places also have subcutaneous adipose tissue. The reasons for the appearance of such formations, in addition to those described above, may be associated with diseases of the thyroid gland. It has been noted that lipomas on the head develop more often in women. Such formations also appear in children, which is often associated with the consumption of large amounts of harmful foods, which leads to clogging of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. This leads to the appearance of compactions. How to get rid of such formations on the head, and which doctor to contact, depends on the characteristics of the disease. Wen in children is carefully monitored and, if necessary, removed.
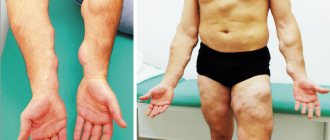
Wen on the leg and arm
Photo of lipoma on the leg
If a wen on an arm or leg has formed at the bend, it is constantly injured, and the tumor gradually becomes denser. If a tumor forms in open areas on the arm, it usually remains small and soft for a long time. It is removed according to indications or if it is located at the bend. Such tumors are less common on the legs. The indications for their removal are similar.
Wen on the genitals
Fatty deposits on the labia appear in the form of small lumps that resemble pimples in appearance. Sometimes when lipomas appear on the labia or clitoris, the fatty contents of the formation are visible, since the skin in these places is thin. Externally, the tumor looks like a tubercle rising above the surface of the skin. A tumor in the groin can be of different sizes. As a rule, it does not cause pain and is discovered accidentally. However, when opening a lipoma on your own, pain, inflammation may occur, and subsequently a fistula .
Men may develop a lump on the scrotum or testicles. As with the formation of such a tumor in other places, it easily moves when pressed and resembles a pea. In the early stages, wen on the scrotum does not cause discomfort, but during inflammatory processes, pain and purulent contents may appear in such a formation.
The appearance of a wen on the penis causes considerable concern among men. The development of such a tumor on the penis is quite rare. Despite the fact that there is usually no pain in such cases, if a lipoma is detected, a man should consult a doctor to prevent its growth.
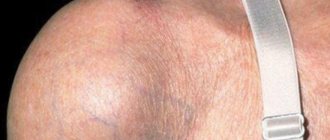
Wen on the back
Photo of a wen on the back
Very often, a lipoma on the back goes unnoticed for a long time. If the wen does not resolve on its own, it gradually grows over time. A person feels such a formation when it begins to increase, thicken, or when inflammation develops. In such a situation, it is necessary to remove the formation surgically, since it will be difficult to get rid of the overgrown seal using conservative methods.
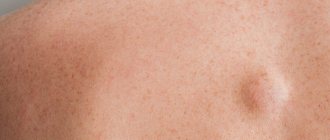
Breast lipoma
Speaking about what a breast lipoma is, it should be noted that lipoma and breast fibrolipoma are benign tumors that rarely become malignant. The mammary gland contains a lot of subcutaneous fat, therefore, this is a favorable area for the development of fatty tissue. Most often, such formations are located in the subcutaneous layers of soft tissue or behind glandular tissue. In more rare cases, they form in the interlobular fatty tissue of the breast, which leads to tissue deformation and pain. If such a formation appears, you must consult a doctor to rule out more serious pathologies.
How can you tell if a lipoma is growing?
The following signs may indicate that the wen formed on the body is increasing:
- sagging education;
- swelling, redness and blood stagnation in the area of the lipoma;
- dysfunction of the organ and tissue near which the lipoma is located;
- discomfort in the tumor area.
If a person with a lipoma experiences similar symptoms, he should definitely consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Manifestations of hernia of the white line of the abdomen
The disease can be suspected if a small bulge is suddenly palpated in the midline of the patient's abdomen. Very often it does not cause pain and can be discovered accidentally by the patient himself or by the doctor during examination. Due to the fact that in a normal state the neoplasm, as such, may not cause pain, one of the indicators that allows one to suspect it is the appearance of pain during heavy work, after eating, or in other situations that lead to increased intra-abdominal pressure. An increase in pain may be associated with tension in organs and other structures fixed to the hernial sac, or as a result of strangulation of the contents of the hernial protrusion, which in turn requires emergency surgical intervention. Painful sensations can radiate to various areas of the chest, abdomen and back. When the muscles of the abdominal wall are relaxed in a horizontal position on the back, the hernial protrusion, and with it the pain, often disappears. In the event of such a formidable and extremely dangerous complication as a strangulated hernia, all the symptoms of an acute abdomen occur and general intoxication of the body increases: the temperature rises, piercing, intensely intensifying abdominal pain appears, nausea and vomiting, retention of stool and gases, and bloody discharge in the stool. , and the hernial protrusion can no longer be reduced in the supine position. Often the symptoms accompanying the disease are disorders of the digestive system such as nausea, heartburn, belching, associated with the entry of the digestive tract into the hernial sac.
