Microsporia is a fungal disease that affects the skin and hair follicles. It may be caused by various fungi of the genus Microsporum: zoophilic or anthropophilic.
Zoophilic diseases are transmitted from domestic animals , mainly cats. Anthropophilic ones get on the skin through contact with people and objects touched by an infected person.
This lesion is easily transmitted between people and can break out in epidemics. If microsporia is detected in educational institutions, quarantine is introduced according to SanPiN standards.
Diagnosis
Microsporia is diagnosed by a qualified dermatologist. The specialist collects the patient’s medical history and also examines his skin and hair. The presence of microsporia is indicated by the following symptoms:
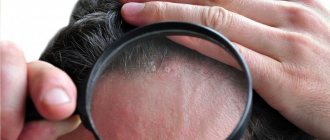
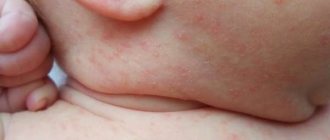
- lesions on smooth skin with a diameter of 0.5 to 3 cm, with a white scaly center and reddish bumpy edges, usually up to 3 pieces in one area;
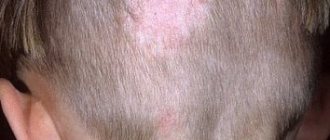
- affected hair, looking like circles up to 5 cm in diameter with crusts or tubercles along the edges; brittle hair that breaks off at a height of 4–6 mm from the head, and the remaining part is covered with a white film;
- peeling of the skin, mild itching.
For both adults and children, the disease causes virtually no physical discomfort, so it is not detected immediately. The incubation period lasts from 5 to 7 days.
At this time, the disease can be transmitted from an infected person to family members or students of the same group, so it is imperative to diagnose not only the patient , but also those around him.
To accurately determine the nature of the lesion, three methods are used simultaneously:
- Wood's lamp. In a darkened room, when using a Wood's lamp, the affected areas of the skin and hair are highlighted with a greenish tint. This method is used to identify lesions in humans and animals. Sometimes it allows you to identify lesions that have not yet become visible to the human eye, since the spores have so far only slightly affected the skin or hair.
- Microscopic examination. A scraping of skin or hair is taken for examination. Under a microscope, spores are detected, their location and quantity. This helps confirm the preliminary diagnosis.
- Cultural research. It is necessary to accurately establish the type of pathogen, since some dermatomycosis is very similar in symptoms to microsporia. For 3 days, scrapings taken from the patient remain in a nutrient medium in which the fungal colony quickly multiplies. After 3 days, it turns out to be so enlarged that doctors are able to carefully examine it and determine the type of fungus.
How long is quarantine for lichen? Features of different types of disease
In childhood, lichen occurs more often than in adults. Experts associate this fact with the child’s lifestyle.
Children's pityriasis rosea almost always occurs after intestinal or respiratory infections, acute fever or vaccination. The exact cause of this type of disease is not known. However, scientists suggest that its causative agent is the seventh herpes virus. The infection can be transmitted not only by contact, but also by airborne droplets. Typically, pityriasis rosea occurs in children over 10 years of age. Although it can often be observed in adults under 35 years of age.
Depriving quarantine in kindergarten is a mandatory event. This is especially true for cases associated with the occurrence of a ringworm type of disease.
Ringworm has two types (trichophytosis and microsporia). People and animals with a fungal infection are at risk of contracting this disease. It is often transmitted through personal belongings and household items that contain spores.
Versicolor or pityriasis versicolor refers to mycoses caused by three types of yeast-like fungus. The latter can live quietly on the child’s skin and at the same time not cause absolutely any pathological changes. However, infectious diseases, seborrhea, hormonal disorders, hyperhidrosis, leukemia, rheumatism, hereditary predisposition or lymphogranulomatosis often become a kind of impetus for the fungal process.
It should be noted that lichen versicolor is not very contagious. Most often, this disease is observed in adolescents. The most common habitats of this type of fungus are areas with a large number of sweat glands.
The reasons for the development of lichen planus are not well understood. Therefore, experts adhere to several theories (hereditary origin, viral, neurogenic, immunoallergic, intoxication).
Children's shingles - what does it look like? How to treat this disease? In medical practice, this disease is called herpes zoster. Its causative agent is Varicella zoster, which is also the causative agent of chickenpox. As soon as a child has chickenpox, the virus “settles” in the nerve ganglia. In the presence of unfavorable factors (for example, with reduced immunity), it is activated.