Tests and diagnostics
If you suspect the development of a wen, you should consult a dermatologist. The doctor examines and interviews the patient, determining how quickly the tumor is growing and what complaints the patient has.
Additional examinations are prescribed to differentiate lipomas from other benign tumors of the skin and subcutaneous fat. For this purpose, the patient may be recommended to conduct the following studies:
- Ultrasound examination of soft tissues - during ultrasound, you can determine the size of the node, carry out a differential diagnosis of a lipoma with an epidermoid cyst and other formations in the soft tissues.
- Histological examination - examination of tissue samples of the formation allows the identification of mature adipocytes. In a long-existing wen, areas of atrophy can be detected. If the presence of lipoblasts is detected, this indicates myxoid liposarcoma .
- MRI – allows you to visualize formations.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is possible to treat wen using folk remedies only if they are practiced as an additional method. Basically, various compresses are used for this purpose.
- Kalanchoe and aloe . A fresh leaf of the selected plant is cut lengthwise and the pulp is applied to the affected area. It can be fixed with a plaster or bandage and worn for several hours. Repeat the procedure daily.
- Onions with soap . A large onion is baked in the oven, then pureed until it becomes a paste. It is mixed with grated laundry soap. The mass is applied to the lesion and fixed. The compress is replaced with a fresh one three times a day. It is recommended to use it for several days, then take a break.
- Honey compress . To prepare it, mix equal parts of salt, honey and sour cream. Apply the mixed mass to the wen and secure the bandage. This compress is carried out every day.
- Vegetable oil compress . Mix equal parts sunflower oil and vodka, soak a cloth in the resulting mass and apply it to the lipoma. Cover the fabric with paper for compresses. Carry out the procedure every day, leaving the compress on for several hours.
- Garlic and lard . Take two parts of fresh lard and one part of garlic, grind everything in a meat grinder, after which the mass is kept on low heat for about 15 minutes. A thin layer of the mass is applied to the formation, covered with a leaf of fresh cabbage and wrapped in a warm cloth. Treatment is carried out every day.
- Red pepper . For such a compress, the fabric is soaked in vodka and 1 tsp is poured onto it. red pepper. Apply it to the formation and hold for about 10 minutes. This compress helps improve blood circulation. However, it can cause burns and allergic reactions.
Diet
Diet for skin diseases
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after a month
- Time frame: three months or more
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles per week
Despite the fact that nutrition does not directly affect the development of wen, it is important for people prone to their formation to adhere to some important rules:
- Do not overeat fatty foods.
- Reduce the amount of salt and sugar in your diet.
- Reduce the amount of baked goods and flour products consumed.
- Drink enough fluids.
Consequences and complications
Dangerous complications of lipoma are the processes that can occur inside such a formation. This is possible with wen of different sizes.
- Adenolipoma - glandular cells appear in the structure.
- Petrified - deposition of calcium salts occurs.
- Ossified - bone tissue is formed inside the capsule.
- Fibrous - connective tissue is involved in growth.
A large formation can lead to disruption of local blood flow. If stagnation is prolonged, tissue necrosis may occur.
Wen that form on internal organs are dangerous. According to statistics, this happens in 2% of cases. Brain lipoma, preperitoneal lipoma, lung lipoma, parasternal lipoma, etc. require constant medical supervision and, if possible, removal, as there is a risk of their degeneration into a malignant tumor. The indication for surgery is, first of all, parasternal lipoma and other types of large internal wen.
Methods for getting rid of formations
There are two ways to get rid of a wen on the shoulder: in the surgeon’s office or at home.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Removal is indicated if the tumor continues to grow, becomes inflamed, or creates difficulties in activity.