As with herpes, shingles is accompanied by a small blistering rash that spreads over the child's body (on the back, stomach, sides). To treat such a disease, you should consult a pediatrician. Usually, when the herpes virus is activated, doctors recommend taking medications containing the active substance - acyclovir.
Requirements for quarantine for the prevention of deprivation in kindergarten
In preschool and school institutions, after detection of a patient, quarantine is established . The patient is sent home or to a special institution for treatment, and the rest of the children are necessarily examined by a dermatologist.
Employees of the institution are required to notify the sanitary and epidemiological station about the situation so that measures can be taken to reduce risks.
During the quarantine period, children must stay at home and not visit playgrounds, public institutions and classes. They can spread the disease.
Every 5 days, a dermatologist is required to check the condition of kindergarten students (the same group in which the patient studied).
Important!
If microsporia is detected in another child, the quarantine is extended for another 45 days.
If we are talking about a permanent kindergarten, from where children cannot immediately go home, quarantine is also prescribed. Basic Rules:
- remove all soft toys and carpets;
- hard toys must be washed in warm water and soap once a day, in nurseries - twice a day;
- children eat in a separate room, they should not visit public places (canteens, shared bathrooms and toilets, playgrounds);
- children are provided with lockers where they put their outerwear; all lockers must be numbered and signed;
- Other personal items (toothbrushes, combs) are also numbered; teachers ensure that they are used strictly by the owner;
- at the end of each day, mattresses and bed linen are disinfected or vacuumed;
- bed linen and clothes of children in quarantine are washed separately from the linen of children from healthy groups.
Causes
The main source of infection are dogs and cats. Penetration of spores occurs not only through direct contact of a child with a sick animal, but when touching objects that have fur or scales on them. The fungus continues to live in the soil for another 1-3 months. Infection can only occur through contact; probable sources of microsporia can be:
- objects touched by the patient (person or animal);
- sick people;
- sick animals;
- the soil.
SanPiN for school
The same measures are being taken in secondary schools as in preschool institutions. Quarantine is established, children are regularly examined by a dermatologist .
An SES worker is involved. Based on his decision, final disinfection of upholstered furniture, walls, floors and ceilings, as well as other things, is carried out.
Final focal disinfection eliminates fungal spores and makes the premises safe for children and working personnel.
Microsporia mainly affects children from 5 to 12 years of age. Starting from puberty, the structure of sebum changes, as well as the composition of hair. As a result, the disease becomes harmless for older schoolchildren, with the exception of weakened girls.
Classification
There are two main options for dividing this pathology. The first classification is based on the area affected by the fungus. The disease is divided into three variants according to this type:
- microsporia of smooth skin;
- scalp;
- damage to the nail plates (extremely rare).
Doctors identify 3 more forms of pathology, which are classified according to the type of pathogen that provoked the development of the disease:
- Zoonotic microsporia. The causative agent is the fungus Microsporum, which parasitizes animals.
- Anthroponotic. Pathogens parasitize another person.
- Geophilic. Mushrooms live in the soil.
Recommendations for parents
During the quarantine period, children are sent home, where they must be kept subject to a number of restrictions. Quarantine should be taken calmly .
It is advisable to immediately explain its importance to the child and reassure him in order to avoid psychological problems. Parents need to accept three things:
- Quarantine is a measure necessary more for those around them than for the child himself. Therefore, even if parents are sure that a preschooler or schoolchild is healthy, they should not take him out into public places. During the incubation period, symptoms of the disease may not be noticeable, but the spores remain active and are transmitted to others.
- A child also poses a potential danger to household members, especially children, pets and weakened women. It is necessary to limit the contact of a potentially sick person with the listed groups.
- All instructions issued by a dermatologist or an employee of the sanitary-epidemiological station, including the requirements for ongoing disinfection, must be followed unquestioningly.
During the quarantine period, you need to provide the child with a separate place and separate things that will not come into contact with the things of other family members.
A separate sleeping place, cutlery and dishes, and toys are provided. Clothes are collected in a special bag and washed separately.
Important!
During the quarantine period, you cannot take documents from an educational institution and submit them to another. We must wait until the end of the dangerous period.