Doctors advise not to expect consequences in the form of tissue necrosis or sepsis. Damage to the capsule walls will result in spillage of the contents. If this happens near blood vessels, there is a risk of lipid embolism. Quite often, infection occurs due to constant friction and scratching of the area.
You need to go to the hospital if inflammation begins, pain appears, or fluid is released.
In the hospital
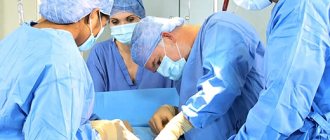
In a hospital setting, the doctor will determine whether the wen near the shoulder is dangerous and what can be done. They mainly use inspection and palpation. To clarify the diagnosis, this is usually enough; an analysis is done to select a method. Standard – surgical intervention. Local anesthesia and a scalpel incision will remove the accumulation of fat cells in half an hour. After the operation there will be a small scar. Less traumatic options:
- Liposuction. The contents are sucked out through the needle; repeated procedures may be required.
- Radio wave. Bloodless, minimal damage to the shoulder.
- Laser. High degree of disinfection, fastest healing possible.
Large tumors require surgery. Small ones - injections with a fissionable substance.
Removing the growth promotes further normal functioning of the organs. The problem may return periodically.
At home
It is better to get rid of lipomas at home using conservative means. Remember: the following will give results only at the beginning of the development of the growth; a decently grown “ball” must be shown to the doctor. When removing a wen on the shoulder at home, you run the risk of getting an infection, and in the worst case, blood poisoning. Self-medication is extremely dangerous. Traditional medicine offers this:
- lotions - change 3-4 times a day, it is advisable to use polyethylene to create a “greenhouse” in the compress;
- Golden Us plant;
- Kalanchoe;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- slurry of laundry soap with baked onions;
- decoction of celandine. Apply before opening the wen;
- ichthyol ointment - makes sense at an early stage.
- balm “Star”;
- cinnamon powder – mix into food to taste;
- pine pollen 0.5 teaspoon with honey 1 tbsp. spoon. Take after meals 2-3 times a day, 3 weeks.
It makes sense to use it for single formations. Attempts at prevention are completely useless; the causes are not clear. Warming up or applying ice will also not do any good. If you have shoulder lipomatosis, consult your surgeon.
Forms of lipomatosis:
- knotty. One or more wen located under the skin;
- diffuse. More severe course and many nodes on the trunk or limbs;
- nodular-diffuse. Diagnosed with a significant number of growths. May appear on internal organs. It is marked by a slow flow.
The success of self-medication also depends on the body’s capabilities and response to the medications used.
List of sources
- Artamonov R.G., Glazunova L.V., Bektashyants E.G., Kuibysheva E.V., Narinskaya N.N. Abdominal lipoma - difficulties of differential diagnosis // Medical scientific and educational journal. - No. 31. -2006.
- Congenital lipomas of the brain and spinal cord: clinical and MRI diagnostics / Bein B.M., Syrchin E.F., Yakushev K.B. // Medical almanac - 2013 - No. 3.
- Dergachev, S.V. Surgical treatment of lipomas in the practice of an outpatient surgeon / S.V. Dergachev [and others] // Outpatient surgery. Hospital-replacing technologies. – St. Petersburg, 2001. – No. 1 (1). – pp. 33–35.
- Encyclopedia of Clinical Oncology: a guide for practicing physicians / edited by. ed. M.I. Davydova, G.L. Vyshkovsky. M.: RLS, 2005. pp. 365-366.
Benign tumor leiomyoma of the kidney
Leiomyoma is a benign tumor arising from muscle fibers . Etiology unknown. The clinical picture depends on the size of the tumor and may include pain and a palpable mass. There are no characteristic diagnostic features. The tumor must be differentiated from kidney cancer. Treatment consists of surgical removal of the tumor; preference is given to resection of the kidney. The prognosis is favorable.
| Author of the article: Denis Viktorovich Butnaru - Head of the Department of Reconstructive Plastic Uronephrology, Research Institute of Uronephrology and Human Reproductive Health, First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenova, Ph.D. |