Routes of infection
Penetration of the infection occurs through contact with a carrier, which can be another person, object, or animals that are already infected with the fungus. There are several types of spores, which determines how they spread among people. There are three main species of Microsporum depending on the main host:
- Zoophilic fungi. The main carriers are cats, dogs and other animals.
- Anthropophilic. People become the main carriers.
- Geophilic. The main habitat is soil, where they remain viable for several months
Risk factor
A shingles quarantine in a children's institution is announced when one or two cases of the disease are observed. The highest incidence of fungus among children occurs in the warm season. As for lichen of viral origin, it, on the contrary, becomes more active in cold seasons.
The development of this pathology in children and adolescents is predisposed by a lack of vitamins, weakened immunity, excessive sweating, fatigue, the presence of ARVI, vegetative neuroses, allergic reactions, and minor damage to the skin.
Folk remedies
In consultation with your doctor, home recipes may be used as additional therapy. Folk remedies can only help in the initial stages of pathology or be used for prevention. The following recipes can be used:
- squeeze the juice from the onions, moisten the napkins and apply to the affected areas every day;
- tincture of lilac flowers: add 2 tbsp to 100 ml of 70% alcohol. l. dried flowers, then strain and lubricate the inflamed areas;
- wash the affected areas with a decoction of celandine: 1 tbsp. l. dry herbs, take a glass of boiling water and hold on low heat for 10 minutes, then cool, strain.
Complications
Ringworm does not pose any danger to the life of a child or adult. With adequate and timely therapy, the hair and skin are completely restored. However, there are situations in which complications of the disease arise if the wrong treatment regimen was prescribed or the doctor was consulted late. The consequences may appear in the following form:
- inflammation, suppuration of the skin (as in the photo);
- Bald spots appear on the head.
- Irreversible hair loss develops.
Treatment prognosis and prevention
The prognosis is usually favorable - complete recovery. After cure, follow-up with a dermatologist for up to three months.
During the illness, the child is isolated, allocated a separate room, toys, dishes, and limiting communication with healthy people.
Daily cleaning with antimicrobial agents, processing dishes, toys, washing clothes and linen at high temperatures are necessary measures against the spread of the disease.
There is no immunoprophylaxis for microsporia. The infection does not leave immunity, and there is a risk of re-infection. To prevent this from happening, teach your child to follow simple hygiene rules and be careful around unfamiliar animals.
Forms of microsporia
The types of microsporia are classified taking into account the depth of skin damage, the prevalence of lesions, the method of infection, and the course of the disease.
Superficial
The surface layer of the skin is affected, on which red scaly spots appear on the body and head, where the hair breaks off, forming bald spots with short stumps.
Exudative
Affects the deeper layers of the epidermis. Bright red spots are visible on open areas of the body, on the surface of which small bubbles with liquid inside form. There is weeping and itching. Serous discharge permeates the skin scales, they stick together, forming a dense crust. Underneath there is erosion, similar to a burn.
Infiltrative-suppurative
Affects the skin to its full depth. It usually appears on the scalp as a raised, dense, painful infiltrate, which gradually softens with the formation of purulent contents. When you press on the node, pus is released from the openings of the hair follicles. Accompanied by fever, intoxication, and enlarged lymph nodes. At the site of the infiltration, a scar or areas devoid of hair are formed.
Sometimes it takes the form of kerion Celsi (honeycomb of Celsus), when the pus flows like honey from a honeycomb, thick and light yellow.
Chronic
Another name is recurrent. It develops with untreated or undertreated microsporia, when the fungus makes itself felt again.
Anthroponotic and zoonotic
If a child becomes infected from an animal, then this form of microsporia is called zoonotic. It is the most common. Anthroponotic is much less common. It is transmitted from person to person or through the patient’s belongings.
Both forms of microsporia manifest themselves with the same symptoms and are treated according to the same regimen.
Atypical forms
They run smoothly and disguise themselves as other skin diseases. Their classification is based on similarities with other diseases.
- Trichophytoid microsporia. Forms many small, vague foci without signs of inflammation. The hair is broken off close to the head. Gradually covers the entire hairline with the formation of bald areas. Often becomes chronic.
- Seborrheic causes severe hair loss and flaking of the skin with the formation of many scales resembling dandruff.
- Rosacea-like appears on the body in the form of pink spots with clear boundaries and slight peeling, reaching very large sizes.
- Psoriasiform. Reminiscent of psoriasis - plaques covered with silvery scales.